- 10 Smart Ways To Access Internet in Any Mobile Phone
- 1. Connect to WiFi Network
- 2. Mobile WiFi Hotspot
- 3. Bluetooth Tethering
- 4. Transfer Mobile Data
- 5. Urgent Data Recharges
- 6. Using OTG Cable
- 6. Through LAN Adapter
- 7. Turn your PC to WiFi Hotspot
- 8. Share PC Internet using USB Cable
- 9. Fake WiFi/GPS/Mobile Data
- 10. Hunt Free Data and Misc Ways
- WIFI Antenna Design
10 Smart Ways To Access Internet in Any Mobile Phone
Within past few decades, mobile phones and their technology has improved so much that they have become more advanced than laptops and computers which are coming to the market right now. Being small and portable, they are even more comfortable to carry and use anywhere. So, mobile users are almost 100 times higher than desktop/laptops users.
Mobile companies embrace this fact and hence they try to make hardware and software in smartphone more and more comprehensive so that almost every task that user do in desktop, he can perform in smartphone too. Among all the important tasks, lots of web-related tasks are also their. So, they have provided lots of ways to even connect internet and access web in mobile phones.
You might know 2 or 3 ways to connect internet in your mobile phone but here, we are telling you 10 cool ways by which you can connect and access internet in your mobile phone . So, if you have an urgent requirement to access internet in your smartphone, we are sure that among these 10 amazing ways, some methods will be able to get you instant internet in your mobile phone.
Before starting the list, let me first keep the trivial method aside which is that if you have mobile data available in your SIM card, you can just turn it on to access internet or recharge your SIM with data pack to have internet in your smart phone.
Now, lets move ahead and know what other interesting ways mobile phone support to allow you access internet in your mobile phone.
1. Connect to WiFi Network
After mobile data, the most widely used and easy way to access internet in your smartphone is through WiFi. When you turn on your mobile phone’s WiFi, it searches for all WiFi hotspots available in your phone’s range. WiFi Hotspots can be both open and password protected. So, if you have login & password to a secure WiFi hotspot, it is recommended to connect to that but if not, you can connect to open WiFi Hotspots which don’t require any password authentication to connect and access internet using them.
Public (open) WiFi Hotspots are not secure, so it is recommended to take preventive measures like installing antivirus apps in your smartphone and spoof MAC address of your mobile phone to hide your identity in the network.
2. Mobile WiFi Hotspot
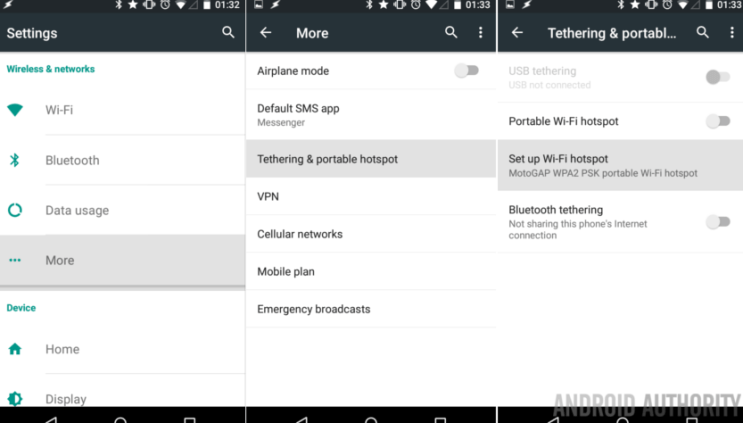
If your colleague or friend has mobile data available in his smartphone, then you can share his mobile data in your smartphone using the “Portable Wi-Fi Hotspot” feature available in his smartphone. In Android smartphone, the feature is available at Settings >> More >> Tethering & portable hotspot and in iPhone, navigate to Settings & Mobile >> Personal Hotspot.
Turn mobile hotspot feature ON in your friend’s phone. Now you and your friends can use internet of the phone where you turned on hotspot feature. You can put password to the hotspot to share it with only those people whom you want.
3. Bluetooth Tethering
If your friend has access to any WiFi hotspot but he can’t share its login details with you for some reason then you can simply ask him to connect to that WiFi network using his smartphone and then share it’s internet through bluetooth in your smartphone.
To do this, follow these steps:
- Connect your friend’s phone to the WiFi network & turn ON its bluetooth
- Pair your mobile phone with your friend’s mobile phone via bluetooth
- Now, go to bluetooth settings in your friend’s phone, tap the gear icon in front of your phone appearing at its paired device list
- A pop-up appears where you need to select “Internet Sharing” and you’re done.
4. Transfer Mobile Data
Some telecom operators provide the feature to transfer mobile data too. In India, Airtel, Idea and Reliance provide the service to transfer mobile data (MBs) to someone in the same network. You can learn how to use this feature here.
This feature can be helpful even if you are miles away from the friend that have mobile data because he can directly send his mobile data balance to your mobile number and you can access internet right away.
5. Urgent Data Recharges
Data recharges normally cost more than pennies. So, if you have mobile balance or money inside your wallet in “pennies”, you can’t purchase a standard data pack either from a mobile shop or using *# USSD mobile codes.
What you can do is purchase emergency data pack recharge which however have a validity of 24 hours but it provides mobile data in MBs in comparison to standard data pack recharges and in small fractions.
For example, in Aircel, you can enjoy 12 MB data for just Rs. 3/- (24-hours validity); in vodafone you can enjoy 40 MB 3G data for Rs. 11/- (24-hours validity) using their emergency recharge USSD codes.
6. Using OTG Cable
If your phone support OTG (On-The-Go) feature and you have used it earlier then you already know it’s use. Using OTG cable, you can directly connect pendrive to your smartphone and exchange data. But do you know that you can connect Keyboard, Mouse and even Data Card (USB Modem) using the OTG cable?
If you never tried, try it now. Connect your working data card to your smartphone using OTG cable, turn off both WiFi and mobile data. Now, if your data card has working internet, you will be able to browse internet straightaway without turning ON/OFF any setting.
6. Through LAN Adapter
This is one uncommon way but yes, you can directly connect LAN wire to your smartphone using LAN adapter and access internet using it. I will not call it a workaround as it is not one but yeah, if you only have access to LAN wire for internet (for example, in university/institute), it might worth buying a Micro-USB to RJ45 LAN Ethernet Port Cable with can provide fast internet access to your smartphone directly using a LAN wire.
7. Turn your PC to WiFi Hotspot
Smartphones have built-in feature to turn create Portable WiFi Hotspot but computers are out of luck in this case. If you have laptop, you might have built-in portable WiFi Hotspot feature (available at location Settings >> Mobile hotspot in Windows 10) which will allow you to share internet connection with nearby devices.
If you only have personal computer in reach, if it runs on Ubuntu then you will have hotspot feature as ubuntu have this feature available inside it’s operating system but if the PC runs in Windows OS, follow this guide to turn your PC into WiFi Hotspot and share its internet connection.
8. Share PC Internet using USB Cable
You can also share your PC internet connection using USB cable. Doing it is easy. Just follow these quick steps and you’ll have access to your PC’s fast broadband internet in no time:
- Connect your mobile to PC via USB cable
- In your mobile, go to Settings >> More >> USB Internet, select PC Version >> Next >> DONE
Complete these two simple steps and you’ll be able to access your PC internet connection in your smartphone via USB Cable. If you can’t able to access internet, go to Network settings in your PC, right-click on the network connection >> properties. Navigate to sharing tab and here ‘tick’ the option that says “Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s internet connection”.
9. Fake WiFi/GPS/Mobile Data
There are many prank apps available online which you can download and install in your Android smartphone to prank your friends with fake Wifi or GPS access. Some of them are even available at Google Play store too. For example – iTroll Android App which can not only let you to fool your friends but you can also fool apps/services which are only accessible with WiFi connection.
10. Hunt Free Data and Misc Ways
Finally, when no other option is available, you can only hunt for offers or other ways to somehow access internet. Some telecom providers provide free or very cheap Facebook & WhatsApp access, make use of their offers. You can even access Facebook using SMS only. Send/receive messages, get notifications, update status and do more with Facebook texts (learn more here). And, how about FRC (First Recharge) offers which comes in new SIM card with free internet balance? 😉
I am sure you enjoyed learning some of these new ways to access internet in your smartphone. If you know any other way, please put it in comments section below.
WIFI Antenna Design
WIFI antennas are on just about every cell phone these days. The WIFI frequencies are the highest of all frequency on the device (relative to cell frequencies, gps, nfc, etc). The WIFI frequency is divided into two bands: 2400-2484 MHz (which also includes bluetooth) and 5150-5850 MHz.
All WIFI antennas support the 2400-2484 MHz band, and typically the WIFI antenna is connected to a chip that does both WIFI and bluetooth. This means designing antennas for WIFI and bluetooth is basically the same thing. Phones now are shipping with the 5150-5850 MHz band included in WIFI, so that the WIFI antenna is often dual band. It is also possible to have two wifi antennas, one for 2.4 GHz and one for the 5 GHz band, although this is less common.
Because WIFI is the highest frequency on the mobile device, the WIFI antenna will be the smallest antenna. A half-wavelength at 2.4 GHz is 6.25 cm (2.5″), and a half-wavelength at 5 GHz is 3 cm or just over an inch. Hence, using quarter-wavelength antennas leveraging the devices groundplane can make for very small wifi antennas. Good quarter-wavelength antennas for WIFI include the IFA antenna and the PIFA antenna.
WIFI antennas are simultaneously used for transmit and receive. Hence, WIFI antennas must abide by FCC and governmental SAR rules. In addition, there are peak antenna gain rules that are specified in dBm. Typically, antenna gain is specified in dB, such as peak antenna gain equals +2 dB. This means that the efficiency times the directivity is +2 dB.
FCC rules often specify gain in dBm. This means that they might say the wifi antenna gain must be less than 10 dBm. This means that the peak Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) must be less than 10 dBm. This number is a function of the conducted power (the power the radio outputs at its terminals, which is typically something on the order of 15 dBm for WIFI), the wifi antenna efficiency, and the directivity of the antenna.
Peak gain [dBm] is basically equal to Conducted_Power [dBm] + Antenna Efficiency [dB] + Directivity [dB]. For instance, if the conducted power is 15 dBm, the antenna efficiency is -3 dB, and the directivity is +4 dB, then the peak gain would be 16 dBm. If the spec for peak gain was 14 dBm, the system could achieve the spec by dropping the conducted power to 14 dBm (a drop of 2 dB).
WIFI antenna efficiencies for handheld mobile devices are typically on the order of -6 dB to -2 dB. The efficiency is decreased due to antenna-antenna coupling and lossy resistance of all the components around the antenna (camera, PCB, glass on the screen, etc).
The WIFI antenna is typically located on the top of the device (near the GPS antenna and diversity cellular antenna). Note that there are no TRP specs, so in general you don’t want the WIFI antenna to have too high of an efficiency, or the SAR and peak gain values will require a large conducted power backoff.
This page on WIFI mobile phone antenna design for smartphones is copyrighted. No portion can be reproduced without permission from the webmaster. Copyright antenna-theory.com, 2012-2014, wifi antennas.