- Ubuntu Wiki
- Booting from EFI
- KERNEL configuration
- References
- 4 Best Linux Boot Loaders
- What is a Boot Loader?
- 1. GNU GRUB
- 2. LILO (Linux Loader)
- 3. BURG – New Boot Loader
- 4. Syslinux
- Лучшие загрузчики Linux
- Что такое загрузчик?
- Лучшие загрузчики для Linux
- 1. Grub
- 2. Burg
- 2. LILO
- 4. Syslinux
- 5. Systemd-boot
- 6. rEFInd
- Выводы
Ubuntu Wiki
UEFI defines a new method of interfacing between PC operating systems and firmware. The UEFI interface is composed of data tables containing platform-related information, plus boot and runtime functions that are available to the operating system and the boot loader. These provide a standard environment for booting and running pre-boot applications.
The table following lists known features found in current EFI/UEFI capable boot loaders and boot managers. (Note: Boot managers present a menu of boot options, whereas boot loaders load a kernel. Many programs can do both tasks, although rEFIt can load a kernel on PC hardware only if it includes an EFI stub loader.)
Key: Yes — feature known to exist, ? — indeterminate feature presence, No — feature does not exist
- e.g. root=/dev/nfs ip=%I:%z:%G:%N, where the utility can generate the needed values based on information it can probe for (1)
- Floating Point Software Assist (2)
- Loading of kernel+initrd occurs using EFI firmware, hence only supports FAT16/32 (but if given 3rd-party EFI drivers can then read: ext2, ext3, ext4, ReiserFS, Btrfs, HFS+, or ISO-9660) (3)
Booting from EFI
All EFI compliant systems have an EFI System Partition (ESP), which is a FAT32 partition containing EFI firmware modules and boot images. Note that there can be one or more system partions. The ESP is effectively the boot partition, and contains the necessary images to boot a system. This boot partition should probably be mounted on a Linux system as /boot/efi for the updating of new kernels and initrd images.
Each vendor «must» use a dedicated directory in \EFI\vendor for the .efi bootloader code.
nshell is the EFI shell. It will execute the boot script called startup.nsh found in the root of an ESP. startup.nsh can be used to load and execute the preferred boot loader. More commonly, a list of boot loaders is maintained in NVRAM variables called Boot####, where #### is a hexadecimal number. The boot order is maintained in the BootOrder variable. These variables can be manipulated in Linux with the efibootmgr utility. If the NVRAM contains no such entries or if they’re all invalid, recent EFI implementations default to using a boot loader of the form \EFI\BOOT\boot.efi, where is an architecture code, such as «x64» for x86-64 or «ia32» for x86.
- IA-32
- x86-64 (aka X64)
- Itaninum
- ARM
- Processor agnostic generic EFI byte code
ELILO, the kernel’s EFI stub loader, Grub 2 (with EFI support), rEFIt, and rEFInd are all processor native executable code.
KERNEL configuration
Build the kernel with the following configuration.
CONFIG_FB_EFI=y CONFIG_FRAMEBUFFER_CONSOLE=y
If EFI runtime services are expected, the following configuration should be selected.
CONFIG_EFI=y CONFIG_EFI_VARS=y or m # optional
To use the EFI stub loader, you must set the following option:
The kernel can then be loaded from an EFI shell or by entering it into the EFI’s boot list in NVRAM. Getting the options right can be tricky, though. Using rEFInd to launch a kernel with EFI stub support can simplify matters.
References
- UEFI specification: http://www.uefi.org
- Intel EFI resources http://www.intel.com/technology/efi/
- EFI scripting language http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/efi-shells-and-scripting/
- DDJ EFI background http://www.ddj.com/embedded/18440624 and http://www.ddj.com/embedded/199500688
- EFI background in OSX book http://osxbook.com/book/bonus/chapter4/firmware/
- ELILO: http://elilo.sourceforge.net/cgi-bin/blosxom
- GRUB: http://www.gnu.org/software/grub/
- rEFIt: http://refit.sourceforge.net
- rEFInd: http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/
EFIBootLoaders (последним исправлял пользователь roguescholar 2023-05-27 12:31:45)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details.
4 Best Linux Boot Loaders
When you turn on your machine, immediately after POST (Power On Self Test) is completed successfully, the BIOS locates the configured bootable media, and reads some instructions from the master boot record (MBR) or GUID partition table which is the first 512 bytes of the bootable media. The MBR contains two important sets of information, one is the boot loader and two, the partition table.
What is a Boot Loader?
A boot loader is a small program stored in the MBR or GUID partition table that helps to load an operating system into memory. Without a boot loader, your operating system can not be loaded into memory.
There are several boot loaders we can install together with Linux on our systems and in this article, we shall briefly talk about a handful of the best Linux boot loaders to work with.
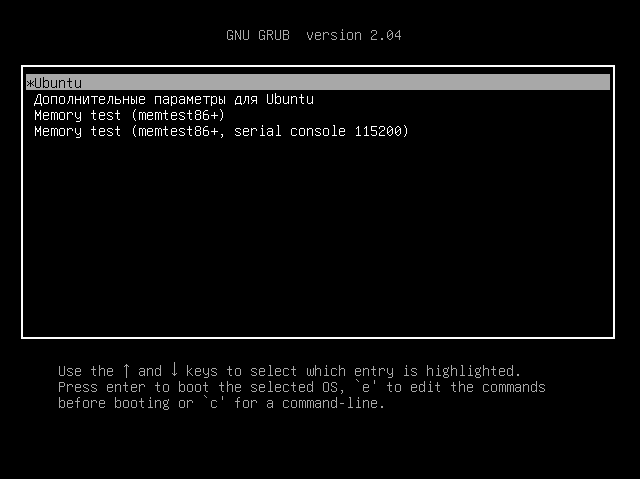
1. GNU GRUB
GNU GRUB is a popular and probably the most used multiboot Linux boot loader available, based on the original GRUB (GRand Unified Bootlader) which was created by Eirch Stefan Broleyn. It comes with several improvements, new features and bug fixes as enhancements of the original GRUB program.
Importantly, GRUB 2 has now replaced the GRUB. And notably, the name GRUB was renamed to GRUB Legacy and is not actively developed, however, it can be used for booting older systems since bug fixes are still on going.
GRUB has the following prominent features:
- Supports multiboot
- Supports multiple hardware architectures and operating systems such as Linux and Windows
- Offers a Bash-like interactive command line interface for users to run GRUB commands as well interact with configuration files
- Enables access to GRUB editor
- Supports setting of passwords with encryption for security
- Supports booting from a network combined with several other minor features
2. LILO (Linux Loader)
LILO is a simple yet powerful and stable Linux boot loader. With the growing popularity and use of GRUB, which has come with numerous improvements and powerful features, LILO has become less popular among Linux users.
While it loads, the word “LILO” is displayed on the screen and each letter appears before or after a particular event has occurred. However, the development of LILO was stopped in December 2015, it has a number of features as listed below:
- Does not offer an interactive command line interface
- Supports several error codes
- Offers no support for booting from a network
- All its files are stored in the first 1024 cylinders of a drive
- Faces limitation with BTFS, GPT and RAID plus many more.
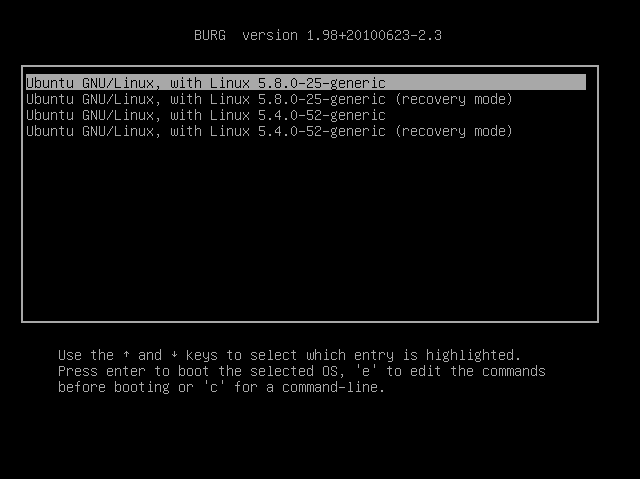
3. BURG – New Boot Loader
Based on GRUB, BURG is a relatively new Linux boot loader. Because it is derived from GRUB, it ships in with some of the primary GRUB features, nonetheless, it also offers remarkable features such as a new object format to support multiple platforms including Linux, Windows, Mac OS, FreeBSD and beyond.
Additionally, it supports a highly configurable text and graphical mode boot menu, stream plus planned future improvements for it to work with various input/output devices.
4. Syslinux
Syslinux is an assortment of light weight boot loaders that enable booting from CD-ROMs, from a network and so on. It supports filesystems such as FAT for MS-DOS, and ext2, ext3, ext4 for Linux. It as well supports uncompressed single-device Btrfs.
Note that Syslinux only accesses files in its own partition, therefore, it does not offer multi-filesystem boot capabilities.
Conclusion
A boot loader allows you to manage multiple operating systems on your machine and select which one to use at a particular time, without it, your machine can not load the kernel and the rest of the operating system files.
Have we missed any tip-top Linux boot loader here? If so, then let us know by using the comment form below by making suggestions of any commendable boot loaders that can support Linux operating system.
Лучшие загрузчики Linux
После того как вы включаете компьютер, как только будет успешно завершено тестирование всего оборудования POST (Power On Self Test) BIOS попытается обнаружить диск с загрузчиком и прочитать дальнейшие инструкции из таблицы разделов MBR или GPT.
Таблица разделов содержит очень важную информацию, во-первых, это непосредственно разметка разделов на диске, а во-вторых, код загрузчика. В таблице разделов GPT код загрузчика вынесен в отдельный EFI раздел, где может быть размещено несколько загрузчиков.
Что такое загрузчик?
Загрузчик — это небольшая программа, которая помогает загрузить операционную систему в память. Без загрузчика это сделать намного сложнее.
В Linux существует несколько загрузчиков, которые мы можем использовать. Все они одинаковы по выполняемым действиям — загружают операционную систему, но немного отличаются по дополнительной функциональности и внешнему виду. В этой статье мы рассмотрим лучшие загрузчики Linux. Перейдем к списку.
Лучшие загрузчики для Linux
1. Grub
Загрузчик Grub самый популярный на данный момент. Он разработан на основе загрузчика созданного Эриком Стефаном Броленом. Grub может загружать практически все операционные системы, в том числе Linux, Windows и даже MacOS. Загрузчик поддерживает установку пароля, редактирование загрузочных записей во время работы, а синтаксис конфигурационного файла очень похож на Grub. Кроме того Grub поддерживает UEFI системы. Операционные системы в меню можно организовать в подпапки, можно загружаться с iso диска или даже по сети.
2. Burg
Загрузчик Burg основан на коде Grub и расшифровывается как Brand-new Unified loadeR from Grub. Ранее он считался самым новым и самым красивым загрузчиком. Он поддерживал различные темы и стили оформления, которые делали меню загрузки очень красивым. Но потом в Grub тоже была добавлена поддержка тем, а разработка Grub свернулась. На данный момент этот загрузчик устарел, он даже не поддерживает установку на раздел с Ext4. А ещё не известно поддерживает ли он UEFI, так как он давно не обновлялся, с этим тоже могут возникнуть проблемы.
2. LILO
Lilo или Linux Loader — это простой, но уже устаревший загрузчик для Linux и других операционных систем. Разработка загрузчика была прекращена в 2015 году. Он не поддерживает такие современные файловые системы, как Btrfs, не поддерживает таблицу разделов GPT, а следовательно и UEFI. Кроме того, в нём нет текстовой консоли для восстановления системы и не поддерживается загрузка по сети. Одно из преимуществ этого загрузчика — это простой файл конфигурации, поэтому он иногда ещё используется для загрузочных ISO образов, хотя там тоже намного популярнее syslinux.
4. Syslinux
Syslinux — это облегченный загрузчик, который используется чаще всего для загрузки с внешних носителей, LiveCD или по сети. Он поддерживает файловые системы FAT, Ext2/3/4 и Btrfs. Его не следует использовать как основной загрузчик для вашей системы, только для ISO образов, поскольку он может загружать только одну операционную систему, которая находится на том же разделе, где расположен загрузчик.
5. Systemd-boot
Это простой загрузчик от systemd, который умеет работать только с образами UEFI. Может использоваться для загрузки системы без Grub. Здесь нет никаких особенных функций, это просто меню, позволяющее выбрать необходимый EFI образ для загрузки. Например, образ ядра Linux или EFI Shell.
6. rEFInd
Это не совсем загрузчик в привычном понимании, а скорее менеджер загрузки, который указывает системе UEFI какую операционную систему стоит запустить, а также может попросить UEFI запустить ядро Linux из папки /boot. Таким образом этот загрузчик не делает никаких действий по загрузке, а просто обращается к UEFI. Зато у него красивый и современный интерфейс. Теперь это самый красивый загрузчик Linux, вместо Burg.
Выводы
Мы рассмотрели лучшие загрузчики Linux. Загрузчик позволяет управлять несколькими операционными системами на одном компьютере и выбирать какую из них вы хотите загрузить в определенный момент. Без него ваш компьютер не сможет загрузить ядро и другие файлы операционной системы.
Если я пропустил здесь какой-нибудь загрузчик Linux, напишите в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.