- ArchPKGs
- Beginner’s Tutorial on Installing mate-desktop on Arch Linux, Manjaro and ArcoLinux
- Table of Contents
- mate-desktop (Extra) link
- Install link
- Update link
- Remove link
- mate-desktop (Community) link
- Install link
- Update link
- Remove link
- mate-desktop (Community Testing) link
- Install link
- Update link
- Remove link
- More Guides
- The Complete Tutorial on Installing kdewebkit on Arch Linux (Manjaro, EndeavourOS)
- The Simplest Guide on Installing neovim-cmp-git on Arch Linux (Manjaro, Parabola)
- How to Install/Update/Remove mingw-w64-libtasn1 on Arch Linux (Manjaro/EndeavourOS)
- How to Install (Update/Remove) chinadns-ng-git on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Artix
- tuc-bin Install (Update/Remove) Tutorial on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Garuda
- How to Install/Update/Uninstall pipebench-git on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Parabola
- How to Install MATE desktop in ArchLinux
- Step 1: Run the latest updates on Archlinux
- Step 2: Install Xorg on ArchLinux
- Step 3: Install MATE Desktop Environment
- Step 4: Install supporting utilities
- Welcome to the MATE desktop environment
- Wrapping up:
- About the author
- Younis Said
ArchPKGs
Beginner’s Tutorial on Installing mate-desktop on Arch Linux, Manjaro and ArcoLinux
3 packages from Extra, Community and Community Testing have the same name ( mate-desktop ). We’d recommend going with either the packages from the official repositories or an AUR package with a good reputation.
Table of Contents
mate-desktop (Extra) link
extra/mate-desktop is «Library with common API for various MATE modules» referring to its own description. To install extra/mate-desktop from Arch official repository (Extra) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, BlackArch and Garuda is pretty simple. This tutorial will be covering how to install/update/remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay .
Install link
Two well known fashions are used to install extra/mate-desktop from Arch official repository (Extra). pacman is what you’re looking for if you are a seasoned Linux user and have the idea of how packages are built. If not, yay is a common alternative to install packages without the hassle of reviewing PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg on your own.
Install with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -S extra/mate-desktop
Install with Yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -S --repo extra/mate-desktop
Update link
Since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distro, there will be no way to update an official package without doing a whole system upgrade due to dependency issues.
Update with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -Syu
Update with Yay (AUR Helper) link
Remove link
Compared to installing and updating packages, removing is the simplest of these three,just choose whether to keep the dependencies that no longer required by other packages and the configuration files generated by the package.
Uninstall with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -R mate-desktop
sudo pacman -Rs mate-desktop
sudo pacman -Rns mate-desktop
Uninstall with Yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -R mate-desktop
yay -Rs mate-desktop
yay -Rns mate-desktop
mate-desktop (Community) link
«Library with common API for various MATE modules» is their description of community/mate-desktop . To install and update community/mate-desktop from Arch community repository (Community) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda, Parabola) is fairly uncomplicated. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install/update/remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay ).
Install link
Two common fashions are used to install community/mate-desktop from Arch community repository (Community). pacman is the choice for you if you’re comfortable using Arch-based distributions and have the knowledge of how packages are built. If not, yay is a popular alternative to install packages without the need to review PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg on your own.
Install with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -S community/mate-desktop
Install with Yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -S --repo community/mate-desktop
Update link
Since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distribution, it is required to do a whole system upgrade before updating a community package due to dependency issues.
Update with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -Syu
Update with Yay (AUR Helper) link
Remove link
Removing packages is the simplest of these three,just choose whether to keep the unused dependencies and the configuration files used by the package.
Uninstall with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -R mate-desktop
sudo pacman -Rs mate-desktop
sudo pacman -Rns mate-desktop
Uninstall with Yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -R mate-desktop
yay -Rs mate-desktop
yay -Rns mate-desktop
mate-desktop (Community Testing) link
It might not be a good practice to install a testing package ( community-testing/mate-desktop ) unless you know what you’re doing.
Quoting from community-testing/mate-desktop ‘s own profile, it is «Library with common API for various MATE modules». To install this package ( community-testing/mate-desktop ) from Arch community testing repository (Community Testing) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda, ArcoLinux) is pretty simple. This guide will cover how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay .
Install link
To enable Community Testing repository on Arch Linux, first you’ll need to uncomment [community-testing] section of /etc/pacman.conf , then use sudo pacman -Syu to refresh the packages list and upgrade your system.
There are two typical fashions to install the unstable version of community-testing/mate-desktop from Arch community repository (Community Testing). pacman is the choice for you if you’re a seasoned Linux user and have the knowledge of how packages are built. Otherwise, yay is a common alternative to install packages without the need to review PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg by yourself.
Install with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -S community-testing/mate-desktop
Install with Yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -S --repo community-testing/mate-desktop
Update link
Since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distribution, it is required to do a whole system upgrade before updating a community package due to safety reason.
Update with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -Syu
Update with Yay (AUR Helper) link
Remove link
Compared to installing and updating packages, uninstalling is the most uncomplicated of these three,all you have to do is choose whether to remove the unused dependencies and the configuration files generated by the package.
Uninstall with Pacman (Default Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -R mate-desktop
sudo pacman -Rs mate-desktop
sudo pacman -Rns mate-desktop
Uninstall with Yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -R mate-desktop
yay -Rs mate-desktop
yay -Rns mate-desktop
More Guides
The Complete Tutorial on Installing kdewebkit on Arch Linux (Manjaro, EndeavourOS)
According to extra/kdewebkit’s definition, it is «KDE Integration for QtWebKit». To install or remove this package (extra/kdewebkit) from Arch official repository (Extra) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, ArcoLinux) is pretty simple. This guide will cover how to install, update and uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
The Simplest Guide on Installing neovim-cmp-git on Arch Linux (Manjaro, Parabola)
neovim-cmp-git is «Autocompletion plugin for Neovim» based on its own gist. To install or remove neovim-cmp-git from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Anarchy, BlackArch and Artix is fairly straightforward. This tutorial will cover how to install, update and remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
How to Install/Update/Remove mingw-w64-libtasn1 on Arch Linux (Manjaro/EndeavourOS)
mingw-w64-libtasn1 is «The ASN.1 library used in GNUTLS (mingw-w64)» referring to its own profile. To install and update mingw-w64-libtasn1 from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix) is quite uncomplicated. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install, update and remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
How to Install (Update/Remove) chinadns-ng-git on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Artix
Quoting from chinadns-ng-git’s definition, it is «Chinadns next generation, refactoring with epoll and ipset». To install and update chinadns-ng-git from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix, Garuda, Anarchy and ArcoLinux is rather straightforward. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install/update/remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
tuc-bin Install (Update/Remove) Tutorial on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Garuda
tuc-bin is «A more powerful alternative to cut, when cut doesn’t cut it (pre-compiled)» referring to its own profile. To install and update tuc-bin from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola) is pretty straightforward. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
How to Install/Update/Uninstall pipebench-git on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Parabola
pipebench-git is «pipebench: Measures the speed of stdin/stdout communication.» referring to its own definition. To install pipebench-git from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Anarchy, Parabola and Artix is relatively simple. This tutorial will taught you how to install, update and remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
More guides… copyright 2023 ArchPKGs. All Rights Reserved.
How to Install MATE desktop in ArchLinux
MATE is a free and open-source desktop environment that is compatible with a variety of Linux distribution. It features a graphical interface that is both straightforward and functional. It is meant to be an unofficial successor to GNOME 2 and an alternative to the GNOME 3 shell as many users were unhappy with the changes. As such, it has preserved and maintained the GNOME 2 code.
In this short, step-by-step guide, you will see how to set up the MATE desktop environment on ArchLinux.
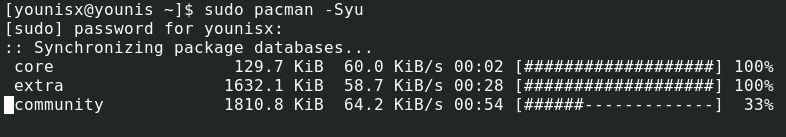
Step 1: Run the latest updates on Archlinux
To make sure everything moves smoothly, you should first consider getting the latest ArchLinux updates. Type in the following command:
If you don’t already have the latest updates installed, the command should get the latest packages for you.
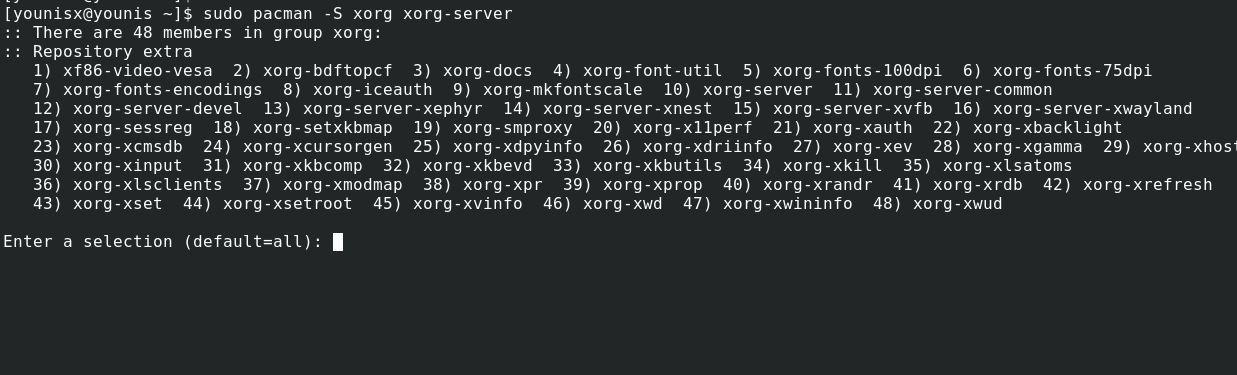
Step 2: Install Xorg on ArchLinux
To support the graphical environment, we will require a windows X System. Here, we’re opting for Xorg, a free and opensource windows x system implementation. Type in the following command to install Xorg:
The command will list all the packages and ask you for confirmation to proceed. Just hit the enter key to confirm.
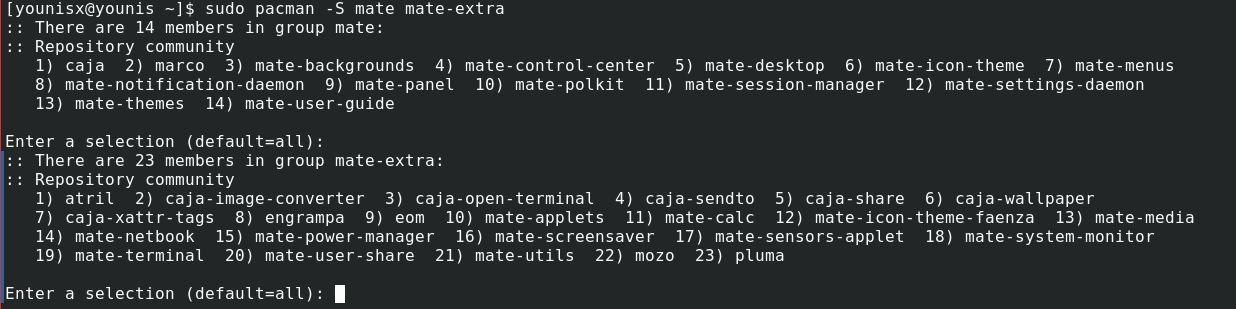
Step 3: Install MATE Desktop Environment
Now that we have installed Xorg, we now can set up MATE on our system. Type in the following command to install the MATE desktop environment:
To install all the packages displayed, just press enter.
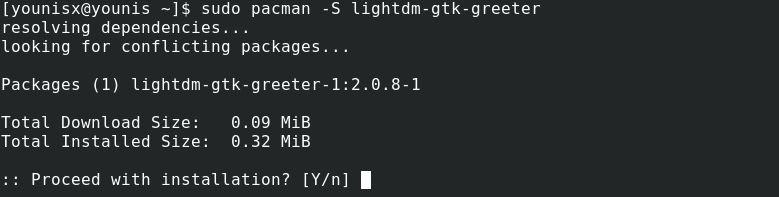
Step 4: Install supporting utilities
Let’s install two utilities to help us with the MATE desktop environment. These supporting tools are the LightDM display manager and greeter. The LightDM display manager manages processes behind graphical logins into MATE, whereas the greeter provides the graphical login interface.
Run the command below to install lightDM
Then install greeter with the following command:
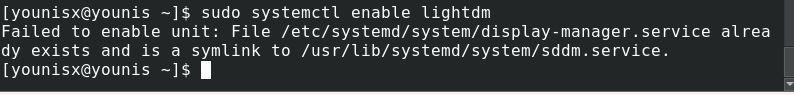
Set the lightDM utility to automatically load on system reboot. Run the command below:
Then restart your system to see changes.
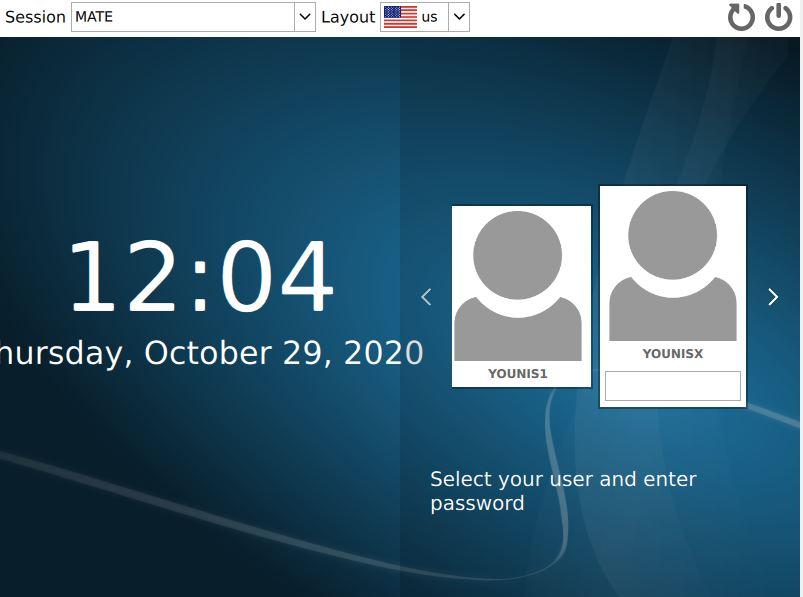
Welcome to the MATE desktop environment
Once the system reboots, you will be displayed the window contents as in the screenshot below:
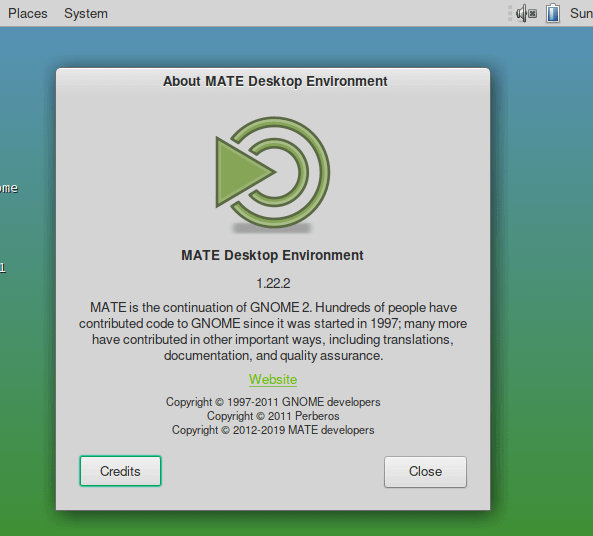
Enter the user credentials and present enter. To learn more about the MATE desktop environment, go to the places tab and click the about button. The window will also show what version you have installed.
Wrapping up:
Unlike its more mainstream alternatives(Windows and macOS), Linux doesn’t limit you to having just one type of interface. It is navigable in so many distributions, with both CLI and GUI interfaces. And one of the best ways to experience Linux in the graphical interface is with MATE’s desktop environment. That’s all we have for you today. Hopefully, this tutorial was both helpful and easy to follow. Stay tuned for more tutorials like this.
About the author
Younis Said
I am a freelancing software project developer, a software engineering graduate and a content writer. I love working with Linux and open-source software.