How to install Ubuntu on VirtualBox?
Are you using VirtualBox inside Windows, or inside Ubuntu? Not sure if its still relevant, but could you please also let us know if your using the Community Edition (i.e. the ones usually found in the official repos) or are you using the Standard Edition (i.e. using the repos provided by Sun/Oracle).
Not an answer, but a Virtualbox networking tutorial will definitely solve thousand problems that may come up. So here you go: dedoimedo.com/computers/virtualbox-network-sharing.html
You can use the regular Ubuntu Desktop iso files. For example in VirtualBox you can boot directly from the iso file (when the iso file is in the host machine). From the live system you can install Ubuntu into a virtual drive created in VirtualBox.
6 Answers 6
- Open VirtualBox and select New . A new window will come out.
- Choose your guest OS and architecture (32 vs. 64 bit, e.g select Ubuntu)
- Set your Base Memory (RAM)
- Click next until it show the vm storage size. Put how much space you need depending on your hardisk and finish the wizard by clicking the create button.
- On VirtualBox main window, select START and pick your MEDIA SOURCE. In your case, select the .iso on your desktop.
- Finish the installation as normal install.
- Remove your installation .iso from the virtual optical disk drive before restarting the VM.
- Install Guest Additions.
Follow this guide:
Open Virtualbox and click at New button.
Setup Wizard will appear and click at Next button.
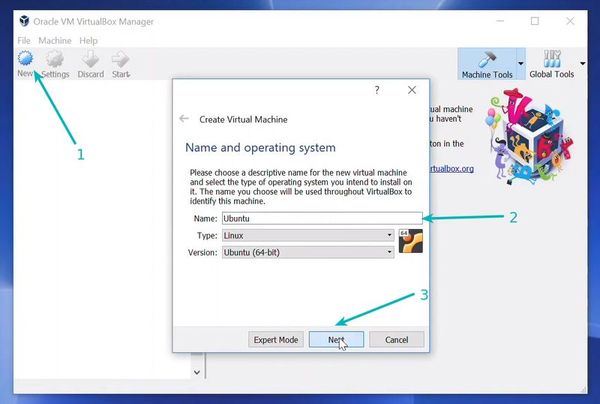
Enter your Virtual Machine name, and choose your guest OS and architecture (32- vs. 64-bit) from the dropdown menu and click Next button.
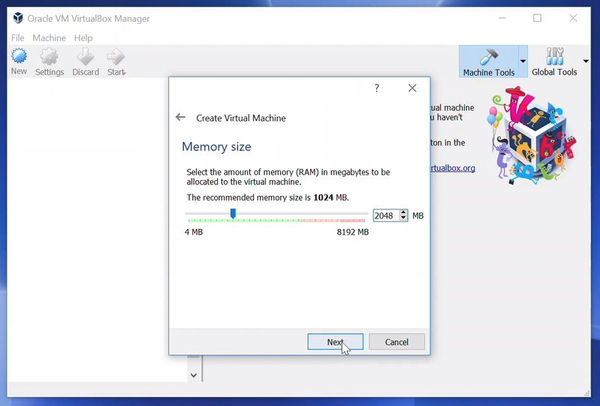
Enter memory (RAM) to reserve for your virtual machine and click Next button.
Leave enough memory to the host OS.
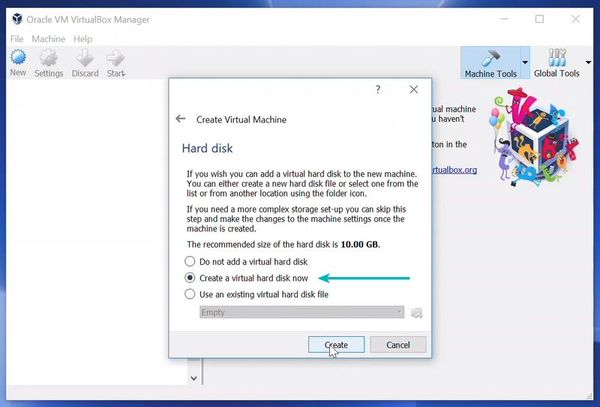
Tick at Startup Disk and Create New Hard disk and click at Next button.
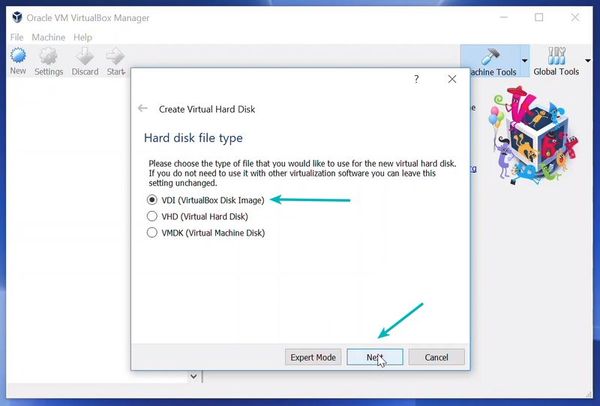
Choose the type of file that you want to use for virtual disk and click Next button.
Choose your storage detail and click Next button.
Enter the size of your virtual disk (in MB) and click Next button.
A dynamically growing virtual disk will only use the amount of physical hard drive space it needs. It is better to be rather generous to avoid running out of guest hard drive space.
You will see the detail of your input here. Click Create button to continue.
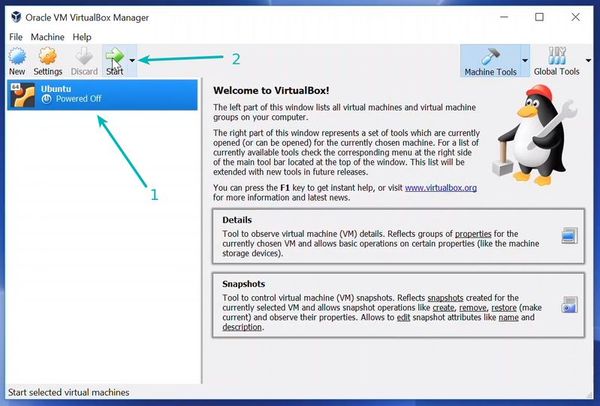
The «New Virtual Machine Wizard» will close and back to VirtualBox Manager. Select your Virtual Machine and click Start button.
«First Run Wizard» will appear and click Next button.
Click at ‘folder’ icon and choose your Ubuntu iso directory.
Select your Ubuntu iso file and click Next button.
In ‘Summary’ box, click Start button.
This screen will appear when it start boot.
After a successful installation we have to remove our installation .iso image from the virtual optical drive before we reboot. This can be done from the «Devices» menu or by removing the .iso from the VM settings:
For smooth graphics, and to be able to use shared folders it is recommended to install the guest additions.
Thanks dear , but problemo is that in Step 12 » Select installation Media» I dont have Disk Drive now its gone rogue . But I do have .iso image in my hard drive. Can u please tell me how to mount it . So i can select it in Step 12
locate from VirtualBox? How, coz when ever i try to run virtual box it immediately show this error » Fatal: No bootable medium found! System halted» And i copied the .iso image in /Home folder.
@UmairMustafa Create the VM with the default settings and then on the First Run Wizard you get when you start the VM, browse to the .iso file. You must tell VirtualBox to use that ISO to boot. Delete the VM and create it again, following the last 4 images and steps carefully.
You have to follow exactly the tutorial. Just run and follow the wizard. Im sure you miss the ‘Click at ‘folder’ icon and choose your Ubuntu iso directory’ part.
Installing Ubuntu under virtual box
- open virtualbox
- than click New
- then click Next
- Set name something like Ubuntu 12.04 (it will automaticly set type to linux)
- Set memory f.e. 1024 MB
- Select Create new hard disk
- Select VDI then Next
- Select Dynamically allocated then Next
- Set location(let it stay its default) and its size (f.e 20GB) then Next
- Then Create
- Then again Create
- Here is two ways
- Install from .iso
- Install from DVD
- Start VM
- There select what kind of installation you want(from iso or from dvd)
- then the installation will start
Go to the home page on Ubuntu’s website and then go to the download section, and get Ubuntu if you haven`t done so already. You can burn the image to a CD or use it as is ISO image. Install VirtualBox if not installed already.
To install Virtualbox you can download it from VirtualBox
Once downloaded, navigate to where the file was downloaded, and then double click on it to install.
Once you have done the previous steps go here for a complete tutorial on how to install Ubuntu inside a virtual box.
Install Linux Inside Windows Using VirtualBox [Step by Step Guide]
Using Linux in a virtual machine allows you to try Linux within Windows. This step-by-step guide shows you how to install Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox.
- You can clean everything from your system and install Linux.
- You can dual boot Linux with Windows and choose one of the operating systems at the boot time.
- You can even install Linux within Windows from Microsoft Store (though this only provides you with the command line version of Linux).
But if you want to use Linux without making any changes to your Windows system, you can go the virtual machine route.
Basically, you install and use Linux like any regular Windows application. When you just want to try Linux for limited use, virtual machines provide the most comfortable option.
In this tutorial, I’ll show you how to install Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox.
Installing Linux inside Windows using VirtualBox
VirtualBox is free and open source virtualization software from Oracle. It enables you to install other operating systems in virtual machines. It is recommended that your system should have at least 4GB of RAM to get decent performance from the virtual operating system.
Requirements
- Good internet connection to download software and Linux ISO. (You can also use some other computer with an internet connection to download these files.)
- Windows system with at least 12 GB of free space.
- Windows system with 4GB of RAM. (It can work with less RAM as well, but your system will start to lag while using Linux in the virtual machine.)
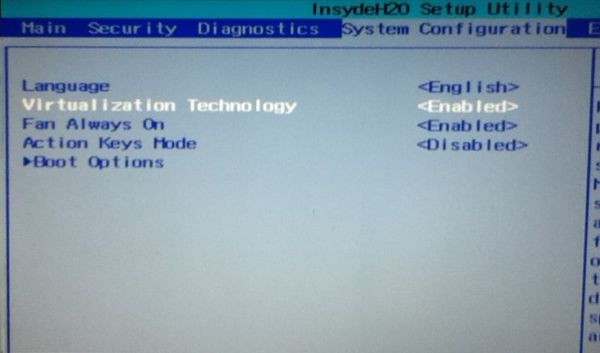
- Make sure to enable virtualization in the BIOS (some system need it)
I am installing Ubuntu 17.10 in this tutorial, but the same steps apply to any other Linux distribution. If you prefer videos, you can watch the one below from our YouTube channel:
Allocate RAM to the virtual OS. My system has 8GB of RAM and I decided to allocate 2GB of it. You can use more RAM if your system has enough extra.
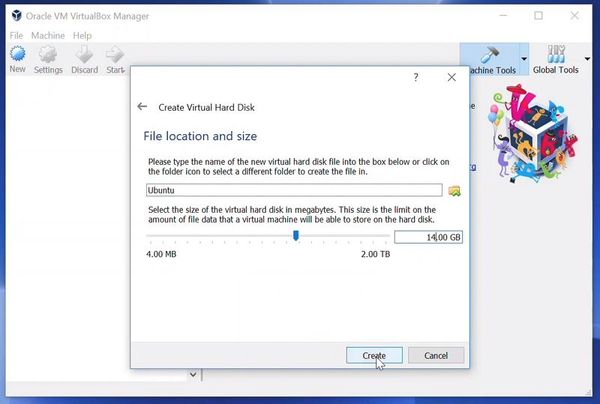
Create a virtual disk. This serves as the hard disk of the virtual Linux system. It is where the virtual system will store its files.
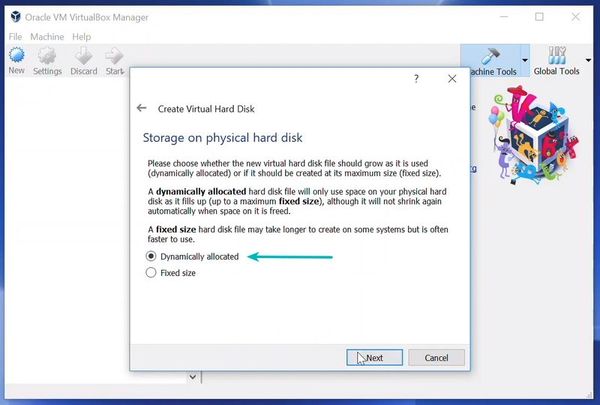
I recommend using the VDI file type here.
You can choose either the “Dynamically allocated” or the “Fixed size” option for creating the virtual hard disk.
The recommended size is 10 GB. However, I suggest giving it more space if possible. 15-20 GB is preferable.
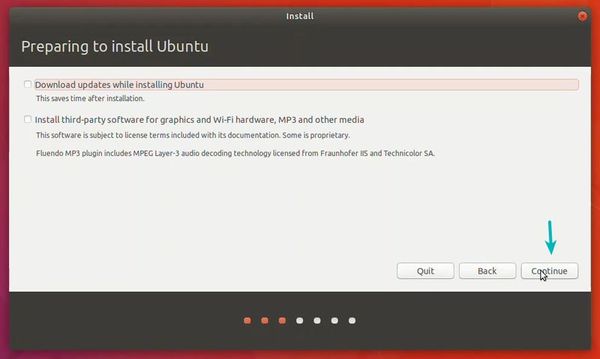
Once everything is in place, it’s time to boot that ISO and install Linux as a virtual operating system.
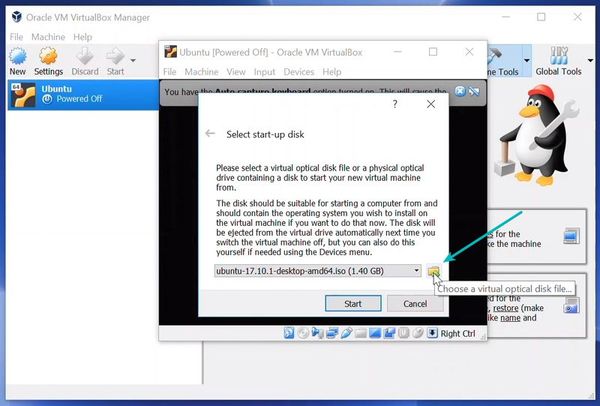
If VirtualBox doesn’t detect the Linux ISO, browse to its location by clicking the folder icon as shown in the picture below:
Soon you’ll find yourself inside Linux. You should be presented with the option to install it.
Things from here are Ubuntu-specific. Other Linux distributions may have slightly different looking steps, but it won’t be complicated at all.
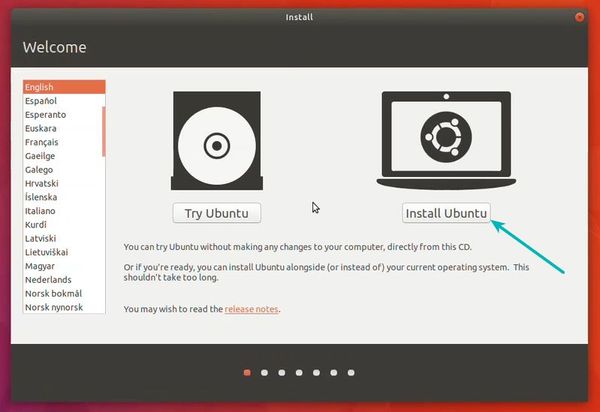
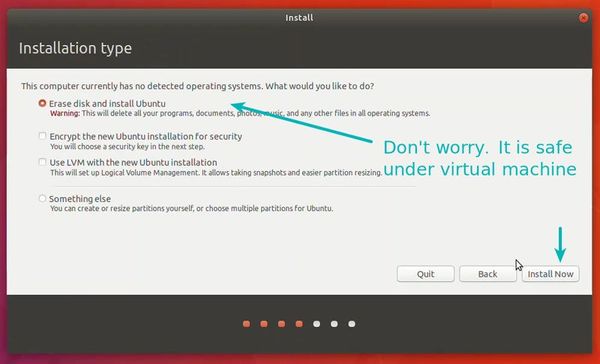
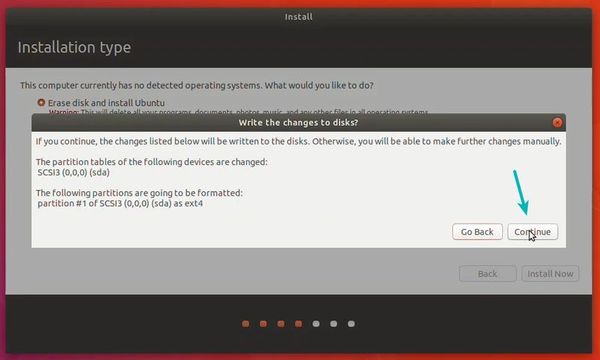
Select ‘Erase disk and install Ubuntu’. Don’t worry. It won’t delete anything on your Windows operating system. You are using the virtual disk space of 15-20GB that we created in previous steps. It won’t impact the real operating system.
Things are pretty straightforward from here.
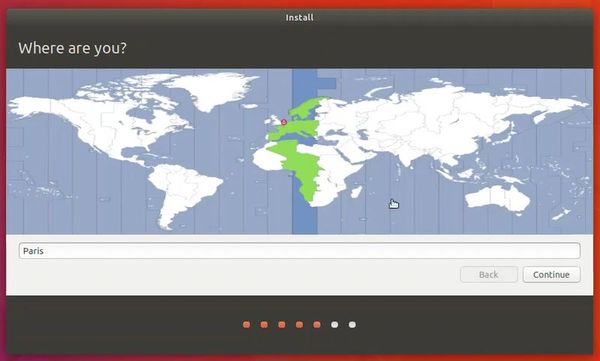
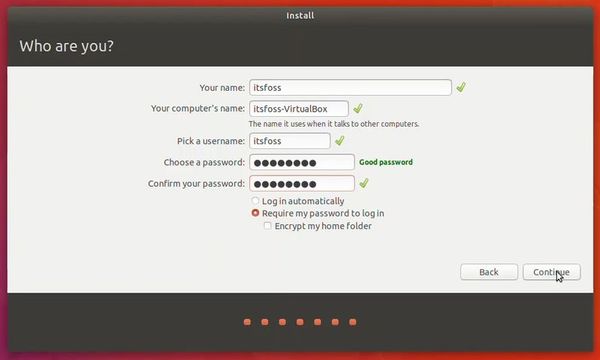
Try to choose a password that you can remember. You can also reset the password in Ubuntu if you forget it.
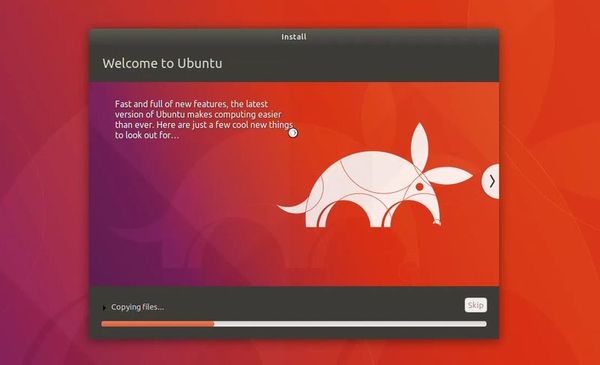
You are almost done. It may take 10-15 minutes to complete the installation.
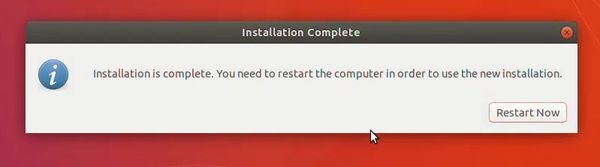
Once the installation finishes, restart the virtual system.
If it gets stuck on the screen below, you may close the VirtualBox.
And that’s all. From now on, just click on the installed Linux virtual machine. You’ll be able to use it directly. The installation is a one time only process. You can even delete the Linux ISO that you downloaded earlier.
I strongly recommend using VirtualBox Guest Additions on Ubuntu for it provides better compatibility and you would be able to use copy-paste and drag-drop between Linux and Windows.
Troubleshooting: AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS
If you face this error while using the virtual machine:
Not in a hypervisor partition (HVP=0) (VERR_NEM_NOT_AVAILABLE).
AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS (or by the host OS) (VERR_SVM_DISABLED).
Result Code:
E_FAIL (0x80004005)
Component:
ConsoleWrap
Interface:
IConsole
This means that virtualization is blocked on your system. You’ll have to activate it in your BIOS settings first.
Reboot your system and as soon as it powers up, press F2/F10/F12 to access BIOS settings. You have to look for the virtualization option in the BIOS and enable it.
Any questions?
That’s all you need to do to install Linux in VirtualBox on Windows.
If you have any doubts, or if you encounter any issues, please feel free to ask your questions in the comment box below.