- How to restart the networking service?
- 18 Answers 18
- For Desktops
- For Servers
- For Servers
- How to Restart Network in Ubuntu
- Restart the network in Ubuntu via the command line
- 1. Restarting the Network Manager Service
- 2. nmcli
- 3. nmtui
- 4. ifup & ifdown
- Restart the network in Ubuntu graphically
- Bonus Tip: Refresh the available network list
- Wrapping Up
- Перезапуск сети в Ubuntu
- Перезагрузка сети в Ubuntu
- Перезапуск сети в NetworkManager
- Команды ifup и ifdown
- Выводы
- Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
- Network Operations
- Stop Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Start Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Status Network Service
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
- Restart Network
- Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
- Fedora and CentOS
How to restart the networking service?
Note that you might reanimate your keyboard, if you unplug and replug it — and it is hot pluggable, i.e. USB.
I also faced similar issue on Gnome 3 on Ubuntu 13.03. Screen disorted as top bar gone. Short keys not worked. As no menu/Activies shown I get no way to operate the system. Luckily console was opened already. So reboot command can be typed.
if you are looking for GUI method just open dash, type «Network» and select that. now press «On/Off» button to turn off and again click to on. your networking is restarted now.
18 Answers 18
For Desktops
sudo service network-manager restart Or on recent Ubuntu versions:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-networkd Ubuntu uses network-manager instead of the traditional Linux networking model. so you should restart the network-manager service instead of the network service. Or use ifup/down.
For Servers
hmm, strange that restarting just networking breaks the system. Does it happen to you too or is it just me?
For Servers
Restarting networking on a desktop machine will cause dbus and a bunch of service to stop and never be started again, usually leading to the whole system being unusable.
As Ubuntu does event based network bring up, there quite simply isn’t a way to undo it all and redo it all, so a restart just isn’t plain possible. The recommended way instead is to use ifdown and ifup on the interfaces you actually want to reconfigure:
sudo ifdown --exclude=lo -a && sudo ifup --exclude=lo -a @waspinator the bug is marked fixed as of march of this year: bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/dbus/+bug/1072518
Worked on Ubuntu Server 16.04.1. Ubuntu Server doesn’t appear to include Network Manager, so askubuntu.com/a/230751/13756 doesn’t work.
How to Restart Network in Ubuntu
Here are 6 ways you can restart the network in Ubuntu and other Linux distros. Also learn to refresh wireless network connection in Ubuntu Linux.
Restart the network in Ubuntu via the command line
If you are using the Ubuntu server edition, you are already in the terminal. If you are using the desktop edition, you can access the terminal using Ctrl + Alt + T keyboard shortcut in Ubuntu.
Now you have several commands to restart the network in Ubuntu. Some (or perhaps most) commands mentioned here should also be applicable for restarting the network in Debian and other Linux distributions.
1. Restarting the Network Manager Service
This is the easiest way to restart your network using the command line. It’s equivalent to the graphical way of doing it (restarts the Network-Manager service).
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager.serviceThe network icon should disappear for a moment and then reappear.
2. nmcli
This is yet another tool for handling networks on a Linux machine. It is a pretty powerful tool that I find very practical. Many sysadmins prefer it since it is easy to use. This tool is a part of the NetworkManager package.
There are two steps to this method: turning the network off and then turning it back on.
sudo nmcli networking offThe network will shut down and the icon will disappear. To turn it back on:
You can check out the man page of nmcli for more options.
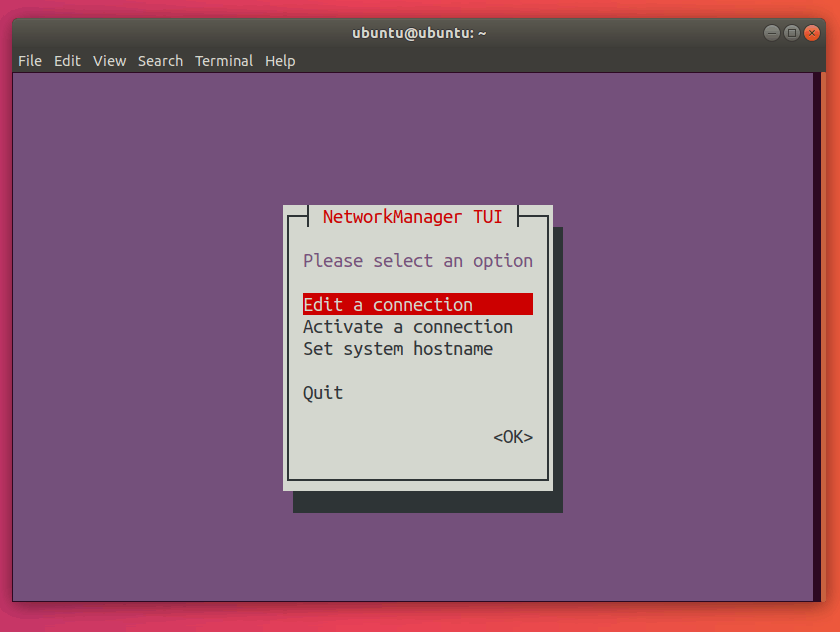
3. nmtui
This is another method often used by system administrators. It is a text menu (in a Terminal User Interface) for managing networks right in your terminal. It is also a part of the Network Manager tool.
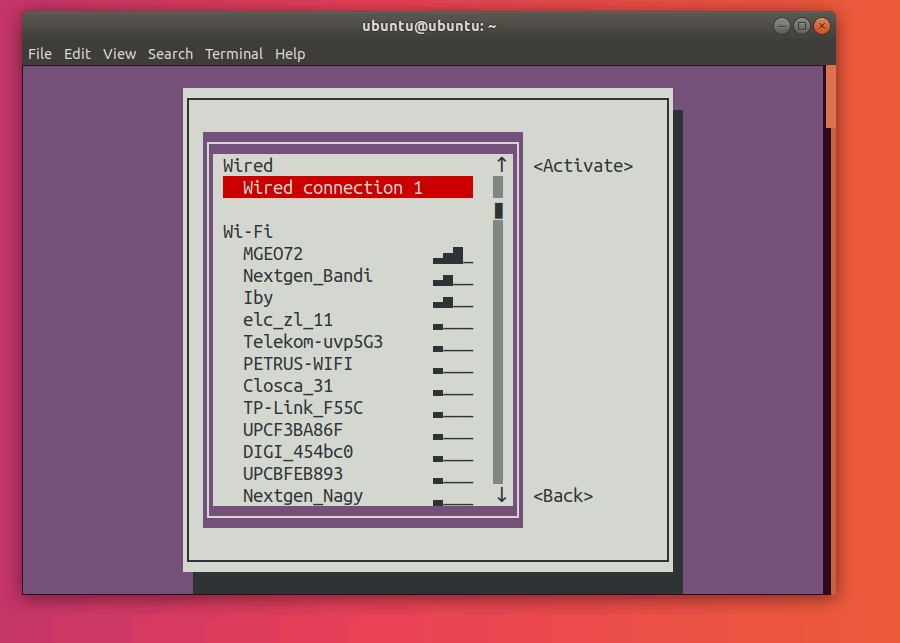
This should open up the following menu:
Note that in nmtui, you can select another option by using the up and down arrow keys.
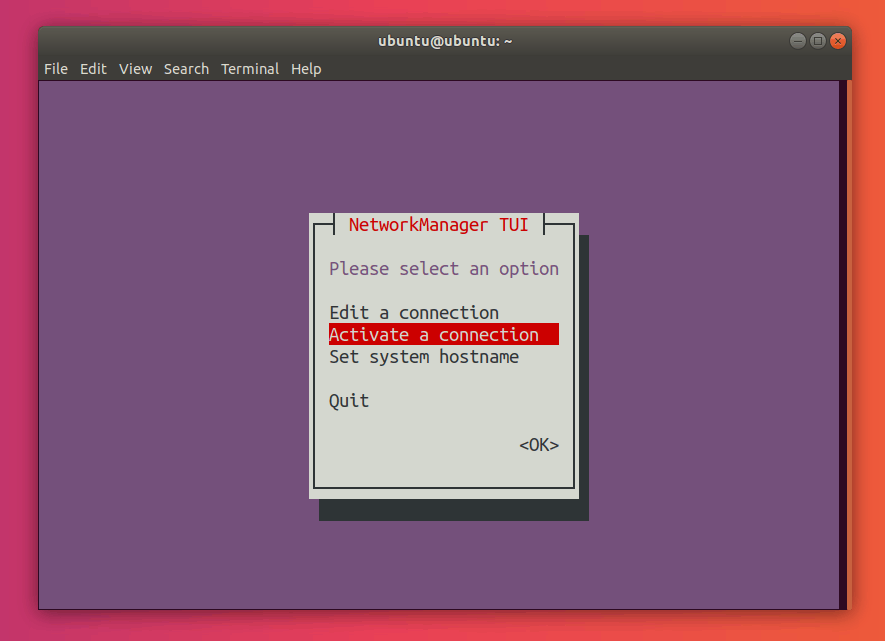
Select Activate a connection:
Press Enter. This should now open the connections menu.
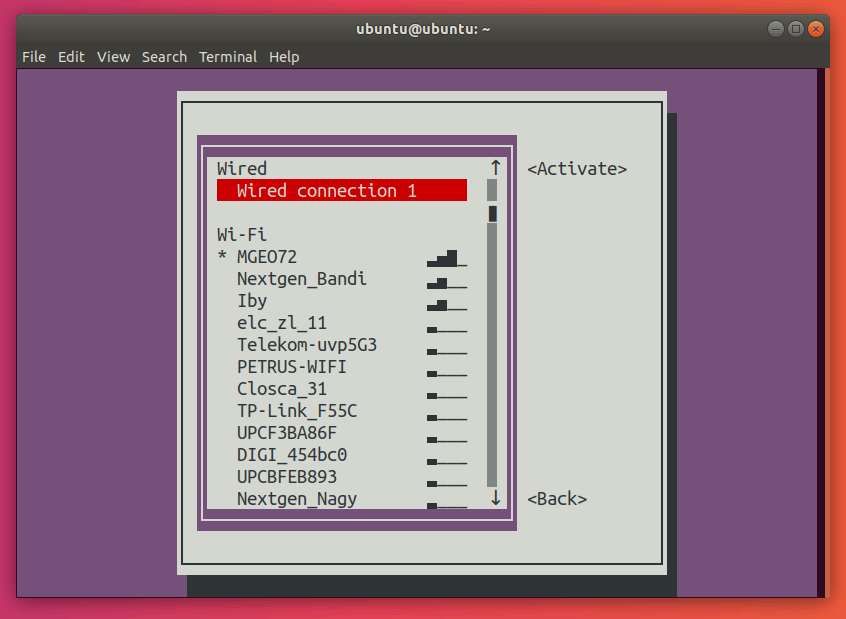
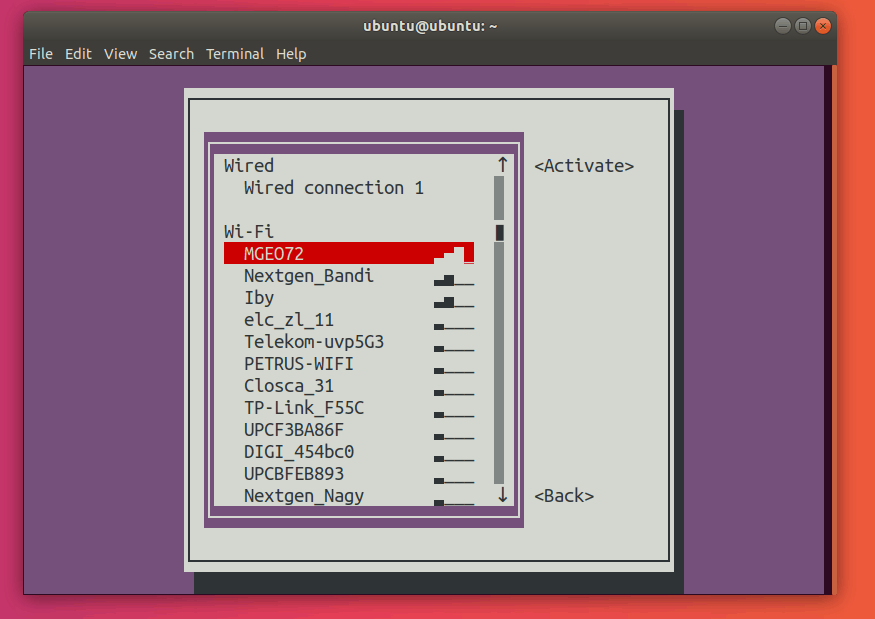
Here, go ahead and select the network with a star (*) next to it. In my case, it’s MGEO72.
Press Enter. This should deactivate your connection.
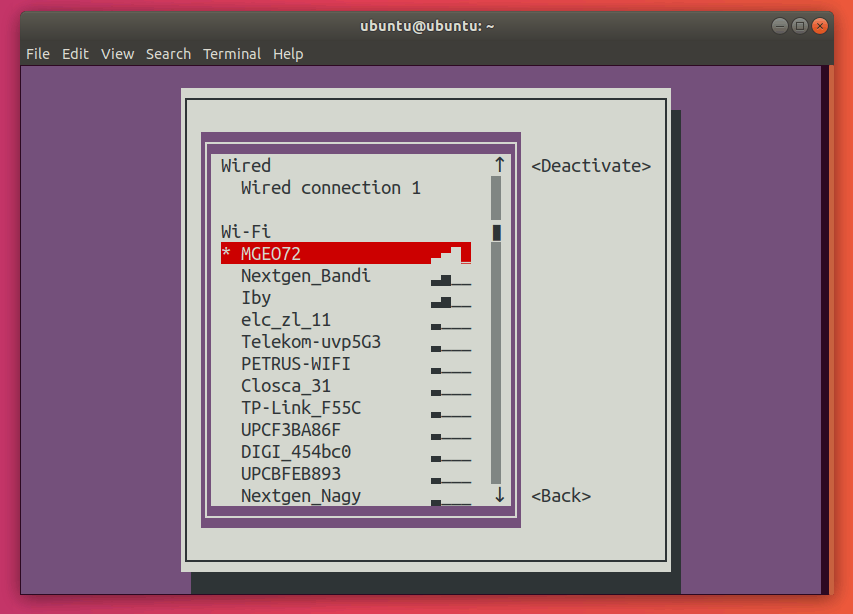
Select the connection you want to activate and press Enter. This should activate the desired connection.
Press Tab twice to select the button, and exit from the main menu. This is how you can restart a connection with nmtui.
4. ifup & ifdown
These commands handle a network interface directly, changing its state to one in which it either can or can not transmit and receive data. It’s one of the must-know networking commands in Linux.
To shut down all network interfaces, use ifdown and then use ifup to turn all network interfaces back on.
A good practice would be to combine both of these commands:
sudo ifdown -a && sudo ifup -aNote: This method will not make the network icon in your systray disappear, and yet you won’t be able to have a connection of any sort.
That’s it! You have successfully restarted your network.
Restart the network in Ubuntu graphically
This is, of course, the easiest way of restarting the network for Ubuntu desktop users. If this one doesn’t work, you can of course check the command line options mentioned in the previous section.
NM-applet is the system tray applet indicator for NetworkManager. That’s what we’re going to use to restart our network.
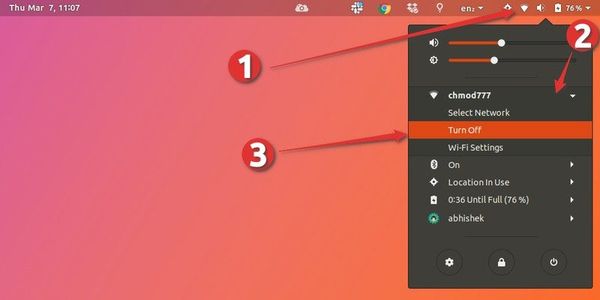
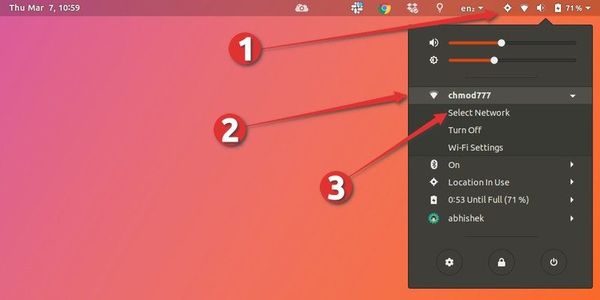
First of all, check out your top panel. You should find a network icon in your system tray (in my case, it is a Wi-Fi icon, since that’s what I use).
Go ahead and click on that icon (or the sound or battery icon). This will open up the menu. Select “Turn Off” here.
The network icon should now disappear from the top panel. This means the network has been successfully turned off.
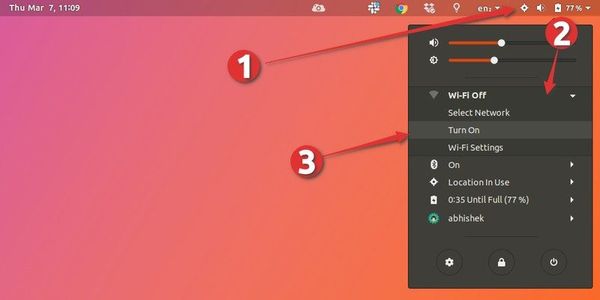
Click again on your systray to reopen the menu. Select “Turn On”.
Congratulations! You have now restarted your network.
Bonus Tip: Refresh the available network list
Suppose you are connected to a network already but you want to connect to another network. How do you refresh the WiFi to see what other networks are available? Let me show you that.
Ubuntu doesn’t have a ‘refresh wifi networks’ option directly. It’s sort of hidden.
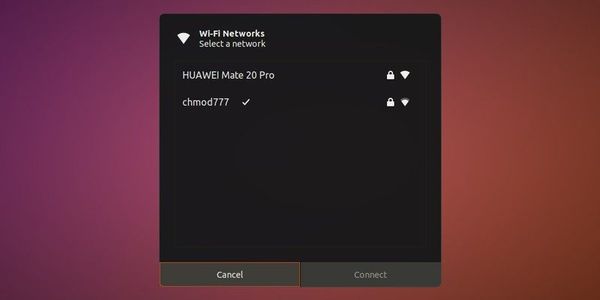
You’ll have to open the setting menu again and this time, click on “Select Network”.
Now, you won’t see the list of available wireless networks immediately. When you open the networks list, it takes around 5 seconds to refresh and show up other available wireless networks.
And here, you can select the network of your choice and click «Connect». That’s it.
Wrapping Up
Restarting your network or connection is something that every Linux user has to go through at some point in their experience. These tools can come in handy for doing the same.
But, if you’re stranded with not finding any wireless interface to connect with (no Wi-fi hardware detected), you can refer to this article.
You can also check out some of the most important networking commands in Linux:
We hope that we have helped you with plenty of methods for handling such issues!
What do you use to restart/handle your network? Is there something we missed? Leave us a comment below.
Перезапуск сети в Ubuntu
В Ubuntu и Debian инициализацией сетевых интерфейсов и настройкой сети занимается специальная сетевая служба — networking. Информация о конфигурации сетевых интерфейсов хранится в файле /etc/network/interfaces.
Если вы что-либо измените в этом файле, нужно будет перезапустить сеть, чтобы применить изменения. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как выполнить перезапуск сети Ubuntu 16.04.
Перезагрузка сети в Ubuntu
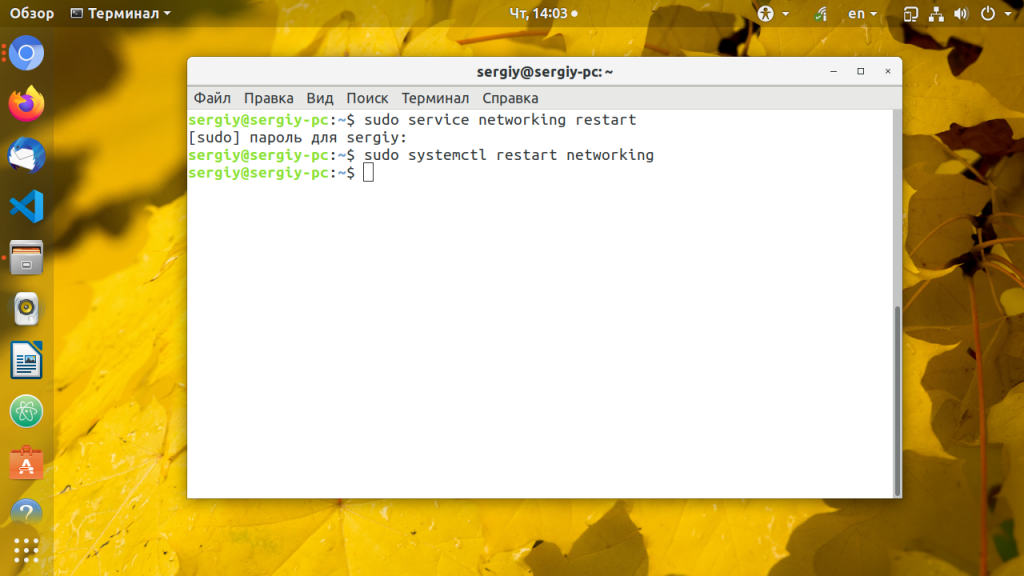
Можно, конечно, выполнить полную перезагрузку компьютера, но это не совсем удобно если можно просто перезапустить сеть Ubuntu. Для перезапуска сети используйте следующую команду:
sudo service networking restart
В современных дистрибутивах уже давным давно используется система инициализации Systemd, поэтому можно использовать команду systemctl вместо команды service:
sudo systemctl restart networking.service
Кроме того, можно перезапустить NetworkManager, это тоже помогает, если сеть настроена через него:
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager
Перезапуск сети в NetworkManager
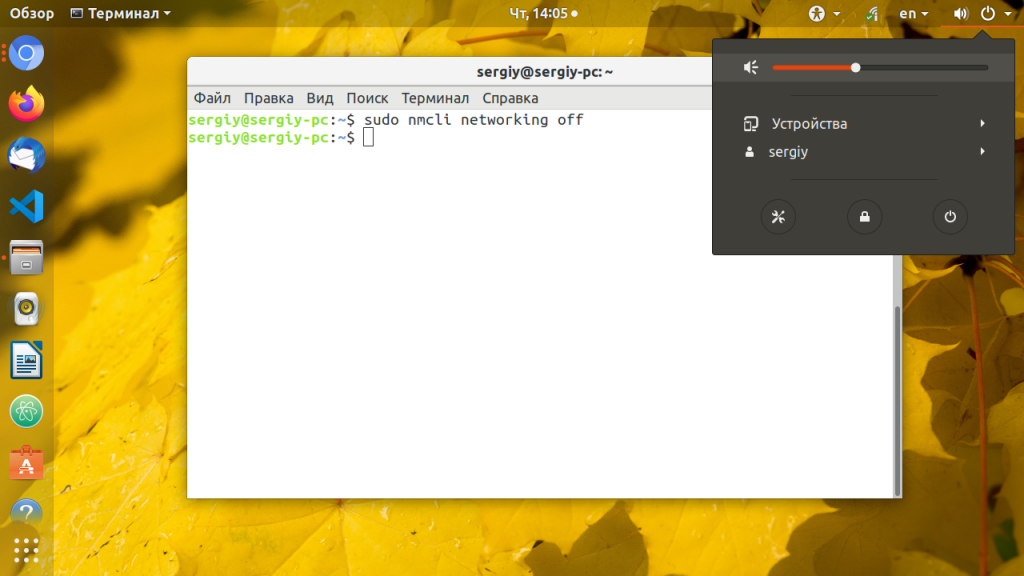
Чаще всего, для управления сетью в современных дистрибутивах используется программа Network Manager. Можно сразу же использовать ещё для наших целей. Просто отключите, а затем включите сеть обратно следующими командами:
sudo nmcli networking off
После отключения сети значок NetworkManager пропадёт с панели, а потом снова появится после включения. Аналогично, вы можете использовать NetworkManager в графическом интерфейсе. Кликните по его иконке, выберите нужное сетевое подключение и нажмите Выключить:
Затем включите его обратно.
Команды ifup и ifdown
Эти команды работают на более низком уровне, они управляют непосредственно самими сетевым интерфейсами. Для перезапуска сети мы можем отключить все интерфейсы, а затем включить обратно:
Вы не увидите никаких изменений в графическом интерфейсе, но когда сетевой интерфейс будет отключён, вы не будете иметь доступа к интернету.
Выводы
Как видите, не всегда обязательно перезагружать компьютер после изменений настроек, в большинстве случаев достаточно перезапустить только нужный сервис. Надеюсь, эта информация была вам полезной.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Restarting, Starting, Stopping, Checking the Status of the Network Service in Linux
In Linux-based operating systems, information about network operations such as network settings, network commands or network configuration is included. In Linux operating systems, as everything is a file, network settings are also kept in files. The settings can be edited with any text editor or by various tools.
Network settings are located in the following files and directories.
/ etc / sysconfig / network file / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts directory / etc / hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/nsswitch.conf / etc / services
Each of the settings files is used for different operations. The files in the network-scripts directory are used for network settings. Network settings are eth0, eth1, etc. according to the network card in files starting with ifcfg. kept by names.
Inside the network settings;
DEVICE - Name of the network card. ONBOOT - The state that the network is activated at startup. BOOTPROTO - How to set network settings (static, dhcp, bootp). IPADDR - IP address. NETMASK - Network mask. BROADCAST - Broadcast address. GATEWAY - Specifies the gateway address.
It also has various settings such as MAC address, Network type. When you want to get IP using DHCP , it will be sufficient to write the DEVICE, BOOTPROTO and ONBOOT settings.
Network Operations
In Linux systems, we can use the following commands to examine the Stop, Start, Restart and Status of our Network services.
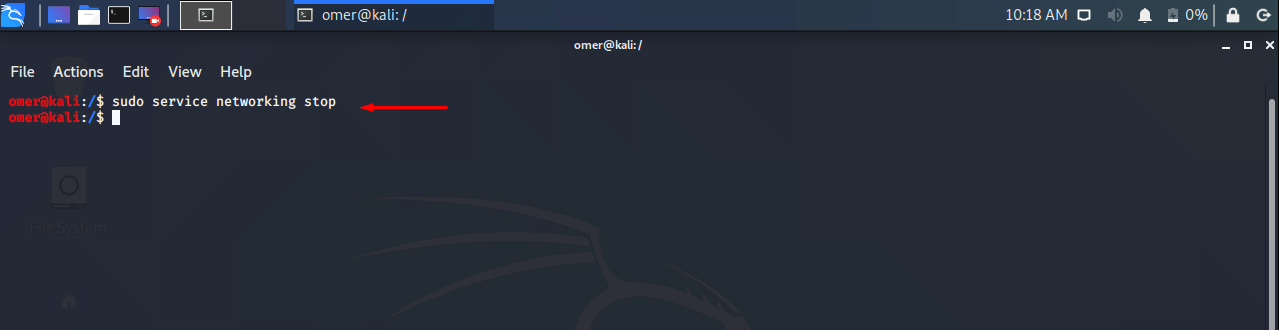
Stop Network Service
You can stop the network service as follows. Check before stopping the service. There will be a problem with your connection. We recommend that you try it in your test environment.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking stop command to service networking stop.
sudo service networking stop
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to systemctl stop network.target.
systemctl stop network.target
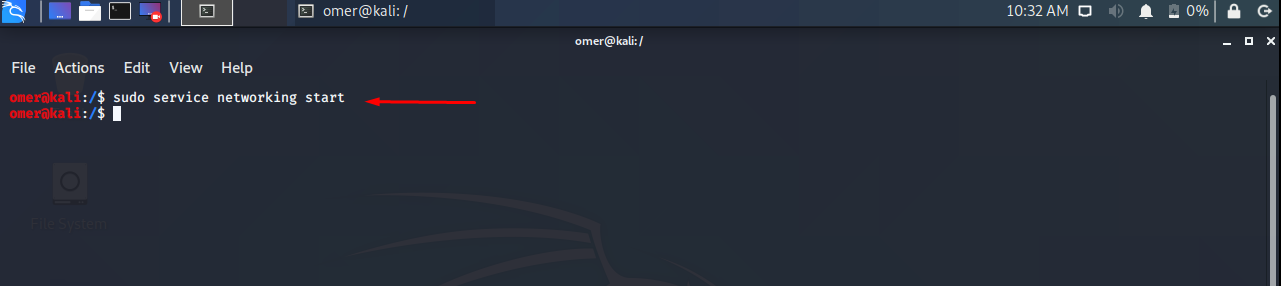
Start Network Service
You can start the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking start.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
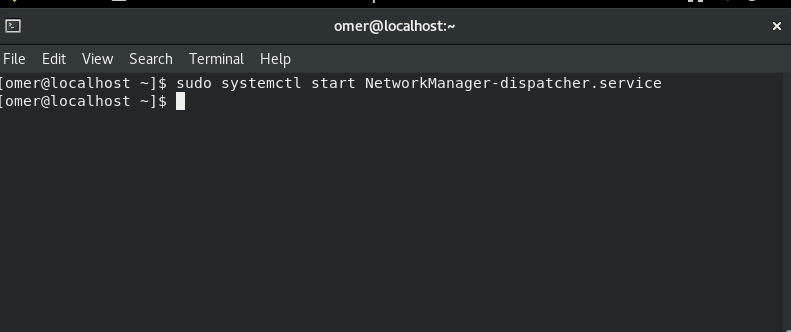
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
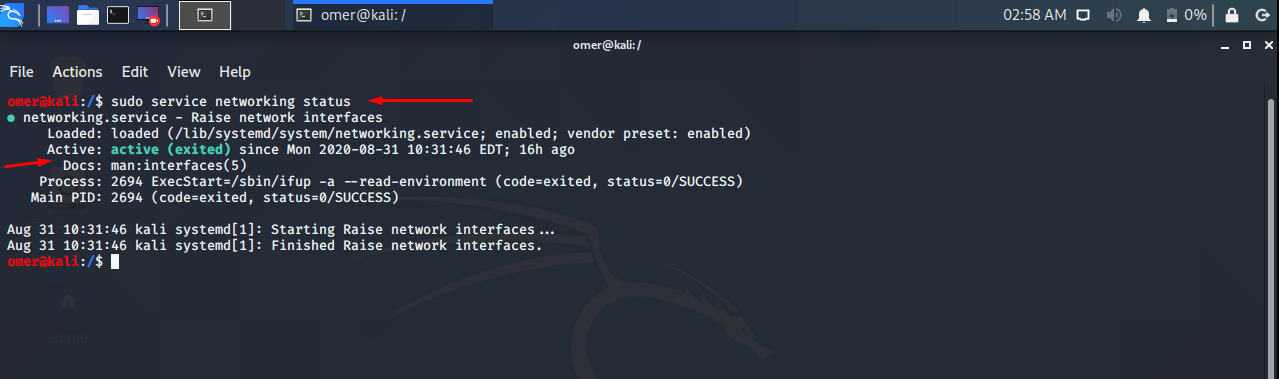
Status Network Service
You can status the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking status.
sudo service networking status
Fedora and CentOS
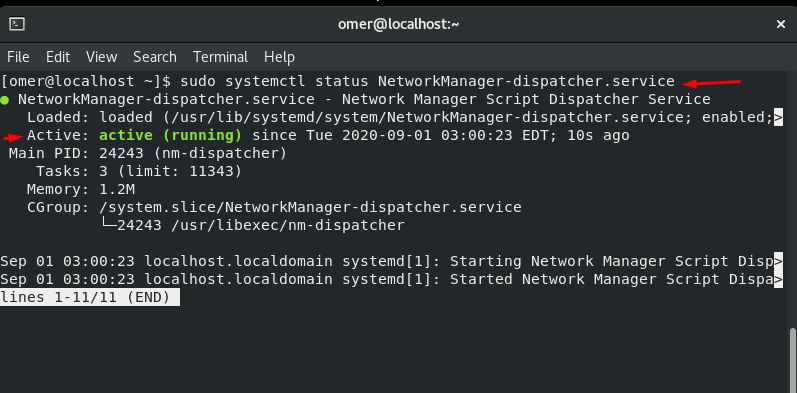
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Restart Network
You can restart the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
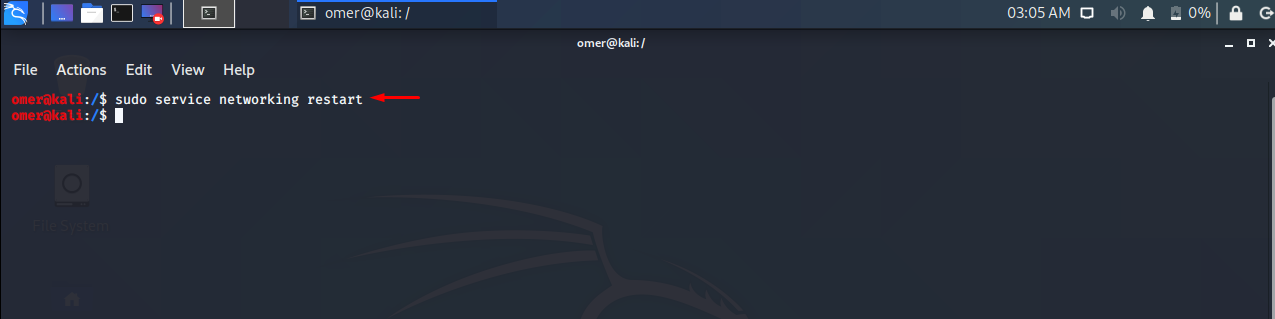
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking restart.
sudo service networking restart
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service