Introduction
This guide shows you how to use the open source Radeon driver for some ATI/AMD graphics cards and APUs, which is part of the xserver-xorg-video-ati package.
This driver provides 2D and 3D acceleration in your video hardware. For the most recent releases of Ubuntu (and its flavours) this driver is usually as fast as the closed-source, proprietary fglrx driver (called AMD Catalyst) from AMD Inc. Furthermore the Radeon driver supports some older chipsets that fglrx does not.
The Radeon driver is already pre-installed in Ubuntu.
Identifying your graphics card or APU
First, check your graphic card name and chipset:
sudo update-pciids #optional command, requires internet
lspci -nn | grep -E 'VGA|Display'
It should report something like this for your graphics card and/or APU:
01:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] RV710 [Radeon HD 4550]
If the report shows two different hardware devices, then you probably have a «hybrid graphics» system, with an iGP (integrated graphics processor inside the CPU) and a dedicated GPU.
Unsupported chips
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and newer: for some most recent graphics cards (R9 285, R9 380/380X, R9 M395X, R9 Nano/Fury/FuryX, RX 460/470/480, RX 550/560/570/580. ) and APUs (Carrizo, Stoney), the open-source AMDGPU driver is enabled by default. For Ubuntu 16.04 LTS AMDGPU-Pro hybrid driver is also available to download here (please read the release notes for known problems and limitations).
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS: if you have Ubuntu 14.04 LTS with Linux kernel 4.4.0 (HWE stack Xenial), you can’t install the proprietary fglrx/Catalyst driver. However the open source AMDGPU driver is available to install through the xserver-xorg-video-amdgpu package.
Supported, but hardware is too old for Unity
These cards will not run Ubuntu’s Unity desktop with 3D acceleration. They will still run Unity, but the CPU will be used for basic drawing and performance may suffer. If you have one of these cards, a lighter desktop (such as XFCE or LXDE, found in Xubuntu and Lubuntu respectively) is recommended.
Vulkan® Open Source Driver
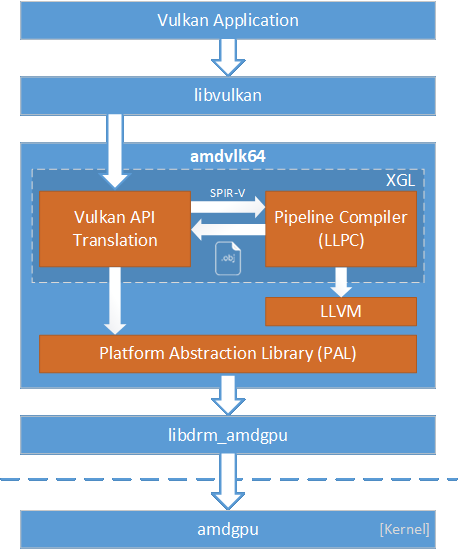
The AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan® is an open-source Vulkan driver for AMD Radeon™ graphics adapters on Linux®.
The driver is built on top of AMD’s Platform Abstraction Library (PAL), a shared component that is designed to encapsulate certain hardware and OS-specific programming details for many of AMD’s 3D and compute drivers. Leveraging PAL can help provide a consistent experience across platforms, including support for recently released GPUs and compatibility with AMD developer tools.
Shaders that compose a particular VkPipeline object are compiled as a single entity using the LLVM-Based Pipeline Compiler (LLPC) library. LLPC builds on LLVM’s existing shader compilation infrastructure for AMD GPUs to generate code objects compatible with PAL’s pipeline ABI.
Product support
The AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan is designed to support a wide range of AMD GPUs:
- Radeon™ RX 7900/7600 Series
- Radeon™ RX 6900/6800/6700/6600/6500 Series
- Radeon™ RX 5700/5600/5500 Series
- Radeon™ RX Vega Series
- Radeon™ RX 400/500 Series
- Radeon™ Pro WX 9100, x200 Series
- Radeon™ Pro W5700/W5500 Series
Note: For Pre-Polaris and Pre-Raven GPUs, please use v-2021.Q2.5 or older release.
Operating system support
The AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan is designed to support following distros and versions on both the AMDGPU upstream driver stack and the AMDGPU Pro driver stack:
- Ubuntu 22.04 (amd64 version)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (amd64 version)
- RedHat 8.6 (x86-64 version)
- RedHat 9.0 (x86-64 version)
The driver has not been well tested on other distros and versions. You may try it out on other distros and versions of your choice.
Feature support and performance
- Vulkan 1.3
- More than 30 extensions
- Radeon™ GPU Profiler tracing
- Built-in debug and profiling tools
- Mid-command buffer preemption and SR-IOV virtualization
The following features and improvements are planned in future releases (Please refer to Release Notes for update of each release):
- Upcoming versions of the Vulkan API
- Hardware performance counter collection through RenderDoc
- LLPC optimizations to improve GPU-limited performance and compile time
- Optimizations to improve CPU-limited performance
How to contribute
You are welcome to submit contributions of code to the AMD Open Source Driver for Vulkan.
The driver is built from source code in four repositories: LLVM, LLPC, XGL, and PAL.
For changes to LLVM, you should submit contributions to the LLVM trunk. Commits there will be evaluated to merge back into the amd-gfx-gpuopen-master branch periodically.
For changes to XGL or PAL, please create a pull request against the dev branch. After your change is reviewed and if it is accepted, it will be evaluated to merge into the master branch in a subsequent regular promotion.
Important By creating a pull request, you agree to allow your contribution to be licensed by the project owners under the terms of the MIT license.
When contributing to XGL and PAL, your code should:
- Match the style of nearby existing code. Your code may be edited to comply with our coding standards when it is merged into the master branch.
- Avoid adding new dependencies, including dependencies on STL.
Please make each contribution reasonably small. If you would like to make a big contribution, like a new feature or extension, please raise an issue first to allow planning to evaluate and review your work.
Important Since PAL is a shared component that must support other APIs, other operating systems, and pre-production hardware, you might be asked to revise your PAL change for reasons that might not be obvious from a pure Linux Vulkan driver perspective.
More information
For more information, including detailed build instructions for both Ubuntu and RedHat Linux, installation instructions, how to get your new driver up and running, runtime settings customisation, and the built-in profiling present in the PAL layer, please head on over to GitHub and check out the README.md in the AMDVLK repository.