- Getting Started with Alpine Linux Apk Command Examples
- 1. Update Alpine Linux Packages
- 2. Search Packages on Alpine Linux Repository
- 3. Install Packages in Alpine Linux
- 4. List Installed Software Packages
- 5. Upgrade Packages in Alpine Linux
- 6. Exclude a Package from Being Upgraded
- 7. Uninstall a Package in Alpine Linux
- 8. Get Help with APK
- How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
- How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
- Install a Package from the Alpine Repository
- Install a Specific Package
- Install Multiple Packages
- Install a Local Package
- Install Multiple Local Packages
- Additional Options for Package Installation
- Interactive
- No Cache
- Quiet
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Prateek Jangid
Getting Started with Alpine Linux Apk Command Examples
Every Linux distribution has its package manager that plays a role in the installation and management of software packages. For Debian/Ubuntu we have an apt package manager.
For RHEL and modern RedHat distributions such as CentOS, Rocky Linux, and AlmaLinux, the package manager is DNF. Of course, we have universal package managers such as snap and flatpak.
In Alpine Linux, APK, short for Alpine Package Keeper, is the package management tool. It retrieves packages and information about the packages from online repositories.
There are two main branches of these repositories:
The main repository contains packages that are directly supported and updated by the Alpine Linux core team. In addition, the packages also come with official documentation and are available for all Alpine Linux releases. Packages from the main repository will always have replacements if they do not go past upstream.
The Community repository includes community-supported packages, which are packages that have been passed from the testing repository where a team of independent users works in close collaboration with Alpine developers to develop packages.
On Alpine, these repositories are located in the /etc/apk/repositories file and you can view them using the cat command.
$ cat /etc/apk/repositories http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.15/main http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.15/community
Now let us proceed and see how to manage packages on Alpine Linux using the apk package manager.
1. Update Alpine Linux Packages
It’s best practice to always refresh the local package lists before installing any software packages. To do this, run the command:
2. Search Packages on Alpine Linux Repository
There are thousands of software packages available in Alpine Linux repositories. To have a glance at all the packages, run the command
The above command generates a long list of packages on the terminal and is not really helpful. Instead, you can search for a specific package that you are interested in.
For example, to search for all instances of nodejs, run the command
# apk search -v nodejs OR # apk search -v | grep -i nodejs
3. Install Packages in Alpine Linux
To install a package on Alpine Linux, use the following syntax:
For example, to install Python3, run the command:
In addition, you can specify multiple packages to be installed in a single command as shown.
# apk add package1 package2
For example, to install Apache web server and MariaDB database server packages, run the command
4. List Installed Software Packages
To list all the installed packages, run the apk info command:
To check if a specific package is installed, use the syntax:
The command prints out the following:
- The version of the package.
- A brief description of the package.
- The website of the parent company.
- The installed size.
For example, to check if MariaDB is installed, run the command:
To extract detailed information about a package, use the -a flag.
With this information, you get additional information such as
- Package dependencies.
- The list of packages that the package contains.
- The packages whose autoinstallation is likely to be affected.
5. Upgrade Packages in Alpine Linux
To upgrade all packages on Alpine Linux, run the following commands in succession:
These commands can be combined into one as follows:
Also, might consider performing a dry run of the upgrade. This simulates the upgrade and shows you how the packages will be upgraded. You can achieve this using the -s option.
6. Exclude a Package from Being Upgraded
Sometimes, you might need to hold back a software package from being upgraded. The reasons for doing this are varied. For example, a new version of a package might be buggy and fraught with issues, and for that reason, you might want to continue using your current version which works smoothly with other applications.
To hold back a package from an upgrade in Alpine Linux, use the syntax shown.
In the example below, we are holding back MariaDB version 10.6.7-r0 from being upgraded.
With that, you can now upgrade the rest of the packages as the MariaDB packages are held to the current version or lower.
7. Uninstall a Package in Alpine Linux
To uninstall a package, use the syntax shown.
For example, to remove or uninstall the MariaDB package, run the command:
8. Get Help with APK
For additional options with an apk package manager, run the command:
Additionally, you can visit the man pages as shown
This wraps up our guide on Alpine Linux apk commands. It’s our hope that you can now easily install and manage packages on Alpine Linux using the apk package manager.
How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
Every Linux distro has pre-installed package managers to install, uninstall, and manage the packages in the system. Alpine Linux also has its package manager which is known as Package Keeper APK. All versions of Alpine come pre-installed with Apk which allows you to perform many package management tasks including updating, searching, installing, uninstalling, listing, and more software packages. However, if you are a beginner in Alpine Linux, you may need a clarification while installing the package. In this short guide, we will explain the methods to install a package on Alpine Linux.
How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
Let’s now divide this section into different parts to explain the approaches that you can try to install the packages on Alpine Linux:
Install a Package from the Alpine Repository
You can install any available package in the Alpine repository and its necessary dependencies. The general syntax of installing any package on Alpine Linux is as follows:
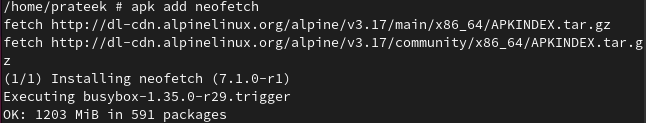
For example, we install the “neofetch” package using the following command:
The previous command installs the neofetch along with all the dependencies it requires. Remember, add the command that installs the newest package if you have multiple repositories.
Install a Specific Package
You can install a specific version of any package that you want to install. You can follow the simple syntax for it:
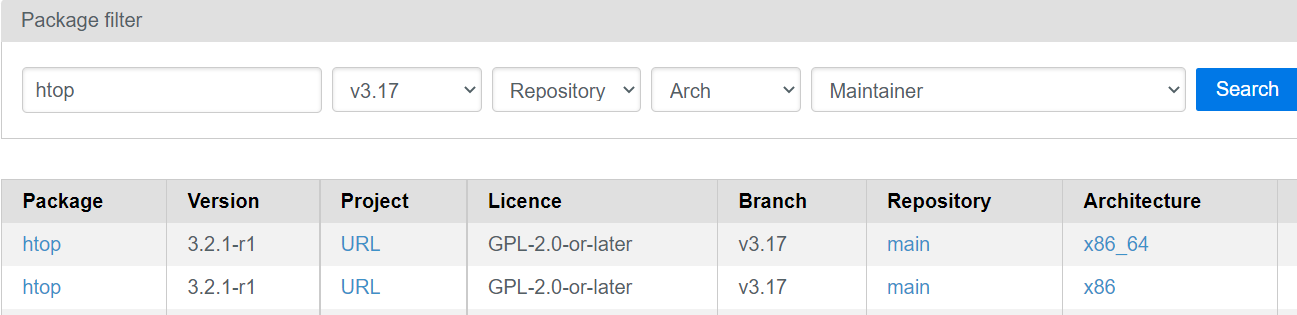
To do this, go to the official website of the Alpine Linux packages. After that, search for the package that you want to install and locate its version. Here, we install “htop”. For that, we find its version.
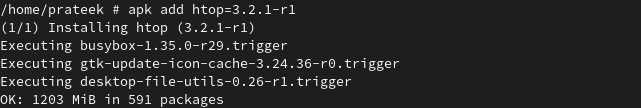
Now, we install the htop using the following command:
Install Multiple Packages
You can install multiple packages at once because you only need to add the name of all the packages that you want to install with the add command.
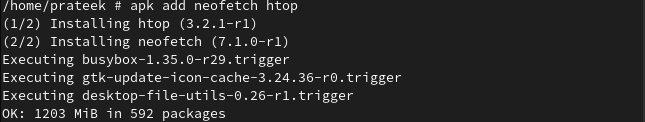
First, we install two packages, “neofetch” and “htop”, using their package name:
You can also install multiple packages with their specific versions.
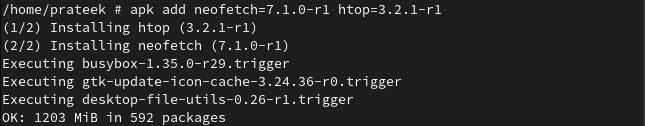
Here, we install the same packages by specifying their versions.
Install a Local Package
You can install a locally available apk package. If your device doesn’t have internet, use the –allow-untrusted flag. For this, use the following command:
Install Multiple Local Packages
When you need to install the multiple local packages on Alpine Linux with all their dependencies, use the following command:
Additional Options for Package Installation
There are several options while downloading the packages on Alpine Linux. With the help of which, you can modify the installation process of the package.
Interactive
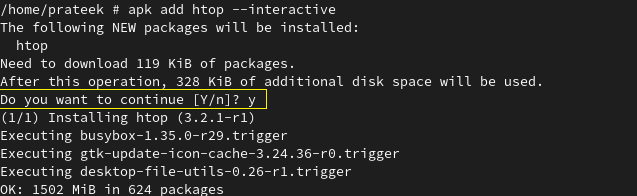
You can use the “-i” or “—interactive” option to prompt the user interaction and ask for confirmation before installing the package. Using this option, you can force the confirmation before starting the installation process. Its syntax is something like this:
Here, we install “htop” with an interactive option using the following command:
You can see that it asks you to continue the installation process. You can complete the installation process by typing “y” or abort the operation by typing “n”.
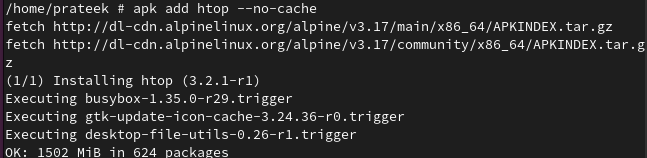
No Cache
While installing a package, if you don’t want to use the local cache path, you can use the “no-cache” option as follows:
We install “htop” without the local cache path:
Quiet
You can install a package without printing any details or information using the “quiet” option as follows:
For example, we install “htop” without printing any information through the following command:
As you can see, the previous command doesn’t print any details and installs “htop”.
Bonus Tip: If you have an older version of Alpine Linux and you want to install a new or updated package, you can use the following command:
Conclusion
This short guide explains how to install a package on Alpine Linux. You can easily install the packages with the help of the Alpine package manager, apk. You have to use the “apk add” command. We have seen many ways to install the packages, like installing the packages from the alpine repositories, installing the local packages, etc.
Apart from this, you can modify your installation process according to your own using many options which we provided with brief details in this tutorial.
About the author
Prateek Jangid
A passionate Linux user for personal and professional reasons, always exploring what is new in the world of Linux and sharing with my readers.