- How to use 7zip Compression tool from Linux Terminal
- Installation
- Usage/Functions
- Create new archive/ add files to existing archive
- List contents of archive
- Delete files from an archive
- Extracting files from archive file
- Updating existing archived files
- Testing integrity of archived files
- Conclusion
- 7zip linux command line
- FUNCTION LETTERS
- SWITCHES
- DIAGNOSTICS
- Backup and limitations
- EXAMPLE 1
- EXAMPLE 2
- EXAMPLE 3
- Установка и использование 7-Zip в Linux
- Установка 7-Zip в Linux
- Установка 7-Zip в Ubuntu, Debian
- Установка 7-Zip в Fedora, CentOS
- Установка 7-Zip в ArchLinux
- Раcпаковка 7zip-архивов
- Распаковать в текущую директорию
- Распаковать в определенную директорию
- Распаковать без сохранения структуры директорий
- Создание 7zip-архива
- Упаковать один файл
- Упаковать несколько файлов
- Упаковать директорию и ее содержимое
- Добавить файлы в существующий архив
- Просмотр файлов в архиве
- Протестировать целостность архива
- Заключение
How to use 7zip Compression tool from Linux Terminal
7-Zip (http://www.7-zip.org/) is a file archiver with highest compression ratio.The tool supports various archive formats such as LZMA2, XZ, ZIP, Zip64, CAB, RAR, ARJ, GZIP, BZIP2, TAR, CPIO, RPM, ISO, most file system images and DEB formats. Developer claims that the compression ratio in the new 7z format is 30-50% better than the ratio in Zip formats.
In this article, we will walk through the practical examples of 7zip utility and their usage.All the below examples have been tested on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS/16.10 and Linux Mint 18 , and the 7zip version we have used is 9.20
Installation
The 7zip utility is not pre-installed on your Ubuntu systems. You have to install it in your system using the following commands.
$ sudo apt-get install p7zip-full
NOTE:In case, you want to use 7zip with rar files, then you’ll have to install the following package as well.
$ sudo apt-get install p7zip-rar
Usage/Functions
In this section, we will discuss the usage of the 7zip tool and the basic features it provides.
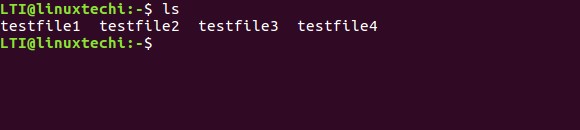
We will be using the files displayed in the following screenshot for performing various operations using 7zip.
Create new archive/ add files to existing archive
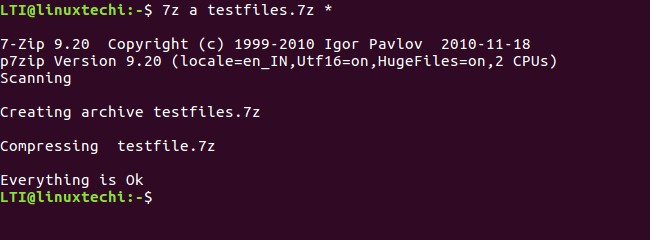
Using the tool, you can package the files in a .7z file. This feature can be accessed using the ‘a’ function letter.
Here’s how you can use this feature:
$ 7z a [archived-filename] [names-of-files-to-be-archived]
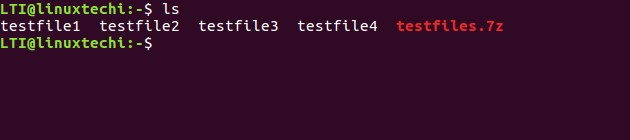
Now to check, whether the archive file is created or not, you can use the ‘ls‘ command.
As you can see in the screenshot above that a .7z archive file (testfiles.7z) has been created. Of course, you can also create/update, say, a .zip file this way.
List contents of archive
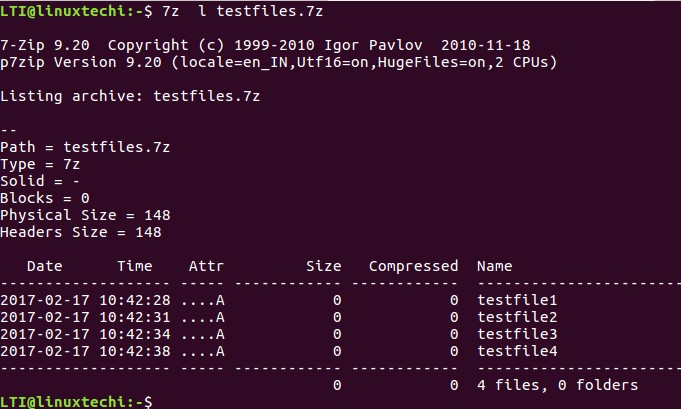
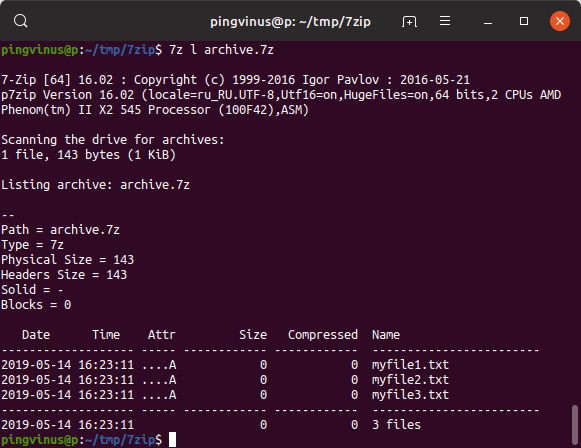
You can use the ‘l’ function letter for listing the contents of an archived file.
Here is the list of files in testfiles.7z archived file.
Delete files from an archive
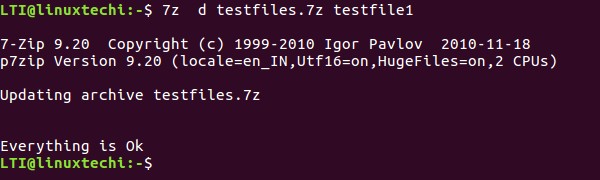
Using the tool, you can also delete a file from an archive file, something which you can do using the ‘d’ function letter.
$ 7z d [archived file] [name-of-file-to-be-deleted]
For example, to delete testfile1, we can use the following command:
$ 7z d testfiles.7z testfile1
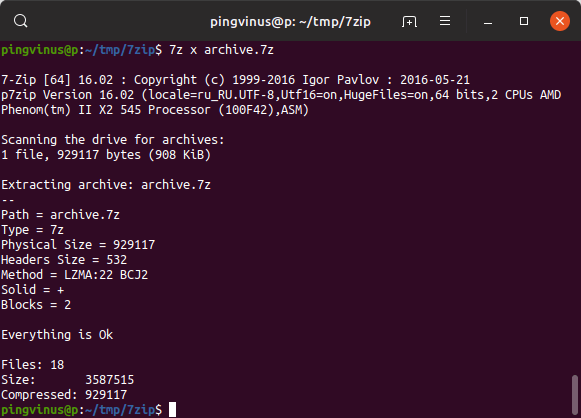
Extracting files from archive file
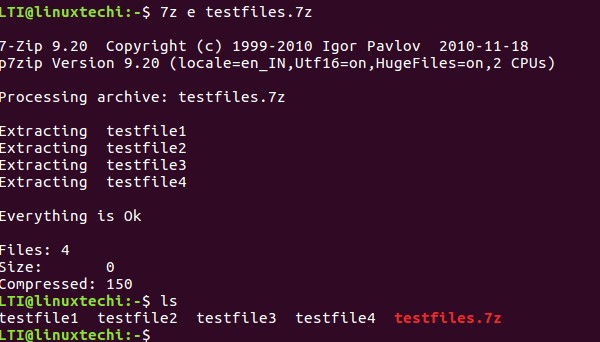
With the help of 7zip, you can extract files from an already existing archive. This feature can be accessed using the ‘e’ function letter.
For example, suppose we want to extract the ‘testfiles.7z’ archive.
Here’s how that can be done:
Updating existing archived files
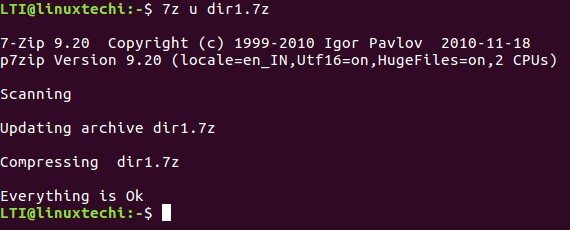
If you want, you can add new files to a previously created archived file, or you can even update the contents of existing files in the archive. This is made possible using the ‘u’ function letter.
$ 7z u [archived-file] [name-of-new-or-updated-file]
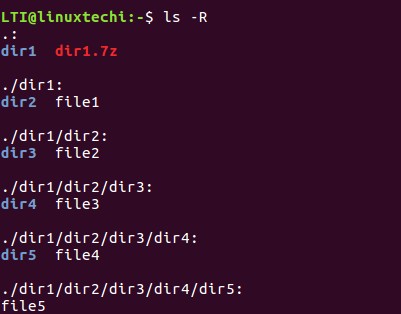
For example, here is the directory structure in which we will perform some update operations.
Let’s say we have already created an archive of the ‘dir1’ directory. And now, due to some modifications in, let’s say, file1, file2 and file3, we want to update the archive.
So, instead of individually adding the modified files again (using the ‘a’ function letter) to the archive, we can perform the operation in a single run by using the following command.
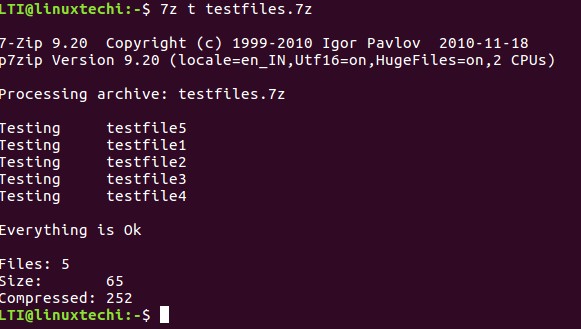
Testing integrity of archived files
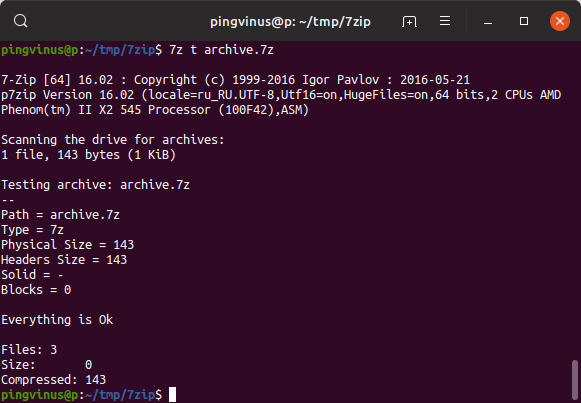
Using the tool, you can also check the integrity of an already existing archive file. Testing integrity is very important, as it tells, whether the contents are properly archived or not.
Sometimes, due to a hardware problem, RAM problem, or heating problem, your files may get affected and the archive isn’t created properly. To check whether the archive is corrupted or not, you can use the ‘t’ function letter.
Above output shows that the contents of the archive are not corrupted.
Conclusion
7 zip tool happens to be one of the best tools for archiving files. It’s available for both Windows and Linux, although only a command line port is available for the latter platform, so a good option for those Linux users whose work involves playing with files on the command line.
What we’ve discussed in this tutorial are only basic features. There are also several advanced options available. Head to the tool’s man page (man 7z) for more information and details.
7zip linux command line
7-Zip is a file archiver with the highest compression ratio. The program supports 7z (that implements LZMA compression algorithm), LZMA2, XZ, ZIP, Zip64, CAB, RAR (if the non-free p7zip-rar package is installed), ARJ, GZIP, BZIP2, TAR, CPIO, RPM, ISO, most filesystem images and DEB formats. Compression ratio in the new 7z format is 30-50% better than ratio in ZIP format. 7z uses plugins to handle archives.
FUNCTION LETTERS
a Add d Delete e Extract l List t Test u Update x eXtract with full paths
SWITCHES
-ai[r[-|0]] Include archives -ax[r[-|0]] eXclude archives -bd Disable percentage indicator -i[r[-|0]] Include filenames -l don’t store symlinks; store the files/directories they point to (CAUTION : the scanning stage can never end because of recursive symlinks like ‘ln -s .. ldir’) -m Set Compression Method (see /usr/share/doc/p7zip-full/DOCS/MANUAL/switches/method.htm for a list of methods) -mhe=on|off 7z format only : enables or disables archive header encryption (Default : off) -o Set Output directory -p Set Password -r[-|0] Recurse subdirectories (CAUTION: this flag does not do what you think, avoid using it) -sfx[] Create SFX archive -si Read data from StdIn (eg: tar cf — directory | 7z a -si directory.tar.7z) -so Write data to StdOut (eg: % echo foo | 7z a dummy -tgzip -si -so > /dev/null) -slt Sets technical mode for l (list) command -t Type of archive (7z, zip, gzip, bzip2 or tar. 7z format is default) -v[b|k|m|g] Create volumes -u[-][p#][q#][r#][x#][y#][z#][!newArchiveName] Update options -w[path] Set Working directory -x[r[-|0]]] Exclude filenames -y Assume Yes on all queries
DIAGNOSTICS
7-Zip returns the following exit codes: 0 Normal (no errors or warnings detected) 1 Warning (Non fatal error(s)). For example, some files cannot be read during compressing. So they were not compressed 2 Fatal error 7 Bad command line parameters 8 Not enough memory for operation 255 User stopped the process with control-C (or similar)
Backup and limitations
DO NOT USE the 7-zip format for backup purpose on Linux/Unix because :
— 7-zip does not store the owner/group of the file. On Linux/Unix, in order to backup directories you must use tar :
— to backup a directory : tar cf — directory | 7za a -si directory.tar.7z
— to restore your backup : 7za x -so directory.tar.7z | tar xf — If you want to send files and directories (not the owner of file) to others Unix/MacOS/Windows users, you can use the 7-zip format.
example : 7za a directory.7z directory Do not use «-r» because this flag does not do what you think. Do not use directory/* because of «.*» files (example : «directory/*» does not match «directory/.profile»)
EXAMPLE 1
7z a -t7z -m0=lzma -mx=9 -mfb=64 -md=32m -ms=on archive.7z dir1 adds all files from directory «dir1» to archive archive.7z using «ultra settings» -t7z 7z archive -m0=lzma lzma method -mx=9 level of compression = 9 (Ultra) -mfb=64 number of fast bytes for LZMA = 64 -md=32m dictionary size = 32 megabytes -ms=on solid archive = on
EXAMPLE 2
7z a -sfx archive.exe dir1 add all files from directory «dir1» to SFX archive archive.exe (Remark : SFX archive MUST end with «.exe»)
EXAMPLE 3
7z a -mhe=on -pmy_password archive.7z a_directory add all files from directory «a_directory» to the archive «archive.7z» (with data and header archive encryption on)
Установка и использование 7-Zip в Linux
Формат 7-Zip впервые появился в 1999 году. Данный формат отличает высокая степень сжатия данных. По сравнению с ZIP степень сжатия 7-Zip может быть на 30-50% лучше. 7-Zip в основном используется среди пользователей Windows.
7-Zip нельзя использовать для создания резервных копий в Linux, так как формат не сохраняет информацию о правах доступа к файлам и данные о владельце.
В данной заметке мы рассмотрим, как установить поддержку 7-Zip в некоторых дистрибутивах Linux, а также как работать с 7zip-архивами.
Установка 7-Zip в Linux
Установка 7-Zip в Ubuntu, Debian
Для установки поддержки 7-Zip в Ubuntu и Debian, а также производных от них дистрибутивах (LinuxMint и др.), доступно три пакета:
- p7zip — базовая версия, которая поддерживает только архивы в формате .7z Представляет собой порт утилиты 7za.exe для POSIX систем.
- p7zip-full — полная версия, которая поддерживает различные алгоритмы сжатия при создании 7zip-архивов, а также другие форматы архивов. Установка данного пакета также обеспечивает поддержку 7-Zip в менеджере архивов File Roller, который используется в Ubuntu.
- p7zip-rar — отдельный модуль для p7zip, позволяющий распаковывать RAR-архивы.
Для установки 7-Zip в Ubuntu (Debian) вы можете установить пакет p7zip-full, а также p7zip-rar для поддержки RAR. Для этого выполните в терминале команду:
sudo apt install p7zip-full p7zip-rarПримечание: В новых версиях Ubuntu (например, в Ubuntu 18.04 и новее) 7-Zip автоматический поддерживается в файловом менеджере Nautilus. Можно создавать и распаковывать 7zip архивы.
Установка 7-Zip в Fedora, CentOS
В дистрибутивах Fedora, CentOS доступны пакеты p7zip, p7zip-plugins.
Для установки используйте следующую команду:
sudo yum install p7zip p7zip-pluginsУстановка 7-Zip в ArchLinux
Для установки поддержки 7-Zip в ArchLinux установите пакет p7zip, который доступен в официальных репозиториях дистрибутива.
Раcпаковка 7zip-архивов
Когда поддержка 7-Zip установлена, то для распаковки .7z файлов вы можете использовать графические утилиты (например, File Roller, Ark), средства файлового менеджера вашего дистрибутива (если есть поддержка), а также командую строку.
Для работы с 7-Zip архивами через командную строку используется команда 7z
Распаковать в текущую директорию
Чтобы распаковать .7z архив в текущую директорию с сохранением структуры директорий, которые находятся внутри архива, выполните в терминале команду:
Файлы архива будут распакованы в текущую директорию. Если в архиве содержатся директории, то при распаковке их структура будет сохранена.
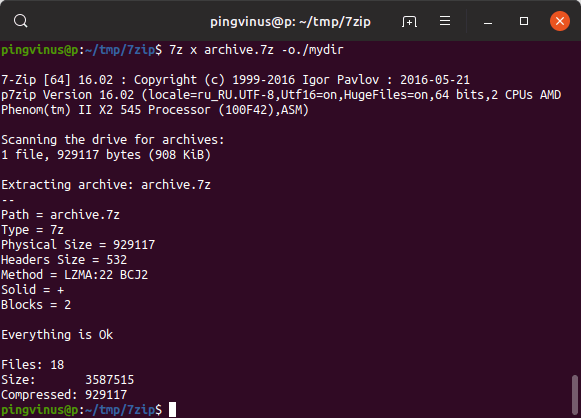
Распаковать в определенную директорию
Чтобы распаковать архив в определенную директорию используется опция -o , за которой без пробела указывается путь до директории.
Распаковать без сохранения структуры директорий
Можно распаковать .7z архив, не сохраняя структуру директорий. То есть, если внутри архива есть директории и файлы в них, то при распаковке все файлы будут распакованы в одну директорию. Для этого используется опция (команда) e .
Создание 7zip-архива
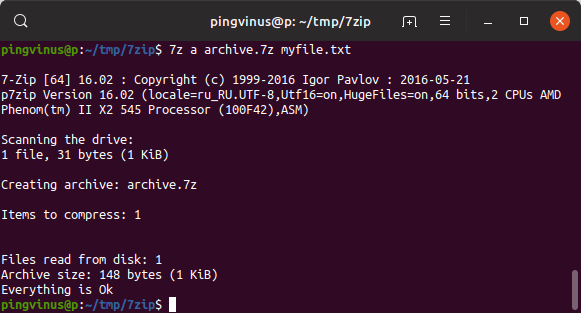
Упаковать один файл
Чтобы создать .7z архив используется следующая команда.
В результате выполнения данной команды будет создан архив archive.7z , который содержит файл myfile.txt
Упаковать несколько файлов
Чтобы упаковать несколько файлов, перечислите их имена через пробел.
7z a archive myfile1.txt myfile2.txt myfile3.txtУпаковать директорию и ее содержимое
Вместо файла, при создании архива, можно указать путь до директории, которую необходимо сжать.
7z a archive.7z /path/to/mydirДобавить файлы в существующий архив
Если архив уже создан, то можно добавлять в него новые файлы. Для этого используется такая же команда, как и для создания архива, только в качестве названия архива указывается существующий файл.
7z a archive.7z myfile123.txtПросмотр файлов в архиве
Для просмотра содержимого архива используется команда:
Протестировать целостность архива
Чтобы проверить целостность архива (проверить, что архив «не битый») используется команда:
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели как установить поддержку 7-Zip в популярных дистрибутивах Linux, а также рассмотрели базовые возможности работы с 7zip-архивами.
Утилита 7z имеет много возможностей. Чтобы получить дополнительную информацию можно использовать следующие команды: