- Driver specific information
- AW859A
- Ampak
- Ampak Devices
- Broadcom
- Broadcom Devices
- Espressif
- Espressif Devices
- ESP8089
- iNet
- iNet Devices
- RDA
- Realtek
- USB-based
- SDIO-based
- RTL8189ES / RTL8189ETV
- RTL8189FTV
- Legacy sunxi-3.4 kernel support
- Driver refusing to load (rt5370sta/8188eu/8189es/8192cu)
- 8188eu driver on sunxi-3.4
- Software Configuration
- Debian/ubuntu with NetworkManager
- Debian/ubuntu without NetworkManager
- Setup with wpa_supplicant and without network manager
- Disabling networkmanager. Fully.
- Simple and dumb WPA setup
- Devices
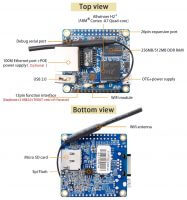
- Orange Pi Zero LTS — это Orange Pi Zero с исправленными проблемами Wi-Fi
- Orange Pi Zero LTS vs. Orange Pi Zero
- Питание Wi-Fi — VCC-1V8 1.8V 1%/0.3A
- Wi-Fi модуль XR819
- XTAL1, XTAL2
- CPUX 1.1V/1.3V/3A
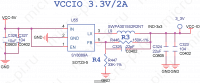
- VCCIO 3.3V/1A
- AVCC 3.3V/1A
- Основные характеристики
- Доступные операционные системы
- Технические характеристики
Driver specific information
For XR819 driver source was included in Allwinner H2 BSP.
Firmware firmware blobs can be found from Armbian firmware repository.
Also some documentation is available now:
May be related to ST cw1XX0 [1].
Initial comparison between cw1200 (drivers/net/wireless/st/cw1200) and xradio driver shows that the source code for two drivers are really similar and the st1200 driver could be improved to support both devices.
A working out-of-tree driver for mainline kernels is at [2].
AW859A
For AW859A driver source was include in Allwinner H616 Orange Pi Zero2 BSP, you can get it from orangepi-build repository.
Firmware firmware blobs can be found from orangepi firmware respository.
Ampak
Ampak combines broadcom wifi and bluetooth chips in single modules.
Ampak Devices
| Device | Type | usb/sdio id | module | sunxi-3.4 kernel | mainline kernel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP6181 | SDIO/UART | 02d0:a962 | See right | bcmdhd | brcmfmac |
| AP6210 | SDIO/UART | 02d0:a962 | See right | bcmdhd | brcmfmac |
| AP6212 | SDIO/UART | 02d0:a9a6 | See right | brcmfmac | |
| AP6330 | SDIO/UART | 02d0:4330 | See right | brcmfmac | |
| AP6335 | SDIO/UART | 02d0:4335 | See right | brcmfmac |
Broadcom
Broadcom Devices
Espressif
Espressif is a fairly young Chinese company.
Espressif Devices
| Device | Type | sdio id | module | sunxi-3.4 kernel | mainline kernel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP8089 | SDIO | 6666:1111 | out-of-tree driver exists |
ESP8089
Firstly, you should use Hans de Goede’s sunxi-wip kernel branch containing various bits and pieces needed to make things work.
Driver itself is currently in its own repository:
git clone https://github.com/jwrdegoede/esp8089.git cd esp8089 git checkout -B cleanup origin/cleanup cd ../linux make -j4 ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnu- modules M=../esp8089 CONFIG_ESP8089=m
Do not forget to copy firmware/*.bin to /lib/firmware/ on the target system.
iNet
iNet Devices
RDA
RDA Microelectronics is a relatively unknown and new chinese chipmaker.
| Device | Type | usb id / sdio id | module | sunxi-3.4 kernel | mainline kernel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA5990P | |||||
| RDA5991 | SDIO | 5449:0145 |
The RDA5990P is a single chip solution which includes Wifi, Bluetooth and an FM radio. Some code for this wifi chip is available in a Rockchip RK3188 kernel tree, but nobody has tested or ported this code yet.
Realtek
USB-based
| Best up-to-date information about Realtek driver in mainline Linux is available from Linux Wireless Project’s Realtek drivers page. |
| Device | Type | USB id | mainline kernel | legacy (sunxi-3.4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTL8188CTV | USB | 0bda:8176 | rtl8xxxu / rtl8192cu | 8192cu |
| RTL8188CUS | USB | 0bda:8176 | rtl8xxxu / rtl8192cu | 8192cu |
| RTL8188ETV | USB | 0bda:0179 | rtl8188eu (staging) | 8188eu (see below) |
| RTL8188EUS | USB | 0bda:8179 | rtl8188eu (staging) | 8188eu (see below) |
| RTL8192CU | USB | 0bda:018a | rtl8192cu | 8192cu |
| RTL8723AU | USB | 0bda:0724 | rtl8xxxu / rtl8723au (staging) | 8723au |
SDIO-based
| Best up-to-date information about Realtek driver in mainline Linux is available from Linux Wireless Project’s Realtek drivers page. |
| Device | Type | SDIO id | mainline kernel | legacy (sunxi-3.4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTL8189ES | SDIO | ?? | out-of-tree driver (see below) | ?? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RTL8189FTV | SDIO | 024c:f179 | out-of-tree driver (see below) | ?? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RTL8723BS RTL8703AS | SDIO | 024c:0523 RTL8189ES / RTL8189ETVDriver has its own repository: git clone https://github.com/jwrdegoede/rtl8189ES_linux.git cd rtl8189ES_linux make -j4 ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnu- KSRC=../linux RTL8189FTVDriver has its own repository: git clone https://github.com/jwrdegoede/rtl8189ES_linux.git cd rtl8189ES_linux git checkout -B rtl8189fs origin/rtl8189fs make -j4 ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnu- KSRC=../linux Legacy sunxi-3.4 kernel supportDriver refusing to load (rt5370sta/8188eu/8189es/8192cu)Please note that sunxi-3.4 kernel is not supported and has been deprecated. When using the rt5370sta, 8188eu, 8189es or 8192cu drivers, which are all for USB based realtek devices, it might occur that the driver refuses to load: ERR: script_parser_fetch usb_wifi_usbc_num failed modprobe: can't load module 8188eu (kernel/drivers/net/wireless/rtl8188eu/8188eu.ko): Cannot allocate memory This is because the usb_wifi_para section is missing from your script.bin: [usb_wifi_para] usb_wifi_used = 1 usb_wifi_usbc_num = 2 Where usb_wifi_usbc_num is the usbc to which your realtek usb wireless chip is attached. Edit the .fex file and create the script .bin as explained in our Manual build howto, and send a patch to sunxi-boards in to our mailinglist. 8188eu driver on sunxi-3.4Please note that sunxi-3.4 kernel is not supported and has been deprecated. Here’s how to compile the latest version from Realtek: Extract the driver/rtl8188EUS_rtl8189ES_linux_v4.1.8_9499.20131104.tar.gz from the RTL8188EUS_RTL8189ES_linux_v4.1.8_9499.20131104.zip file and extract it. These instructions assume your linux-sunxi directory is in the same directory as your rtl8188EUS_rtl8189ES_linux_v4.1.8_9499.20131104 directory. It’s also assumed that you’ve configured the kernel to include the 8188eu driver that’s part of linux-sunxi. make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- -C ../linux-sunxi/ M=`pwd` modules copy the 8188eu.ko file over to the device and then install it into your kernel with the following commands (on the device as root): modprobe -r 8188eu rm -rf /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/drivers/net/wireless/rtl8188eu install -p -m 644 8188eu.ko /lib/modules/`uname -r`/kernel/drivers/net/wireless/ /sbin/depmod modprobe 8188eu There are two changes you may want to make in include/autoconf.h : 1. The default is to output a LOT of logging and you can disable that by commenting out the following line: #define CONFIG_DEBUG /* DBG_871X, etc. */ 2. The default is to disable the activity LED on the wifi device which you may want to see to know that it’s working. You can change that by un-commenting the following line: Software ConfigurationDebian/ubuntu with NetworkManagerNetworkManager uses its own wpa_supplicant configuration. That is the reason why manually editing /etc/network/interfaces to use wpa_supplicant does not work together with NetworkManager. You have to disable all interfaces in /etc/network/interfaces e.g. by commenting out each line by inserting «#» as a first character. You even have to disable Ethernet section to use wifi in network manager. Here is an example # interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8) auto lo iface lo inet loopback #allow-hotplug eth0 #iface eth0 inet dhcp #auto eth0 #iface eth0 inet static #address 192.168.101.50 #netmask 255.255.255.0 #gateway 192.168.101.1 #broadcast 192.168.101.255 #auto wlan0 #iface wlan0 inet dhcp # wpa-ssid YOUR-NETWORK-NAME # wpa-key-mgmt WPA-PSK # wpa-group TKIP CCMP # wpa-psk YOUR-NETWORK-KEY At your desktop there should emerge a network icon from NetworkManager in the task bar. You can edit the network setting with the gui dialogs. Debian/ubuntu without NetworkManagerSetup with wpa_supplicant and without network managerThere are many tutorials out there on how to do this. Here is a good one. Disabling networkmanager. Fully.Even with the common trick of putting the following in /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf the despotic NetworkManager still will be messing up your careful setup from /etc/network/interfaces, and you might, once again, be left without wifi upon the next reboot. To stop NetworkManager from running altogether, you can run the following (as root): echo "manual" > /etc/init/network-manager.override Now, at least on ubuntu, your wifi driver, wpa_supplicant and ifupdown will not be smacked about anymore. Simple and dumb WPA setupInstall the following packages, if they are not installed already: apt-get install wireless-tools wpasupplicant Edit /etc/network/interfaces and add the following: auto wlan0 iface wlan0 inet dhcp wpa-ssid YourSSID wpa-psk YourWPASharedKey This is the most basic, but static, setup possible for wifi. If you need anything more, you need to read up on wpa_supplicant, or run through one of the tutorials referenced above. DevicesThe following devices all come with an built-in wifi chip. Orange Pi Zero LTS — это Orange Pi Zero с исправленными проблемами Wi-FiOrange Pi Zero LTS — это одноплатный компьютер на базе SoC Allwinner H2+: 4 ядра ARM Cortex-A7 с тактовой частотой 1.2 ГГц и GPU Mali400 MP2 с частотой 600 МГц. Объём оперативной памяти — 256 или 512 Мбайт DDR3 SDRAM. Orange Pi Zero LTS поможет разработчикам в реализации различных проектов в области Интернета вещей (IoT). Orange Pi Zero LTS наделён 2 МБ памяти SPI Flash и слотом для карты microSD. Порт Micro-USB служит для подачи питания. Доступ к различным интерфейсам (UART, I2C, SPI) обеспечивается за счёт 26-пинового и 13-пинового разъёмов, последний позволяет подключать адаптер для монитора, переходник на два дополнительных USB-порта, микрофон и наушники. Для облегчения работы с 13-пиновым интерфейсом есть плата расширения и NAS. Есть сетевой порт 10/100M Ethernet и адаптер беспроводной связи Wi-Fi с поддержкой стандартов IEEE 802.11b/g/n и слот для антенны. Питание Orange Pi Zero LTS осуществляется от 5-вольтового адаптера через разъём micro-USB, пины питания или PoE, рекомендуется использовать источник питания с силой тока 2 А. Работает под Android, Debian Linux, Ubuntu, Armbian, системы Raspbian и др.. Orange Pi Zero LTS vs. Orange Pi ZeroЕсли технические характеристики Orange Pi Zero LTS не отличаются от Orange Pi Zero, между платами все же есть некоторые различия. Питание Wi-Fi — VCC-1V8 1.8V 1%/0.3AБыли удалены резисторы R66 и R69, из за них было проблематично подключиться к беспроводной сети (подробнее тут Orange Pi Zero — обсуждение — 4PDA). Wi-Fi модуль XR819Был удалён конденсатор C160 и добавлен C372, а подключённый к LDO-OUT конденсатор стал на 0.22uF вместо 2.2uF. XTAL1, XTAL2Изменению подверглась и схема включения резонатора на 24 МГц. CPUX 1.1V/1.3V/3AБыл заменён резистор R235 на другой номиналом в 10к 1%. VCCIO 3.3V/1AПитание портов теперь осуществляется с помощью SY8089A 3.3В на 2А вместо старого SY8008B 3.3В на 1А. Стало SY8089A 3.3V/2A, также убрали и ключ Q11 AO3423-PMOS: AVCC 3.3V/1AБыло удалено питание AVCC. Основные характеристики
Доступные операционные системыОС: Android 4.4 ОС: Ubuntu server dolphin ОС: debian desktop ОС: Raspbian server ОС: openwrt ОС: Android dolphin ОС: Lubuntu 14.04 ОС: Debian server dolphin ОС: Ubuntu Core 16.04 ОС: Armbian 5.90 Ubuntu bionic next ОС: Armbian 5.91 Debian buster next Технические характеристики
detector |