- How to Run Script on Startup in Linux
- Creating Script for Autostart
- How to Run Script on the System Boot
- How to Run Script on User Log In
- 1. GNOME Autostart in GUI
- 2. GNOME Autostart Manually
- 3. Autostart using Systemd
- Wrapping Up
- Other ways for auto-start script in Kali Linux?
- 1 Answer 1
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- How to execute shell script on Kali Linux startup?
- 3 Answers 3
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
How to Run Script on Startup in Linux
Sometimes you may want to run your shell script on the system startup or when the user logs in. For example when you need to run any desktop application, change screen resolution settings, start the remote desktop service, etc.
You can do this in a few ways. The first way — use the autostart feature in your desktop environment, for example, GNOME or KDE. The second way — use the Systemd initialization system which is used in most distributions nowadays. In this article I will explain how to run script on startup in Linux.
Creating Script for Autostart
Maybe you already have a script that you want to run on startup. But if it is not, or you want to practice with another bash shell script, it is pretty straightforward to create one. Let’s create an example script in the /usr/local/bin directory which prints «Hello world» into a file. This directory usually is used for custom binaries, so you can use it for storing your scripts too. In this article I will use the path to the script /usr/local/losst-script.sh. The following script creates file with the output in the current user home directory.
sudo vi /usr/local/losst-script.sh #!/bin/bash
echo «Hello world» > ~/file
After saving the script, make it executable using the following command:
sudo chmod ugo+x /usr/local/losst-script.sh
You can executable the shell script and ensure that it works. Now let’s have a look at how to add it into the system autostart.
How to Run Script on the System Boot
Systemd does not have any place where you can add scripts that you want to run on the system startup. But you can create systemd unit file which will run your script. Use the following command to do this:
sudo systemctl edit —force —full script.service
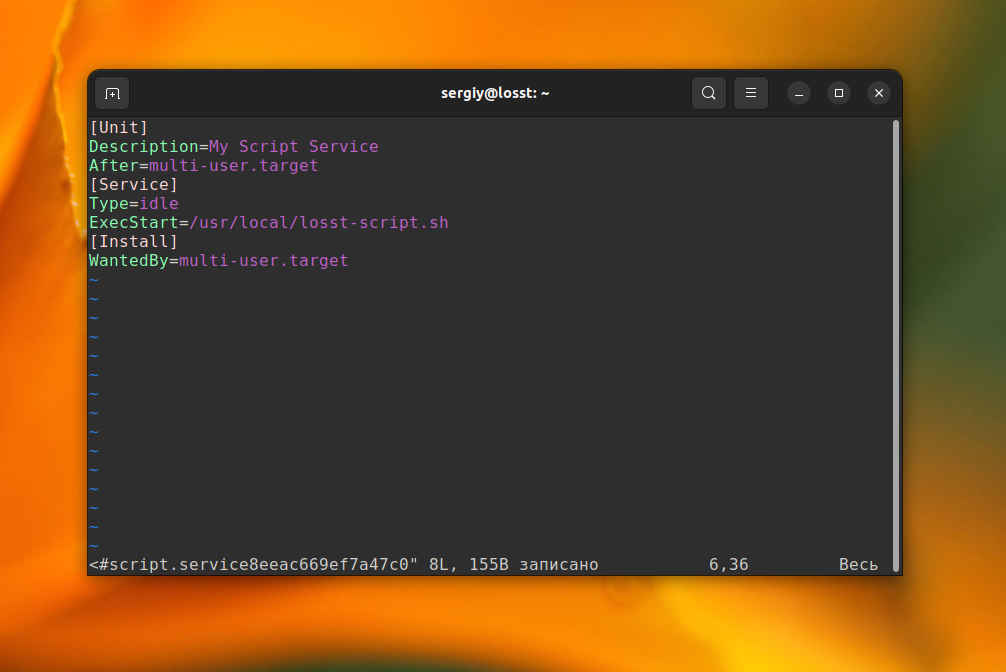
The command will open a text editor. Paste these lines into it:
[Unit] Description=My Script Service After=multi-user.target [Service] Type=idle ExecStart=/usr/local/losst-script.sh [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
You should set the path to the script or a required command into the ExecStart parameter. Note that I have used the Idle service type here, which means that the process will not fork. Now, let’s add this systemd service to autostart:
sudo systemctl enable srcipt
If Systemd can’t find your new service, update information about systemd configuration files using this simple command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
After this, the script will be started on the system startup. Reboot the system and find the file with the «Hello world» content in the /root directory to ensure that everything works fine.
If you prefer to use the old approach to autostart custom scripts with rc.local file, you can create the /etc/rc.local file, make it executable, and use the path to the file into the ExecStart parameter in the unit file. After this, you will be able to use this file as well as before Systemd came.
How to Run Script on User Log In
1. GNOME Autostart in GUI
You can configure this using a graphical user interface. Run the Startup Applications utility from the main menu. Also, you can run this utility in the terminal:
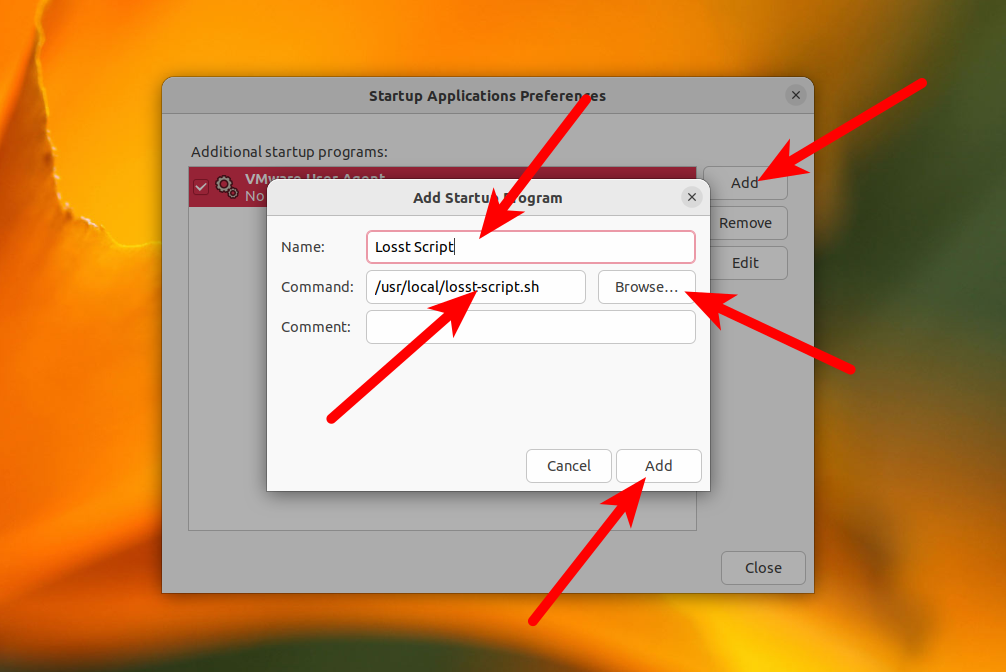
Here press the Add button. Then, in a new modal window paste a full path to your script in the Command field. Also, you can choose the path to the script in the filesystem using the Browse button. After this press the Add button at the bottom of the modal window:
The script will be started after GNOME finishes loading. You can reboot the system and ensure that you have the file with the «Hello world» text in your home folder.
2. GNOME Autostart Manually
Everything described in the previous section can be done manually, without the Startup Applications utility. Shortcuts for applications that must be started automatically are located in two directories:
- /etc/xdg/autostart/ — for all users;
- ~/.config/autostart/ — for the current user.
Create a new shortcut with the *.desktop extension which will run your script in one of the folders above with the following lines:
vi ~/.config/autostart/script.desktop [Desktop Entry] Name=Script Type=Application Exec=/usr/local/losst-script.sh
Here you should paste the path to the script executable into the Exec field. Then paste the name of the shortcut into the Name field and save the changes. After this, your script will be started automatically as well as in the previous section. The Startup Applications can see this shortcut, so you can manage it there too.
3. Autostart using Systemd
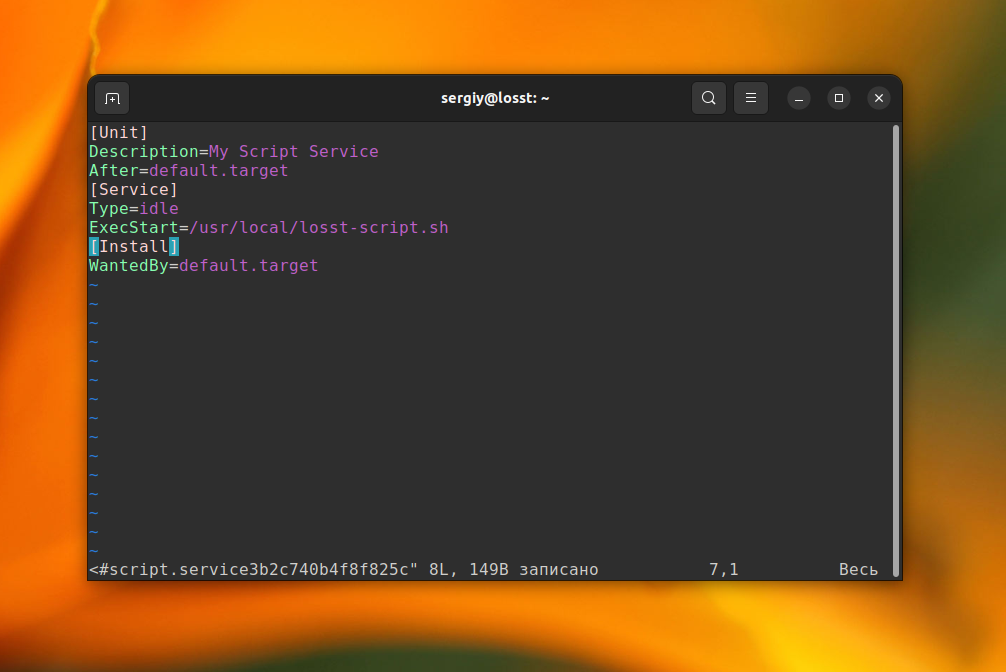
The Systemd initialization system can start a dedicated set of services for each user. You can manage these services using the systemctl utility with the —user option. Use this command to create a new user unit file for your script:
systemctl edit —user —force —full script.service [Unit] Description=My Script Service After=default.target [Service] Type=idle ExecStart=/usr/local/losst-script.sh [Install] WantedBy=default.target
The unit file will be created only for the current user. For this case, it will be placed in the /home/sergiy/.config/systemd/user/script.service file. Pay attention, that multi-user.target here is not available, so you should use default.target. Now, add this unit to autostart:
systemctl enable —user script.service
After this, you can reboot the system and ensure that everything works fine.
Wrapping Up
Now, you have learned how to run a script on startup in Linux. It may be difficult for new users, but you also can read the article about Services Autostart in Linux and How to Manage Services in Linux to understand how it works better.
Found a mistake in the text? Let me know about that. Highlight the text with the mistake and press Ctrl+Enter.
Other ways for auto-start script in Kali Linux?
So I’m basically wanting to get a script to run on system boot. It’s basically an SSH callback. I’ve tried a few ways that I’ve gotten to work in the past on other distributions, but having a little bit of difficulty here. First thing I’ve tried was adding the /path/to/script.rb to /etc/rc.local. However, this file does not exist on the latest version of Kali Linux. I tried to create it and replicate my old Ubuntu rc.local file, but it didn’t run on system startup. Next thing I tried was creating an executable bash script in /etc/init.d/, following the update-rc.d script.sh defaults and making the file executable. Restarted and nothing. If I run the script manually, it works. I tried to redirect the output to a file in the tmp folder, but it doesn’t appear that there are any errors from what I’m understanding. Are there any other ways to get an auto run script started other than these two methods? Seem to be the most common way to get this working, but it’s just not doing it for me.
1 Answer 1
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.17.43537
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
How to execute shell script on Kali Linux startup?
I need to execute a shell script on a Kali Linux startup. I am using 2016.1 version of Kali Linux. i tried many things like rc.local , init.d , X11 and GDM3 config etc. but I couldn’t get it work. This is the shell script that I want to execute:
#!/bin/bash xrandr --newmode 1366x768 85.500 1366 1494 1624 1798 768 770 776 795 +hsync -vsync xrandr --addmode VGA-0 1366x768 xrandr --output VGA-0 --mode 1366x768 Is the file executable? Can you run it from an interactive shell? What did you try wth your different approaches (which files did you edit how)?
can you place the script in /etc/profile.d/ ? Any script in that directory should run when you log in. Or maybe put it in /etc/bashrc ?
3 Answers 3
You can add an item in ~/.config/autostart ,
e.g Open ~/.config/autostart/myscript.desktop , and paste the following contents
[Desktop Entry] Name=MyScript GenericName=A descriptive name Comment=Some description about your script Exec=/path/to/my/script.sh Terminal=false Type=Application X-GNOME-Autostart-enabled=true And make sure the script is executable.
@reboot :EXAMPLE: @reboot macchanger -r eth0 (I got this from a video so im giving credit where credit is due) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OcVE6rQ9_FU 04:38:57
I see you’re attempting to force a custom resolution in your monitor in every boot.
I have not used Kali Linux myself, but I’m willing to guess you could add the commands to an .xprofile file in your home directory, as most display managers would run the content of the file when initializing.
If you don’t have this file in your home directory, just create it, paste your commands in it, save it and reboot. You can see more about this in this article from the ArchWiki.
You must log in to answer this question.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.17.43537
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This site is not affiliated with Linus Torvalds or The Open Group in any way.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.