How to Fix “failed to mount /etc/fstab” Error in Linux
In this article, i will explain how to solve “failed to mount /etc/fstab” boot error in Linux. The file in question contains descriptive information concerning the filesystems the system can mount automatically at boot time.
This information is static and is read by other programs on the system such as mount, umount, dump and fsck. It has six important filesystem mount specification fields: the first field describes the block special device or remote filesystem to be mounted, the second field defines the mount point for the filesystem and the third specifies the filesystem type.
The fourth field defines the mount options associated with the filesystem, and the fifth field is read by dump tool. The last field is used by fsck tool to establish the order of filesystem-checks.
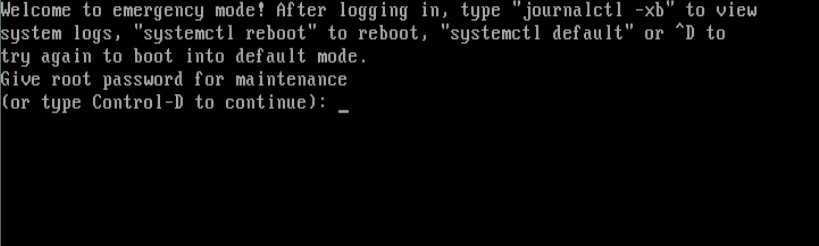
After editing the /etc/fstab to create an automount and rebooting my system; it booted into emergency mode showing the error message below.
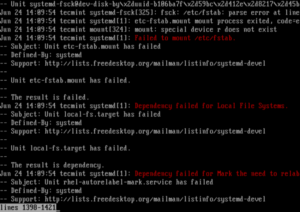
I logged in as root from the interface above, and typed the following command to look through the systemd journal; then I saw the errors shown in the screen shot (indicated using red).
As you can see, the main error (failure of etc-fstab.mount unit) lead to several other errors (systemd unit dependency issues) such as failure of local-fs.target, rhel-autorelabel-mark.service etc.
Causes of “failed to mount /etc/fstab” Error in Linux
The error above may result from any of the issues below, in the /etc/fstab file:
- missing /etc/fstab file
- wrong specification of filesystem mount options,
- failing mount points or
- unrecognized characters in the file.
To solve it, you can use the original file if you created a backup, otherwise comment out any changes you made using the “#” character (and also ensure that all the uncommented lines are filesystem mount lines).
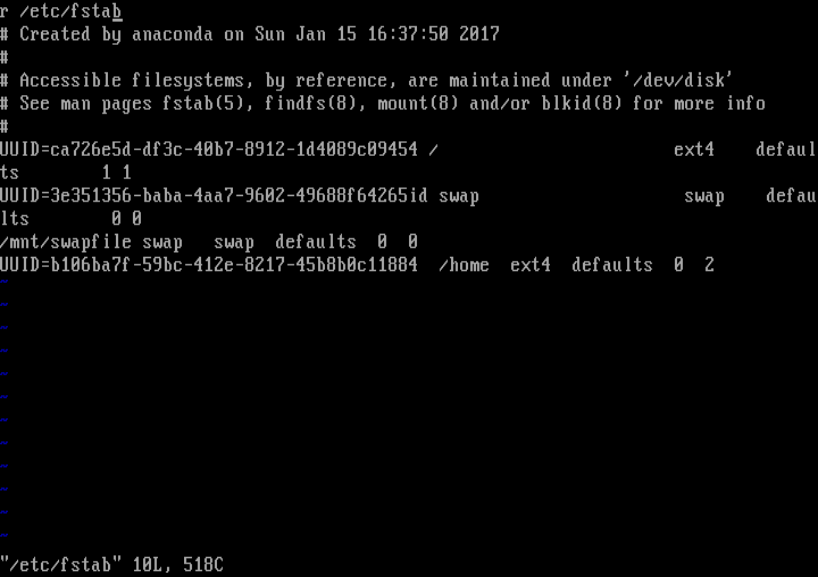
So I opened the /etc/fstab using vi/m text editor to check for any errors.
I realized I had typed an “r” letter at the beginning of the file as shown in the screen shot above – this was recognized by the system as a special device which did not actually exist in the filesystem, thus resulting to the sequential errors shown above.
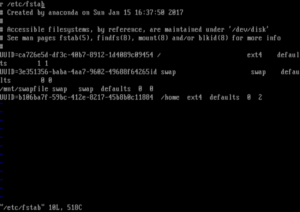
This took me several hours before noticing and fixing it. So I had to remove the letter, commented out the first line in the file, closed and saved it. After running a reboot, the system booted well again.
How to Avoid Such Issues in the Future
To avoid encountering such issues on your system, take note of the following:
Always create a backup of your config files before editing them. In case of any errors in your configs, you can revert to the default/working file.
Secondly, check config files for any errors before saving them, certain applications offer utilities to check syntax of config files before running the application. Use these utilities where possible.
However, if you happen to get any system errors messages:
First look through the systemd journal using the journalctl utility to determine what exactly caused them:
If you can’t resolve the errors in one way or the other, run to any of the millions of Linux forums on the web and post the issue there.
Do check out some useful related articles.
That’s it for now. In this article, I explained how to solve the “failed to mount /etc/fstab” boot error in Linux. Once again, to avoid such issues (or if you encounter any boot issues), remember to follow the guidelines offered above. Lastly, you can add your thoughts to this guide via the feedback form below.
Как исправить “failed to mount /etc/fstab” в Linux
В этой статье я расскажу, как решить проблему «failed to mount /etc/fstab» в Linux.
В рассматриваемом файле содержится описательная информация о файловых системах, которые система может смонтировать автоматически во время загрузки.
Эта информация является статической и считывается другими программами в системе, такими как mount, umount, dump и fsck.
Он имеет шесть важных спецификаций для установки файловой системы: первое поле описывает блокировку специального устройства или удаленной файловой системы, второе поле определяет точку монтирования для файловой системы, а третья – тип файловой системы.
Четвертое поле определяет параметры монтирования, связанные с файловой системой, а пятое поле считывается инструментом дампа. Последнее поле используется инструментом fsck для определения порядка проверки файловой системы.
Четвертое поле определяет параметры монтирования, связанные с файловой системой, а пятое поле считывается инструментом дампа.
Последнее поле используется инструментом fsck для определения порядка проверки файловой системы.
После редактирования /etc/fstab для создания automount и перезагрузки моей системы; Linux загрузился в аварийный режим, показывая сообщение об ошибке:
Я зарегистрировался как root из интерфейса выше и набрал следующую команду, чтобы просмотреть журнал systemd
Как вы можете видеть, основная ошибка (отказ модуля etc-fstab.mount) приводит к нескольким другим ошибкам (проблемы с зависимостью системы systemd), такие как отказ локального -fs.target, rhel-autorelabel-mark.service и т. д.
Причины ошибки
Приведенная выше ошибка может возникнуть из-за любой из нижеперечисленных проблем в файле /etc/fstab:
- отсутствует файл / etc / fstab
- неправильная спецификация параметров монтирования файловой системы,
- сбой точек монтирования или непризнанные символы в файле.
Чтобы решить эту проблему, вы можете использовать исходный файл, если создали резервную копию, иначе закомментируйте любые изменения, сделанные вами с помощью символа «#» (а также убедитесь, что все строки без комментирования – строки монтирования файловой системы).
Я понял, что набрал буква «r» в начале файла, как показано на скриншоте выше – это было признано системой как специальное устройство, которое фактически не существовало в файловой системе, что привело к появлению последовательных ошибок.
Мне потребовалось несколько часов, прежде чем заметить и исправить это.
Поэтому мне пришлось удалить лишнюю букву,закомментировать первую строку в файле, закрыть и сохранить его.
После перезагрузки система снова загрузилась.
Как избежать таких проблем в будущем
Чтобы избежать возникновения таких проблем в вашей системе, обратите внимание на следующее:
Всегда создавайте резервную копию своих файлов конфигурации перед их редактированием.
В случае каких-либо ошибок в ваших конфигурациях вы можете вернуться к файлу по умолчанию / работе.
Во-вторых, проверьте конфигурационные файлы на наличие ошибок перед их сохранением, некоторые приложения предлагают утилиты для проверки синтаксиса файлов конфигурации перед запуском приложения.
Используйте эти утилиты, где это возможно.
Однако, если вы получаете сообщения о системных ошибках:
Сначала просмотрите журнал systemd с помощью утилиты journalctl, чтобы определить, что именно вызвало их: