- ArchPKGs
- How to Install (Update, Remove) archlinux-appstream-data-pamac on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Anarchy
- Table of Contents
- Install archlinux-appstream-data-pamac link
- Using Pacman link
- Using Yay link
- Update archlinux-appstream-data-pamac link
- Using Pacman link
- Using Yay link
- Uninstall archlinux-appstream-data-pamac link
- Using Pacman link
- Using Yay link
- More Guides
- Beginner’s Guide on barry Installation on Arch Linux (Manjaro/ArcoLinux)
- postman6-bin Install, Update and Uninstall Tutorial on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Garuda
- dbus-nosystemd Install/Update/Remove Tutorial on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, BlackArch)
- Installing wps-office-cn in One Line of Command on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, Parabola)
- Guide on Install (Update, Uninstall) iacs on Arch Linux (Manjaro/BlackArch)
- A Straightforward Guide on precached Installation on Arch Linux, Manjaro and ArcoLinux
- How to Install Pamac GUI Package Manager in Arch Linux
- Method 1: Installing Pamac from the AUR
- Method 2: Installing Pamac from the Chaotic-AUR (Recommended)
- Conclusion
- Pamac – Easily Install and Manage Software on Arch Linux
- How to Install Yaourt in Arch Linux
ArchPKGs
How to Install (Update, Remove) archlinux-appstream-data-pamac on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Anarchy
«Arch Linux application database for AppStream-based software centers (Fixed for pamac-aur and pamac-all packages)» is their description of archlinux-appstream-data-pamac . To install this package ( archlinux-appstream-data-pamac ) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda, ArcoLinux, Anarchy, Parabola) is fairly uncomplicated. This tutorial will be covering how to install, update and remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay .
Table of Contents
Install archlinux-appstream-data-pamac link
Two common methods are used to install archlinux-appstream-data-pamac from AUR. pacman is the choice for you if you are familiar with Arch-based distributions and have the knowledge of how packages are built. Otherwise, yay is a popular alternative to install packages without the trouble to review PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg by yourself.
Using Pacman link
sudo pacman -S --needed git && git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/archlinux-appstream-data-pamac.git && cd archlinux-appstream-data-pamac && makepkg -si
- Install git if needed (not installed before).
- clone the package’s git repository from AUR.
- cd into the folder of the repository.
- Use makepkg to build the package. Also, it will automatically be installed with pacman if built successfully.
Using Yay link
yay -S archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
Update archlinux-appstream-data-pamac link
Just like installing AUR packages, updating them is practically the same. All you have to do is pull it from source then re-build it. Nonetheless, it is still a good practice to upgrade your whole system first with sudo pacman -Syu before updating any packages to avoid breaking your system, since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distro.
Using Pacman link
Before running the command, make sure you are in the directory of the repository you previously cloned:
git pull && makepkg -si - pull from the package’s git repository.
- Build the package with makepkg , then update it with pacman .
Using Yay link
Uninstall archlinux-appstream-data-pamac link
Uninstalling packages is the easiest of these three,just choose whether to purge the unused dependencies and the configuration files used by the package.
Using Pacman link
sudo pacman -R archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
sudo pacman -Rs archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
sudo pacman -Rns archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
Using Yay link
yay ‘s uninstalling command is just a pacman wrapper, running with the same parameters will do the trick:
yay -R archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
yay -Rs archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
yay -Rns archlinux-appstream-data-pamac
For more information about installing/updating AUR packages or how to install yay , please refer to Two Ways to Install Packages from AUR written by NoCache.
More Guides
Beginner’s Guide on barry Installation on Arch Linux (Manjaro/ArcoLinux)
barry is «Barry is an Open Source application that provides a Desktop GUI, synchronization, backup, restore and program management for BlackBerry ™ devices.» referring to its outline. To install or remove barry from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda and ArcoLinux is pretty simple. This tutorial will be covering how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
postman6-bin Install, Update and Uninstall Tutorial on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Garuda
Referring to postman6-bin’s profile, it’s «Build, test, and document your APIs faster. (Compatible with v6 team collections)». To install and update postman6-bin from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, BlackArch) is fairly uncomplicated. This tutorial will cover how to install, update and uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
dbus-nosystemd Install/Update/Remove Tutorial on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, BlackArch)
According to dbus-nosystemd’s own gist, it is «Freedesktop.org message bus system». To install and update dbus-nosystemd from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix, RebornOS) is fairly uncomplicated. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install/update/remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
Installing wps-office-cn in One Line of Command on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, Parabola)
wps-office-cn is «Kingsoft Office (WPS Office) CN version — an office productivity suite» based on its own description. To install or uninstall this package (wps-office-cn) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda, RebornOS, ArcoLinux) is quite uncomplicated. This guide will be covering how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
Guide on Install (Update, Uninstall) iacs on Arch Linux (Manjaro/BlackArch)
«IBM i Access Client Solutions provides a Java based, platform-independent interface for IBM iAccess/iSeries (formerly known as AS400).» is their outline of iacs. To install and update iacs from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola and Garuda is rather easy. This tutorial will be covering how to install, update and remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
A Straightforward Guide on precached Installation on Arch Linux, Manjaro and ArcoLinux
According to precached’s description, it is «A Linux process monitor and pre-caching daemon». To install and update precached from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix and RebornOS is comparatively uncomplicated. This guide will cover how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
More guides… copyright 2023 ArchPKGs. All Rights Reserved.
How to Install Pamac GUI Package Manager in Arch Linux
Missing a software center in Arch Linux? You can install and use Manjaro’s Pamac package manager in Arch without much trouble.
- Installing from the AUR
- Installing from the Chaotic-AUR (Recommended as the developers of Garuda Linux sign packages)
Both are command line methods, but you are an Arch user, and I believe you can handle the command line a bit, can you not?
Method 1: Installing Pamac from the AUR
If you have an AUR helper like Yay installed already, getting Pamac is really easy.
Otherwise, you’ll have to go the challenging route.
First, update your system as Arch is a rolling release distribution and do not support partial upgrades. Enter the following command in the terminal to update your Arch Linux system.
Then you need to install all the packages of the base-devel package group and git by entering the command below.
sudo pacman -S --needed base-devel gitNow you need to build and install archlinux-appstream-data-pamac, libpamac-aur and pamac-aur respectively.
Enter the following commands replacing the package name with packages you want to install for all the 3 packages.
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/archlinux-appstream-data-pamac.git cd archlinux-appstream-data-pamac makepkg -siIn this case, the AUR package pamac-aur have other AUR packages as dependencies. So you have to build and install them before installing the main package. This hassle can be avoided by using an AUR helper.
Building and installing packages from AUR may fail due to outdated PKGBUILD and there are plenty of them in the AUR. Also, you need to manually update AUR packages if there is an update, as AUR packages don’t update when you update your system with Pacman.
In my opinion, you should use the next method. You don’t have to bother building and updating Pamac manually when there is an update.
Method 2: Installing Pamac from the Chaotic-AUR (Recommended)
Chaotic-AUR is a repository for Arch Linux maintained by the developers of Garuda Linux. Packages of this repo are signed and can be trusted. When you add this repo, you can install Pamac using Pacman directly.
Let’s add the repo by entering the following commands.
sudo pacman-key --recv-key FBA220DFC880C036 --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com sudo pacman-key --lsign-key FBA220DFC880C036 sudo pacman -U 'https://cdn-mirror.chaotic.cx/chaotic-aur/chaotic-keyring.pkg.tar.zst' 'https://cdn-mirror.chaotic.cx/chaotic-aur/chaotic-mirrorlist.pkg.tar.zst'The above command just installs the keyring and mirrorlist for the repo. You also have to add the repo to the end of /etc/pacman.conf. Here I will use nano to edit the file.
The resulting file should look something like this.
. # An example of a custom package repository. See the pacman manpage for # tips on creating your own repositories. #[custom] #SigLevel = Optional TrustAll #Server = file:///home/custompkgs [chaotic-aur] Include = /etc/pacman.d/chaotic-mirrorlistNow update your system using Pacman and install Pamac by the entering the following command.
Once installed, you can access the GUI from Application Menu and CLI using the pamac command.
In case you don’t like Pamac, you can remove it along with its dependencies and configuration files using pacman via the following command:
Conclusion
When I started using Arch Linux, I was also very skeptical about installing AUR packages as they took a long time to build and many times refused to build due to outdated PKGBUILD. I wish we had Chaotic-AUR earlier kudos to the Garuda Linux developers.
Note that there are other variants of Pamac available in the AUR which support Flatpak and Snaps. But in this tutorial, I have mentioned the variant with only Appstream and AUR support.
What’s your opinion on adding a 3rd party repos like Chaotic-AUR on Arch Linux? Which method would you use to install Pamac?
Pamac – Easily Install and Manage Software on Arch Linux
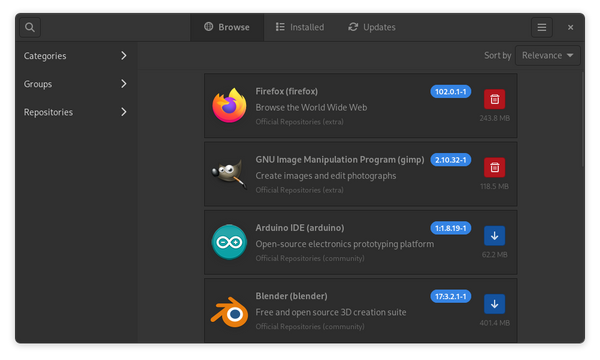
Arch Linux is one of the most popular Linux distribution available despite its apparent technicality. Its default package manager pacman is powerful but as time always tells, it is a lot easier to get certain things done using a mouse because GUI apps barely require any typing nor do they require you to remember any commands; and this is where Pamac comes in.
Pamac is a Gtk3 frontend for libalpm and it is the GUI tool that Arch Linux users turn to the most when they aren’t in the mood to manage their software packages via the terminal; and who can blame them? It was specifically created to be used with Pacman.
It enables users to search for and install applications on their computer with easy-to-follow steps. Users can also browse for new applications, check for updates, and uninstall unwanted packages. Would you like to try out Pamac? Read on.
Yaourt is a command line program which complete pacman for installing third party additional software in Arch Linux. If you have installed Arch Linux from scratch, Yaourt program won’t be installed by default. You need to install it manually as shown.
How to Install Yaourt in Arch Linux
To install Yaourt on Arch Linux, run the following commands.
$ sudo pacman -S --needed base-devel git wget yajl $ cd /tmp $ git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/package-query.git $ cd package-query/ $ makepkg -si && cd /tmp/ $ git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/yaourt.git $ cd yaourt/ $ makepkg -si
Once Yaourt installed on your PC, you can use this command to install Pamac on your workstation as shown.
Launch Pamac when the installation is complete by either right-clicking on its icon in your system tray or selecting “Add/Remove Software” in your menu.
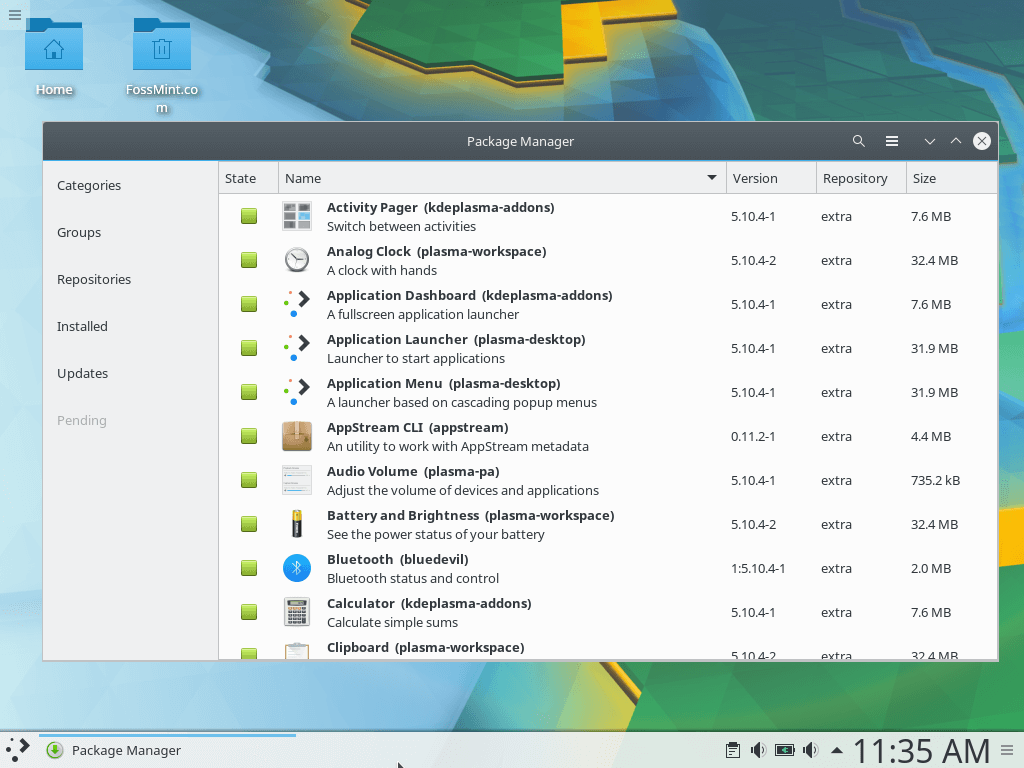
You will notice that Pamac’s UI is divided into 6 sections:
- Categories – list all available software applications into specific category.
- Groups – for installing packages from specific groups e.g. gnome, base, etc.
- Repositories – for installing packages from specific repositories e.g. Core, Community, etc.
- Installed – for viewing all installed apps including packages that are still downloading and orphaned packages.
- Updates – for viewing all available package updates..
- Pending – for viewing software pending updates.
Pamac gives users access to both official packages from Arch repositories and un-official packages from the community-driven AUR repo and if you want, you can enable AUR support on your PC by tweaking the preferences option from the menu.
Pacman has other frontend tools that work with it but Pamac has proven to be the most used. Have you had any experience with it, or maybe its alternatives? Share your thoughts with us in the comments section below.