- ArchPKGs
- Full Guide on Installing kdeconnect-bluetooth on Arch Linux (Manjaro/BlackArch)
- Table of Contents
- Install link
- Using pacman (Package Manager) link
- Using yay (AUR Helper) link
- Update link
- Using pacman (Package Manager) link
- Using yay (AUR Helper) link
- Uninstall link
- Using pacman (Package Manager) link
- Using yay (AUR Helper) link
- More Guides
- How to Install pipewire-git (Full Tutorial) on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, ArcoLinux)
- How to Install whatsapp-for-linux in Single Line of Command on Arch Linux, Manjaro and EndeavourOS
- Beginner’s Tutorial on mingw-w64-libjxl Installation on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, Artix)
- A Complete Guide on rubyripper Installation on Arch Linux/Manjaro/EndeavourOS
- Guide on Install (Update/Remove) hplip-plugin on Arch Linux/Manjaro/EndeavourOS
- A Straightforward Tutorial on r-snpstats Installation on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Parabola
- How to Connect to a Bluetooth Device on Arch Linux
- Connecting and Getting Bluetooth Adapter Ready
- Connecting to a Bluetooth Device using GNOME Bluetooth
- Blueman for Connecting to a Bluetooth Device
- Connecting to a Bluetooth Device using Bluedevil
- About the author
- Shahriar Shovon
ArchPKGs
Full Guide on Installing kdeconnect-bluetooth on Arch Linux (Manjaro/BlackArch)
«Adds communication between KDE and your smartphone, with a bluetooth backend» is the developer’s outline of kdeconnect-bluetooth . To install kdeconnect-bluetooth from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola, Artix) is quite uncomplicated. This tutorial will taught you how to install/update/remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay .
Table of Contents
Install link
Two well known approaches are used to install kdeconnect-bluetooth from AUR. pacman is the choice for you if you’re an experienced Linux user and have the idea of how packages are built. If not, yay is a popular alternative to install packages without the hassle of reviewing PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg yourself.
Using pacman (Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -S --needed git && git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/kdeconnect-bluetooth.git && cd kdeconnect-bluetooth && makepkg -si
- Install git if needed (not installed before).
- clone the package’s git repository from source.
- cd into the directory.
- Use makepkg to build the package. Also, it will automatically be installed with pacman if built successfully.
Using yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -S kdeconnect-bluetooth
Update link
Updating AUR packages is almost the same as installing them. Simply pull it from upstream then re-build it. Even so, it is still recommended to upgrade your whole system first with sudo pacman -Syu before updating any packages to avoid dependency issues, since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distribution.
Using pacman (Package Manager) link
Before running the command, make sure you’re in the directory of the repository you previously cloned:
git pull && makepkg -si - pull from the package’s git repository.
- Use makepkg to build the package. Also, it will automatically be updated with pacman if built successfully.
Using yay (AUR Helper) link
Uninstall link
Uninstalling packages is the simplest of these three,all you have to do is choose whether to purge the dependencies that no longer required by other packages and the configuration files used by the package.
Using pacman (Package Manager) link
sudo pacman -R kdeconnect-bluetooth
sudo pacman -Rs kdeconnect-bluetooth
sudo pacman -Rns kdeconnect-bluetooth
Using yay (AUR Helper) link
yay -R kdeconnect-bluetooth
yay -Rs kdeconnect-bluetooth
yay -Rns kdeconnect-bluetooth
For more details about how to install AUR packages or how to get yay , please refer to Two Ways to Install Packages from AUR written by NoCache.
More Guides
How to Install pipewire-git (Full Tutorial) on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, ArcoLinux)
pipewire-git is «Low-latency audio/video router and processor (GIT version)» based on its description. To install pipewire-git from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Anarchy, ArcoLinux) is quite easy. This guide will cover how to install/update/remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
How to Install whatsapp-for-linux in Single Line of Command on Arch Linux, Manjaro and EndeavourOS
Quoting from whatsapp-for-linux’s own profile, it is «An unofficial WhatsApp desktop application for linux». To install this package (whatsapp-for-linux) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS and Artix is quite simple. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install/update/remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
Beginner’s Tutorial on mingw-w64-libjxl Installation on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro, Artix)
mingw-w64-libjxl is «JPEG XL image format reference implementation (mingw-w64)» based on its definition. To install and update this package (mingw-w64-libjxl) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Garuda, RebornOS, ArcoLinux, Anarchy) is quite easy. This tutorial will cover how to install/update/remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
A Complete Guide on rubyripper Installation on Arch Linux/Manjaro/EndeavourOS
rubyripper is «Secure audiodisc ripper» referring to its outline. To install rubyripper from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, ArcoLinux) is quite straightforward. This guide will taught you how to install/update/remove the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
Guide on Install (Update/Remove) hplip-plugin on Arch Linux/Manjaro/EndeavourOS
«Binary plugin for HPs hplip printer driver library» is the developer’s profile of hplip-plugin. To install and update hplip-plugin from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola) is fairly easy. This guide will taught you how to install/update/remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
A Straightforward Tutorial on r-snpstats Installation on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Parabola
«SnpMatrix and XSnpMatrix classes and methods» is their definition of r-snpstats. To install and update this package (r-snpstats) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, BlackArch, Artix and ArcoLinux is pretty uncomplicated. This tutorial will show you step-by-step how to install, update and remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
More guides… copyright 2023 ArchPKGs. All Rights Reserved.
How to Connect to a Bluetooth Device on Arch Linux
Bluetooth is one of the widely used protocol there is. These days we have so many Bluetooth devices all around us. We have Bluetooth keyboard, mouse, headset and many more. Even the old phones have Bluetooth. It is used so widely because of its low energy consumption, which is idea for portable devices.
On Linux operating systems such as Arch Linux, sometimes it’s a bit tricky to use a Bluetooth device. But once you set it up correctly, it works flawlessly. In this article, I will show you how to connect a Bluetooth device to your Arch Linux machine. Let’s get started.
Connecting and Getting Bluetooth Adapter Ready
NOTE: No matter how to connect to a Bluetooth device, you must follow this section of the article for Bluetooth to work on Arch Linux.
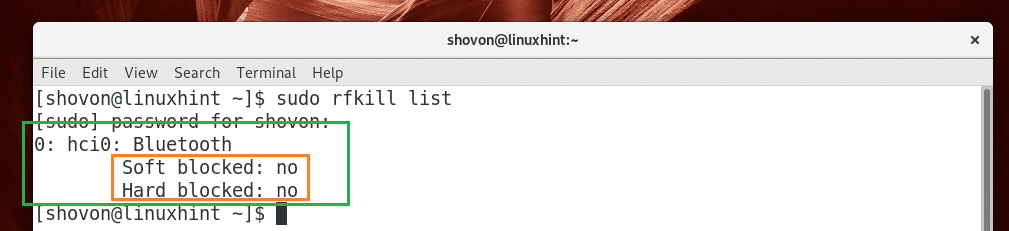
First connect your Bluetooth adapter and check whether your Bluetooth adapter is blocked with the following command:
As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, the Bluetooth adapter is not blocked.
If it is blocked, run the following command to unblock it.
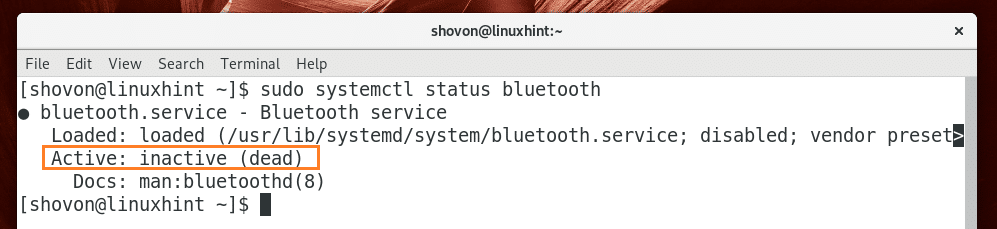
Now check whether Bluetooth service is enabled with the following command:
As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, the Bluetooth service is not running.
Now start the Bluetooth service with the following command:
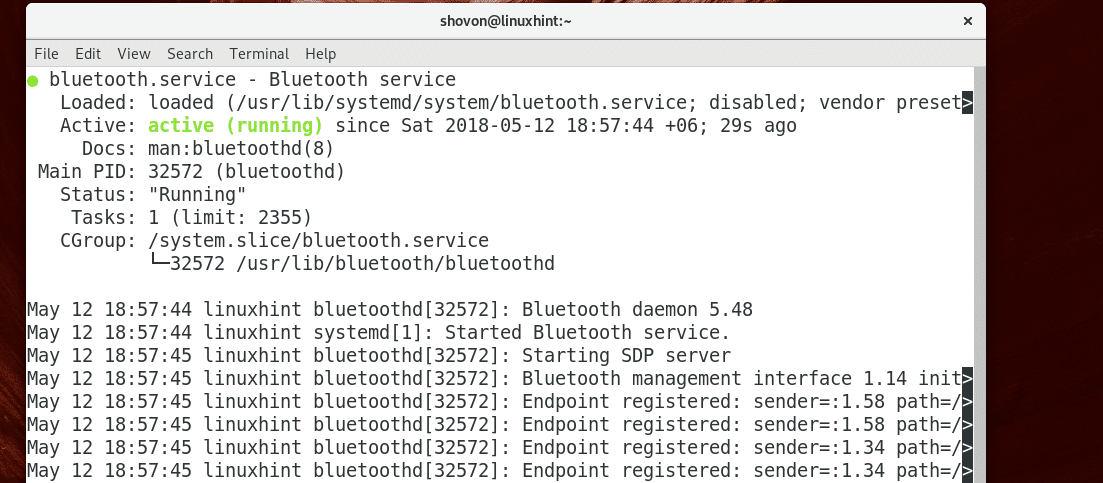
Now check whether the Bluetooth service is running with the following command:
As you can see from the screenshot below, the Bluetooth service is now running.
Now that you’ve completed all this step, you’re ready to move on to the next step.
Connecting to a Bluetooth Device using GNOME Bluetooth
GNOME Bluetooth is the default Bluetooth application for GNOME 3 desktop environment. In this section I will show you how to use it to connect to a Bluetooth device.
First click on the notification area of GNOME 3, and then click on the arrow after the Bluetooth icon as marked in the screenshot below.
Then click on Bluetooth Settings as marked in the screenshot below.
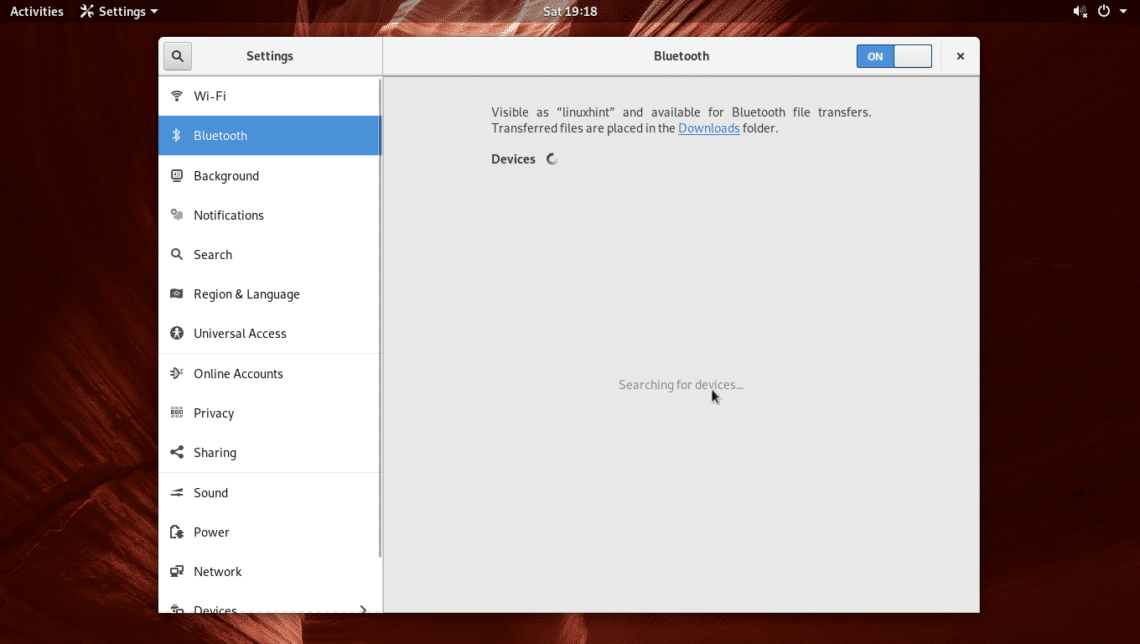
Bluetooth Settings should be opened as you can see from the screenshot below.
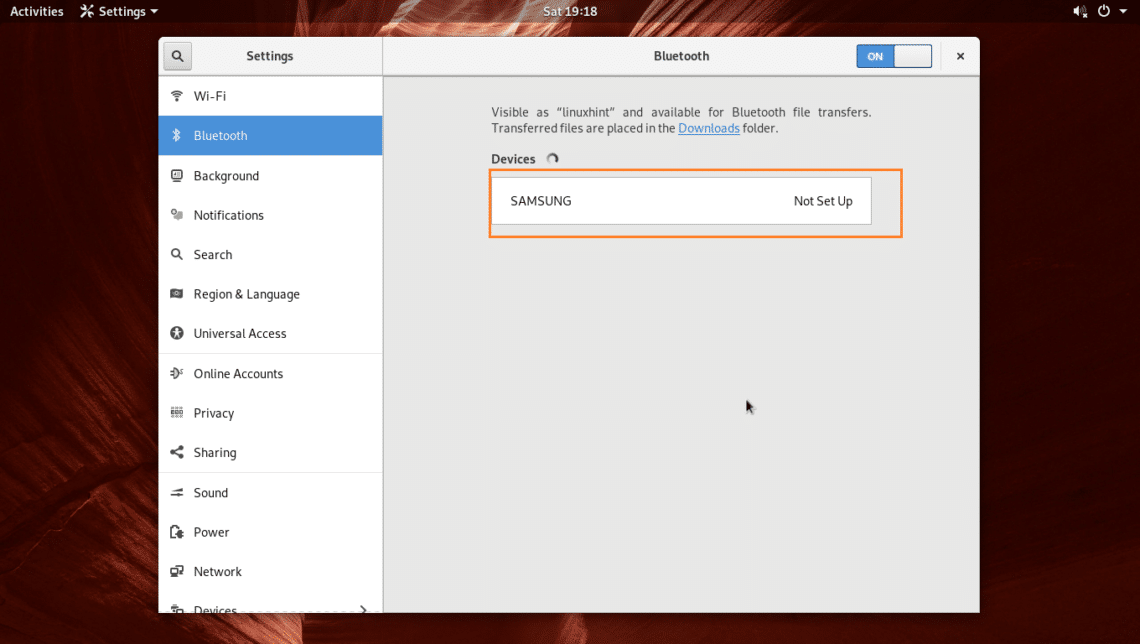
Now turn on Bluetooth on the device you want to connect to your Arch Linux machine and make sure Discoverable or Visibility is turned on on that device. As you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below, my Samsung Galaxy SM-G361H Android 5.1 smart phone is listed. Now you have to pair with the device you want to connect to your Arch Linux machine. Just click on the device from the list.
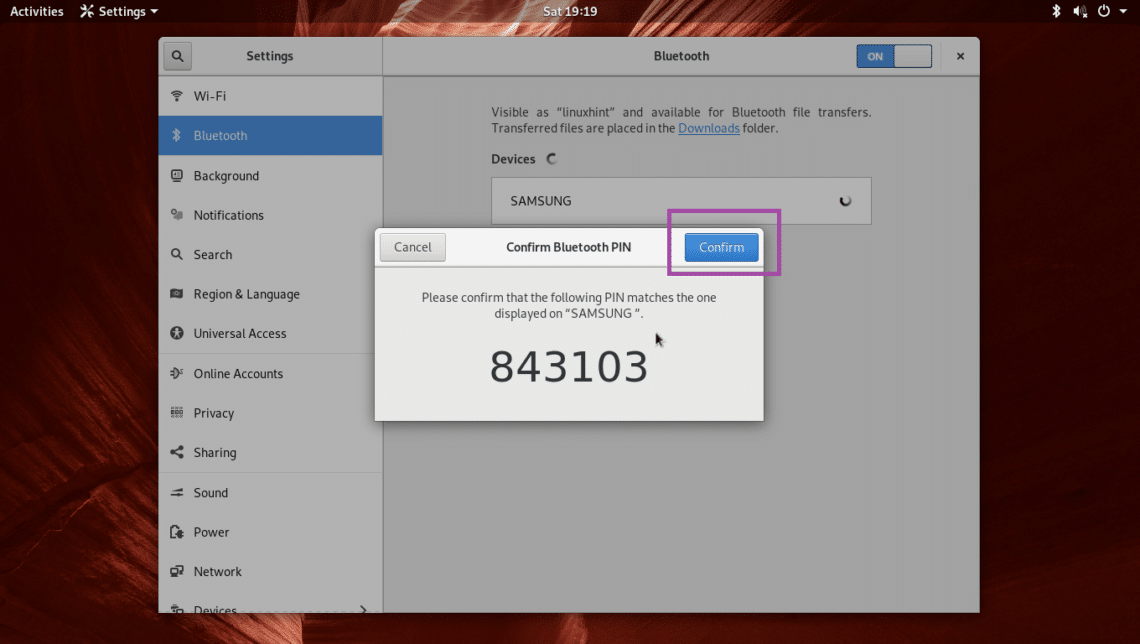
You should see the following window. In most cases, all you have to do is press the OK button on your Bluetooth device that you want to connect. Afterwards, press the Confirm button on your Arch Linux machine as marked in the screenshot below.
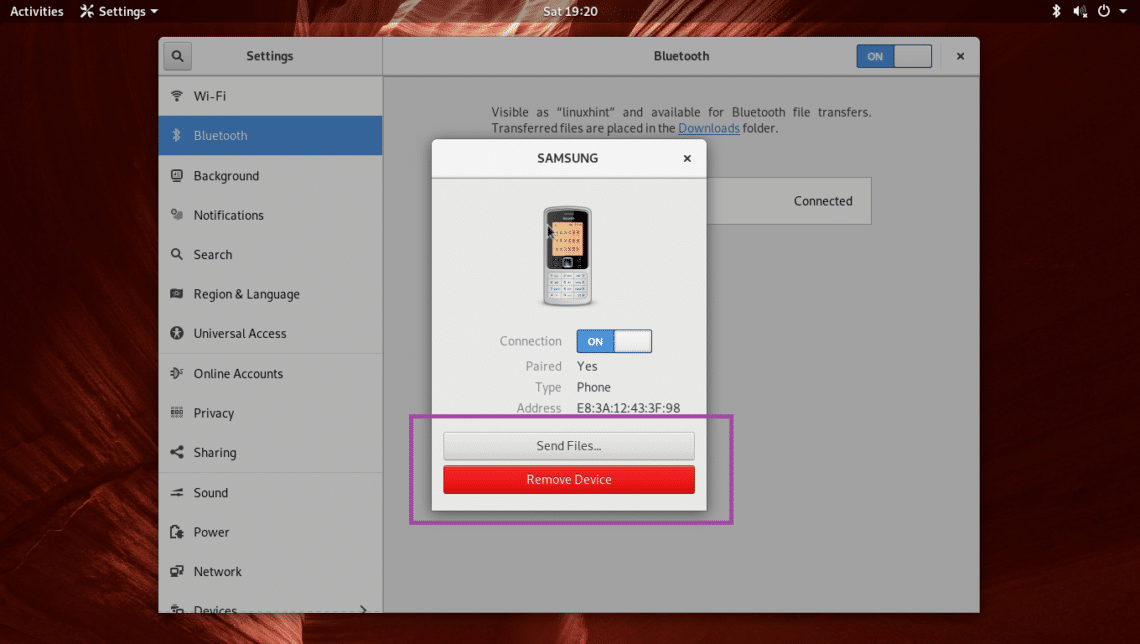
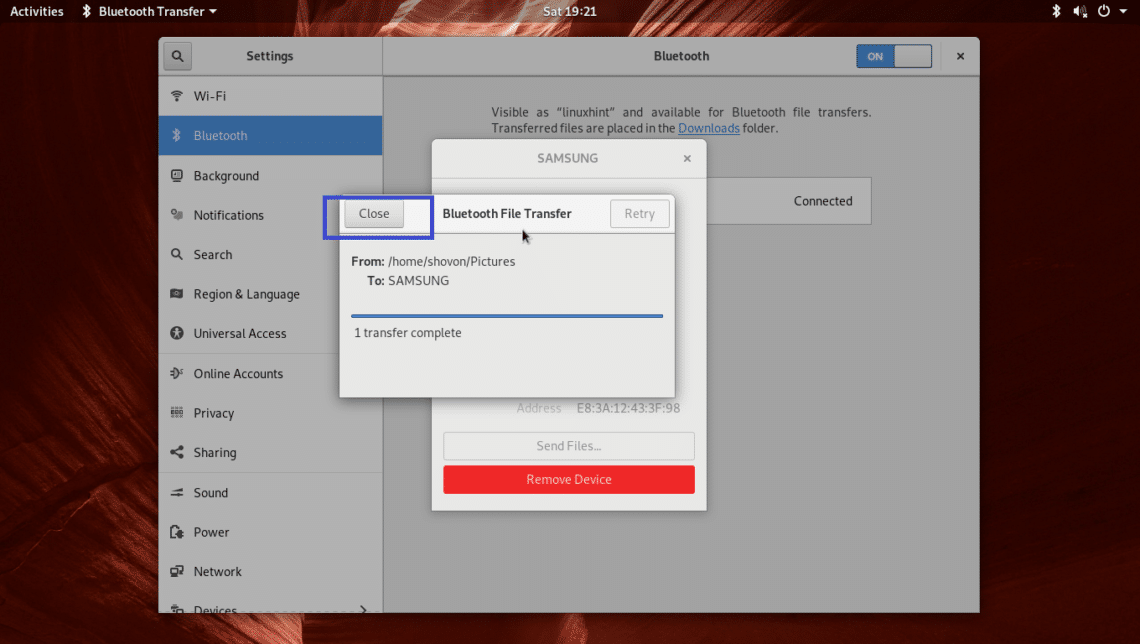
Your Bluetooth device should be paired. Now if your Bluetooth device supports file transfer, then click on the paired device from the list.
And you should see the following window. You can click on the Send Files… button to send a file or Remove Device button to remove the Bluetooth device from the list. Let’s try sending a file to my Samsung Galaxy smartphone using Bluetooth.
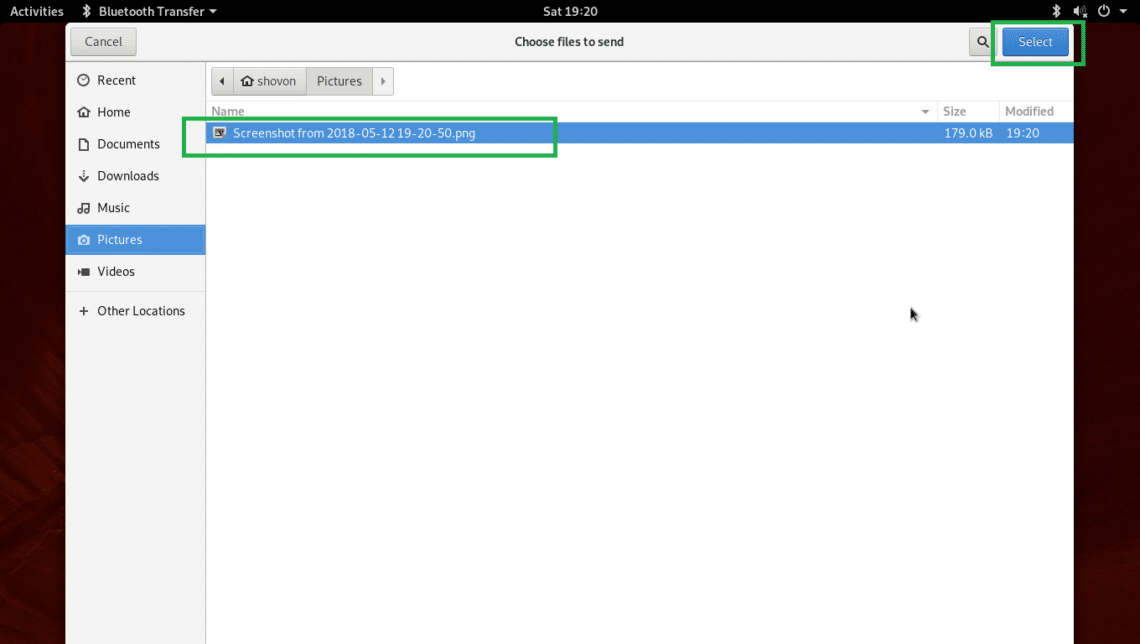
Once you click on the Send Files… button, a File Browser should open up as you can see in the screenshot below. Select your desired file and click on Select.
You should see the following Bluetooth File Transfer dialog box. Now you have to confirm the file transfer from your Bluetooth device.
Once you’ve confirmed the file transfer operation on your Bluetooth device, the file should be transferred to your Bluetooth device. Afterwards click on the Close button as marked in the screenshot below.
Blueman for Connecting to a Bluetooth Device
Blueman is a desktop environment independent app for connecting to a Bluetooth device. It is not installed by default on Arch Linux, but it is available in the official package repository of Arch Linux.
Before installing Blueman, first update the pacman package repository cache with the following command:
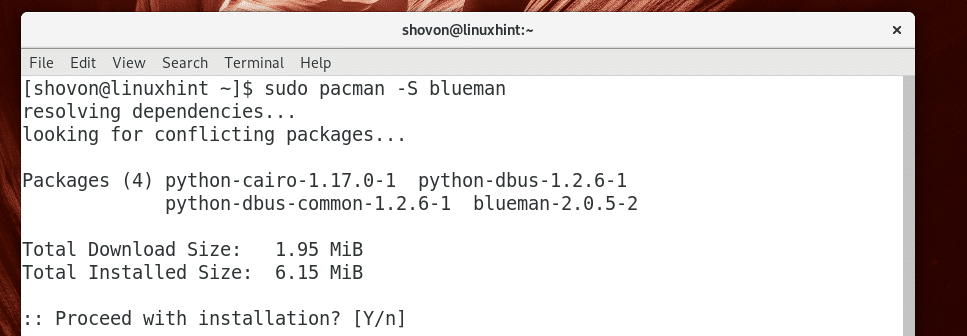
Now install Blueman with the following command:
Now press y and then press to continue.
Blueman should be installed.
Now to start Blueman, go to the Application Menu and search for Blueman. You should find a Bluetooth icon as marked in the screenshot below. Click on it.
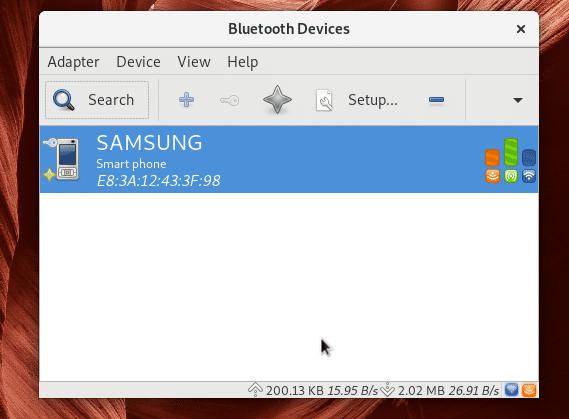
Blueman should start. As you can see from the screenshot below, the paired device is still listed.
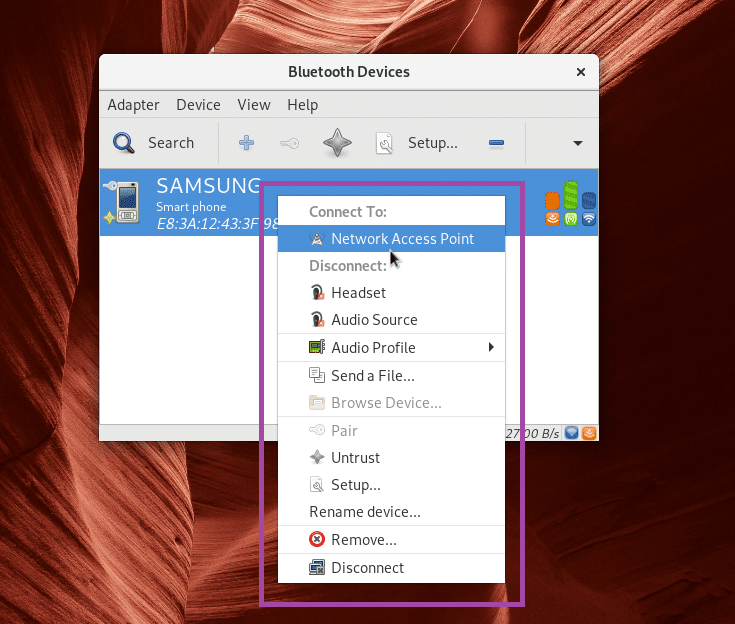
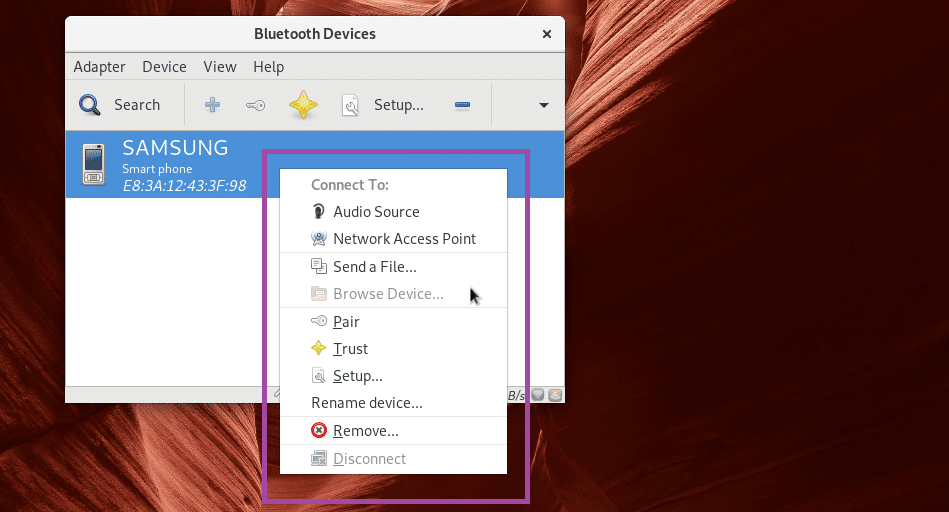
You can right click on it and more options should show up as you can see from the marked section of the screenshot below. Click on Remove to remove the paired device.
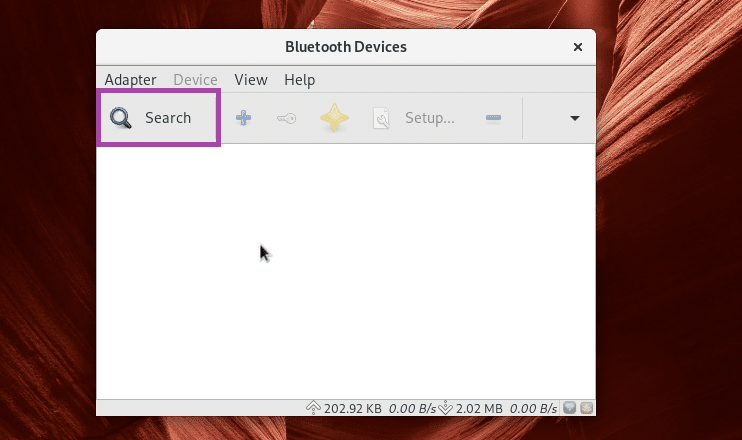
Now to search for Bluetooth devices, click on Search.
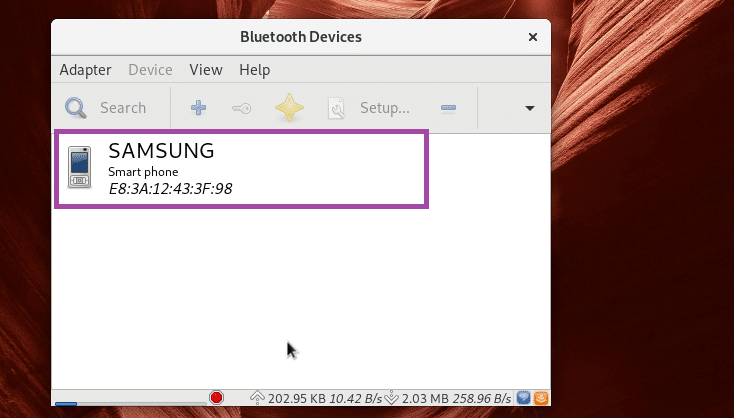
Your Bluetooth devices should be listed.
Press the right mouse button and you should see a menu as marked in the screenshot below. You can pair, send files and do other things from there. It is out of the scope of this article to show you how it works. So it for you to figure out.
Connecting to a Bluetooth Device using Bluedevil
On KDE 5 Plasma Desktop, the default Bluetooth manager is Bluedevil.
To start Bluedevil, right click on the Bluetooth icon from the KDE Panel and click on Configure Bluetooth…
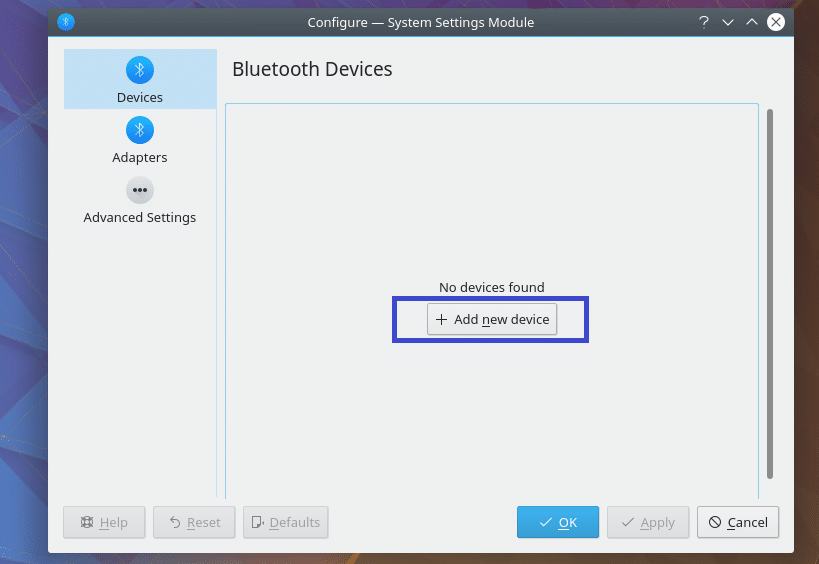
Bluedevil should start. Now click on Add new device to add a new device.
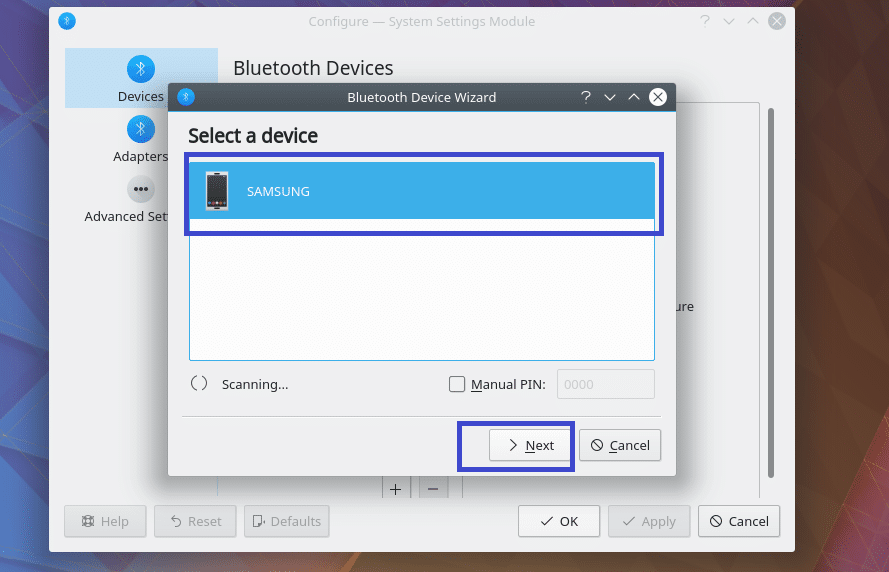
Your device should show up. Select it and follow the wizard, you should be connected.
It is out of the scope of this article to show you everything. But you should be able to figure things out now.
That’s how you connect to a Bluetooth device on Arch Linux. Thanks for reading this article.
About the author
Shahriar Shovon
Freelancer & Linux System Administrator. Also loves Web API development with Node.js and JavaScript. I was born in Bangladesh. I am currently studying Electronics and Communication Engineering at Khulna University of Engineering & Technology (KUET), one of the demanding public engineering universities of Bangladesh.