- How to Install ADB and Fastboot on Linux
- Installing ADB and Fastboot on Linux
- Installing ADB on Debian or Fedora
- Adding System-wide ADB and Fastboot on Linux
- How to install and use ADB and Fastboot on Ubuntu
- Getting started: Installing ADB, Fastboot, and getting your Android device ready
- Transferring files from computer to mobile
- Transferring files from mobile to computer
- Installing APK packages
- Uninstalling APK packages
- Additional commands
- Conclusion
- About the author
- David Adams
How to Install ADB and Fastboot on Linux
Android, being an open-source OS, is very customizable. You can customize it by adjusting device settings to your preference, using themes and apps, and so on. While some customizations can be achieved only after rooting your device, there are many others that can be done using ADB commands. ADB works like a bridge between Android devices and computers. However, before you can control your phone or tablet using ADB commands, you must set up ADB on your Windows, macOS, or Linux computer. In this guide, we’ll check out how we can install ADB and Fastboot on Linux.
ADB and Fastboot are multi-purpose command-line tools. By using ADB and Fastboot commands on your computer, you can get detailed information about your Android device, uninstall system apps without root, install apps, push or pull files, backup data, debug your device, enable and disable features and customize it in many ways. If you are interested in exploring the geeky aspect of owning an Android device, let’s start with installing ADB and Fastboot on Linux first.
Installing ADB and Fastboot on Linux
- Open the Settings app on your Android device and enable USB debugging via Developer settings.
- Download the latest Android SDK Platform-Tools for Linux.
- Extract the downloaded zip file to your computer’s desktop.
- Now, open a Terminal window. You can launch the Terminal either by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T keyboard shortcut or using an app launcher.
- When the Terminal window is opened, type the path to the extracted platform-tools folder in the following format: cd / path to the extracted platform-tools folder /
- For instance, if you extracted the zip file on your desktop, the command line would look like this. Here, cd means “change directory”.
cd /Users/Technastic/Desktop/platform-tools_r33.0.3-linux/platform-tools/
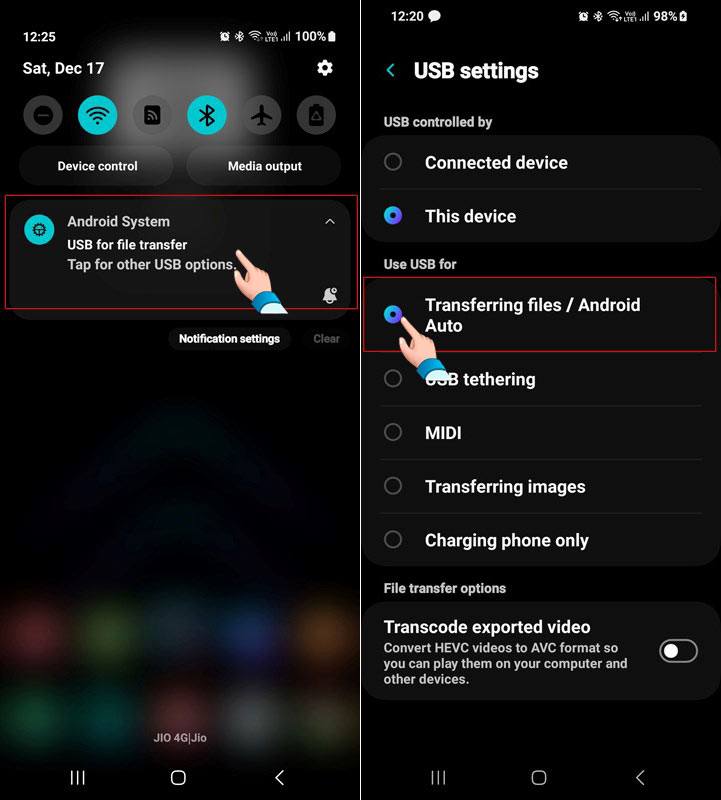
adb devices or ./adb devices 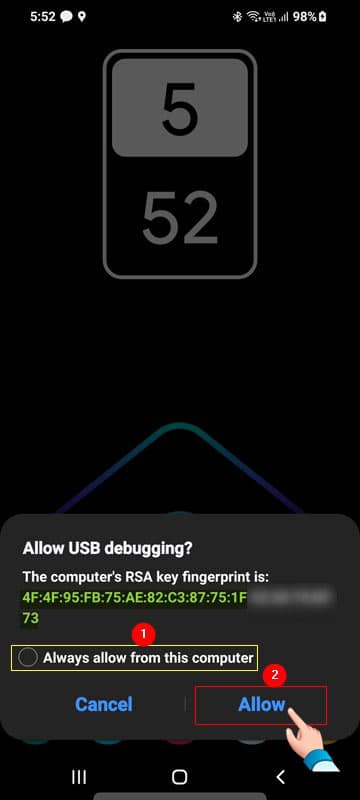
Installing ADB on Debian or Fedora
As a Linux user, you must be aware that there are a number of Linux distros like Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, Elementary OS, Deepin OS, etc. While the steps to install ADB and Fastboot on Linux described above should work on most distros, there are some in which you need to take a little different course. For instance, on Fedora/SUSE and Debian/Ubuntu, you don’t need to download the Android SDK Platform-Tools. Instead, you can use a command in the Terminal to install ADB drivers directly.
In case you are a Fedora/SUSE-based Linux user, you can use the following command to install ADB and Fastboot on your PC.
sudo yum install android-tools
Those who use a Debian/Ubuntu-based Linux distribution, execute the command line given below to set up ADB.
sudo apt-get install android-tools-adb
In these Linux distributions, you are supposed to add “./” before ADB commands. Thus, you have to use ./adb devices in place of adb devices .
Adding System-wide ADB and Fastboot on Linux
In a normal installation, you’ll be able to access ADB and Fastboot only by launching the Terminal from the platform-tools directory. However, if you give system-wide access to ADB, you’ll be able to use ADB commands by launching the Terminal anywhere. Please note that if you have a 64-bit system, you’ll have to install libstdc++ and glibc.i686 on your computer first.
In order to enable system-wide ADB on Linux, launch the Terminal and execute the following command.
sudo gedit .bashrc
The command will open the file in the Gedit text editor. Add the path of the platform-tools folder at the end of the file and save the changes.
export PATH=$:/home/Technastic/Desktop/platform-tools_r33.0.3-linux/platform-tools/ That’s it! You can now use ADB and Fastboot commands from any location on your Linux PC.
How to install and use ADB and Fastboot on Ubuntu
ADB (Android Debug Bridge) and Fastboot allow us to manage Android mobile devices from the computer. After reading this tutorial, you’ll know how to install and use ADB and Fastboot to control your Android cell phone.
Getting started: Installing ADB, Fastboot, and getting your Android device ready
Before starting, you need to enable your phone Developer Options submenu. I have a Redmi 9 cell phone, but the steps are similar in most Android devices.
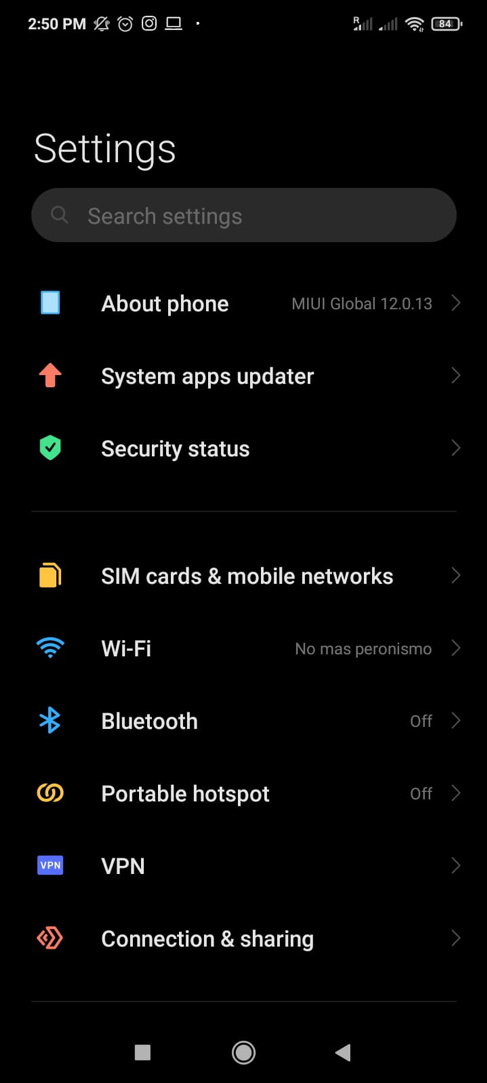
To start, on your phone, tap Settings and select About Phone; in the screenshot below, it is the first option; some Android devices have this option at the bottom of the Settings menu.
Tap MIUI Version several times until you see Developer Options are enabled.
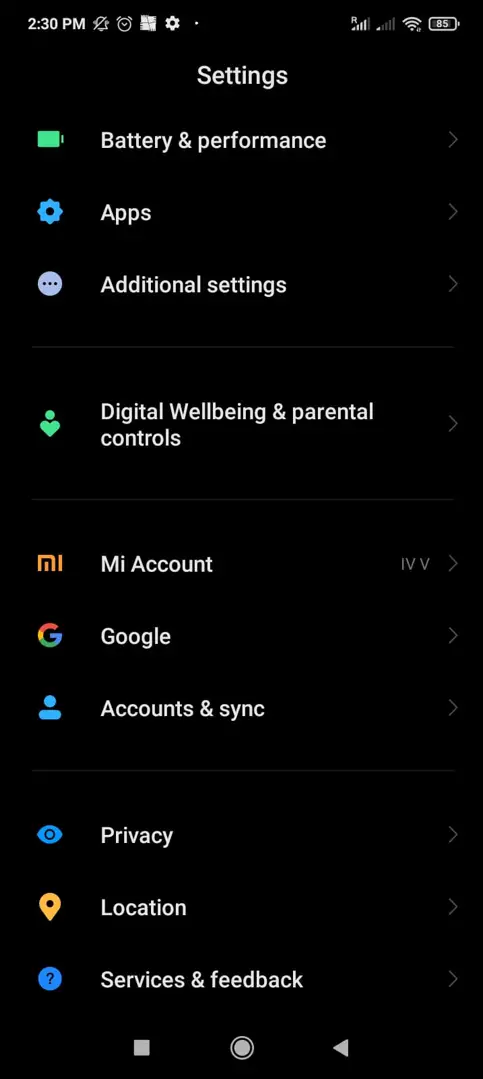
Go back to the Settings menu, scroll down to find, and tap Additional Settings.
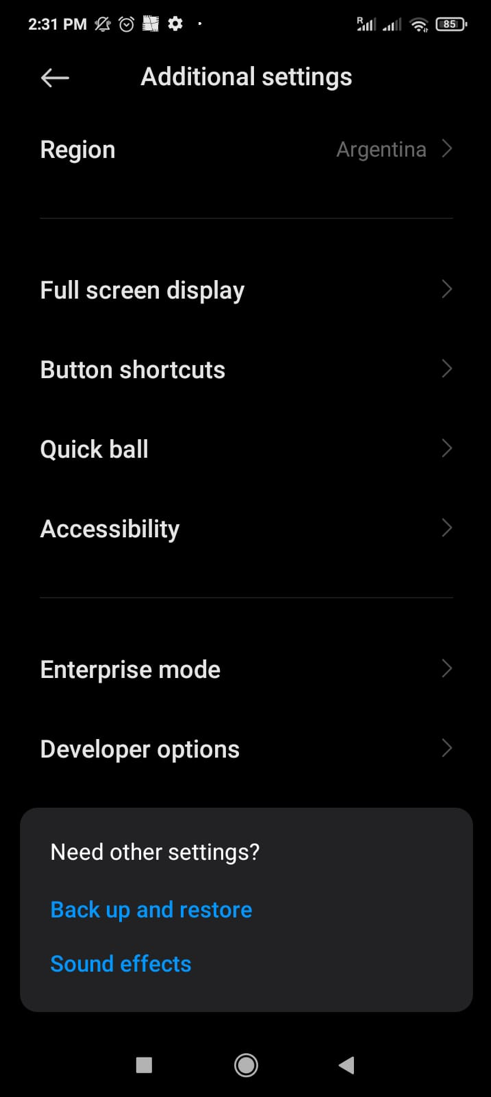
Would you please scroll down to find Developer options and tap it?
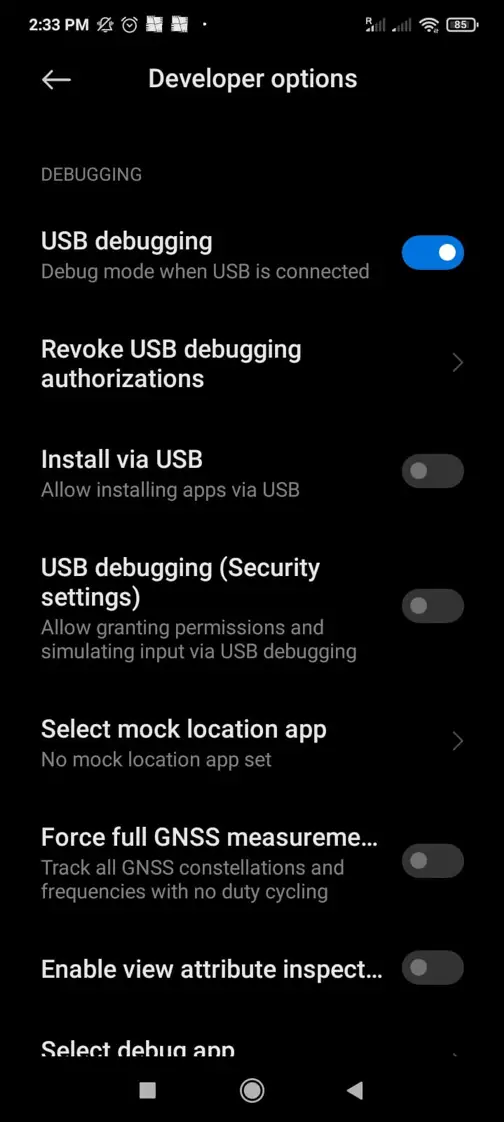
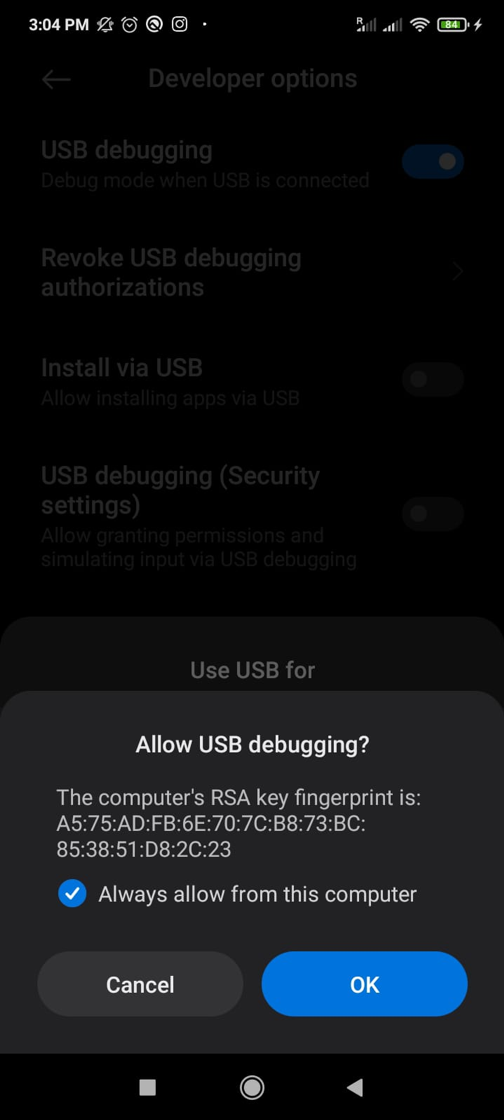
Enable USB Debugging as shown in the following screenshot.
Tap the confirmation box “I’m aware of possible risks, and assume all possible consequences voluntarily” and press OK.
Now you can install ADB and Fastboot from your Ubuntu computer.
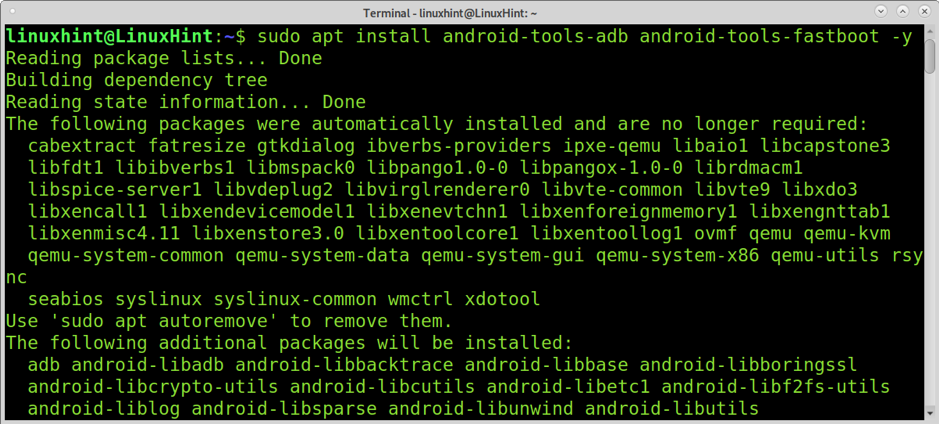
First, install Android Debug Bridge and Fastboot using the apt command as shown in the screenshot below.
To start the ADB server, run the following command.
Your phone device allows USB debugging when requested by tapping OK, as shown in the image below. In some cases, this prompt on the mobile appeared in the next step.
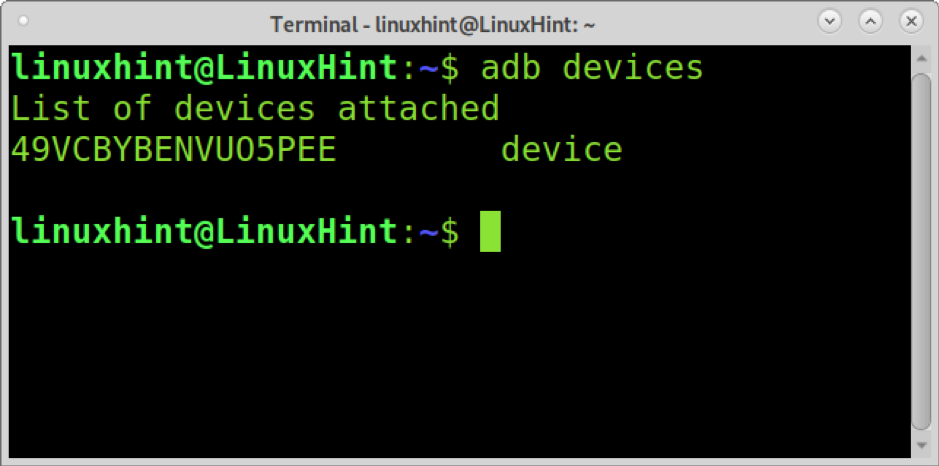
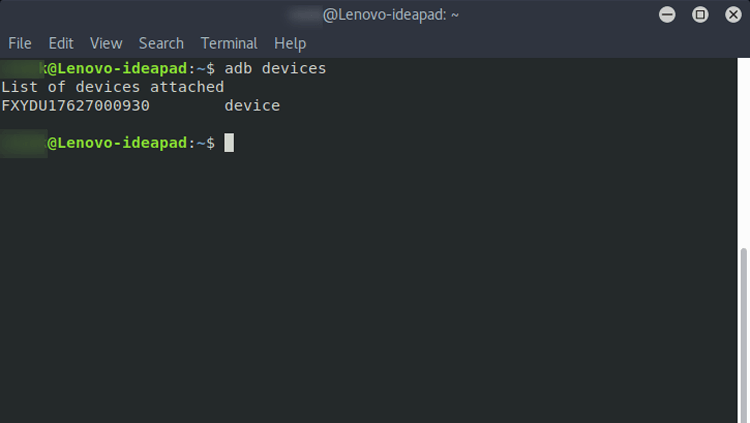
To see if your device was properly detected, you can run the following command.
As you can see, the device was detected properly.
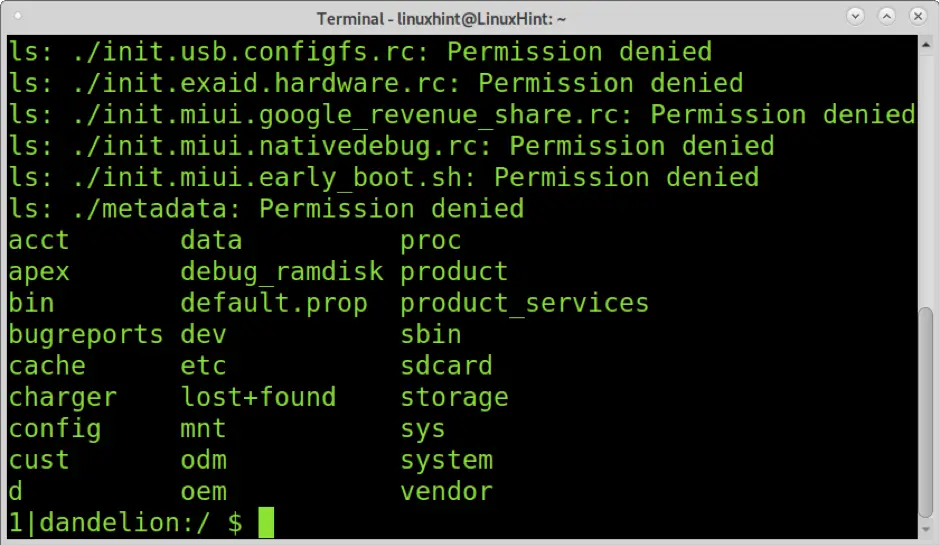
You can open a shell on your Android device by running the command below.
As you can see, the pwd command shows I’m in the system root directory. The ls command will list all files and directories inside. You can browse all directories using the same Linux syntax.
Transferring files from computer to mobile
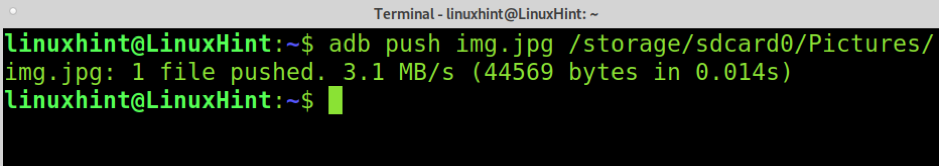
The following command shows how to send files from your computer to your mobile device. To do it, you need to run adb with the push option followed by the file you want to copy to your phone and your phone’s path where the file will be stored.
The command below is used to copy the img.jpg file to /storage/sdcard0/Pictures/. You can learn file and directory paths by browsing the shell as explained previously (adb shell).
Transferring files from mobile to computer
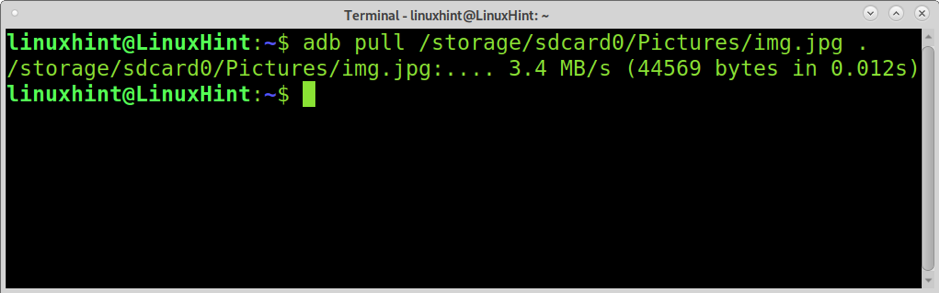
You also can copy files from your mobile device by using the pull option as shown in the example below, in which the file img.jpg is copied into the computer’s current directory (.).
Installing APK packages
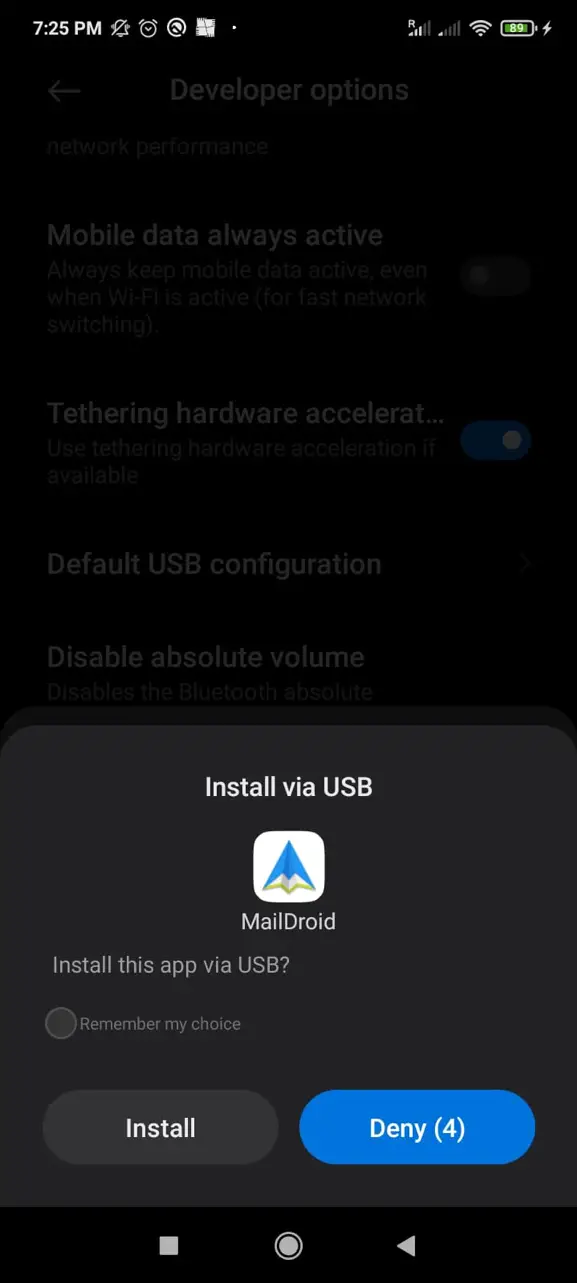
Adb also allows you to install applications on your mobile device. To do it, you need to enable the Install via USB located in the Developer Options submenu in your phone Settings, as shown in the image below.
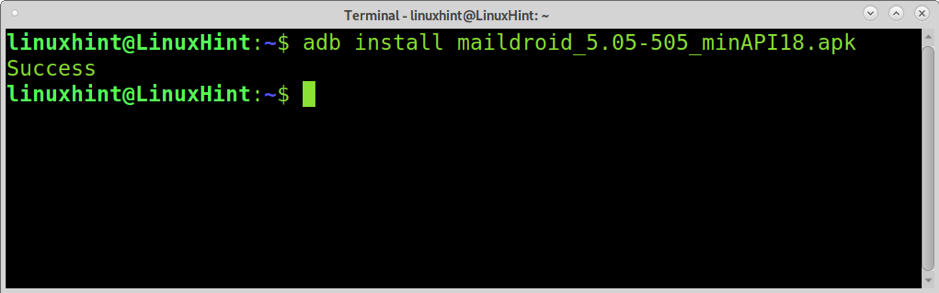
Once the Install via USB option was enabled, you can install any apk supported package by adding the install option followed by the apk package as shown below.
Your phone will request your confirmation, as shown in the screenshot below; tap Install to get the application installed.
If the application were properly installed, you would see the “Success” message shown in the following screenshot.
Uninstalling APK packages
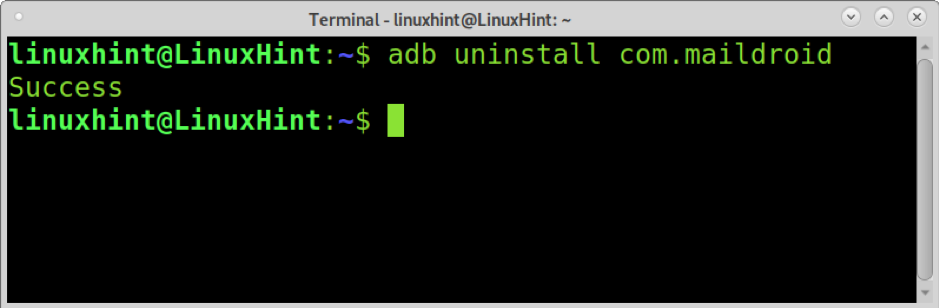
You also can uninstall applications from your mobile device using your computer. Instead of using the install option explained previously, you need to use the uninstall option.
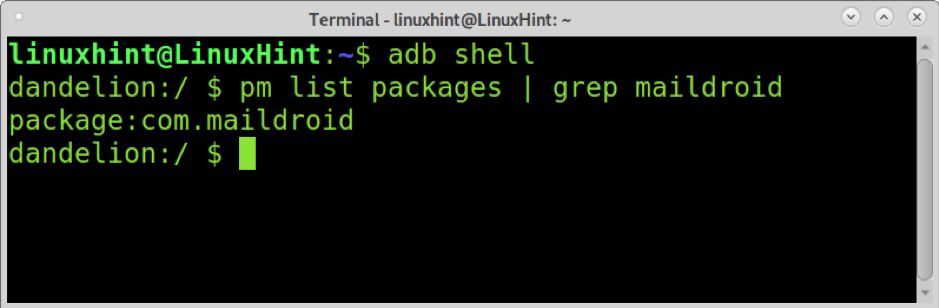
Before uninstalling a package, you need to see its name; you can do it by opening a shell on your Android device and running the command of the example below (replace maildroid with the app name you want to find).
As you can see, the package name is com.maildroid. To remove it, run:
Additional commands
The following command can be used to change your phone resolution.
The command below allows you to edit your mobile’s dpi (dots density or Dots per inch).
Stock recovery doesn’t support flashing custom ROMs. The Fastboot command below can be used to install a custom recovery such as CWM or TWRP.
The command below allows you to fully wipe your mobile to install a custom ROM.
Conclusion
Both Adb and Fastboot allow users to operate their Android devices from the computer. Learning to use these applications is mandatory for anyone dealing with mobile devices. It is important to highlight that the applications explained in this tutorial are multi-platform, including Linux, MacOS, and Windows.
I hope this tutorial on Adb and Fastboot was useful. Keep following Linux Hint for more Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.