- 13 Apk Commands for Alpine Linux Package Management
- Alpine Linux Packages and Repositories
- 1. Update Alpine Linux
- 2. Search for an Availability of Packages
- 3. Get a Description of an Installed Package
- 4. Install Packages in Alpine Linux
- 5. Check Installed Package in Alpine Linux
- 6. List Files Associated with a Package
- 7. List Dependencies of a Package
- 8. Find the Installed Size of a Package
- 9. List All Installed Packages
- 10. Upgrade Alpine Linux
- 11. Hold a Package Upgrade
- 12. Remove a Package in Alpine Linux
- 13. Getting Help with Apk Command
- How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
- How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
- Install a Package from the Alpine Repository
- Install a Specific Package
- Install Multiple Packages
- Install a Local Package
- Install Multiple Local Packages
- Additional Options for Package Installation
- Interactive
- No Cache
- Quiet
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Prateek Jangid
13 Apk Commands for Alpine Linux Package Management
Alpine Linux is an independent, free, and open-source Linux distribution based on BusyBox and musl. It is a lightweight and security-oriented Linux distribution that comes in a small footprint (about 160 MB).
For this reason, it’s widely used in creating containers that are lightweight and standalone units that provide an isolated environment to deploy and run applications.
Alpine Linux targets users who desire simplicity, security, and efficient resource utilization. It is designed for x86, x86-64. AArch64 and ARM architectures.
Like any other Linux distribution, Alpine Linux comes with its own package manager known as apk (Alpine Package Keeper) and comes pre-installed on all Alpine Linux distributions.
Apk handles all the package management operations including searching, installing, upgrading, listing, and removing software packages just to mention a few. In this guide, we showcase commonly used Apk command examples in Alpine Linux.
Alpine Linux Packages and Repositories
Before we look at the various apk commands that you can leverage to manage your packages, let us touch on Alpine Linux repositories.
Alpine Linux has two repositories enabled by default: the main and community repositories.
- The main repository comprises packages that are rigorously tested and approved to be officially hosted by the Alpine Linux core development team.
- The community repository, on the other hand, comprises community-supported packages which are ported from the edge or testing repositories.
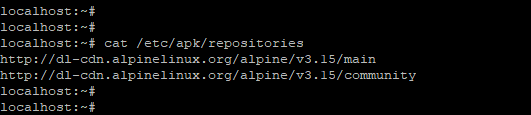
On your local Alpine Linux system, you can find the repositories in the /etc/apk/repositories file, you can use the cat command to view them as follows.
Having looked at the repositories, let us straight away jump into managing packages using the apk package manager.
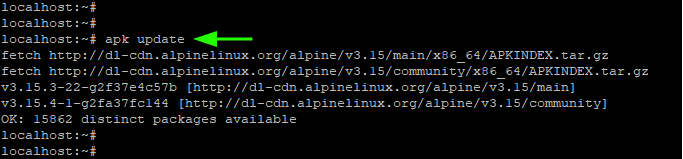
1. Update Alpine Linux
To update the repositories and package lists on Alpine Linux, run the command
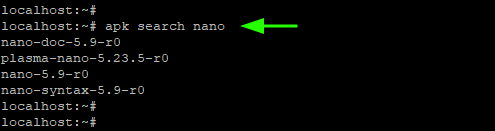
2. Search for an Availability of Packages
Before installing packages, it’s worthwhile to check if the packages have been officially been hosted in the repositories. To do so, use the syntax:
For example, to search for a nano package in the repositories, run the command:
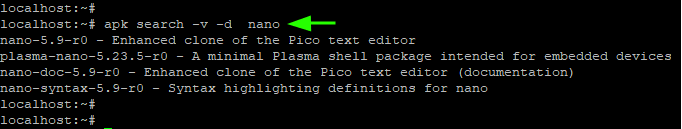
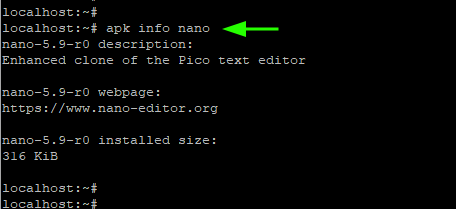
3. Get a Description of an Installed Package
To get a description of a package in the repositories, about the package pass the -v and -d flags as shown. The option -d is short for description whilst the -v option prints out verbose output.
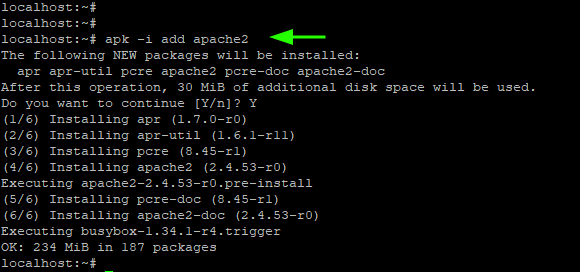
4. Install Packages in Alpine Linux
To install packages on Alpine Linux, use the syntax:
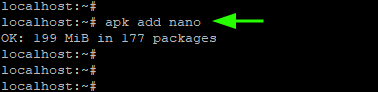
For example, to install the nano text editor, run the command:
Additionally, you can install multiple packages in a single command using the syntax:
$ apk add package1 package2
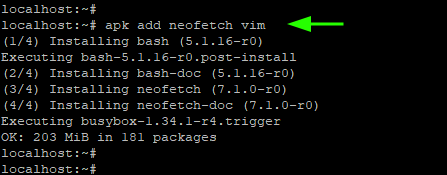
For example, the command below installs neofetch and vim editor at a go.
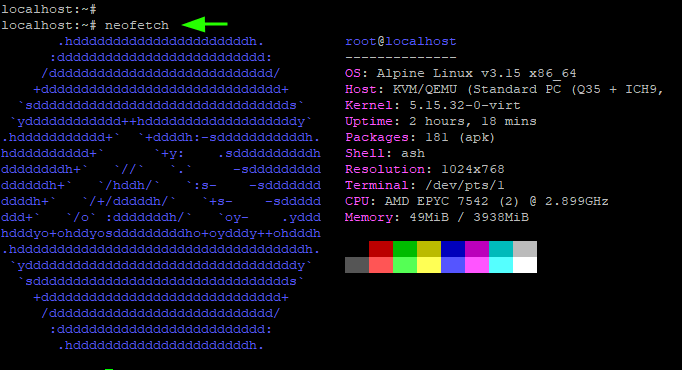
You can confirm if you installed neofetch by running the command:
This populates information about the operating system such as OS type, kernel, uptime, and underlying hardware such as CPU and memory.
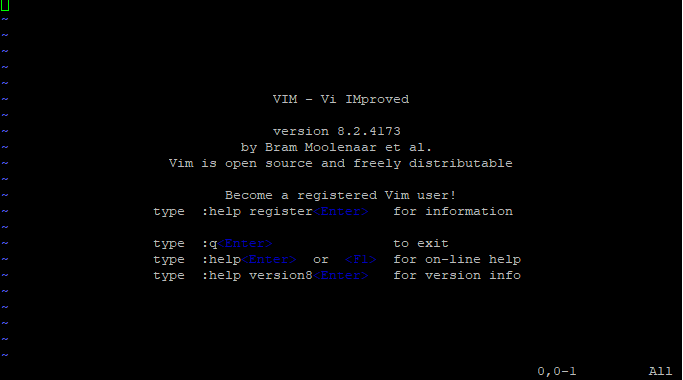
To confirm that vim editor is installed, simply run the vim command without any arguments and this will display information about vim.
The -i option prompts for user interaction when installing packages. It causes apk to ask you whether to continue with the installation of the package or abort.
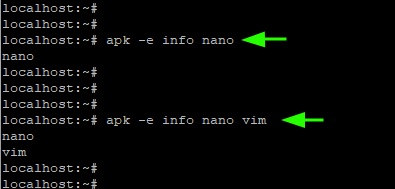
5. Check Installed Package in Alpine Linux
To probe if a certain package is already installed, use the syntax:
In this example, we are checking if Nano is installed.
In addition, you can check if multiple packages exist by listing them in the same line. For this example, we are verifying if both nano and vim are installed.
To list additional information such as the version and size of the installed package simply run:
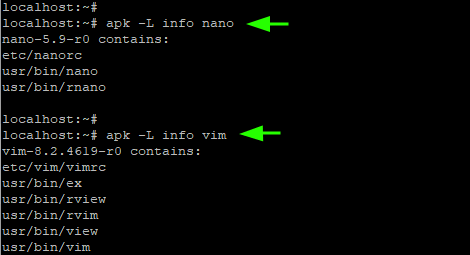
6. List Files Associated with a Package
The -L flag allows you to list the files associated with a package, which includes the binary and configuration files and other files.
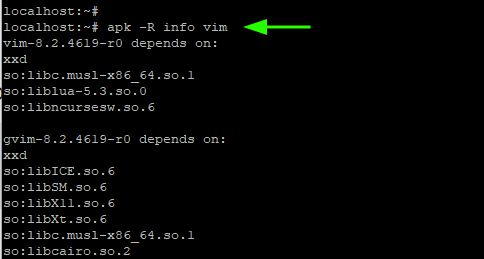
7. List Dependencies of a Package
With the -R option, you can list the packages that the package depends on. In the following example, we are listing the dependencies that vim depends on.
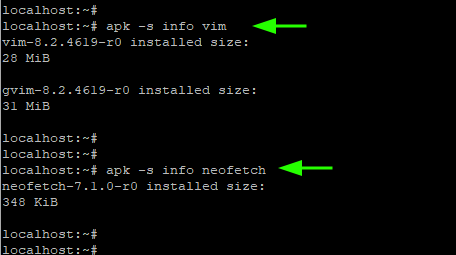
8. Find the Installed Size of a Package
To view the installed size of a package, use the -s option (lowercase) as follows:
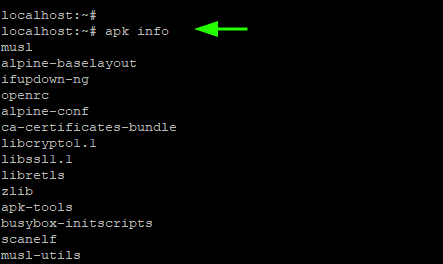
9. List All Installed Packages
To list all installed packages on Alpine Linux, run the command:
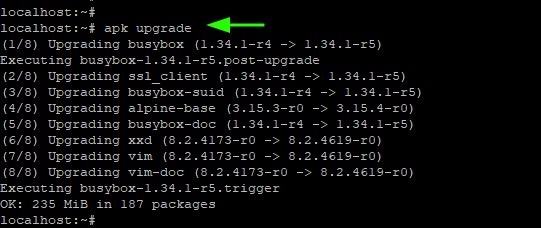
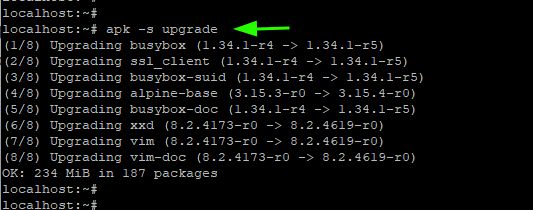
10. Upgrade Alpine Linux
To upgrade all the packages on Alpine Linux to their latest versions, run the command
To perform a dry run of the upgrade, pass the -s option. This merely runs a simulation and shows the versions that the packages will be upgraded to. It does not upgrade the packages.
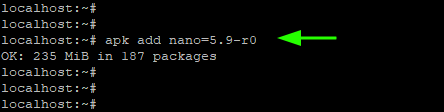
11. Hold a Package Upgrade
There are instances where you may want to keep a few packages back from an upgrade. For instance to keep nano in its current version – nano-5.9-r0 – run the command.
This will exempt the nano package from the upgrade as other packages are upgraded to their latest versions.
To later release the package for the upgrade, run:
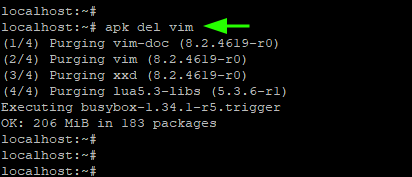
12. Remove a Package in Alpine Linux
If you no longer require a package, you can remove it using the syntax:
For example, to delete vim, run the command.
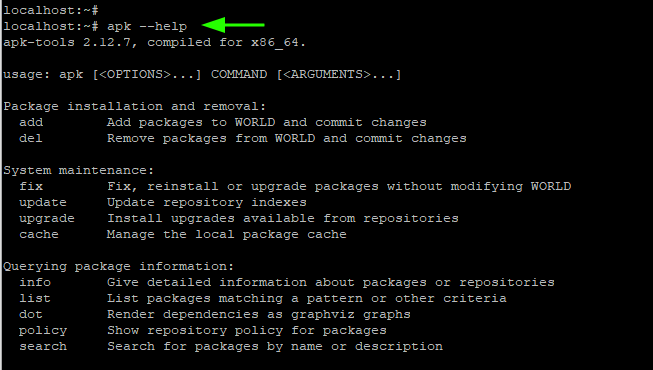
13. Getting Help with Apk Command
For additional apk commands, you can browse the apk help catalog as shown
In this guide, we focussed on Alpine apk command examples. We hope that this will help you as you get started installing and managing packages on Alpine Linux.
How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
Every Linux distro has pre-installed package managers to install, uninstall, and manage the packages in the system. Alpine Linux also has its package manager which is known as Package Keeper APK. All versions of Alpine come pre-installed with Apk which allows you to perform many package management tasks including updating, searching, installing, uninstalling, listing, and more software packages. However, if you are a beginner in Alpine Linux, you may need a clarification while installing the package. In this short guide, we will explain the methods to install a package on Alpine Linux.
How to Install a Package on Alpine Linux
Let’s now divide this section into different parts to explain the approaches that you can try to install the packages on Alpine Linux:
Install a Package from the Alpine Repository
You can install any available package in the Alpine repository and its necessary dependencies. The general syntax of installing any package on Alpine Linux is as follows:
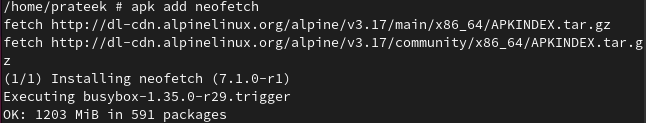
For example, we install the “neofetch” package using the following command:
The previous command installs the neofetch along with all the dependencies it requires. Remember, add the command that installs the newest package if you have multiple repositories.
Install a Specific Package
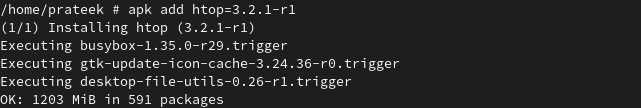
You can install a specific version of any package that you want to install. You can follow the simple syntax for it:
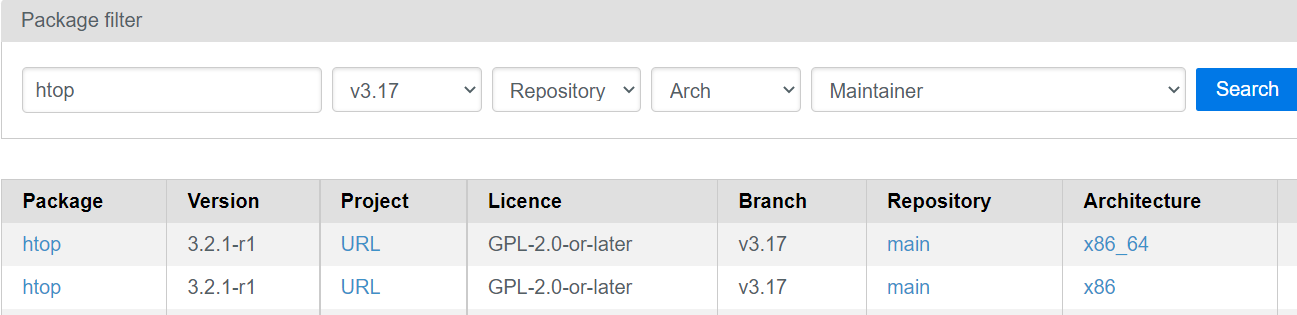
To do this, go to the official website of the Alpine Linux packages. After that, search for the package that you want to install and locate its version. Here, we install “htop”. For that, we find its version.
Now, we install the htop using the following command:
Install Multiple Packages
You can install multiple packages at once because you only need to add the name of all the packages that you want to install with the add command.
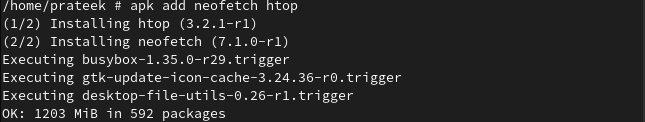
First, we install two packages, “neofetch” and “htop”, using their package name:
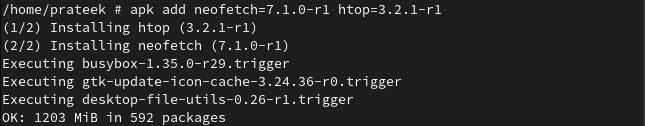
You can also install multiple packages with their specific versions.
Here, we install the same packages by specifying their versions.
Install a Local Package
You can install a locally available apk package. If your device doesn’t have internet, use the –allow-untrusted flag. For this, use the following command:
Install Multiple Local Packages
When you need to install the multiple local packages on Alpine Linux with all their dependencies, use the following command:
Additional Options for Package Installation
There are several options while downloading the packages on Alpine Linux. With the help of which, you can modify the installation process of the package.
Interactive
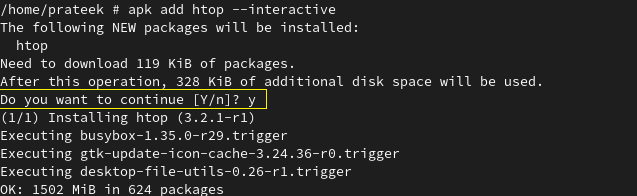
You can use the “-i” or “—interactive” option to prompt the user interaction and ask for confirmation before installing the package. Using this option, you can force the confirmation before starting the installation process. Its syntax is something like this:
Here, we install “htop” with an interactive option using the following command:
You can see that it asks you to continue the installation process. You can complete the installation process by typing “y” or abort the operation by typing “n”.
No Cache
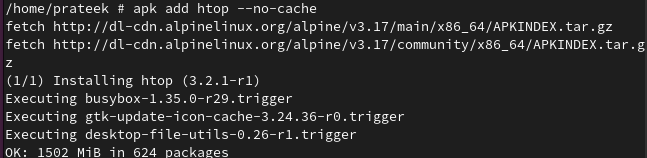
While installing a package, if you don’t want to use the local cache path, you can use the “no-cache” option as follows:
We install “htop” without the local cache path:
Quiet
You can install a package without printing any details or information using the “quiet” option as follows:
For example, we install “htop” without printing any information through the following command:
As you can see, the previous command doesn’t print any details and installs “htop”.
Bonus Tip: If you have an older version of Alpine Linux and you want to install a new or updated package, you can use the following command:
Conclusion
This short guide explains how to install a package on Alpine Linux. You can easily install the packages with the help of the Alpine package manager, apk. You have to use the “apk add” command. We have seen many ways to install the packages, like installing the packages from the alpine repositories, installing the local packages, etc.
Apart from this, you can modify your installation process according to your own using many options which we provided with brief details in this tutorial.
About the author
Prateek Jangid
A passionate Linux user for personal and professional reasons, always exploring what is new in the world of Linux and sharing with my readers.