- Bluetooth менеджер linux mint
- Bluetooth¶
- Blueman¶
- Systemd-rfkill¶
- Bluez¶
- How to install Blueman on Linux Mint or Ubuntu 20.04
- 1. Run System Update
- 2. Install Blueman on Linux Mint or Ubuntu
- 3. Open Bluetooth Manager
- 4. Search and Pair Device
- 5. Send and receive files via Blueman
- 6. Set up NAP / DUN
- How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
- How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
- How to connect Bluetooth headset using the terminal in Linux Mint
- How to connect Bluetooth headset using Graphical Interface in Linux Mint
- Conclusion
Bluetooth менеджер linux mint
Great bluetooth app but with a generic bluetooth mouse, the connection is sluggish and i need toclick to make the cursor move (it moves after 3 seconds). The bluetooth mouse was connected when the error happend. The app works great with my Razor mouse.
now bundeled with with Mint21. It takes a lot of random trial and error to get anything connected, very frustrating, usually works in the end, average connect time is 30 minutes of messing around.
I had issues connecting my Bose 700 to the BT, looking online for an answer I found this software and it’s so much better then the built-in LM/LMDE one, so so much!
I was having problems connecting my mouse, this program fixed it. Work quite nicely.
A very useful program, it works without any problems. Many thanks to the developer!
Excellent! Meilleur que celui d’origine qui est plus esthetique qu’efficace :p
Its the bluetooth manager for humans,
i had problem with bad music interpretation via BT audio receiver with preinstalled bluetooth manager, but now its OK 🙂
I had endless issues with Blueberry and eventually found out about Blueman. I installed the PulseAudio bluetooth module and everything works like a charm.
I could pair various head sets. Mpow flame and two other Chinese Bluetooth headsets. It worked well for hours and many times. My Cambridge Silicon Radio — CSR V4.0 dongle came with only Windows Drivers so I was glad to find that Linux had packages that supported it. At one point my headset would not receive sound properly, I could not switch between A2DP and another audio type for the headset. I either dropped connection or played the sound out of phase and distorted reminiscent of the Jazz in Planet of the Apes. I hunted around looking for information on it but could not find a one-stop solution explaining how this software works with the dongle. Some discussion on killing multiple processes but I’m not sure what happened. My phone handles all these headsets automatically so connecting to Linux is a comparatively elaborate process. After giving up for a day I plugged in for a fresh start and managed to get one headset up and running. My conclusion is that Linux Mint does a very good job and that the sound is usually very clear and good considering the low cost of the equipment I used but there is an opportunity somehow for more people to get involved and educate the rest of us on what makes all this magic happen or how to use the tools to troubleshoot and fix connection issues..
So far seems good. Would like a tad more info about what some of icons & graphics are actually referring to.
Absolutely brilliant . connects instantly, and to be honest, works far better than it did when the computer ran on Windows 7 with the standard software,
Had trouble with the default bluetooth manager in KDE 18, devices would be paired but failt to connect/setup as the wrong device type was auto-assigned and no option is proveded to change that, in Blueman you assign device type during the initial pairing operation which avoids the issue. The interface is rather clunky and takes a while to work out how to use it, also removing devices often fails!! But overall it works, so well done.
Bluean is great! I removed blueberry because it did not work at all, installed blueman in stead. blueman worked on first attempt! Great!
just installed Linux Mint 19, worked right away with my CSR 4.0 dongle plugged in
yea the only one bluetooth tool that works 4 me (Linux Mint17.3)
Doesn’t exist in package manager anymore. Doesn’t pair with headphones.
Will NOT pair with phone! The Battle is lost.
lol as ryannerd said.. finally works per knielson’s suggestion. add new ppa: cschramm/blueman
Bluetooth¶
Bluetooth can be disabled by using a software kill switch.
On some laptops, a hardware kill switch is also provided either via a special function key or key combination or a dedicated physical button or mechanism.
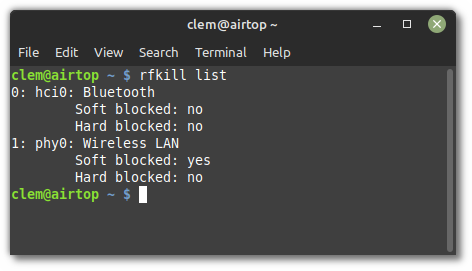
Using the rfkill command, you can see the state of these switches.
The output lists the state of software and hardware kill switches for all your wireless devices:
In the picture above you can see that Bluetooth is neither Soft blocked nor Hard blocked and is therefore enabled.
You can use rfkill to block (i.e. disable) or unblock (i.e. enable) bluetooth:
rfkill block bluetooth rfkill unblock bluetooth
Blueman¶
Blueman is the default Bluetooth Manager in Linux Mint.
It provides the little Bluetooth icon in your system tray.
To disable Bluetooth right-click the tray icon and select Turn Bluetooth Off .
To enable Bluetooth right-click the tray icon and select Turn Bluetooth On .
The very first time you open Blueman it asks if Bluetooth should be enabled automatically.
To check whether this feature is enabled open a terminal and type:
gsettings get org.blueman.plugins.powermanager auto-power-on
It auto-power-on is set to true , Blueman automatically unblocks Bluetooth at startup.
If you want to persistently disable Bluetooth you need to set auto-power-on to false :
gsettings set org.blueman.plugins.powermanager auto-power-on false
The auto-power-on option was recently removed in Blueman’s master branch. It’s still present in Blueman 2.3.2 but it’s likely to disappear in newer versions.
Systemd-rfkill¶
Systemd provides a service which saves the state of your kill switches during shutdown and restores them on the next boot.
This service is a core part of systemd and is installed in Linux Mint by default.
Blueman runs after systemd-rfkill, so if Blueman’s auto-power-on setting is enabled it overrides systemd-rfkill.
Bluez¶
Bluez is the Bluetooth stack used by Blueman.
Bluez has a setting called AutoEnable in the file /etc/bluetooth/main.conf .
If you don’t want Bluez to automatically enable Bluetooth during boot set this option to false.
© Copyright 2020, Linux Mint Revision 92937742 .
Versions latest Downloads pdf html epub On Read the Docs Project Home Builds Free document hosting provided by Read the Docs.
How to install Blueman on Linux Mint or Ubuntu 20.04
Blueman is an alternative Bluetooth manager to system default that relies on GTK and can be expanded using plugins. In addition to “normal” data transmission (sending / receiving/searching) using OBEX, Blueman also features “Dial-up Networking” (DUN) or Personal Area Networking (PAN). Furthermore, Blueman can be used as an interface for input and output devices such as a Bluetooth keyboard, mouse, or headset.
Key Features
- Use a cellular network ( 3G / EDGE / GPRS ) via DUN
- Create local Bluetooth networks (= PAN / NAP / PAND )
- /dev/rfcommBind services to ports
- Connect and use Bluetooth headsets
- Save Bluetooth devices as favorites
- Show all visible (accessible) devices
- Display information about local and remote (already known) devices
- Search, fill and delete cell phone memory (internal and expandable)
- Receive files via Bluetooth
- Define a shared folder for file sharing via OBEX / FTP
- Remote control computer / use a mobile phone as a remote control
1. Run System Update
Use the APT package manager and run the system update command that will not only fetch and install the latest packages required by the already installed programs but also refresh the system repo.
2. Install Blueman on Linux Mint or Ubuntu
The packages to install Blueman Bluetooth manager are already available in the official repository of Ubuntu, thus we just need to use APT to get and set them up.
sudo apt install blueman sudo apt install bluez bluez-obexd
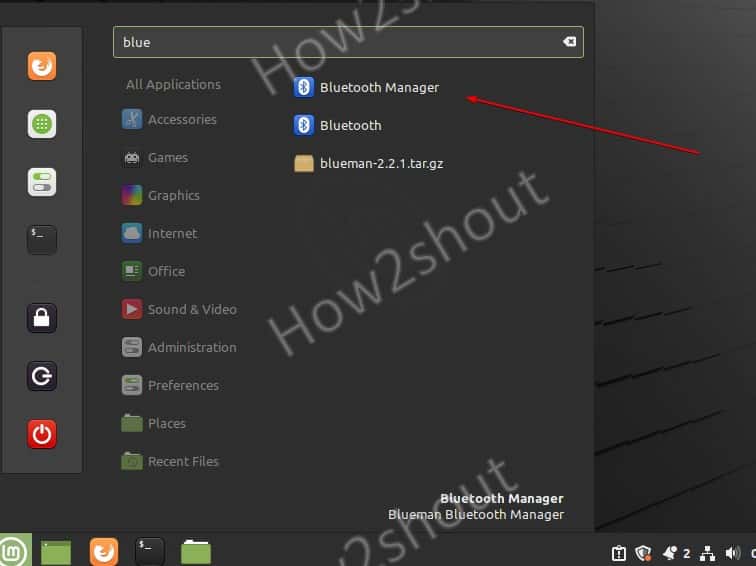
3. Open Bluetooth Manager
Go to Application launcher and search for Bluetooth this will give you the icon of the application, click it to run.
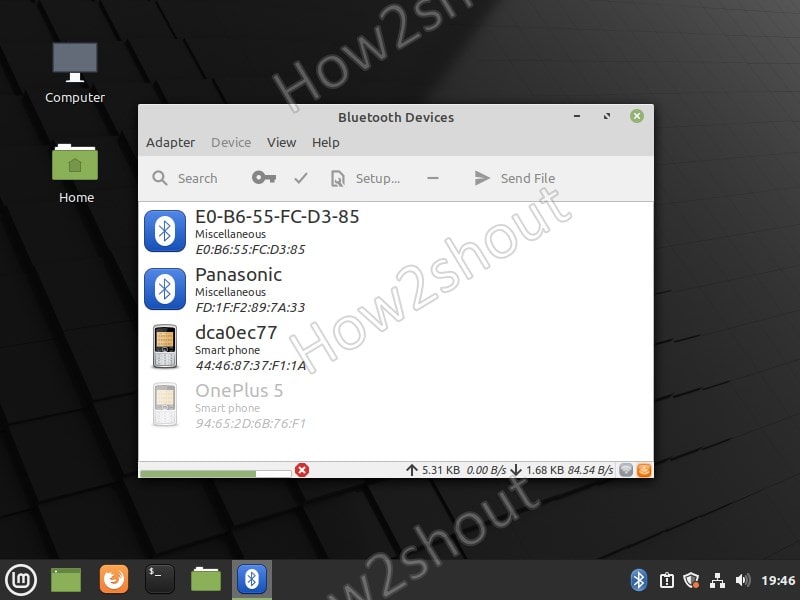
4. Search and Pair Device
Click on the Search icon of the Blueman and search the nearby Bluetooth devices, soon all the devices will appear on the screen. Select the one you want to pair and follow the steps. First, accept the Keypair on the Desktop and then on a smartphone to pair successfully.
5. Send and receive files via Blueman
To send files to a mobile phone click on “Send file” given in the menu, or to integrate the mobile phone directly into the respective file manager using OBEX / FTP. In the latter case, the mobile phone is integrated directly as removable storage (will not work with all phones).
6. Set up NAP / DUN
The “NMPANSupport” plug-in works without any further changes. And the same for DUN that allows the internet connection from the cell phone to work directly on Linux via Bluetooth and NetworkManager.
Right-Click on the connect mobile device via Bluetooth and select Serial ports → Dial-up Networking”. The setup then runs almost automatically. After confirmation on the mobile phone to allow the use. However, make sure from the DUN settings you have used the right APN.
How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology that is meant to connect electronic devices to share data or connect for media-related purposes. The major application domain of Bluetooth technology is to use it for media-related tasks or sharing data. Bluetooth allows two devices to connect without requiring any modem, network, or any third medium. Therefore, it is the prior choice of users to share files/data (within a short-range). Users may connect the speakers with any computing device or smartphone to play music/movies, or to have a handset calling and texting access.
Following the importance of this technology, this guide provides a demonstration to connect Bluetooth headset to the Linux Mint system.
How do I connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint
This section contains the procedural guide to connect Bluetooth headset on Linux Mint using the Command Line Interface, and Graphical User Interface methods:
How to connect Bluetooth headset using the terminal in Linux Mint
To connect Bluetooth to your Linux Mint, you must follow the steps provided below.
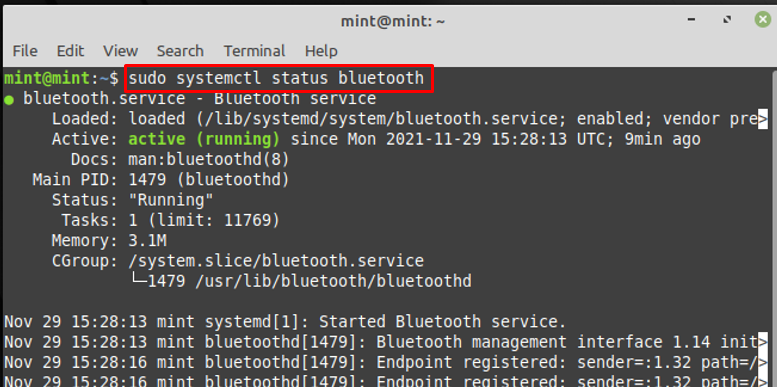
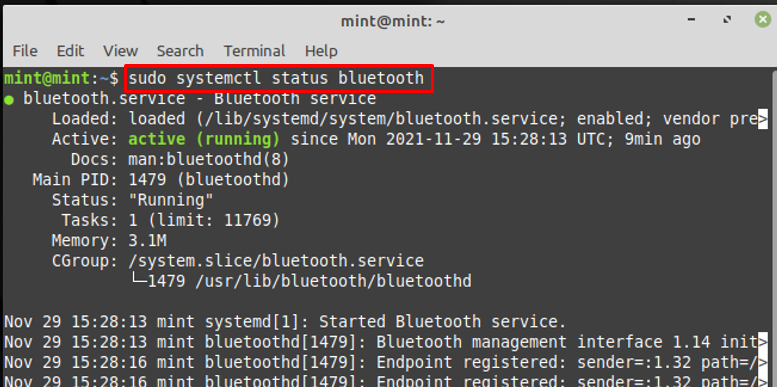
Step 1 : Before getting into details, check the status of Bluetooth service with the help of the command written below:
If the service is disabled or not working; you may provide the following commands to start and enable the Bluetooth service.
$ sudo systemctl start bluetooth
$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth
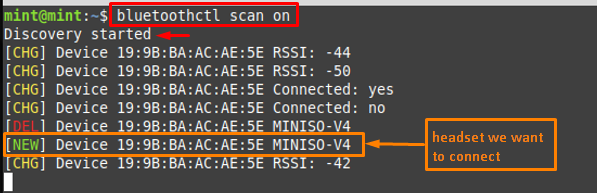
Step 2 : Ensure that your system’s Bluetooth is discoverable to all nearby devices. For this, use the discoverable option of bluetoothctl as shown in the below-mentioned command.
Note : The bluetoothctl is a Linux-based utility to manage Bluetooth devices on the system
Now, scan for the devices by issuing the below-stated command.
The above command lists down the available devices with their MAC (Media Access Control Address) addresses as well. As in our case, the device is “MINISO-V4“, so we have noted its MAC address.
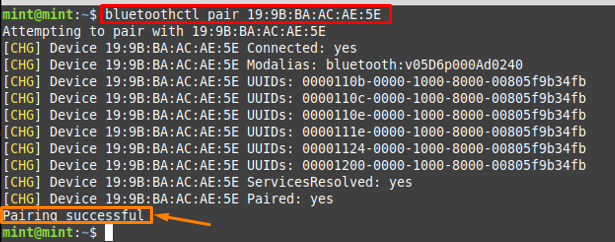
Step 3 : Pair the specific device using the following syntax. For instance, the command provided below will pair the “MINISO-V4” headset using its MAC address.
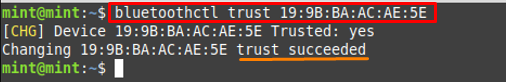
After pairing, it is recommended that you must trust the paired device with the help of the command written below.
After pairing, check for the list of paired devices by using the command written below. And you will get your paired devices list in the output.
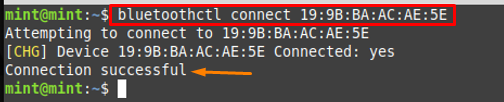
Step 4 : And after pairing, connect that Bluetooth headset device with the help of the command provided below. Upon successful connection, the “Connection successful” message is returned.
Step 5 : Unpair or Disconnect
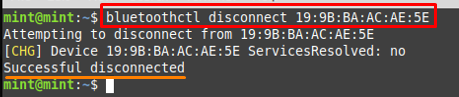
However, if you want to disconnect any device then you would execute the bluetoothctl command in the following way.
You can unpair any device by using the remove keyword as shown in the command below.
How to connect Bluetooth headset using Graphical Interface in Linux Mint
If your Bluetooth manager is working fine, then you will find the Bluetooth symbol on the desktop taskbar as seen in the image below.
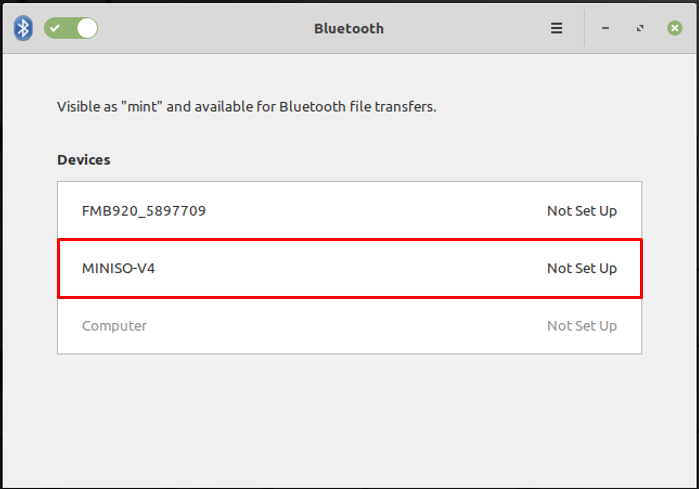
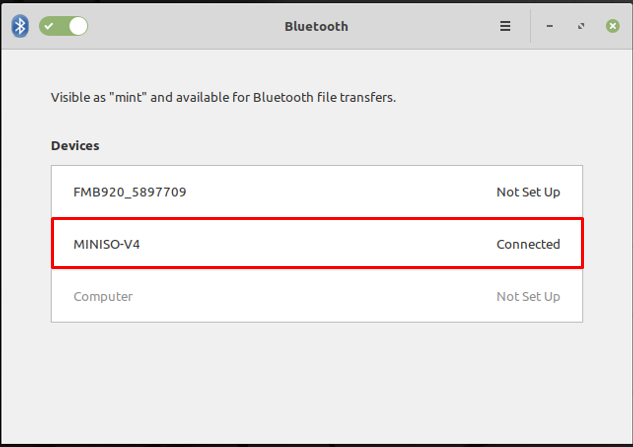
Upon clicking, all the devices will be displayed as can be seen in the image below and here the name of the headset device is “MINISO-V4”.
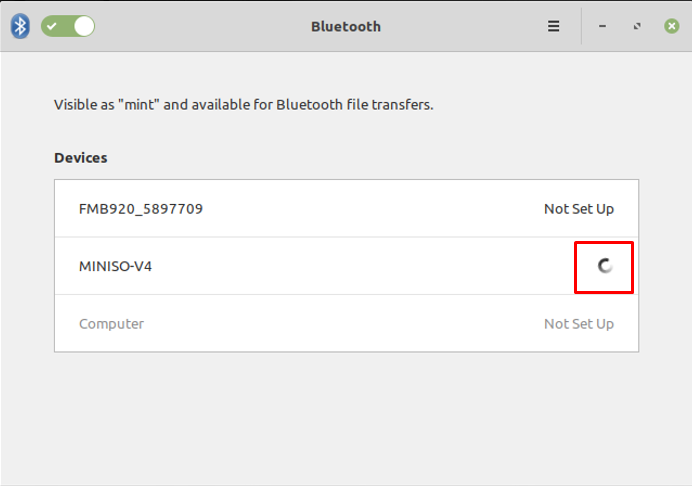
After clicking on the Bluetooth headset name, the connection will be made instantaneously.
And the status will be changed to “Connected” as displayed below.
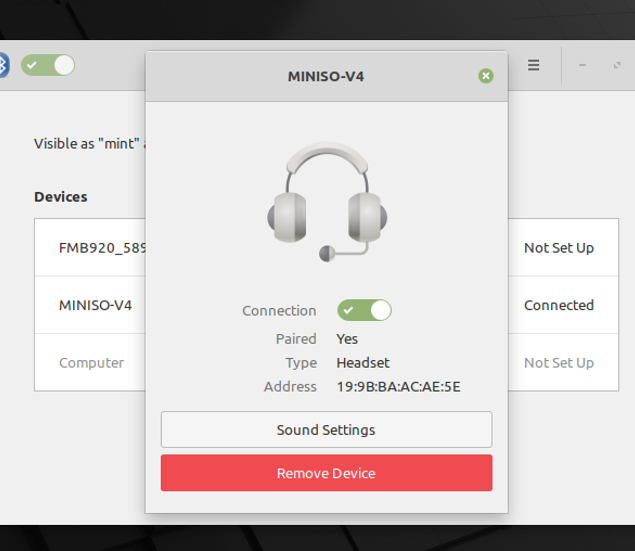
You can get further details by clicking on it and after doing so the interface obtained is displayed below.
From the image shown above:
– You can disconnect your headset by clicking on the “Remove Device” button
– To get detailed sound settings, you can click “Sound Settings”
Conclusion
Wireless technology has improved the accessibility of several devices in a network. Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology being used to connect electronic devices, share data or play any music. This guide provides a detailed demonstration to use Bluetooth to connect your headset to the Linux Mint system. We have also provided the installation and configuration of the Bluetooth manager on Linux Mint; this configuration is required as in many cases users are not able to get the nearby devices.