- What is firmware?
- Using non-free firmware on a Debian system
- Debian 12 (bookworm) and later
- How to disable detection and use of non-free firmware
- Older releases
- Firmware during the installation
- Installation images with firmware
- Firmware on removable media
- Firmware on removable media and preseeding
- Firmware after installation
- Firmware missing from Debian
- Location of firmware files
- Debian 8 «Jessie» and newer
- Debian 7 «Wheezy», Debian 6.0 «Squeeze»
- List of firmware in Debian
- Прошивки устройств (firmware) в Linux
- Прошивки в Kali Linux
- Прошивки в Debian
- Прошивки в Ubuntu, Linux Mint
- Прошивки в Arch Linux, Manjaro, BlackArch
- Как установить все прошивки устройств
What is firmware?
Firmware refers to embedded software which controls electronic devices. Well-defined boundaries between firmware and software do not exist, as both terms cover some of the same code. Typically, the term firmware deals with low-level operations in a device, without which the device would be completely non-functional (read more on Wikipedia).
Many devices require firmware to operate. Historically, firmware would be built into the device’s ROM or Flash memory, but more and more often, a firmware image has to be loaded into the device RAM by a device driver during device initialisation.
A few firmware images are Free Software and Open Source but unfortunately almost all of them are non-free, which means that Debian cannot include them as normal in the archive under main or contrib.
Using non-free firmware on a Debian system
Debian 12 (bookworm) and later
For Debian 12 onwards, all the packaged non-free firmware binaries that Debian can distribute have been moved to a new component in the Debian archive, called non-free-firmware. If you’re upgrading from an older release of Debian and you need these firmware binaries, you should update the apt sources.list on your system to use this new component. If you only had the non-free component enabled on your system to allow you to install firmware, you can safely remove that now.
Debian’s installation and live images now include all of those firmware packages. The system should automatically detect, load and install the firmware available for your devices, where possible. There are a small number of cases where Debian can’t do this, typically because of not being allowed to distribute the needed firmware binaries.
If you are booting the Debian installer over the network, that will not include all the firmware packages in the initramfs. This is a deliberate choice due to the extra space needed for all the firmware here. Many/most users will already need to modify the initramfs when setting up netboot, so an extra step here is reasonable. Adding the firmware blobs to your initramfs is easy: simply grab the appropriate cpio archive for your target release from https://cdimage.debian.org/cdimage/firmware/ and append it directly to the initramfs file.
How to disable detection and use of non-free firmware
From Debian 12, the installer will automatically check for needed firmware blobs and add them as required. If you would prefer it not to, add
to the installer boot parameters as described in the installation guide
Older releases
For Debian 11 (bullseye) and older, Debian did not include firmware on official installation and live images. The following sections should help you if you need firmware there.
Firmware during the installation
In some cases the installer detects the need for non-free firmware and prompts the user to make the firmware available to the installer to complete the installation. This can happen, for example, with wireless network cards which often require non-free firmware to function (see ipw2200 for an example).
Installation images with firmware
An easy method is to use an installer image that includes all non-free firmware packages directly. See https://cdimage.debian.org/cdimage/unofficial/non-free/cd-including-firmware/
Firmware on removable media
You can also download the firmware archive for your platform and unpack it into a directory named firmware in the root of a removable storage device (USB/CD drive). You can find firmware downloads for your Debian version at https://cdimage.debian.org/cdimage/firmware/. When the installer starts, it will automatically find the firmware files in the directory on the removable storage and, if needed, install the required firmware.
In some cases, firmware supplied on removable media may not be detected automatically (e.g. 740503). In these situations, drop to the console (Ctrl+alt+F2) and manually mount(8) your removable storage on a temporary directory (e.g. /media).
Firmware on removable media and preseeding
- The needed firmware files are assumed to be in a directory named firmware on a FAT partition formatted with mkfs.vfat and labelled FIRMWARE.
- The following addition is made to the installer’s kernel command line. It is a single command but has been broken here for readability. Press TAB when the installation choice is highlighted to make the command line visible. A variation on this technique is presented elsewhere.
Installation+Archive+USBStick preseed/early_command="modprobe vfat ; sleep 2 ; mount /dev/disk/by-label/FIRMWARE /media ; cp -a /media/firmware /lib"
Once the network is configured, Debian-Installer can fetch firmware from Debian repositories.
Firmware after installation
The isenkram and other tools can prompt to install the appropriate firmware and other hardware support packages when the hardware is plugged in. This mostly relies on packages declaring via AppStream what hardware they support. This might not work for all firmware, so read on for another solution.
If you still see missing firmware console messages when the initramfs is updated (for example whenever a kernel update is applied):
W: Possible missing firmware /lib/firmware/i915/skl_guc_62.0.0.bin for module i915
Then you can use apt-file or the Debian package contents search to look for the package that contains the firmware files, install it and then update the initramfs:
$ apt-file search skl_guc_62.0.0.bin firmware-misc-nonfree: /lib/firmware/i915/skl_guc_62.0.0.bin $ sudo apt install firmware-misc-nonfree $ sudo update-initramfs -c -k all
Firmware missing from Debian
If the missing firmware is not available in Debian or if you still see missing firmware console messages even when you have the right firmware-* package installed, you can download and install the firmware from the linux-firmware repository, e.g. for i915 firmware:
mkdir firmware cd firmware wget -r -nd -e robots=no -A '*.bin' --accept-regex '/plain/' https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/firmware/linux-firmware.git/tree/i915/ sudo mv *.bin /lib/firmware/i915/ sudo update-initramfs -c -k all
Location of firmware files
Debian 8 «Jessie» and newer
udev used in Debian Jessie and later, only checks one directory for firmware files: /lib/firmware. See 729252 for details.
Debian 7 «Wheezy», Debian 6.0 «Squeeze»
- /lib/firmware/$(uname -r) — Firmware provided by a package, specific for a kernel.
- /lib/firmware/ — Firmware provided by a package, valid for all kernels.
- /usr/local/lib/firmware — Location for manually installed firmware.
- /usr/lib/hotplug/firmware — Firmware provided by a package, valid for all kernels
List of firmware in Debian
To find which package provides a given firmware file, you can use this search page:
https://www.debian.org/distrib/packages#search_contents
Firmware/List lists firmware distributed by Debian.
Прошивки устройств (firmware) в Linux
Прошивки могут сбить с толку, поскольку не все пользователи помнят о них, и прошивки не всегда предустановлены в дистрибутивы Linux. При этом прошивки также важны для нормальной работы устройств как и драйверы (модули ядра), которые обычно уже имеются в системе, поскольку являются частью ядра Linux.
Из-за отсутствия прошивки устройство может не работать полностью или частично.
Название пакетов прошивок различается в дистрибутивах (причём иногда различается неочевидно, например, перестановкой слов). Пакеты прошивок могут содержать как прошивки для устройств различных производителей, так и для устройств одного производителя.
Иногда прошивки одного производителя разбиты на пакеты, например, пакет firmware-intel-sound содержит прошивки для звуковых устройств Intel, а пакет firmware-iwlwifi содержит прошивки для беспроводных карт Intel.
Бывают случаи, когда прошивки устройств одного типа и одного производителя разделены на разные пакеты, например пакеты firmware-ath9k-htc и firmware-atheros содержат прошивки беспроводных адаптеров Atheros.
Примеры проблем, которые могут вызвать отсутствующие прошивки:
Прошивки в Kali Linux
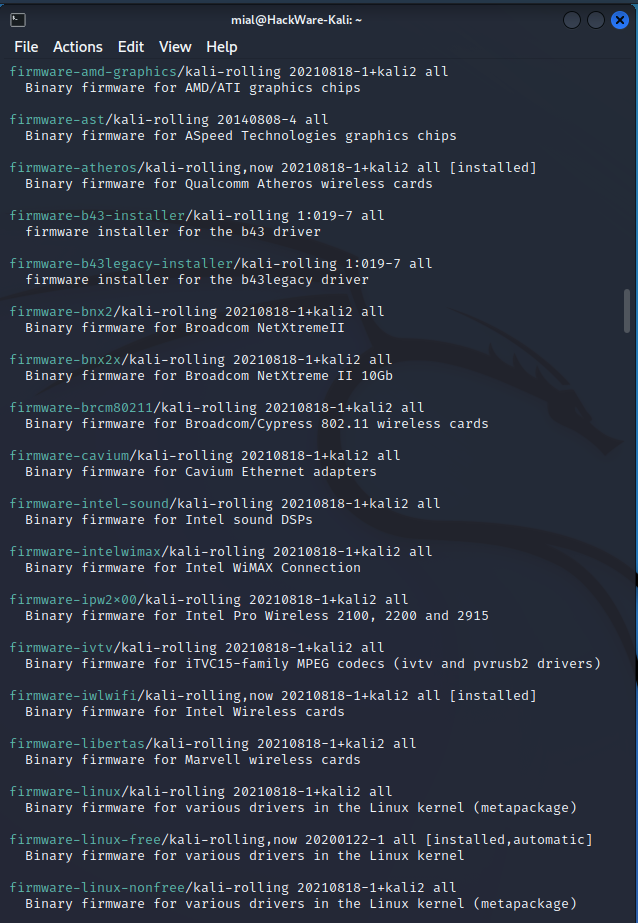
В Kali Linux имеется несколько пакетов с прошивками, например:
Первые два пакета содержат прошивки, которые ранее были включены в ядро Linux. В первом пакете содержатся прошивки, которые соответствуют Debian Free Software Guidelines, во втором — остальные, не соответствующие Free Software Guidelines. Большая часть прошивок попала в пакет non-free. А в третьем пакете собраны… ещё прошивки.
Кроме этих пакетов имеются пакеты, содержащие прошивки для определённых устройств определённых производителей, например, firmware-realtek, firmware-atheros, firmware-iwlwifi.
В репозитории Kali Linux также имеется два метапакета:
- firmware-linux — включает в себя firmware-linux-free и firmware-linux-nonfree
- kali-linux-firmware — включает в себя bluez-firmware, firmware-amd-graphics, firmware-atheros, firmware-brcm80211, firmware-intel-sound, firmware-iwlwifi, firmware-libertas, firmware-linux, firmware-misc-nonfree, firmware-realtek, firmware-sof-signed, firmware-ti-connectivity, firmware-zd1211
Для того, чтобы не испытывать в будущем проблем с Wi-Fi и другими устройствами, рекомендуется установить пакет kali-linux-firmware, который установит большинство необходимых прошивок.
В Kali Linux удобно искать по пакетам прошивок командой вида
apt search СТРОКА_ДЛЯ_ПОИСКА
В качестве СТРОКИ_ДЛЯ_ПОИСКА можно указать название устройства, производителя, чипсет устройства, название файла прошивки, если вы его знаете.
Прошивки в Debian
В Debian кроме уже знакомых по Kali Linux пакетам firmware-linux-free, firmware-linux-nonfree и firmware-misc-nonfree имеется также уже знакомый метапакет firmware-linux, объединяющий предыдущие два.
В дополнении к рассмотренным, имеются прошивки для устройств отдельных производителей, например, firmware-iwlwifi, firmware-ath9k-htc, firmware-atheros, firmware-amd-graphics и другие.
Прошивки в Ubuntu, Linux Mint
В этих дистрибутивах прошивки не делятся на free и nonfree и помещены в один пакет под названием linux-firmware.
Кроме этого пакета, также имеются прошивки для определённых производителей, например firmware-ath9k-htc, nouveau-firmware и другие.
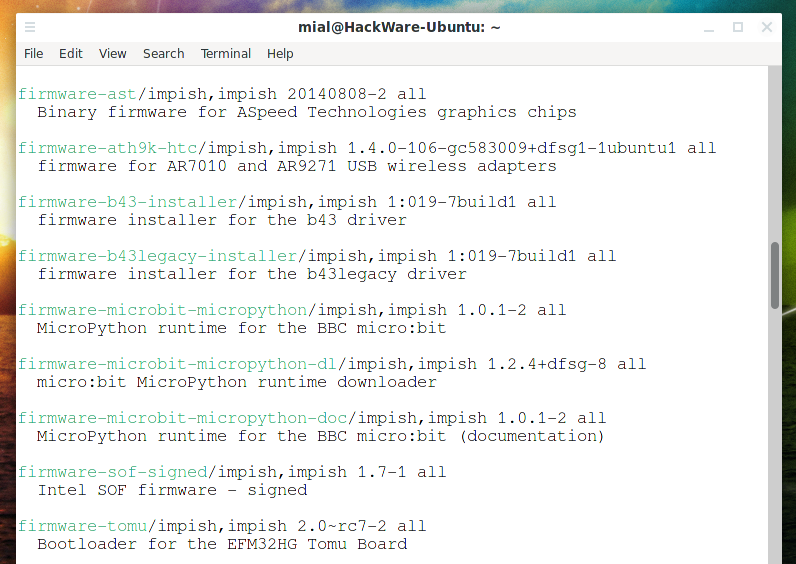
В целом, в Ubuntu и Linux Mint большинство прошивок собрано в единый пакет linux-firmware и это удобно!
Но поиск пакетов прошивок командой вида
apt search СТРОКА_ДЛЯ_ПОИСКА
практически бесполезен если вы пытаетесь найти по модели устройства, чипсету или файлу прошивки. Если вы выполнили поиск и не нашли отдельного пакета для вашего устройство, то скорее всего нужная вам прошивка содержится в пакете linux-firmware.
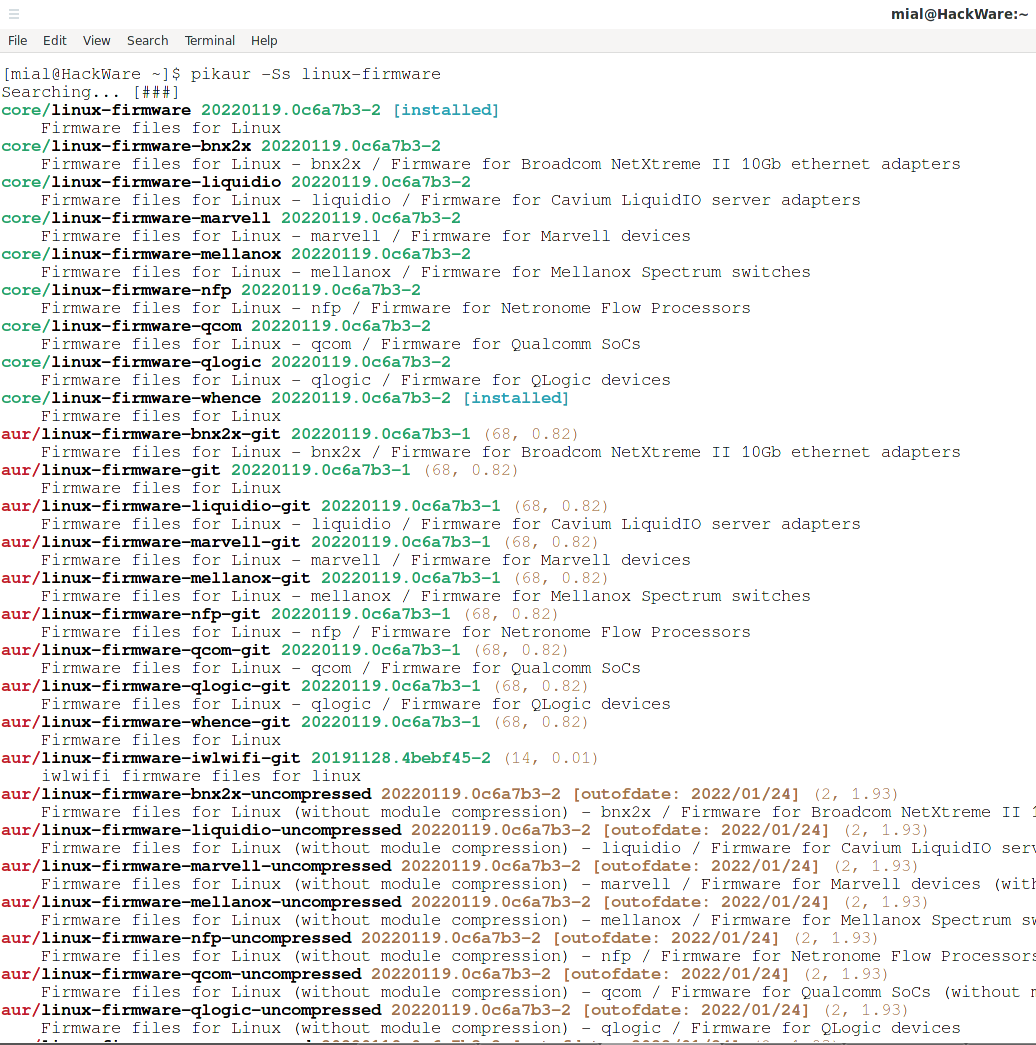
Прошивки в Arch Linux, Manjaro, BlackArch
До недавнего времени все прошивки были собраны в одном пакете linux-firmware. Но некоторые крупные и редкие прошивки были выделены в отдельные пакеты, подробности в статье «Изменения в пакете linux-firmware: требования к ядру, выделение больших файлов в отдельные пакеты».
Как установить все прошивки устройств
Чтобы в будущем избежать возможных проблем из-за отсутствующих прошивок, рекомендуется установить их, поскольку они занимают относительно немного места на диске. Ранее многие прошивки были частью ядра (что понятно, учитывая их важность), но были убраны из ядра, видимо, для экономии места.
Установка основных пакетов прошивок выполняется следующими командами.
В Kali Linux:
sudo apt install kali-linux-firmware
sudo apt install firmware-linux firmware-misc-nonfree firmware-iwlwifi firmware-ath9k-htc
В Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
sudo apt install linux-firmware firmware-iwlwifi firmware-ath9k-htc
В Arch Linux, Manjaro, BlackArch:
sudo pacman -S linux-firmware