- A Step-by-Step Guide on Running Java Programs in the Terminal on Linux
- Installing and Verifying JDK Version in Linux
- Compiling and Executing Java Programs in Terminal
- How to Run Java Program in Terminal Ubuntu Linux
- Running Command-Line Java Programs on Linux
- Enabling and Viewing Java Console on Linux or Solaris
- Other helpful code examples for running Java programs in the terminal on Linux
- Conclusion
- How to Run Java Programs in Ubuntu
- Running Java programs in Ubuntu
- Step 1: Install Java compiler
- Step 2: Compile Java program in Linux
- Step 3: Run the Java class file
- How to Run Java from Command-line in Linux
- How to Run Java through Command-line
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
A Step-by-Step Guide on Running Java Programs in the Terminal on Linux
Learn how to run Java programs in the terminal on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. Follow our step-by-step guide to install and verify JDK, compile and execute Java programs, run command-line Java programs, and enable and view Java Console on Linux or Solaris.
- Installing and Verifying JDK Version in Linux
- Compiling and Executing Java Programs in Terminal
- How to Run Java Program in Terminal Ubuntu Linux
- Running Command-Line Java Programs on Linux
- Enabling and Viewing Java Console on Linux or Solaris
- Other helpful code examples for running Java programs in the terminal on Linux
- Conclusion
- How to run java in terminal Linux?
- How to run java on terminal?
- How to run a java program in Linux?
- How to run java in terminal Ubuntu?
Java is a popular programming language that is widely used for web development, mobile development, and app development. One of the main advantages of Java is its cross-platform compatibility, which means that Java programs can be executed on different operating systems, including Windows, Mac, and Linux. In this guide, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to run Java programs in the terminal on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. We will cover the installation and verification of the Java Development Kit (JDK), the compilation and execution of Java programs in the terminal, running command-line Java programs on Linux, and enabling and viewing the Java Console on Linux or Solaris.
Installing and Verifying JDK Version in Linux
Before running java programs on ubuntu or any other Linux distribution, you need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK). The JDK is a software development environment that provides tools to develop, debug, and run Java programs. The following steps show you how to install and verify the JDK version in Linux:
- Open the terminal on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
- Type the following command to install the JDK:
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk Compiling and Executing Java Programs in Terminal
After installing the JDK, you can start writing Java programs and running them on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution. Here are the steps to compile and execute Java programs in the terminal:
- Open the terminal on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
- Create a new file with the “.java” extension and write your Java program.
How to Run Java Program in Terminal Ubuntu Linux
In this video I am going to show you How to install Java JDK 10 on Ubuntu Linux ( with Duration: 11:41


Running Command-Line Java Programs on Linux
In addition to running java programs in the terminal on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution, you can also run command-line Java programs. Here is how to do it:
- Open the terminal on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
- Write your Java program and save it with the “.java” extension.
import java.io.*;public class CommandLine < public static void main(String[] args) < try < Process p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("ls -l"); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(p.getInputStream())); String line = null; while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) < System.out.println(line); >> catch (IOException e) < e.printStackTrace(); >> > Enabling and Viewing Java Console on Linux or Solaris
The Java Console is a debugging tool that allows you to view and debug Java applets and applications. Here are the steps to enable and view the Java Console on Linux or Solaris:
- Open the terminal on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
- Navigate to the Java installation directory.
cd /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/lib/amd64/ Other helpful code examples for running Java programs in the terminal on Linux
In Java case in point, java compiler linux terminal code example
sudo apt install default-jdkIn Java case in point, java run linux command code sample
Process p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("ls -la /home"); BufferedReader stdInput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(p.getOutputStream())); String result; while ((result = stdInput.readLine()) != null) In Java , for instance, run java from terminal
//Run this line to compile javac programName.java//Run this line to run java programNameIn Java , for instance, run java from terminal linux
//To compile, type javac filename.java//To run the generated class file, use java filenameIn Java , for example, how to run a java file in terminal code sample
javac FirstJavaProgram.javaConclusion
In this guide, we have provided a step-by-step guide on how to run Java programs in the terminal on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. We covered the installation and verification of the Java Development Kit (JDK), the compilation and execution of Java programs in the terminal, running command-line Java programs on Linux, and enabling and viewing the Java Console on Linux or Solaris. By following these steps, you can easily run Java programs on Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution, and take advantage of the cross-platform compatibility of the Java language.
How to Run Java Programs in Ubuntu
So, you have started learning Java programming? That’s good.
And you want to run the java programs on your Linux system? Even better.
Let me show how to run Java in terminal in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions.
Running Java programs in Ubuntu
Let’s go in proper steps here.
Step 1: Install Java compiler
To run a Java program, you need to compile the program first. You need Java compiler for this purpose.
The Java compiler is part of JDK (Java Development Kit). You need to install JDK in order to compile and run Java programs.
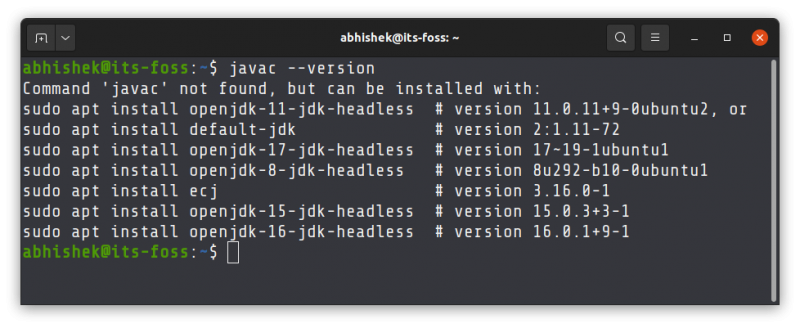
First, check if you already have Java Compiler installed on your system:
If you see an error like “Command ‘javac’ not found, but can be installed with”, this means you need to install Java Development Kit.
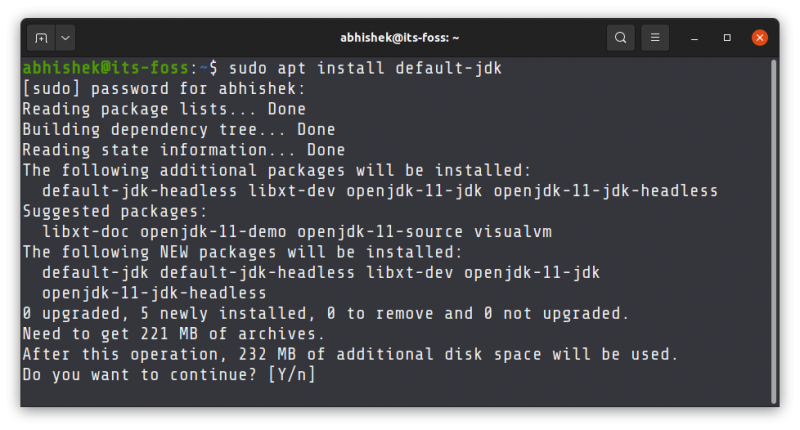
The simplest way to install JDK on Ubuntu is to go with the default offering from Ubuntu:
sudo apt install default-jdkYou’ll be asked to enter your account’s password. When you type the password, nothing is seen on the screen. That is normal. Just enter your password blindly. When asked, press the enter key or Y key.
The above command should work for other Debian and Ubuntu based distributions like Linux Mint, elementary OS etc. For other distributions, use your distribution’s package manager. The package name could also be different.
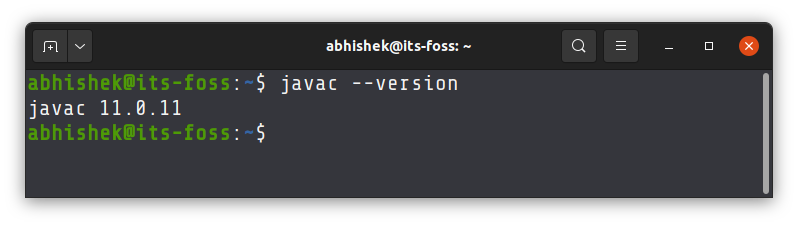
Once installed, verify that javac is available now.
Step 2: Compile Java program in Linux
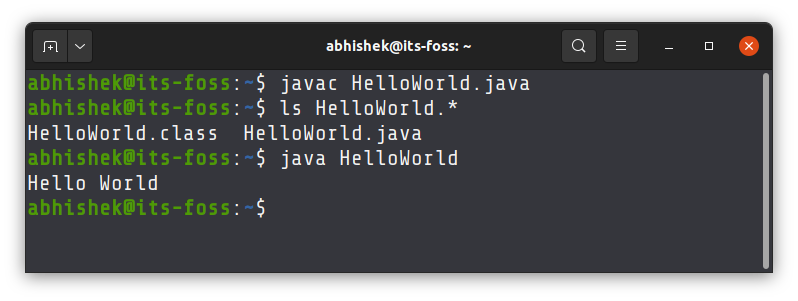
You need to have a Java program file for this reason. Let’s say you create a new Java program file named HelloWorld.java and it has the following content:
You can use Nano editor in terminal or Gedit graphical text editor for writing your Java programs.
If there is no error, the above command produces no output.
When you compile the Java program, it generates a .class file with the class name you used in your program. You have to run this class file.
Step 3: Run the Java class file
You do not need to specify the class extension here. Just the name of the class. And this time, you use the command java, not javac.
This will print Hello World on the screen for my program.
And that’s how you run a Java program in the Linux terminal.
This was the simplest of the example. The sample program had just one class. The Java compiler creates a class file for each class in your program. Things get complicated for bigger programs and projects.
This is why I advise installing Eclipse on Ubuntu for proper Java programming. It is easier to program in an IDE.
I hope you find this tutorial helpful. Questions or suggestions? The comment section is all yours.
How to Run Java from Command-line in Linux
Java is the world’s popular software development platform that James Gosling develops. It is designed to support multiple platforms like Linux, macOS and Windows. Mobile and Desktop applications can also be developed using Java language.
Java language is one of the most popular high-level object-oriented programming languages. It comes with a simple syntax and easily understandable for beginners, as it is very secure and economical to use. Java is the platform-independent software, and it also provides an auto garbage collection facility.
How to Run Java through Command-line
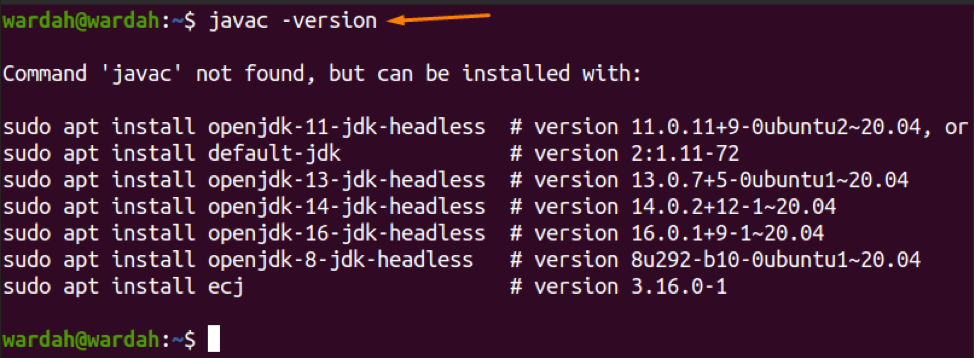
To run the java program in Linux, we need to verify if Java Development Kit (JDK) is available in the system and its version.
To confirm it, type the following command:
(Javac command-line tool is used for the compilation of java programs)
The Javac command tool is not available in my system. We have multiple commands to download it, as mentioned in the above image.
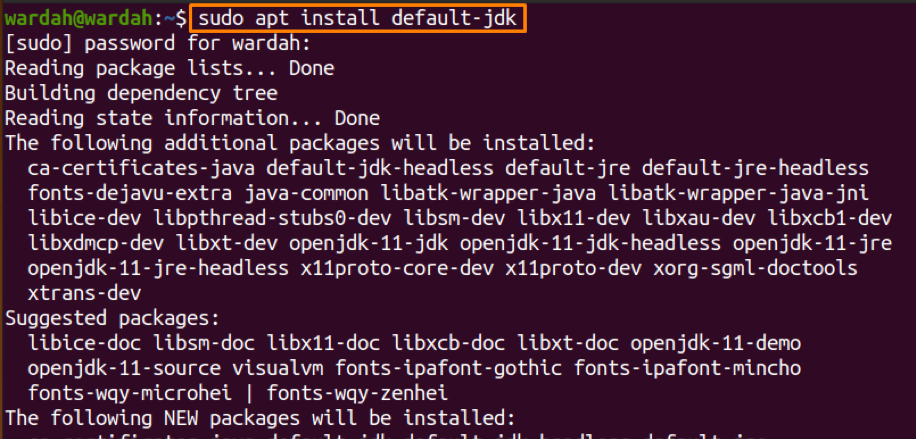
Let’s go with the default-jdk command to get it:
To verify the installation of javac, type:
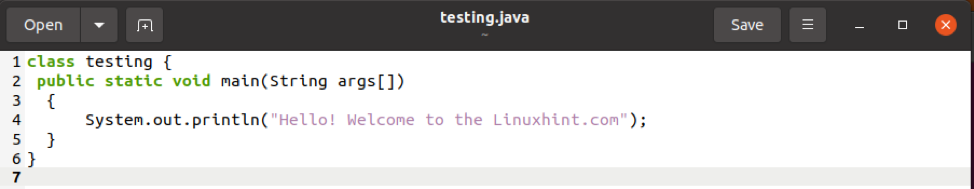
Now, write a Java program in the text file and save it with .java extension.
Suppose I created a file named “testing.java” and write a simple program in it:
(Keep in mind that your class name should be the same as the file name)
Compile the testing.java file on the terminal using the javac command:
Now, execute the Java program by calling its class name in the terminal:
Conclusion
Java is the high-level language of the modern era supported by the Java Development Kit (JDK). JDK is a package that helps to run java and is used for the development of software packages.
Java language comes with a simple syntax that is easy to get for beginners, and it is one of the most usable object-oriented programming languages.
We have seen in this article that how to install and run Java applications on the terminal.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.