- Add all users to group linux
- How to Add a User to a Linux Group
- What is a User Group in Linux
- Primary Group
- Secondary Groups
- How to Create a User Group
- How to Add User to Group
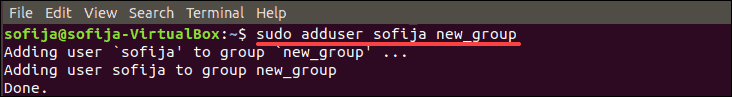
- Add an Existing User to an Existing Group
- Add a User to Multiple Groups at Once
- Create a User and Add to Group
- Change a Users Primary Group
- How to Remove a User From a Group
- Delete a Group
- How to List Groups in Linux
- Other Common Groups
- How to Add a User to a Group in Linux
- Adding Users to a Group in Linux (2023)
- What is a User Group in Linux
- Primary Group
- Secondary Group
- How to Add New Users in Linux
- How to Create a User Group in Linux
- How to Add Users to Groups
- Add Existing User to An Existing Group
- Add User to Multiple Groups
- Create a New User and Assign a Group
- View a User’s Groups
- How to Remove a User from a Group
- Delete a Group in Linux
- How to Change a User’s Primary Group
- How to List All User Groups in Linux
- Manage Users and Groups in Linux Terminal
Add all users to group linux
Recently I found that in I needed to add all the interactive users on my system to the same user group, in this case to allow them access to the network manager applet. If you only have a couple of user accounts doing this by hand isn’t too difficult, but I have quite a few different accounts on my system so I wanted to see if I could come up with a ‘one liner’ to do the job…
In order to add a user to a group you need to be running as root.
$ su Password:
$ sudo -i Password:
First you need work out how to get a list of user accounts on the system, in this case I’m doing this by extracting all the username fields from the password file.
# cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ‘:’ -f1
root
daemon
:
:
:
nobody
user1
user2
user3
:
:
:
sshd
Since you only want a list of interactive users I’ll filter out those that don’t have a home directory (assuming that all home directories are in the /home directory) using grep.
# cat /etc/passwd | grep /home | cut -d ':' -f1
user1
user2
user3
By combining this with a for loop we can iterate through all the interactive users and add each one to the netdev group so that they can use the network manager applet.
# for ID in $(cat /etc/passwd | grep /home | cut -d ‘:’ -f1); \
> do (adduser $ID netdev);done
The user `user1′ is already a member of `netdev’.
Adding user ‘user2’ to group ‘netdev’ .
Adding user user2 to group netdev
Done.
Adding user ‘user3’ to group ‘netdev’ .
Adding user user3 to group netdev
Done.
How to Add a User to a Linux Group
In Linux, a group is a unit in which you can manage privileges for several users simultaneously. Linux groups allow you to manage multiple user permissions quickly and easily.
In this tutorial learn how user groups work in Linux, and how to add users to specific groups.
- A system running Linux
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
- Access to a terminal window/command line (Ctrl-Alt-T, Ctrl-Alt-F2)
What is a User Group in Linux
In Linux, different users have different roles or responsibilities. Some users might need the ability to execute applications, while others are restricted from accessing specific files and folders.
Groups let you create categories of users with pre-set permissions. Instead of managing permissions for each user account, you can simply add a user to a group to grant the appropriate permissions.
Primary Group
The primary group is set to the logged-in user. Any files the user creates are automatically added to that group. A user can only belong to one primary group at a time. A primary group with the same name as the user is created, and any files created by the user are included in that group.
Secondary Groups
A user can belong to any number of secondary groups (including none). Secondary groups are created to manage individual files and software applications. Members of the group inherit the read, write, and execute privileges for that group.
Note: Refer to our in-depth guide on how to create users in Linux for more info on user management.
How to Create a User Group
1. To create a new group, enter the following:
2. Replace new_group with the name you want for your new group.
How to Add User to Group
Add an Existing User to an Existing Group
1. Use the adduser command to add a user to a group:
sudo adduser user_name new_group2. Use the useradd command to add a user:
sudo useradd –G new_group user_name3. You can also use the usermod command to add a user to a group:
sudo usermod –a –G group_name user_nameThe usermod command uses the –append and –group options to append the user to a particular group. Without using –append , the user could be dropped from other groups.
Add a User to Multiple Groups at Once
Use the usermod command to specify multiple groups to add to:
sudo usermod –a –G new_group,new_group2,new_group3 user_nameCreate a User and Add to Group
1. This is useful for creating a new user on the fly for a specific software application. Enter the following:
sudo useradd –G new_group new_user2. Next, assign a password to the new user:
Change a Users Primary Group
All previous commands have been used to manage the secondary groups a user belongs to. In most cases, a user’s primary group is the same as their username.
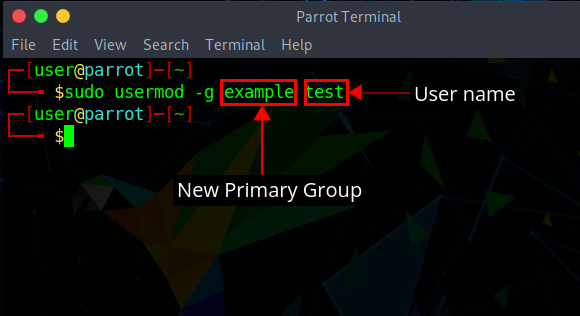
To change a users primary group, enter the command:
sudo usermod –g new_group user_nameThe lower-case –g specifies the primary group. (Upper-case –G refers to a secondary group.) A user can only have one primary group, so the old primary group user_name won’t be primary anymore for this user.
How to Remove a User From a Group
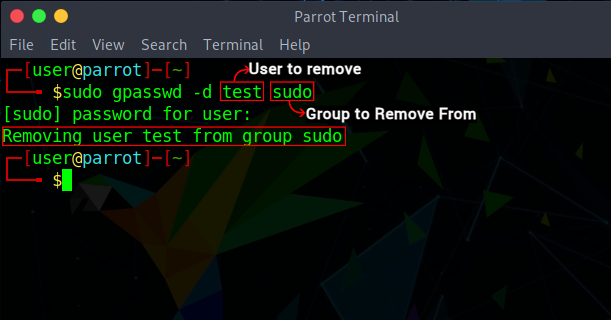
The gpasswd tool is used for managing groups. To remove a user from a group:
sudo gpasswd –d user_name new_groupNote: The gpasswd tool can also be used for other administrative tasks such as defining group administrators and setting a password for access to group resources. Use the Linux man command man gpasswd for details.
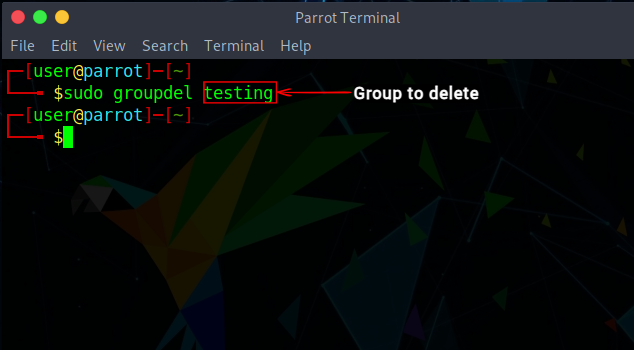
Delete a Group
To delete a group, use the command:
How to List Groups in Linux
Linux comes with several different groups by default. Some of these, like the sudo group, can be used to grant permissions. Others are hidden, used for system tasks.
1. To view a list of groups on your system by displaying the /etc/groups file:
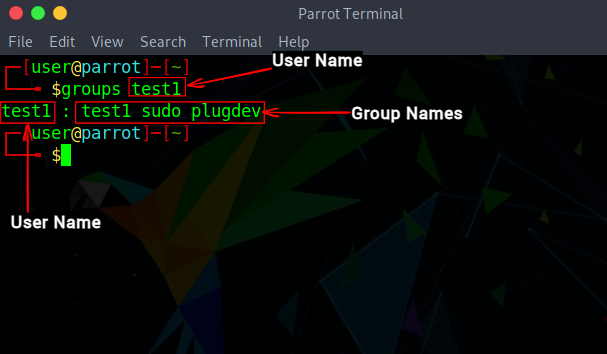
2. To display the groups that a user belongs to with the groups command:
3. The image above shows the groups that the logged-in user ‘sofija’ belongs to. You can display groups for a different user by specifying the username:
4. Another method to display the groups a user belongs to, including user ID (uid) and group ID (gid), is to use the id command:
Other Common Groups
There are a several common group names you might encounter in Linux:
- sudo – A member of this group can use the sudo command to elevate their privileges
- wheel – This is an older method of granting sudo-like privileges
- cdrom – Allows the user to mount the optical drive
- adm – Allows the user to monitor Linux system logs
- lpadmin – Allows the user to configure printers
- plugdev – Allows the user to access external storage devices
You should now have a good understanding of Linux groups and how to add and remove members from those groups. For more information on specific commands, you can enter the man command to display a manual in your terminal window.
How to Add a User to a Group in Linux
Assume you are a system administrator of a big project, and you often receive complaints from the QA team that the development team is messing up the codebase and vice versa. Upon close inspection, you find out that two teams are a part of the same group, sharing the same codebase. So you ask your senior to help with the problem, and he advises you to make two groups for all the users of the development and QA teams. But, you have no clue how to add users to a group in Linux. Well, we are here to help solve this problem. In this article, we have explained how to create a new group, create new users, and then add a user to a group in Linux.
Adding Users to a Group in Linux (2023)
Before we demonstrate how to create groups, create users, and add new or existing users to these groups, we first need to learn about what is a user group in Linux. So let’s look at what are user groups and then move on to adding users to a group.
What is a User Group in Linux
Generally, an organization is divided into teams, with each team having a different function and every member of the organization is part of a team. Similarly, in a multi-user system, every user is part of a group having a different set of privileges like reading, writing, or executing permissions for a shared resource within the group. There are two types of groups in Linux:
Primary Group
Whenever you log in to a session, you are part of the primary group. Generally, the primary group bears the same name as the username in Linux. Any file or process created by you is part of this group and cannot be accessed by users of other groups by default. Information such as user id, group id, etc. about a primary group is stored in the file – /etc/passwd .
Secondary Group
Secondary groups or supplementary groups are useful when you need to share access to any files or processes with a particular group of users. Only the root user or users with sudo privileges can assign new permissions or add new users to the secondary groups.
A user can only be part of one primary group but can be part of multiple secondary groups. Now that you know the basics of user groups in Linux, let us now see how to create new users and add them to a group.
How to Add New Users in Linux
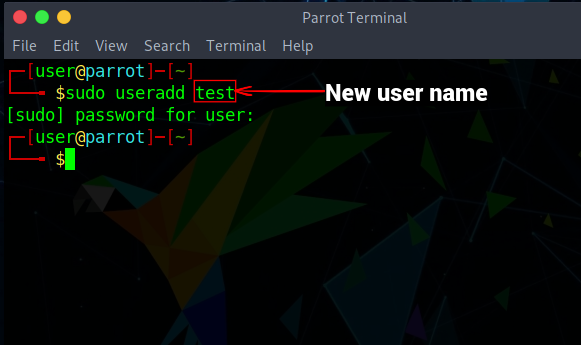
To create new users, use the useradd command as per the following syntax:
Some of the options to pair up with the command are:
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -d | The new user will be created using a new directory name as the value for the user’s login directory |
| -e | This is used to specify the date on which the user account will get deactivated |
| -u | This will create a new user with a specific user-id |
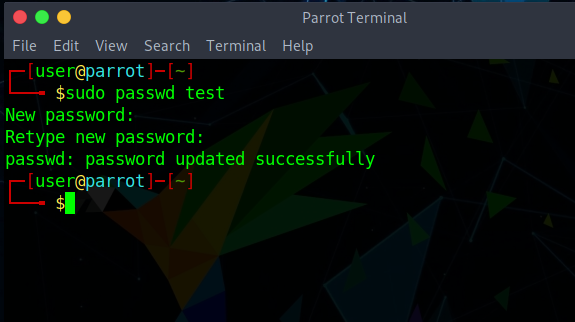
The new user you create will only be a part of the primary group initially. Once you create a new user, assign them a new password using the passwd command, as shown below:
Here, you will be prompted to enter the new password and then asked to re-enter the password for confirmation. At this point, the user can now log in to the system with the new username and password you just created.
How to Create a User Group in Linux
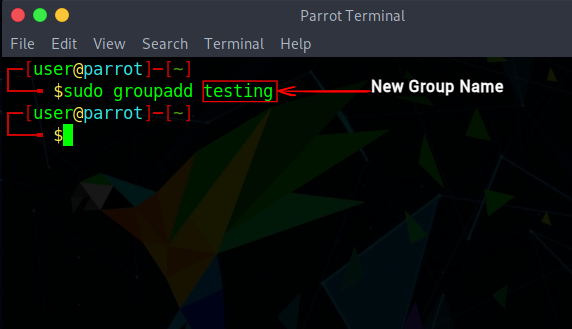
Now that you have created a new user, you can start creating groups and adding users to them. To create a new group, use the groupadd command. Be sure to give a unique name to the new group name, or it will clash with other existing group names. Here’s what the syntax looks like:
How to Add Users to Groups
Once you have created a group, you can now start adding users to it. Only a root user or a user with sudo access can add users to different groups.
Add Existing User to An Existing Group
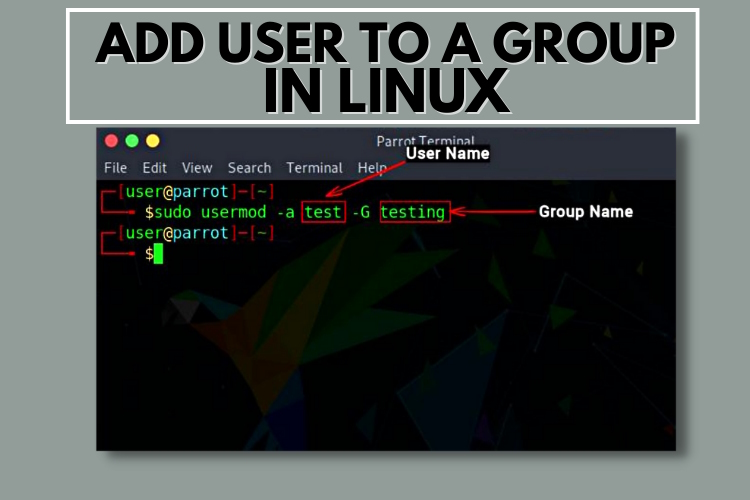
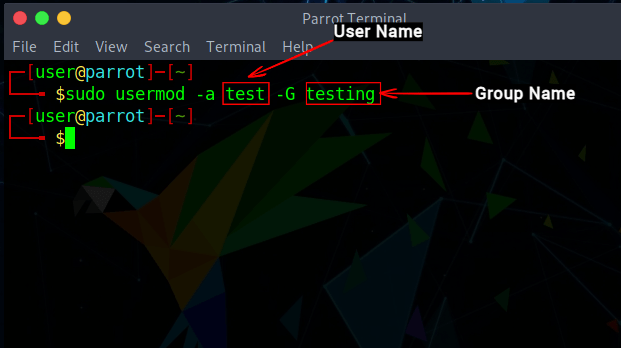
To add an existing user to a group, use the usermod command whose syntax we have highlighted below:
Here, the -a option stands for append (add at the end) and it adds the user to an existing group and the -G flag is used to specify the name of the group to which the user is being appended. There is no option for verbose output with this command, except it gives a warning if the user or the group does not exist.
Add User to Multiple Groups
The usermod command in Linux can also be used to add a user to multiple groups with essentially the same options as a single group, as shown below. Be sure to specify the group names without any spaces.
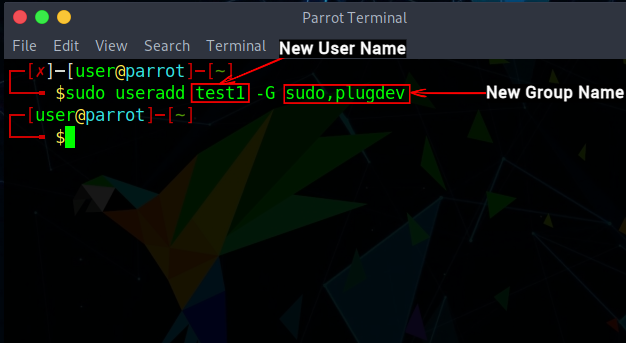
Create a New User and Assign a Group
You can add a new user to a group all with a single command om Linux. The useradd command lets you create a new user and then add a user to the specified groups. The syntax to add a new user using the useradd command is:
View a User’s Groups
To view all the groups associated with a user, you can use either the groups command or the id command. Check you the syntax shown below:
If the is left blank, then it will show the group names for the current user only.
How to Remove a User from a Group
To remove a user from a group in Linux distros, you can use the gpasswd command, as per the syntax given below:
In addition to removing a user from a group, the gpasswd command is also used for various administrative tasks such as defining group administrators or setting a group password, etc.
Delete a Group in Linux
To delete any secondary group in Linux, you can use the groupdel command:
How to Change a User’s Primary Group
All the commands we have discussed till now apply to the secondary group and their users. To change a user’s primary group in Linux, use the following syntax:
You must be wondering what’s the difference between the -g and -G flags. The -g flag is used for primary groups, whereas the -G flag is used for secondary groups.
How to List All User Groups in Linux
A user which gets created at the time of installation is known as a system user and is part of many default groups in Linux. The information about every group in the system is stored in the file – /etc/group . To list all groups in the system, use the following syntax:
Manage Users and Groups in Linux Terminal
Managing groups is a useful task that could come in handy during various operations, especially if you are a system administrator. Here, we have shown you some easy Linux Terminal commands to create a new user, create new groups, add a new user to a group, and more. So, we hope this article solves your problems. If it doesn’t, let us know in the comments below, and we will help you out.