- 3 Key Factors That Determine the Range of Bluetooth
- Radio Spectrum
- Transmit Power
- Receiver Sensitivity
- Other Factors
- What Is The Range Of Bluetooth And How Can It Be Extended?
- Bluetooth Range
- Is Bluetooth A Short-distance Technology?
- How Far Does Bluetooth Reach?
- Range Depends On The Class Of Bluetooth
- Can We Extend Bluetooth Range?
- A Word Of Caution
- Understanding Bluetooth Range
- Radio Spectrum
- PHY
- Receiver Sensitivity
- Transmit Power
- Antenna Gain
- Path Loss
3 Key Factors That Determine
the Range of Bluetooth
A fit-for-purpose solution, Bluetooth ® technology allows developers to create wireless innovations that best meet the needs of their target use case. While the most well-known Bluetooth use cases, such as audio streaming and wearables, are built with short-range connectivity in mind, this is not because of an inherent limit to the effective range of the technology. Bluetooth has the flexibility to be as precise as less than a meter or to reliably connect devices more than a kilometer apart. When determining signal range and reliability at greater distances, several factors need to be considered.
Radio Spectrum
Radio spectrum stretches from 30 Hz to 300 GHz. The lower the frequency, the longer the range. However, the lower the frequency, the lower the data rate it can support. As a result, selecting a radio spectrum comes with tradeoffs between range and data rate.
Bluetooth ® technology uses the 2.4 GHz ISM spectrum band (2400 to 2483.5 MHz), which enables a good balance between range and throughput. In addition, the 2.4 GHz band is available worldwide, making it a true standard for low-power wireless connectivity.
Transmit Power
Think of transmit power like the volume of your voice. The louder you speak, the farther away someone can hear you, but the more energy it takes.
Choosing a transmit power level is a design tradeoff between range and power consumption. The higher the transmit power, the more likely the signal can be heard at longer distances, and the longer the effective range. However, increasing the transmit power increases the power consumption of your device.
Bluetooth ® technology supports transmit powers from -20 dBm (0.01 mW) to +20 dBm (100 mW).
Receiver Sensitivity
Bluetooth ® technology specifies that devices must be able to achieve a minimum receiver sensitivity of -70 dBm to -82 dBm, depending on the PHY used. However, Bluetooth implementations typically achieve much higher receiver sensitivity levels of -95 dBm or better.
Think of receiver sensitivity as a measure of how well you can hear or the quietest sound you can hear and understand. Receiver sensitivity is the measure of the minimum signal strength a receiver can interpret. In other words, it’s the lowest power level at which the receiver can detect a radio signal, maintain a connection, and still demodulate data.
Other Factors
Learn more about other factors, such as path loss, antenna gain, and PHY, that play a key role in determining the effective range of a Bluetooth solution. And check out the Bluetooth range estimator to see how far Bluetooth ® range can go for you.
What Is The Range Of Bluetooth And How Can It Be Extended?
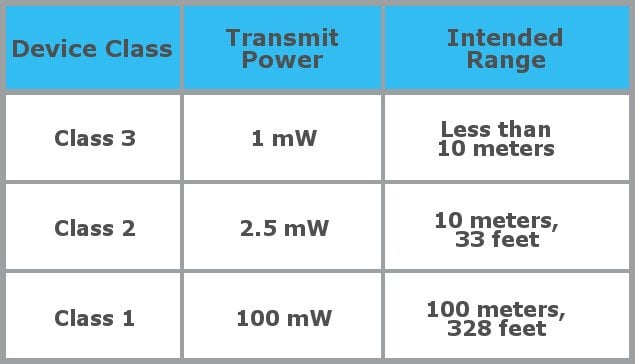
The range of Bluetooth depends on its class and there are three main classes of Bluetooth: Class 1 : transmits at 100 mW with a range of 100 meters. Class 2 : Most Bluetooth headsets and headphones transmit at 2.5 mW with a range of 10 meters. Class 3 : transmits with 1 mW at a range of less than 10 meters.
The range of Bluetooth depends on its class and there are three main classes of Bluetooth:
- Class 1 : transmits at 100 mW with a range of 100 meters.
- Class 2 : Most Bluetooth headsets and headphones transmit at 2.5 mW with a range of 10 meters.
- Class 3 : transmits with 1 mW at a range of less than 10 meters.
Recommended Video for you:
I remember exchanging Linkin Park hits on my sliding Sony Ericsson phone with a friend. Later, I “amplified” the sound by forcing it to pass through a cone made by the palm of my hand and imitating a speaker. Before the Internet of Things revolutionized wireless communication technology, Bluetooth technology was THE thing. 

Bluetooth Range
Is Bluetooth A Short-distance Technology?
There is a common misconception that although Bluetooth is not a visual connection technology, it can only work over short distances. That’s not true. No… gluing the phone sleeves together would not accelerate the speed of transmitting information between them, just as pressing harder on the joystick buttons will not speed up your car. Bluetooth or radio waves behave like any other wave, such as sound waves.
How Far Does Bluetooth Reach?
The distance the wave travels depends both on how loud you scream and on the obstacles that surround it, and on the sensitivity of the listener. So the louder you scream, the further the voice will travel, in part due to the hardware – the structure of the voice box, lung capacity, etc. This means that Bluetooth is power-dependent or, in terms of Bluetooth technology, class -dependent.
Range Depends On The Class Of Bluetooth
There are three classes that offer three standard intended ranges. Class 1 devices transmit at 100 mW with a range of 100 meters or 328 feet. Class 2 devices transmit at 2.5 mW with a range of 10 meters or 33 feet. Most Bluetooth headsets and headphones are common Class 2 devices. Lastly, Class 3 devices transmit at 1 mW with a range of fewer than 10 meters. Note that these are intended ranges, and this is where the other part comes in. Ranges can be drastically reduced by obstacles between the two devices, such as walls, which attenuate the signals. Thus, the range is affected by transmitting power, receiver sensitivity and obstacles near the device. Also Read: What’s The Difference Between Bluetooth And Infrared Transmission?
Can We Extend Bluetooth Range?
Spatial constraints hamper communication when the devices are part of a larger, widely distributed network. Newer versions of Bluetooth have ranges from about 250 feet to 800 feet, so updating your device seems to be the most lucrative solution. However, ranges can also be stretched by using signal repeaters, intermediate devices that capture, amplify, and then transmit or repeat signals without distortion. For example, a device with a range of 33 feet that is connected to a 1000 foot repeater can enjoy a range of 1,000 feet. You could also take matters into your own hands. There are several DIY methods you can find on YouTube to extend Bluetooth ranges by tinkering with Bluetooth modules in your device, so take a soldering iron, a couple of screwdrivers and wake up your inner engineer. Another cost-effective method is to align your devices so that their signals cannot be interrupted by obstacles. Also Read: Will Turning Off Wifi And Bluetooth Expose You To Less Radiation?
A Word Of Caution
Bluetooth proved to be very useful for a decade and made enormous progress. However, due to a major flaw – security – it fell to the level of an almost extinct device. In terms of security, Bluetooth was a major setback. Attacks such as BlueSnarfing, which ambushed phones from Nokia and Ericsson, allowed attackers to connect and manipulate devices without authentication. Nevertheless, its contributions will be appreciated by introverts and revelers for posterity.
Understanding Bluetooth Range
The effective, reliable range between Bluetooth devices is anywhere from more than a kilometer down to less than a meter.
What Determines Bluetooth Range?
The longer answer to the question about the range of Bluetooth ® technology is it depends.
Unlike other wireless technologies, Bluetooth technology is designed to support a wide range of achievable ranges between two devices, providing developers tremendous flexibility to create wireless solutions that best meet the needs of their target use case.
Several key factors influence the effective range of a reliable Bluetooth connection, including the following:
Radio Spectrum
Radio spectrum stretches from 30 Hz to 300 GHz. The lower the frequency the longer the range. However, the lower the frequency the lower the data rate it can support. As a result, selecting a radio spectrum comes with tradeoffs between range and data rate.
Bluetooth® technology uses the 2.4 GHz ISM spectrum band (2400 to 2483.5 MHz), which enables a good balance between range and throughput. In addition, the 2.4 GHz band is available worldwide, making it a true standard for low-power wireless connectivity.
PHY
The physical layer (PHY) of a wireless technology defines the modulation scheme and other techniques it uses to send data over a specific radio frequency (RF) band. This includes the number of channels available, how effectively those channels are utilized, the use of error correction, the guards in place to counter interference, and much more. If you compare RF communication to verbal communication, you can think of the PHY as defining the speed and clarity of your speech. Both impact the range at which you can be heard.
Bluetooth® technology provides multiple PHY options, each with different characteristics that determine effective range and data rates.
Receiver Sensitivity
Receiver sensitivity is the measure of the minimum signal strength a receiver can interpret. In other words, it’s the lowest power level at which the receiver can detect a radio signal, maintain a connection, and still demodulate data. Think of receiver sensitivity as a measure of how well you can hear or the quietest sound you can hear and understand.
Bluetooth® technology specifies that devices must be able to achieve a minimum receiver sensitivity of -70 dBm to -82 dBm, depending on the PHY used. However, Bluetooth implementations typically achieve much higher receiver sensitivity levels. For example, average implementations of the Bluetooth LE 125K (Coded) PHY are achieving a receiver sensitivity of -103 dBm.
Transmit Power


Bluetooth® technology supports transmit powers from -20 dBm (0.01 mW) to +20 dBm (100 mW).
Antenna Gain
The antenna converts electrical energy from the transmitter into electromagnetic energy (or radio waves) and vice-versa for the receiver. Antenna location, package size, and design can greatly impact how effective the signal is transmitted and received. And types and sizes of antenna and their efficiency in converting electrical to electromagnetic energy and focusing the direction of the energy can vary greatly.
The effective antenna gain is relevant for both the transmitting and receiving antenna. The directional influence of an antenna is similar to speaking or listening through a cone to focus the energy of the sound.
Bluetooth® technology designers can choose to implement a variety of antenna options. Antenna design is as much an art as it is a science. Bluetooth devices typically achieve an antenna gain in the range of –10 dBi to +10 dBi.
Path Loss
Path loss is the reduction in signal strength that occurs as a radio wave propagates through the air. Path loss, or path attenuation, occurs naturally over distance and is impacted by the environment in which the signal is being transmitted. Obstacles between the transmitter and the receiver can deteriorate the signal.
Attenuators can be anything from humidity and precipitation, to walls, windows, and other obstacles made of glass, wood, metal, or concrete, including metal towers or panels that reflect and scatter radio waves. While radio waves can pass through objects, the amount of attenuation and effective path loss varies with the type and density of the obstruction. Think about when you are trying to hear someone in the next room and the difference between the volume and clarity of what you can hear if the wall that separates you is made of wood compared to concrete.