- Bluetooth Stereo Audio Adapter – DIY Intro & Review
- Quick Start
- Add a Battery
- The MH-M38 Module
- DIY Bluetooth Stereo Speaker
- Supplies
- Step 1: Disassemble Bluetooth Headset and Identify the Power and Audio Connections
- Step 2: Disassemble Speakers and Identify the Power and Audio Connections
- Step 3: Make Connections !
Bluetooth Stereo Audio Adapter – DIY Intro & Review
Presented here is a shortcut to build your own bluetooth stereo audio adapter for listening ‘wire-free’ stereo music on the go! The one and only building block of this project is a Chinese bluetooth audio transfer module – the MH-M28. MH-M28 module is a low-power bluetooth system that supports the latest Bluetooth 4.2 transmission, offers lossless stereo audio playback, and handles bluetooth wireless transmission up to 20 meters when the module is connected to a mobile phone, television, or any other device that supports bluetooth audio transfer.
Quick Start
Just to set the module in operation, connect a stereo headphone to the 3.5mm stereo audio socket of the module, and plug the output cable of your usb power bank into the micro-usb socket of the module.
After the module is powered up, you can see you’re your mobile phone searches for the bluetooth name “MH-M28” and plays music if the bluetooth connection is established. Note that if the bluetooth connection is unavailable, blue indicator in the module flashes quickly but remains lit if a valid wireless link is there in between the module and the bluetooth appliance. When the bluetooth is playing, the indicator light flashes slowly.
Add a Battery
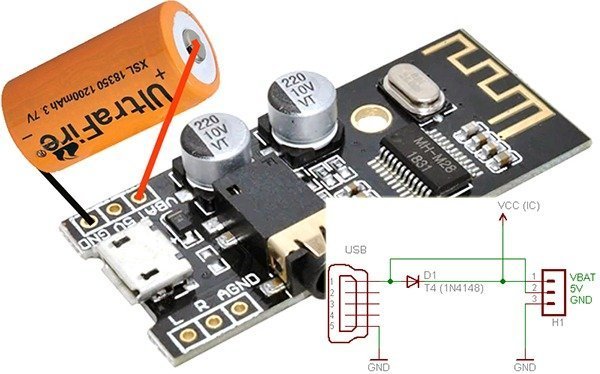
While travelling (or in a leisure time) you can ofcourse keep your mobile phone in a secure place and listen music if a power bank is available to run the module. However the module has an option to connect a single-cell (1S) Li-ion battery (3.7v/300mA minimum) through two header points. If a battery is there it’ll get charged through the usb power supply, and the module continue to run on battery when usb power input is removed. Internal schematic of the relevant portion (and a setup pointer) is given below. Note that there’s no dedicated Li-ion battery charger electronics available on board (it’s just a tricky recipe).
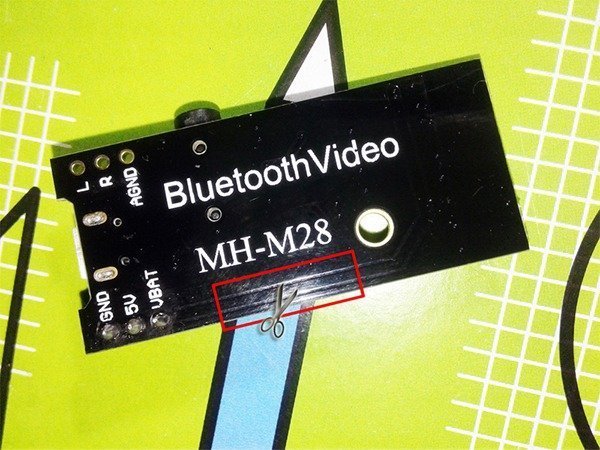
As you can see here, there’s no wrong polarity input protection mechanism across the VBAT terminals so take extreme care while connecting the battery because incorrect polarity will kill the module immediately. Another problem is the lack of a master power on/off switch which is really less favorable when you want to mount your module with battery inside an enclosure. Anyway if you have good dexterity you can cut the positive power track in the rear of the module to add an external power switch. Refer next image and bang on!
The MH-M38 Module
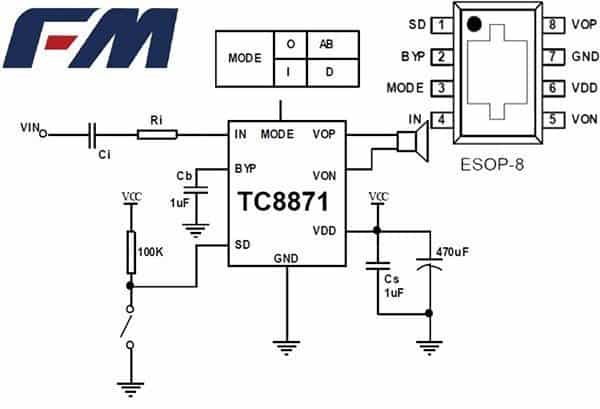
Let me introduce another powerful member of the family – the MH-M38 module which is very similar to M28 but with a stereo amplifier for driving loudspeakers. The additional stereo amplifier is based on two TC8871, the non-FM interference class AB/D audio power amplifier chip from Fuman Electronics, China.
Key features of TC8871 is included below:
- FM without interference, high efficiency, excellent sound quality
- High output power (THD + N
- ESOP package for the 5W (2Ω load) and 3.5W (3Ω load), 3W (4Ω load)
- Power-down mode leakage current is small
- External adjustable gain, integrated feedback
- Wide operating voltage range of 2.0V ~ 5.0V
- Compatible with XS9871A, SC4871,TC8871, HXJ8002, SC8002B
Next is the application circuit diagram of TC8871 made up by the author. Thanks to the support from Shenzhen Fuman Electric Co. Ltd.
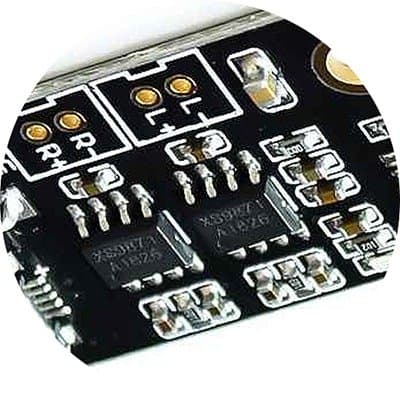
For the reason that there’re many drop-in replacements for TC8871, you may find audio ICs with other numbers in the same MH-M38 modules but sold by different sellers. It’s seemed that the most popular, pin-to-pin, alternative is XS9871A (next figure).
There’s a common thought that bluetooth audio will never be sweet as wired due to its compression methods, however that is not true. Now, some codecs allow for lossy, and others allow for completely lossless (nothing is lost and all are retained from the original) audio streaming. By definition, lossless means an audio file that typically has a high bitrate and comes in a variety of formats such as FLAC, WAV, or ALAC.
If you know what you are doing, these modules are good just for the fun, but do not expect to learn/hack anything. It’s good for someone just wants to make an inexpensive stereo bluetooth headset and/or stereo bluetooth speaker. The modules, centered on customized chips, are available without concise user guides on how to play with them up. But now I think you learned many things from this article, and you may now know how to properly hook them up. Enjoy!
DIY Bluetooth Stereo Speaker
Nowadays most of the phone manufacturers are now skipping 3.5mm audio jack. This makes little tricky to connect to old school external speakers which needs aux input. Either you will need to buy an adapter USB to aux or an bluetooth receiver which can be connected to these speakers.
I had received stereo speaker as free gift when I had bought new laptop. It is powered by connecting to any USB port which outputs 5V 1amp and needs to connect its audio pin to audio jack.
As fas as input is concerned its limited to wired one, so I thought to extend it to make it wireless with the help of bluetooth headset. So here we will be converting a wired stereo speaker to bluetooth speaker.
I am using a bluetooth headset (which was I found it in my junk stuff 🙂 , right now its battery is dead).
I choose this bluetooth headset, because both needed similar power 5V 1amp input (300mAh for headset). So in case you don’t have similar specs devices; you might need to use different power source or use simple voltage and current divider circuit to power speaker and bluetooth headset.
Also make sure the speakers has builtin amplifier as the output from bluetooth headset won’t drive the speakers. You can buy separate class-D 2 channel amplifier to drive the speakers.
Supplies
2. Bluetooth headset, should be stereo.
3. (optional) class D 2 channel amplifier.
4. (optional) USB power source as per specification of speakers and amplifier.
5. Four 1k — 10k resistors (all of same value, for coupling)
6. Prototype board (to put above resistors)
8. Soldering wire and iron
Step 1: Disassemble Bluetooth Headset and Identify the Power and Audio Connections
After disassembling the bluetooth headset, I figured out its power input and audio output connections. These should be very easy to identify on other bluetooth headsets as well; just check where battery has connected (that will be power input) and the speaker output where the left and right speakers are connected.
Please identify whether the audio output has common ground between left and right channel, by measuring the resistance between L+ and R+ OR L- and R-. If resistance is zero then its common grounded. You don’t need to follow below step.
In my case for bluetooth headset, both right and left channel has separate ground. We need common ground as the USB speaker’s audio input has common ground. To make common ground you will need to put resistive or capacitive coupler between left and right channel. (You can search about it).
There are some complex schematics to achieve it, but I found simpler resistive coupler to make it work, and use input power’s ground as common ground. Simply get four same valued resisters (between 1k to 10k) and connect them to each L+, L-, R+, R-. And then connect resisters of L+, L- together to get left audio output and vice versa for right audio output.
Below is the link which I have referred on StackExchange (thanks to StackExchange )
Step 2: Disassemble Speakers and Identify the Power and Audio Connections
Disassemble the one of the speaker to revel its circuit board.
There should be connections made to input the 5V DC from USB cable. And there should be audio input connections on it which should be connected to 3.5 mm aux cable.
Step 3: Make Connections !
1. Connect two wires on circuit board of speakers where the 5V input is fed. And connect these wires to input power to bluetooth headset. Make sure you maintain the polarity.
2. Connect the resistive coupler to L+, L-, R+, R- audio out pins to bluetooth headset. (In case your bluetooth headset has common ground, still I would suggest to put some resistance between similar range 1k- 5k to L and R output as it must be amplified output from bluetooth board, and it might fry out the components on speakers audio input)
3. Connect the couplers output (L and R) to L and R on speakers circuit board.
4. Connect input power’s (-ve) terminal as ground for audio input . (It might give some audible white noise in case the input DC source has some noise. I am yet to figure out correct solution to it. But still current solution is functional)
5. Now inspect all connections with multimeter using its short circuit test to check whether you have not made any unwanted short circuit connections 🙂
6. Put back the speaker’s back cover and attach the bluetooth headset, I have kept it external so that I can use its controls. Also it has mic so that I can use it for calls as well.
7. Power it ON and pair it with phone !! Enjoy the wireless bluetooth speakers !