The 5 Best Graphical Backup Tools for Ubuntu and Linux Mint
In this guide, we review the best graphical user interface backup tools for Ubuntu and Linux Mint operating systems. These Linux backup tools are also installable and work on Ubuntu flavors such as Lubuntu, Kubuntu, and Xubuntu and other derivatives such as elementary OS, Zorin OS, and more.
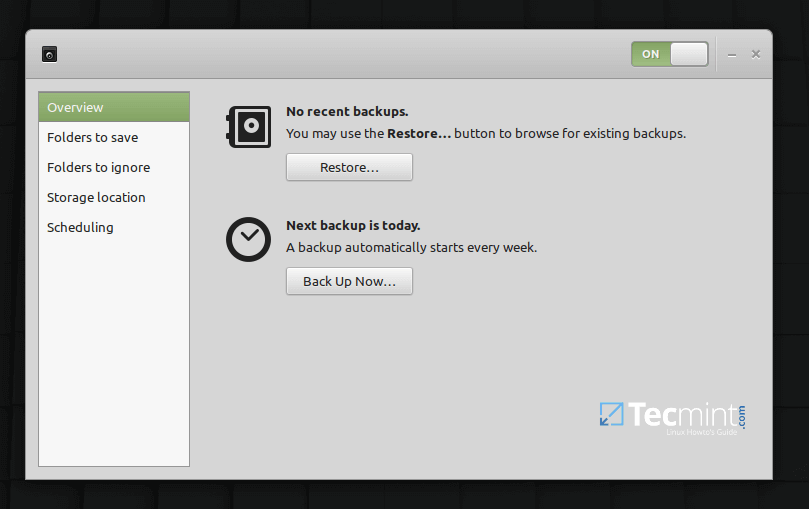
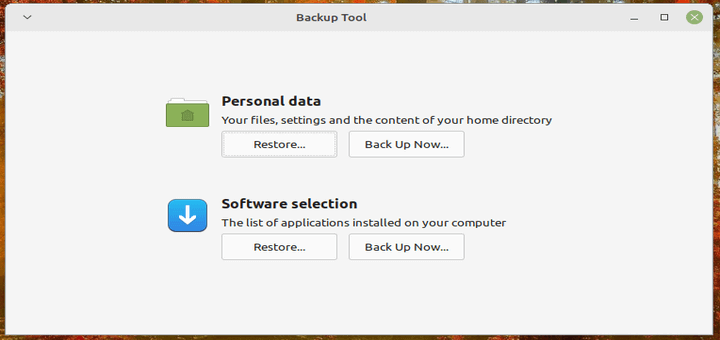
1. Déjà Dup
Déjà Dup is an open-source simple yet powerful personal backup tool that makes backup incredibly easy. It uses duplicity (encrypted bandwidth-efficient backup using the rsync algorithm) as the backend. It supports local, off-site (or remote), or cloud backup locations such as Google drive. It securely encrypts data for safe transactions and compresses data for faster transmission.
It also features incremental backups that allow you to restore from any particular backup, schedules regular backups, and integrates well with GNOME desktop environment.
To install Déjà Dup in Ubuntu and Linux Mint, open a terminal window and run the following command:
Alternatively, you can also install it as a snap as follows. This requires you to have snapd package installed on your system.
$ sudo snap install deja-dup --classic
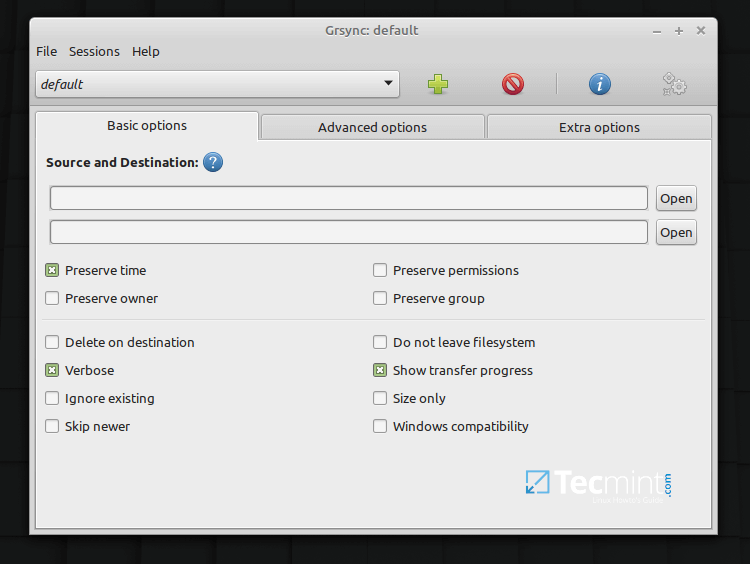
2. Grsync
Grsync is an open-source simple, great, and easy to use graphical user interface for the popular rsync command-line tool. It currently supports only a limited set of the most important rsync features, however, it can be used effectively to synchronize directories, files, and make backups. It comes with an efficient interface and supports the storage of different sessions (you can create and switch between sessions).
To install Grsync on your system, simply run the following command:
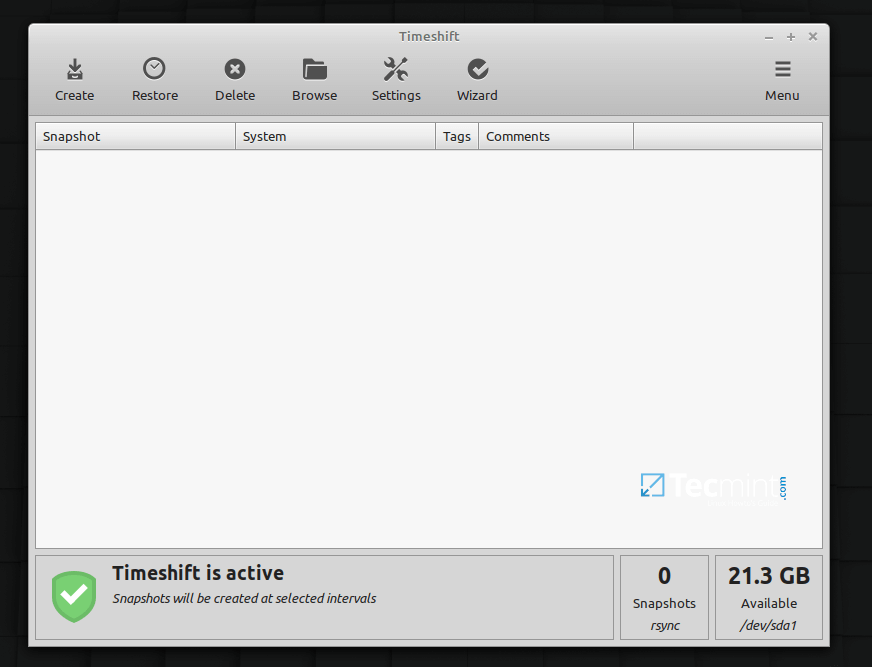
3. Timeshift
Timeshift is an open-source powerful backup and system restore tool for Linux that requires little setup. It is used to create filesystem snapshots in two modes: RSYNC mode where snapshots are taken using rsync+hardlinks on all systems and BTRFS mode where snapshots are taken using the in-built features only on BTRFS systems. By default, user data is excluded in snapshots because the program is designed to protect system files and settings.
Timeshift features scheduled snapshots, multiple backup levels (hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, and boot), and exclude filters. Importantly, snapshots can be restored while the system is running or from Live CD/USB. Besides, it supports cross-distribution restoration and so much.
You can install Timeshift package available in the Launchpad PPA for supported Ubuntu release, by issuing the following commands:
$ sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/timeshift $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install timeshift
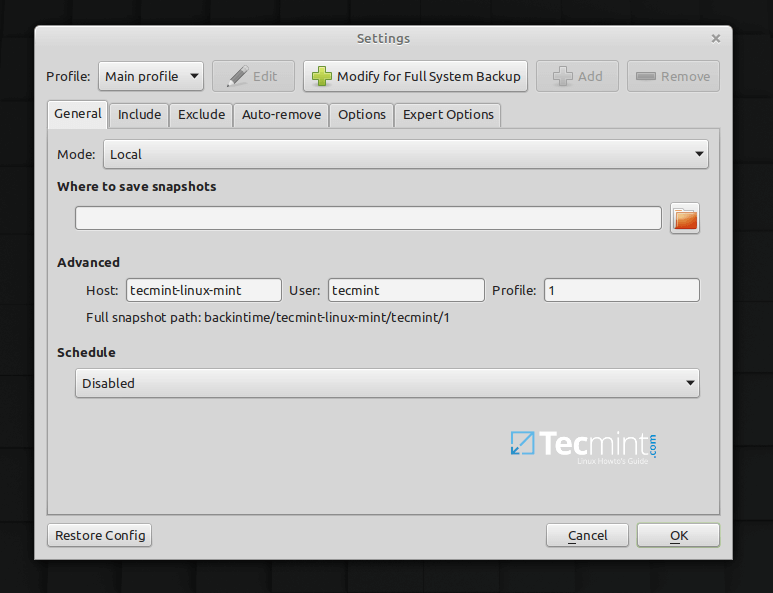
4. Back In Time
A simple open-source backup tool for Linux desktops, Back In Time comes with a Qt5 GUI ‘backintime-qt‘ application which will run on both Gnome and KDE based desktop enthronements and a command-line client ‘backintime’.
Backups are stored in plain text (which enables for the restoration of files even without Back in Time) and files ownership, group, and permissions are stored in a separate compressed plain text file fileinfo.bz2.
The Back In Time package is included in Ubuntu repositories, you can install it as shown.
$ sudo apt-get install backintime-qt4
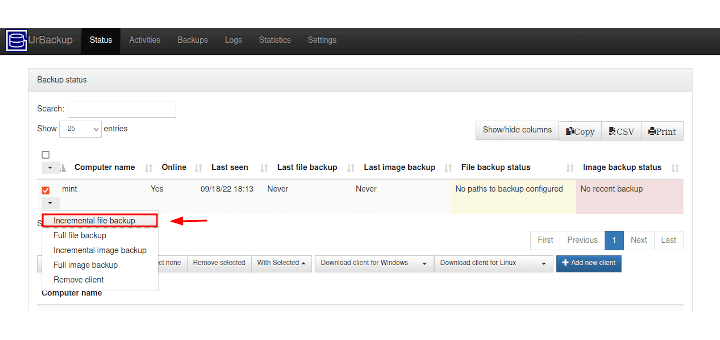
5. UrBackup
Last but not least, we have UrBackup, an open-source fast, easy to set up backup tool. Unlike most of the tools we have looked at before, UrBackup has a client/server architecture. It has configurable (but next to no configuration) clients for Linux, FreeBSD, and Windows operating systems.
It features full and incremental image and file backups, file metadata such as last modified is backed up, image and file backups while the system is running, fast calculation of file tree differences, easy to use file and image restore (via restoring CD/USB stick),
UrBackup also features consistent backups of used files on Windows and Linux, e-mail alerts, if a system isn’t backed up for some configurable period of time, reports about backups can be sent to users or administrators. Also, it comes with a web interface used for managing the client, which shows the status of the clients, ongoing activities and statistics, and modifying/overriding client settings.
The main limitation of UrBackup is that image backups only work with NTFS formatted volumes and with the Windows client.
To install UrBackup, run the following commands to add its PPA and install it:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:uroni/urbackup $ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install urbackup-server
That’s all! The above are the best graphical backup tools for Ubuntu and Linux Mint operating systems. Do you have some thoughts to share? Have your say, via the comment form below.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
12 thoughts on “The 5 Best Graphical Backup Tools for Ubuntu and Linux Mint”
I use MakuluLinux the latest version. I tested Timeshift which was standard in makululinux. But after backing up the root (including all files) and /home to my 1TB external drive, I was left with zero files on the external drive. Not a particularly useful program. Tested then dejadup, same problem, no backup! Reply
Just for information: Urbackup (beta) now (partly) supports image backup on Linux. See https://forums.urbackup.org/t/server-2-5-22-client-2-5-16/10442#linux-image-backups-4 Reply
Nice to see the instructions for installing the software. How do I find out where it was put and how to start it?” Search and search and search Google. ..Welcome to Linux !! 😉 Reply
I’ve been using Timeshift since 2019 but I gave up using it this month. It is just pretty annoying that it has to take so much disk space. Reply
I’m using KDE (Kubuntu) – I think it is 20.10.1 (64-bit), but I don’t yet know how to find out the version I’m running. sda Window 7 partitions (unbootable because Linux overwrote my boot partition (MBR)) 500GB
The data partition is NTFS – both are accessible from Linux sdb1 /boot (2GB)
sdb2 swap (8.8GB)
sdb3 / (50GB)
sdb4 extended (remainder of hdd)
sdb5 /home (350GB)
sdb6 /mnt (/ntfs-data-on-sdb) (remainder – 150gb or so) sdc 1tb an unused Linux installation and a 500GB NTFS partition for data
sdd 1tb external – ntfs for backup
sde (several 500GB Passport-type USB drives and several thumb drives) I’m trying to find a backup for data – just sync to a partition on an external drive to maintain an uncompressed duplicate of my data partition that can be used as-is, if my primary is lost. I don’t want incremental here, just a copy, maintained when I run a manual backup. I also need a backup for system images. Incremental is good, but every now and then I want a full image that has a simple path to restoration to an empty drive – that will BOOT after restoration (drive replacement/upgrade), as well as can be restored over the same (current) system (obviously the restore app would need to be on a live thumb drive) – in case the current system develops problems and I want to turn the clock back without affecting my data. I try to run both backups at the same time – data & system, and draw a line under my journal entries with the date & the name of the image backup. I don’t want any “auto” backups. I keep an online document where I record changes I make to my system between backups, so if I have to restore one, I know what to do to get back to where I was before the glitch. **How do I know where all of my configurations are? I really really like the app image concept, where everything an app needs is ALL kept together in ONE directory – that’s actually what I thought I would be getting with Linux, but it seems app pieces are flung everywhere in Linux also (like Windows). I was thinking of backintime or deja dup for system images.
Deja Dup says it ” integrates well with GNOME desktop environment”
Does that mean it DOESN’T “integrate” well with the KDE desktop?
Looking at BackinTime, it seems to provide enough (include/exclude) that it would probably do for my data, too, IF it syncs – that is makes the target match the source, only adding, changing, & deleting files as necessary to accomplish that. Will backintime do that? The image files must also be able to restore EVERYTHING (except /home) including /boot partition – everything the restoration needs to boot the restored system. Oh. and I want a GUI interface that I can set up profiles for backups. I don’t feel comfortable enough with Linux to type backup instructions on the fly in the Terminal. Thank you,
AnneF Reply
Hello, Sorry I’m late… Fix Win7 bootloader with “boot-repair-disk-32bit.iso !” Search it to get the ISO image for USB install! With mutlibootusb that doesn’t format USB, or deletes the files on it!
Or
With YUMI that doesn’t format USB, or deletes the files on it! I’d borrow a Windows OS computer to do one, or the other. If you have a W7 ISO install along that with one of the above, and use that to FIX the Bootloader! Steps…
Boot from the Windows 7 USB. Fill in the Language to install, Time and currency format, and Keyboard or input method. Select Next. Select Repair your computer. On the screen, choose the Windows 7 installation you want to repair. Choose Startup Repair. Follow any prompts and accept any suggested changes. Wait. Choose Finish to restart Windows I wish I had Windows 7 Pro rather than W10 Bloated OS. on my Dual Boot with W10 and Mint 20.04 and soon with Tails OS for Try boot with Linux boot loaders on its own 500MB Partition with / as root so NOT to mess with Windows booting! Good luck Reply