- RebelLion420 / TermuxArchSetup2020.md
- Установка ArchLinux ARM рядом с Android без chroot
- Нам потребуется
- Все действия Вы выполняете на свой страх и риск.
- Я использовал
- Часть 1: Подготовка
- Часть 2: Поиск и решение проблем
- Проблема 1: ping не работает
- Проблема 2: Не работает DNS
- Если Вы запороли PATH
- Ставим необходимые пакеты
- Проверяем gcc
- Часть 3: Подготовка к работе без chroot
- Нужно заранее позаботится о Root.
- Часть 4: Поехали!
- Что дальше
- Послесловие
- Arch linux arm on android
RebelLion420 / TermuxArchSetup2020.md
So, to get started you need to get the base OS installed using the instructions from the official docs .
$ pkg install bsdtar wget proot tergent tmux openssh
Tmux is a multiplexer that lets you run multiple persistent windows and sessions on a single terminal. I had trouble getting it working in the Arch proot, so a workaround is configuring tmux from your host Termux and then creating a tmux session and starting the chroot from there. For more information on using tmux read this article, and to learn how to customize the appearance and behaviors more try this one as well as looking at the tmux-plugins Github organization for community-built add-ons.
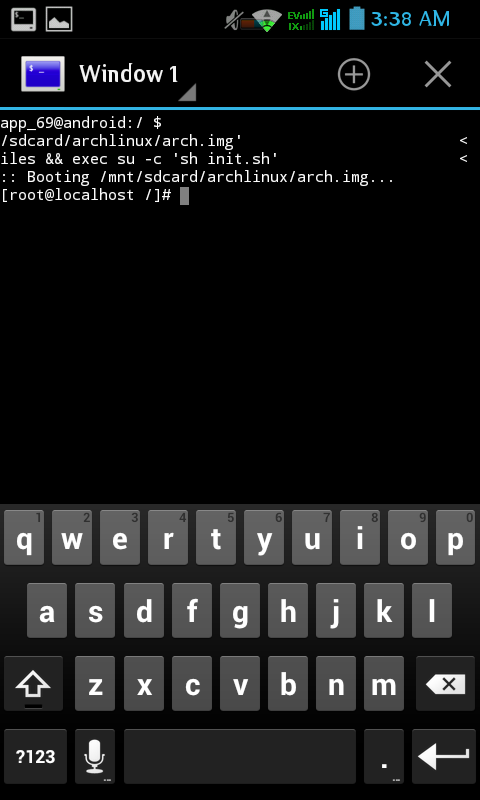
This should download and install the Arch system. The install itself will take around 10-30 minutes depending on your device. When the process finishes you’ll be in a root shell in your new Arch distro! Of course like any new Linux distro, not everything will work out of the box.
You will want to change the password and maybe even the username of your new Linux user. This can be done with 2 commands.
$ useradd -mG root -s /bin/bash
Once you’re user is set up, you can use a crash-tested script I made that should run through and handle any exceptions. If not, it should at least make it easy enough to figure out what went wrong. First download and run it with sudo to avoid repeating your password:
$ wget —no-check-certificate ‘https://docs.google.com/uc?export=download&id=107Fh0l_p0ItVkUufOhP9to-OU_6KYhPW’ -O fresharch.sh
If all the instructions were followed correctly yay should install and you’ll have a functional Arch Linux with AUR support on your Android device.
Установка ArchLinux ARM рядом с Android без chroot
Я испробовал множество средств для установки Linux на свое Android устройство, но все они или не работали вовсе, или были слишком глючные. К счастью я использую на ПК ArchLinux и узнав о проекте ArchLinux ARM решил попробовать его в деле. И не просто установить в chroot, а заставить его работать и без него.
Нам потребуется
- Прямые руки
- Android устройство
- Root доступ
- Busybox
- Эмулятор терминала
- Свободное место
- ADB(для удобства)
Все действия Вы выполняете на свой страх и риск.
Я использовал
- Устройство Android 4.2 с 512Мб ОЗУ, ядро Linux 3.4.5 armv7l
- Эмулятор терминала ConnectBot
- Управление суперпольпользователем SuperSU
- BusyBox v1.20.0
Часть 1: Подготовка
1. Скачаем архив с ArchLinux ARM с зеркала:
wget http://mirror.yandex.ru/archlinux-arm/os/ArchLinuxARM-armv7-latest.tar.gz mv ArchLinuxARM-armv7-latest.tar.gz ArchLinuxARM.tar.gz adb push ArchLinuxARM.tar.gz /sdcard/ Дальнейшие действия необходимо проделывать на Android устройстве
2. Создаем файл для будущего образа с помощью make_ext4fs.
Если у вас есть отдельный раздел на карте памяти — желательно использовать его. В моем случае 16Гб SD карта была забита важными данными и возможности сдвинуть главный FAT раздел не было.
В зависимости от настроек /sdcard может быть как внешней, так и внутренней картой памяти.
cd sdcard make_ext4fs -l 3221225472 arch.img3221225472 это 1024*1024*1024*3, следовательно будет создан образ в 3Гб. Размер образа определите для себя по вкусу. Помните что на FAT32 нельзя создать файл больше 4Гб
3. Примонтируем образ и распакуем файлы ArchLinux ARM
mount -o rw,remount / mkdir /arch busybox mount /sdcard/arch.img /arch tar -xvf ArchLinuxARM.tar.gz -C /arch/4. Несмотря на то, что наша цель — обойтись без chroot, для базовой настройки и проверки работоспособности chroot все же нужно сделать. В противном случае обновлять, доставлять пакеты Вам придется уже на боевой системе.
busybox mount -t proc none /arch/proc busybox mount -o rbind /dev /arch/dev busybox mount -t tmpfs none /arch/tmp busybox mount -o size=10%,mode=0755 -t tmpfs none /arch/run chroot /arch /bin/bashЧасть 2: Поиск и решение проблем
Проблема 1: ping не работает
ping 8.8.8.8 socket: Permission denied Вспоминаем, что у Android серьезная система разграничения прав. И в нем существует пермишен на «Полный доступ к сети». Без этого пермишшена пользователи не могут получить полный доступ к сокетам. То что надо.
Вернемся к Android консоли и пропишем комманду id:
uid=2000(shell) gid=2000(shell) groups=1003(graphics),1004(input),1007(log),1009(mount),1011(adb),1015(sdcard_rw),1028(sdcard_r),3001(net_bt_admin),3002(net_bt),3003(inet),3006(net_bw_stats)У вас вывод может быть другой
groupadd -g 3003 inet usermod -a -G inet root Но вот незадача, chroot не обновляет group. Поможет вот такой «хак»:
ping 8.8.8.8 PING 8.8.8.8 (8.8.8.8) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=59 time=89.6 ms 64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=2 ttl=59 time=88.6 ms Проблема 2: Не работает DNS
Удаляем симлинк на systemd и запишем нормальные DNS:
rm /etc/resolv.conf echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" > /etc/resolv.confЕсли Вы запороли PATH
Если произошло такое, что простые комманды вида ls,cat,su не работают(не видятся) системой, Вы можете попробывать вызвать их напрямую: /system/bin/ls, /system/bin/cat, /system/xbin/su.
Или перезагрузить устройство.
Ставим необходимые пакеты
pacman -S gcc htop iotop sudo opensshПроверяем gcc
Часть 3: Подготовка к работе без chroot
Самое главное, что позволяет ArchLinux работать без chroot рядом с андроидом — тот факт, что папки и файлы ArchLinux и андроид различны и не мешают друг другу.
Если Вы не уверены в том, что файлы не пересекутся, выполните эти команды из Android консоли:
ls /etc/ > /sdcard/ls.txt ls /arch/etc/ > /sdcard/ls2.txt busybox grep -F -f /sdcard/ls.txt /sdcard/ls2.txtПокажет пересечение файлов. У меня это выглядит так:
dhcpcd.conf hosts securityВыполним копирование файлов из /etc/ в /arch/etc/ из Android:
cp -Ra /etc/* /arch/etc/ cp -a /sbin/adbd /arch/usr/bin/Ключ -a обязателен, так как при использовании обычного -R права скопированы не будут.
Нужно заранее позаботится о Root.
Android приложения требуют, что бы комманда su сразу же давала доступ к суперпользователю и не запрашивала пароль.
passwd mv /usr/bin/su /usr/bin/su.rЧасть 4: Поехали!
Создадим нужные каталоги и воспользуемся mount —bind что бы виртуально заменить директорию, не изменяя ее на диске.
mkdir /lib mkdir /bin mkdir /xbin mkdir /opt mkdir /usr mkdir /home mkdir /run mkdir /srv mkdir /tmp mkdir /var busybox mount --bind /arch/etc /etc busybox mount --bind /arch/opt /opt busybox mount --bind /arch/home /home busybox mount -o size=10%,mode=0755 -t tmpfs none /run busybox mount --bind /arch/srv /srv busybox mount -t tmpfs none /tmp busybox mount --bind /arch/sbin /sbin busybox mount --bind /arch/usr/ /usr busybox mount --bind /arch/var/ /var busybox mount --bind /arch/lib/ /lib busybox mount --bind /arch/usr/bin/ /bin /bin/bash Если что-то сделано неправильно, Вы можете перезагрузить устройство и попробовать снова. Порядок монтирования важен. При ошибке с монтированием стандартные команды могут взятся из ArchLinux до того, как все каталоги будут смонтированы.
Что дальше
В итоге мы имеем практически полноценный ArchLinux за исключением systemd с свежими версиями пакетов.
Можно установить http, php, mysql. При правильной настройке на уменьшение потребления памяти даже на моем смартфоне с ОЗУ 512Мб они работали корректно.
Можно установить иксовые библиотеки и с помощью X сервера для Android пользоваться ПО для линукса. xterm заработал корректно.
Можно собирать любые программы (и, о нет, ядра) для Linux без ПК.
Можно установить Java для ARM и использовать Java приложения.
Послесловие
Большой проблемой остается systemd и его привязка к PID 1. Для того, что бы сохранить PID 1 нужно влезть в init андроида и прописать exec после инициализации устройств. Это можно сделать заменив init андроида shell скриптом, но тогда остается вопрос что делать с оригинальным init андроида. Так как место на загрузочном диске ограничено несколькими мегабайтами, нужно будет использовать switch_root в заранее созданный образ. Мне пока не удалось завести systemd таким способом.
Мне 16, и это моя первая публикация. Конструктивная критика приветствуется.
Arch linux arm on android
Installing Archlinux in Android Devices. Some devices, such as allwinner devices have archlinux port natively. But how about common android devices?. Yes you can still install it, this archlinux arm will use android kernel, and access it via VNC server. Although the performance still not better than native install, but it’s usable for computing.
This tutorial is outdated, the apk was unpublished in play store. If you want to follow these post, you need com.azlinux765.alinstaller packages, that you can search on google. Follow these post at your own risk.
At least for better performance your android specification must be:
— 256 mb ram (Minimum), less if you don’t want install desktop environment.
— 600 mhz, 1ghz is recommended.
— SD Card free space for Archlinux is 1.5gb (minimum but not suitable if you want to install more productive application), 4GB is recommended
— Rooted only devices
Apps that you need on Android (install it from playstore)
1. Arch Linux Installer. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.azlinux765.alinstaller
Search on google com.azlinux765.alinstaller you will find the package. But i’m not sure if it still work or not for Android devices (2018 & up). On these post i’m using Ice Cream Sandwich OS.
2. Install Android Terminal Emulator
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=jackpal.androidterm
3. Install Android VNC Viewer
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=android.androidVNC
4. PC Keyboard
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.pocketworkstation.pckeyboard
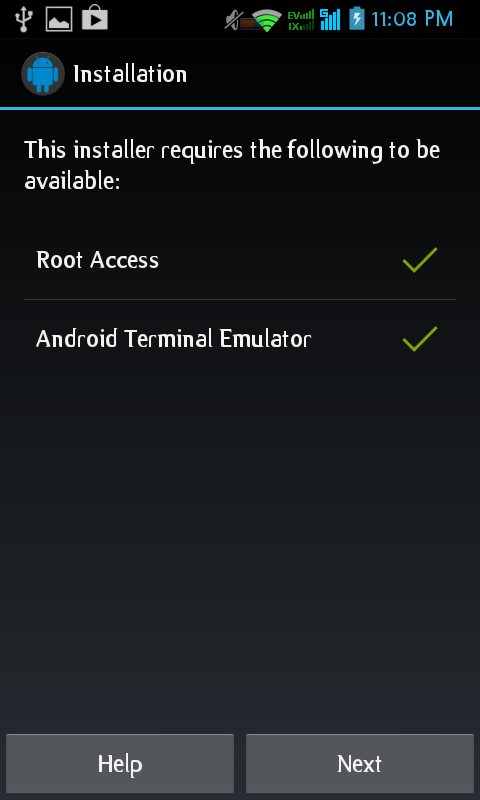
Install all the packages. Change the keyboard input into pc keyboard mode. Then open Archlinux Installer. Here’s the GUI Archlinux Installation:
Then, tap on Download/Install Arch Linux, and tap allowed on Root access, and here’s status of your devices:
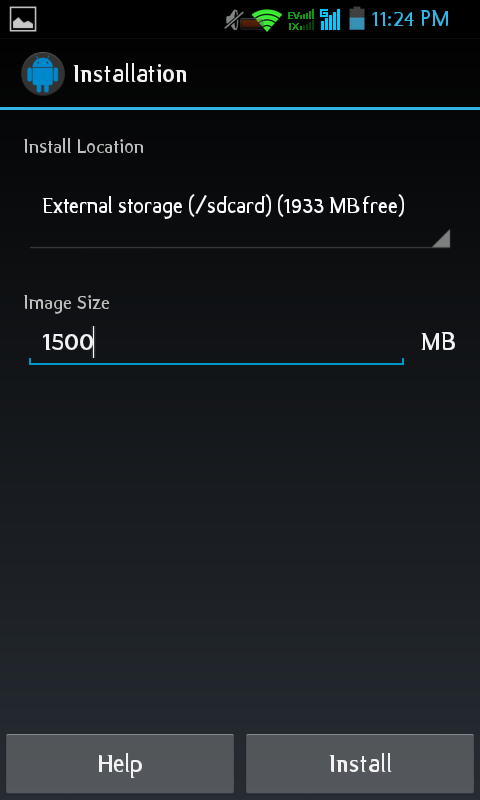
Then tap on «Install» this will create Archlinux image on SDcard, and download the filesystem of archlinux:
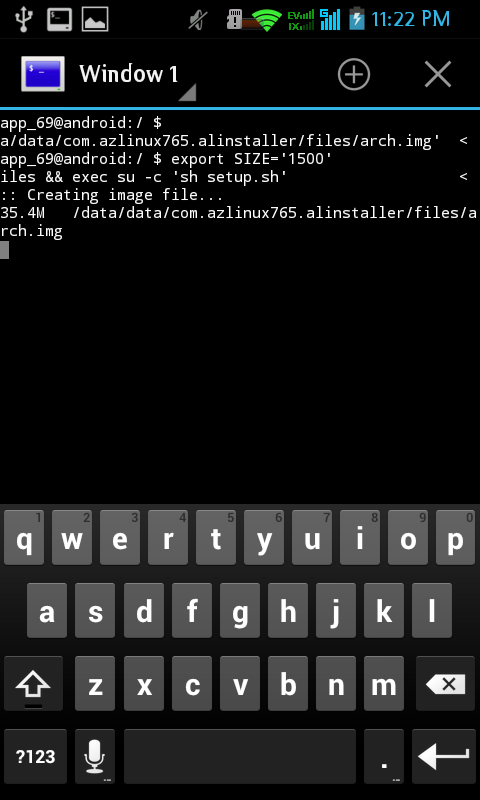
Enter to continue, you will be back on Arch Linux Installer Menu, and «Run Arch Linux» Button will be up. Tap on it to start arch linux:
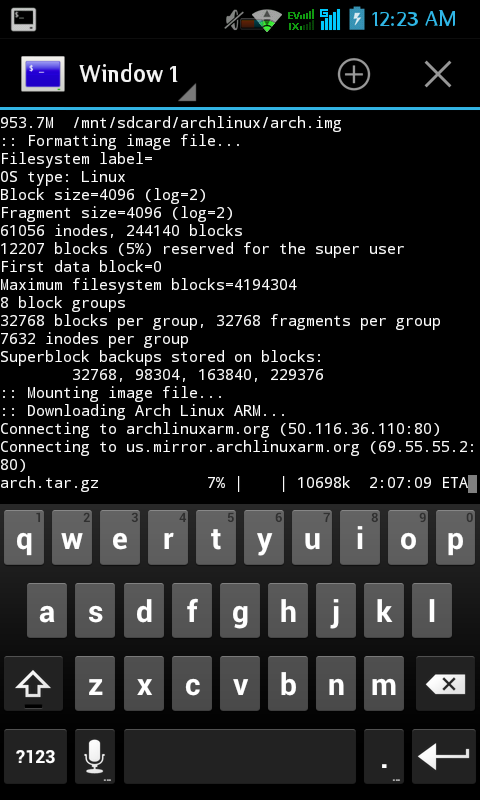
And you will go to Android Terminal Emulator. Archlinux is running:
Note: If you run android terminal emulator by «run archlinux» do not close force the android terminal emulator, because you can’t shutdown or exit system from archlinux to android, the process will be run up on the background. To fix this, you must reboot your devices, and start run archlinux again.
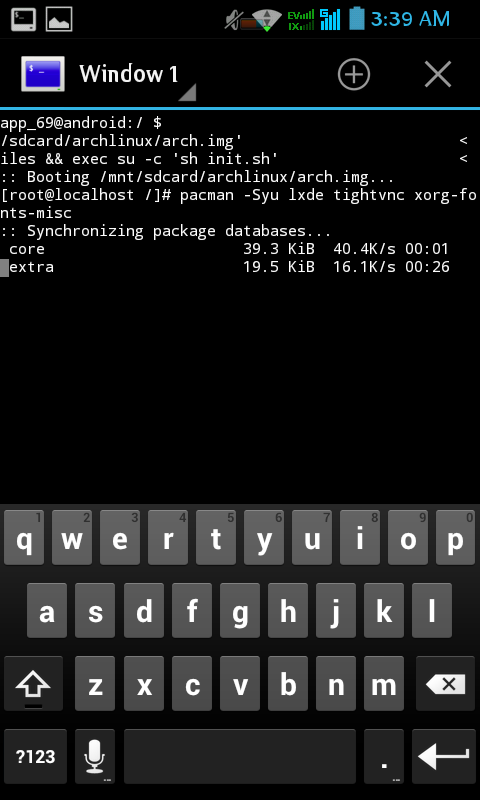
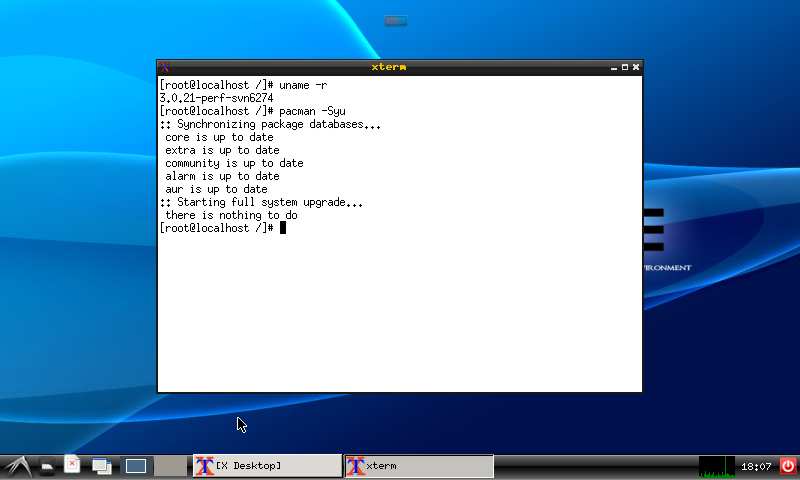
Oke when arch is up, upgrade the system by pacman -Syu, and for this example i want to install lxde, so this the package you need if you want to install too.
rm -r /root/.vnc
rm -r /tmp/.X*
export HOME=»/root»
export USER=»root»
export DISPLAY=»:1″
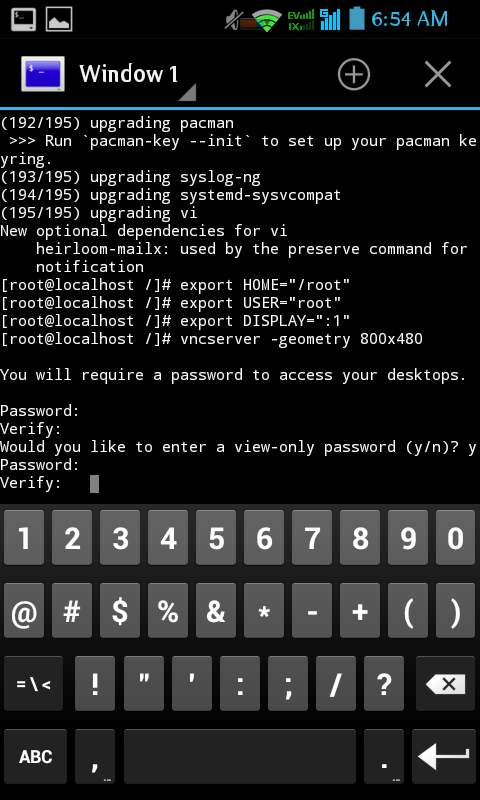
vncserver -geometry 800×480
On VNCserver -geometry, change into your android resolution, on my devices (HISENSE E G909 is 800×480) . Then save, by CTRL+X using pc keyboard.
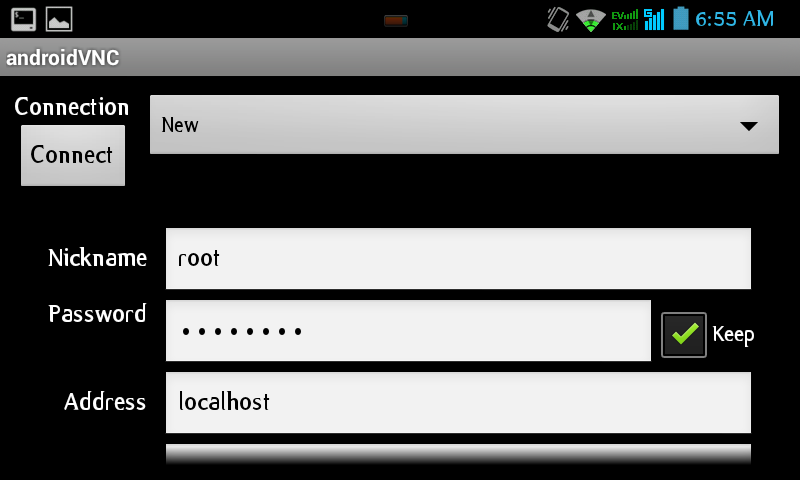
Now, click hom e on your android, then, run Android VNC Viewer. Set like this , Nickname : root, password: set same as previous t hat you create start.sh
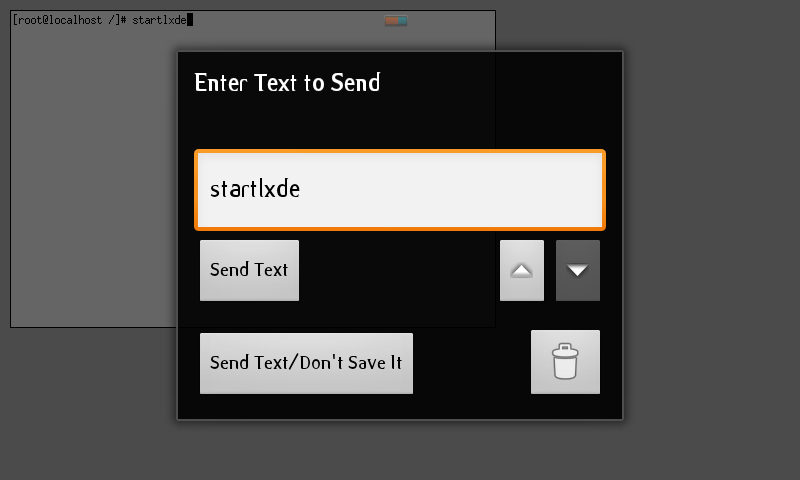
For input, tap on menu button on android, then send text, «startlxde» to start lxde :
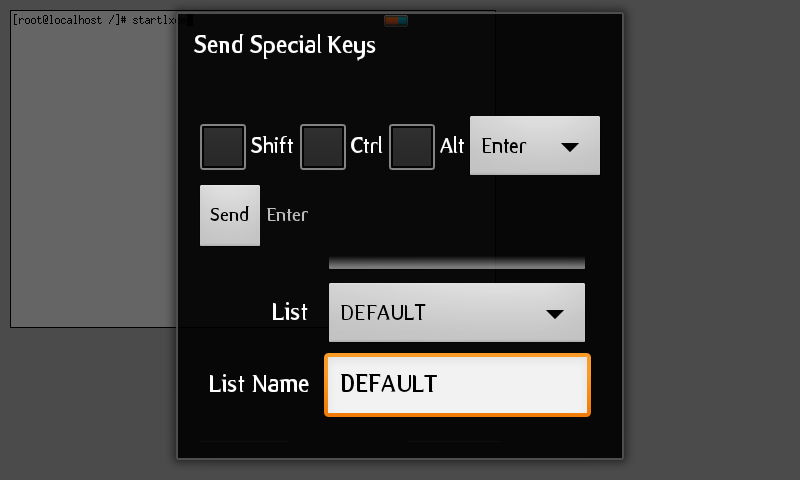
Then send enter keys (again f rom menu b utton — > send keys:
Now your desktop ready to use:
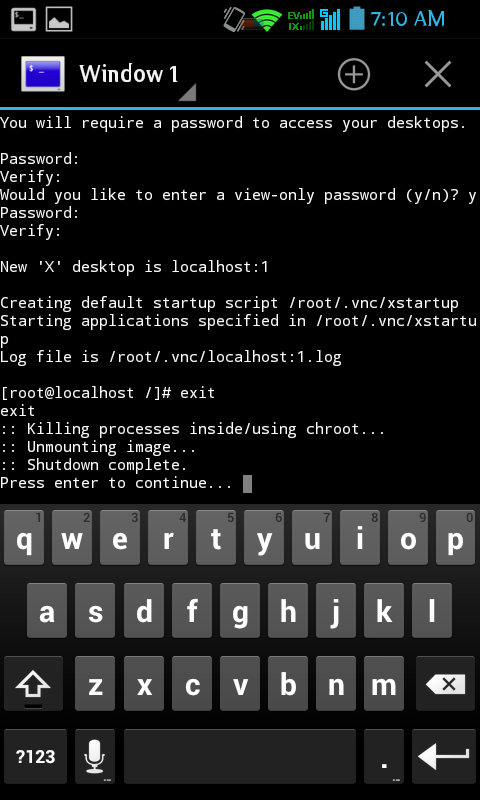
Now try to install some apps, same as archlinux pc version, but with limited software, make sure your sd card have more spaces. If you done playing with archlinux arm. Disconnect vnc server, then, go to android termina l em ulator. then type exit, to shutdown.
If done, if you wan t to start it again, when run Arch Linux, start s tart.sh script again, then set vnc, then connect. That ‘s it. Enjoy.
All content based on Arch Linux Installer Documents sites , with some my trial & error.