- Introduction
- Resistive Touch Screen
- Toradex Embedded Linux Offerings
- BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project
- Torizon
- Input Libraries
- libinput
- Display Servers and Frameworks
- Qt
- See also
- Touch Screen Calibration (Linux)
- Introduction
- Resistive Touch Screen
- Toradex Embedded Linux Offerings
- BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project
- Torizon
- Input Libraries
- libinput
- Display Servers and Frameworks
- Qt
- First Steps with Capacitive Touch Display 10.1 Inch LVDS
- Getting Started
- What I need to order
- Where do I order
- Cable Connection
- Connections on Ixora
- Connection on Apalis Evaluation Board
- Connections on Iris Carrier Board
- Connections on Verdin Development Board
- Connections on Dahlia Carrier Board
- Installation on Embedded Linux
- TorizonCore 5
- Reference Images for Yocto Project 5
- Adjusting the Brightness
- Touch Screen
- Touch Screen Calibration
Introduction
Touch screen under Embedded Linux requires a kernel module that receives the hardware signals and exports them as an input device to be read in user space by a library.
As an example, if you are using Boot to Qt image with Capacitive Touch Display 7″ Parallel, your setup will look like the following flowchart:
On the other hand, if you are using Ångström X11 image with Resistive Touch Display 7″ Parallel, your setup will look like the following flowchart:
In this article, touch screen calibration will be discussed applied to different libraries and its methods to correctly calibrate your touchscreen display.
Resistive Touch Screen
Touch screen calibration almost always implies calibrating a resistive touch, since the capacitive touch panels usually are calibrated by default. It means that this article is most useful if you have a resistive touch panel.
Read the following article to learn more about Resistive Touch Screen on our Embedded Linux BSPs.
Toradex Embedded Linux Offerings
BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project
Select your BSP version from the tabs below:
BSP 5 provides Weston/Wayland support, as described in the BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project Software. The Reference Multimedia Image comes with weston-touch-calibrator which can be used to calibrate the touch screen:
You may need to change the default Weston configuration to make it work, though. See how we have implemented the weston-touch-calibrator container on Touch Screen Calibration (Torizon) as an example implementation. For example, possibly you’ll have to update the weston.ini.
On BSP 3, some SoMs are supported with X11 and others with Weston/Wayland, as described in the page BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project Software. Since there is only a console image, it is up to you add a calibration program, or to tweak values as explained in the corresponding graphics framework documentation.
BSP 2.x automatically performs a calibration upon first boot and will continue to ask for calibration in every boot until it is successfully completed.
The calibration application can be found in /usr/bin/xinput_calibrator .
Torizon
Torizon uses Weston and Libinput. Toradex provides a container for touch screen calibration. For more details read Touch Screen Calibration (Torizon).
Input Libraries
Touch screen calibration concerning the input libraries is provided in this section.
libinput
libinput is a library to handle input devices in Wayland compositors and to provide a generic X.Org input driver. It provides device detection, device handling, input device event processing and abstraction so minimize the amount of custom input code compositors need to provide the common set of functionality that users expect.
Concerning Toradex offerings, Libinput is used by:
Calibration
For static configuration via udev, one can set the LIBINPUT_CALIBRATION_MATRIX udev property as a environment variable with the following udev rule:
You can use the following command line examples to create a file with the udev rule.
echo 'ENV="1 0 0 0 1 0"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules echo 'ENV="1 0 0 0 -1 1"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules echo 'ENV="-1 0 1 0 1 0"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules echo 'ENV="-1 0 1 0 -1 1"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules Further information on the LIBINPUT_CALIBRATION_MATRIX, please access the documentation.
Display Servers and Frameworks
Touch screen calibration concerning display servers (such as Xorg and Wayland) or standalone frameworks (such as Qt) is provided in this section.
Qt
The Qt framework supports different input methods. Regardless of this article’s information, please also consult the official Qt documentation.
The Qt for Device Creation demo image uses libinput, therefore please refer to the previous libinput section for touchscreen calibration information.
See also
Touch Screen Calibration (Linux)
This page has not been fully updated to reflect the changes made in Toradex Linux BSP 6. Some information may still apply to Toradex Linux BSP 6 configurations. If you encounter issues, please Send Feedback.
If you are using version 5 LTS, please visit the 5 LTS version documentation.
Introduction
Touch screen under Embedded Linux requires a kernel module that receives the hardware signals and exports them as an input device to be read in user space by a library. 


Resistive Touch Screen
Touch screen calibration almost always implies calibrating a resistive touch, since the capacitive touch panels usually are calibrated by default. It means that this article is most useful if you have a resistive touch panel. Read the following article to learn more about Resistive Touch Screen on our Embedded Linux BSPs.
Toradex Embedded Linux Offerings
BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project
BSP 5 provides Weston/Wayland support, as described in the BSP Layers and Reference Images for Yocto Project Software. The Reference Multimedia Image comes with weston-touch-calibrator which can be used to calibrate the touch screen:
You may need to change the default Weston configuration to make it work, though. See how we have implemented the weston-touch-calibrator container on Touch Screen Calibration (Torizon) as an example implementation. For example, possibly you’ll have to update the weston.ini.
Torizon
Torizon uses Weston and Libinput. Toradex provides a container for touch screen calibration. For more details read Touch Screen Calibration (Torizon).
Input Libraries
libinput
libinput is a library to handle input devices in Wayland compositors and to provide a generic X.Org input driver. It provides device detection, device handling, input device event processing and abstraction so minimize the amount of custom input code compositors need to provide the common set of functionality that users expect.
Calibration
For static configuration via udev, one can set the LIBINPUT_CALIBRATION_MATRIX udev property as a environment variable with the following udev rule:
You can use the following command line examples to create a file with the udev rule.
echo 'ENV="1 0 0 0 1 0"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules echo 'ENV="1 0 0 0 -1 1"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules echo 'ENV="-1 0 1 0 1 0"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules echo 'ENV="-1 0 1 0 -1 1"' > /etc/udev/rules.d/libinput.rules Further information on the LIBINPUT_CALIBRATION_MATRIX, please access the documentation.
Display Servers and Frameworks
Touch screen calibration concerning display servers (such as Xorg and Wayland) or standalone frameworks (such as Qt) is provided in this section.
Qt
The Qt framework supports different input methods. Regardless of this article’s information, please also consult the official Qt documentation.
The Qt for Device Creation demo image uses libinput, therefore please refer to the previous libinput section for touchscreen calibration information.
First Steps with Capacitive Touch Display 10.1 Inch LVDS
This article provides information on how to start working with the Capacitive Touch Display 10.1 Inch LVDS, which includes how to set up the hardware (wiring), install and configure the necessary drivers for a touch demo.
Getting Started
What I need to order
The Capacitive Touch Display 10.1 Inch LVDS can be ordered with many Toradex computer on modules and carrier boards. See the compatible products.
Where do I order
Cable Connection
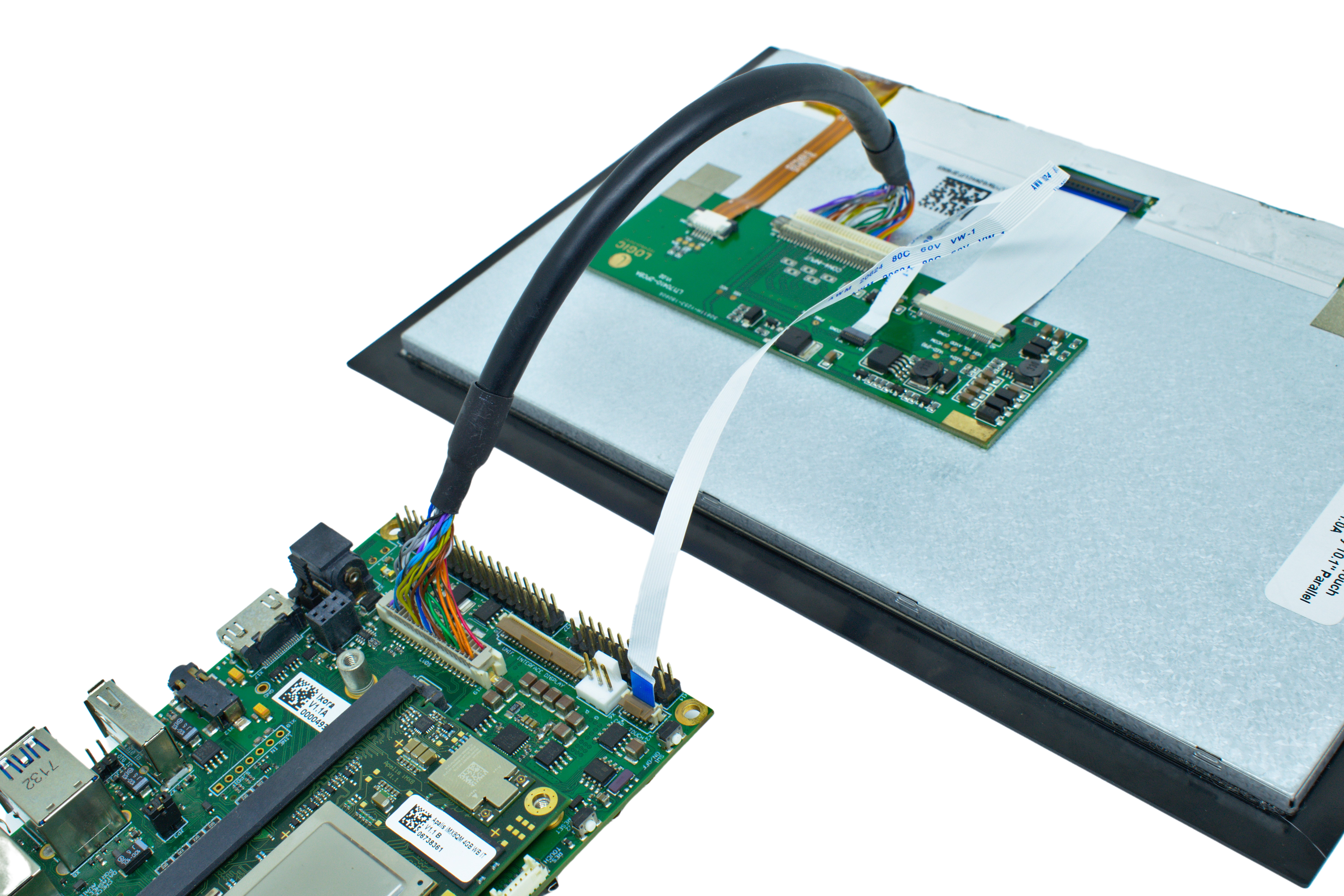
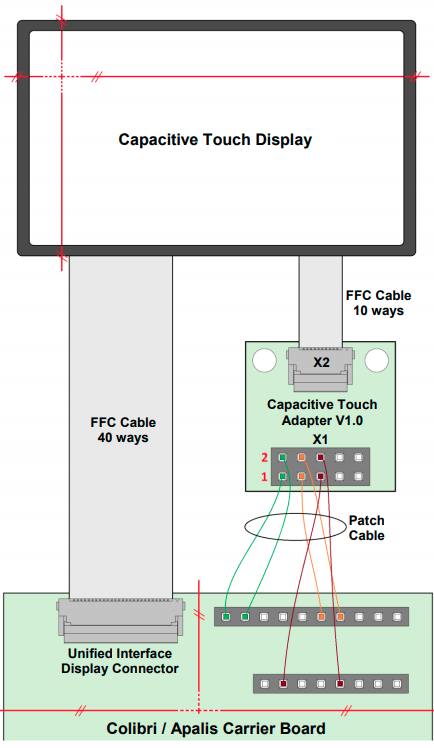
This topic provides pin connection details regarding connecting the Capacitive Touch Display 10.1 Inch LVDS to the carrier boards. Connect both the LVDS cable and the flat ribbon cable for the touch controller to the display.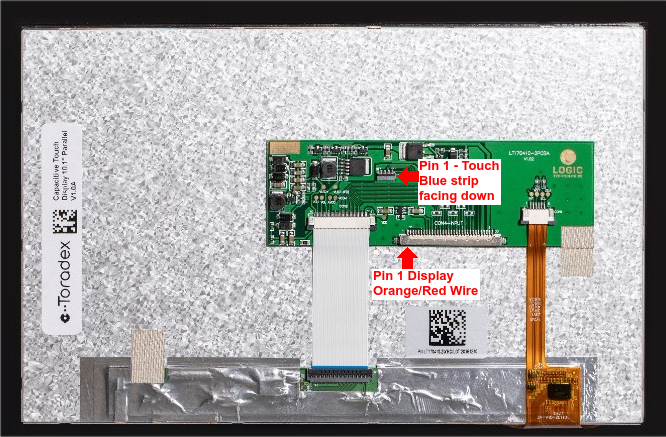 
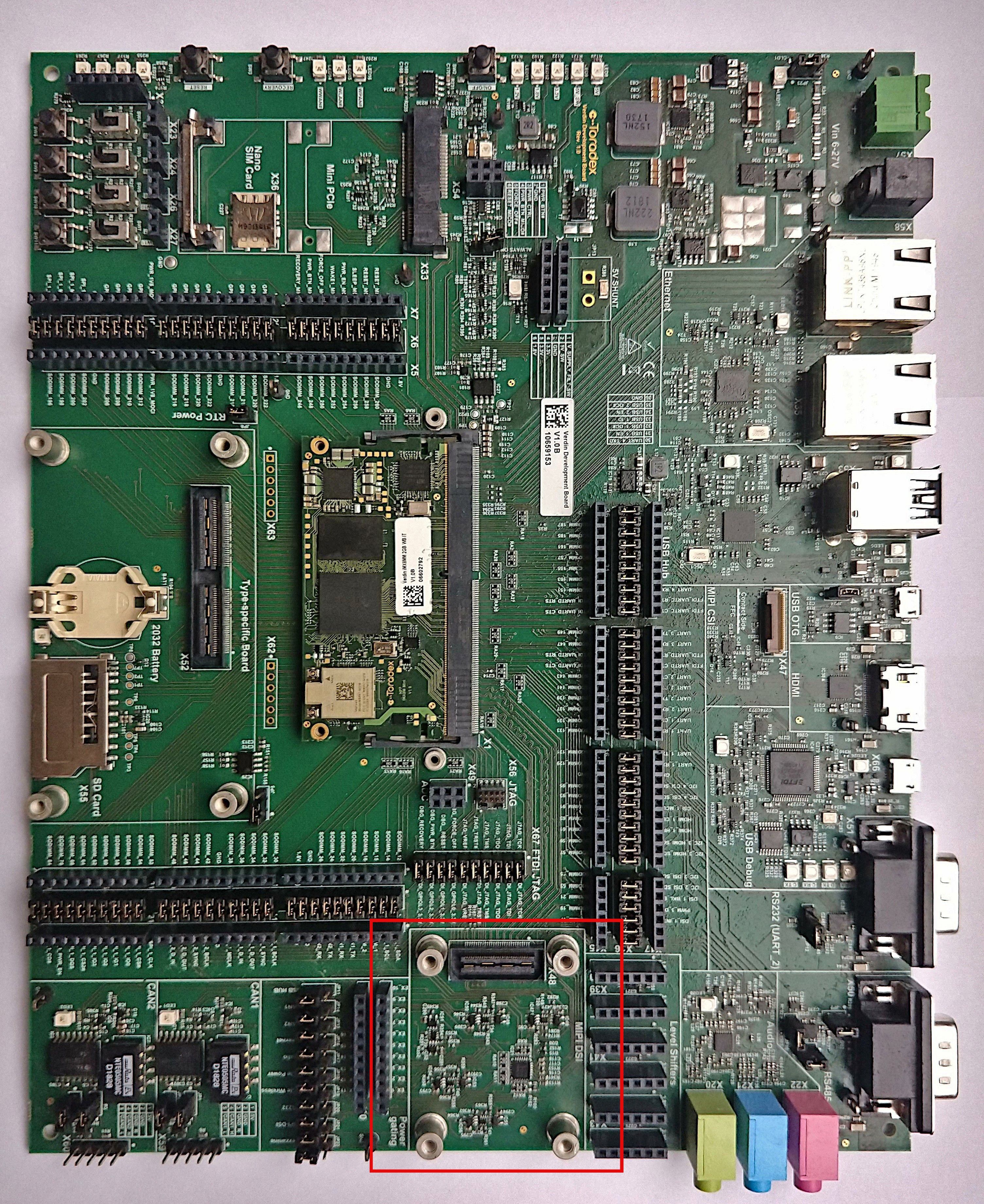
Connections on Ixora
Important! The LVDS connector is directly connected to the power input connector. For this reason, use only 12V (+/-10%) power supplies with the board. Otherwise, you can damage the LVDS display or observe a malfunction.
See the picture below for the direct connection from the display to the Ixora board. Make sure to connect the pin 1 side of both display and touch controller to the respective pin 1 of the carrier board.
Connection on Apalis Evaluation Board
Important! The LVDS connector is directly connected to the power input connector. For this reason, use only 12V (+/-10%) power supplies with the board. Otherwise, you can damage the LVDS display or observe a malfunction.
Connect the LVDS connector of the Display into the LVDS Connector (X13) of the carrier board. 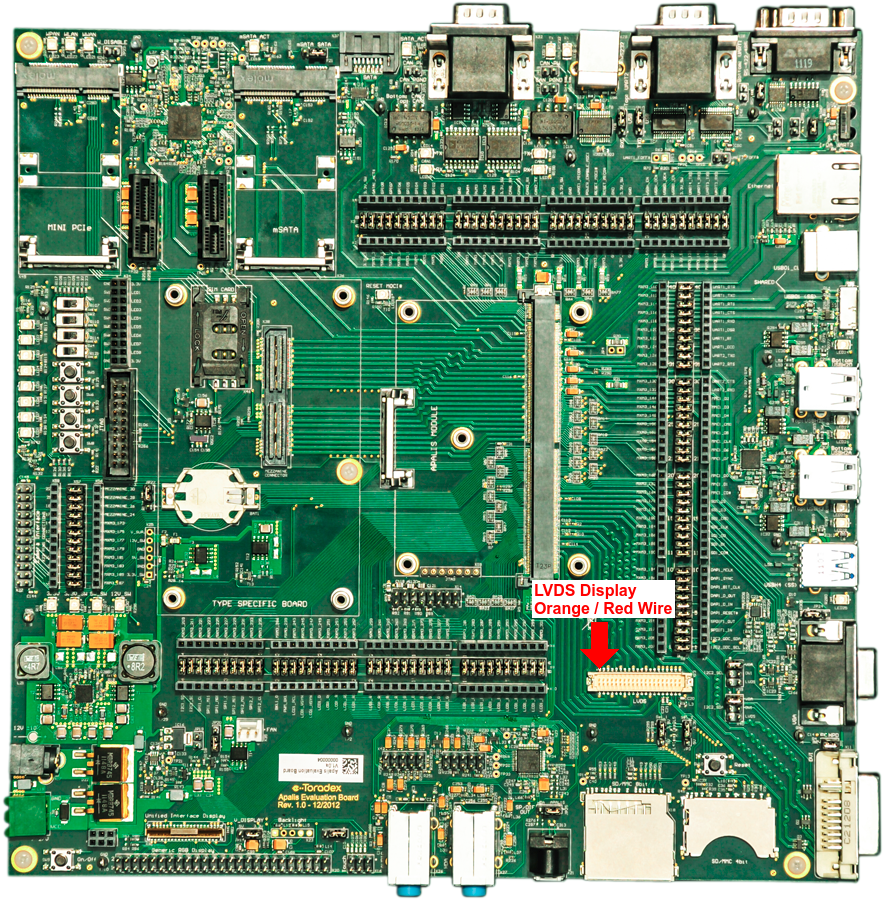
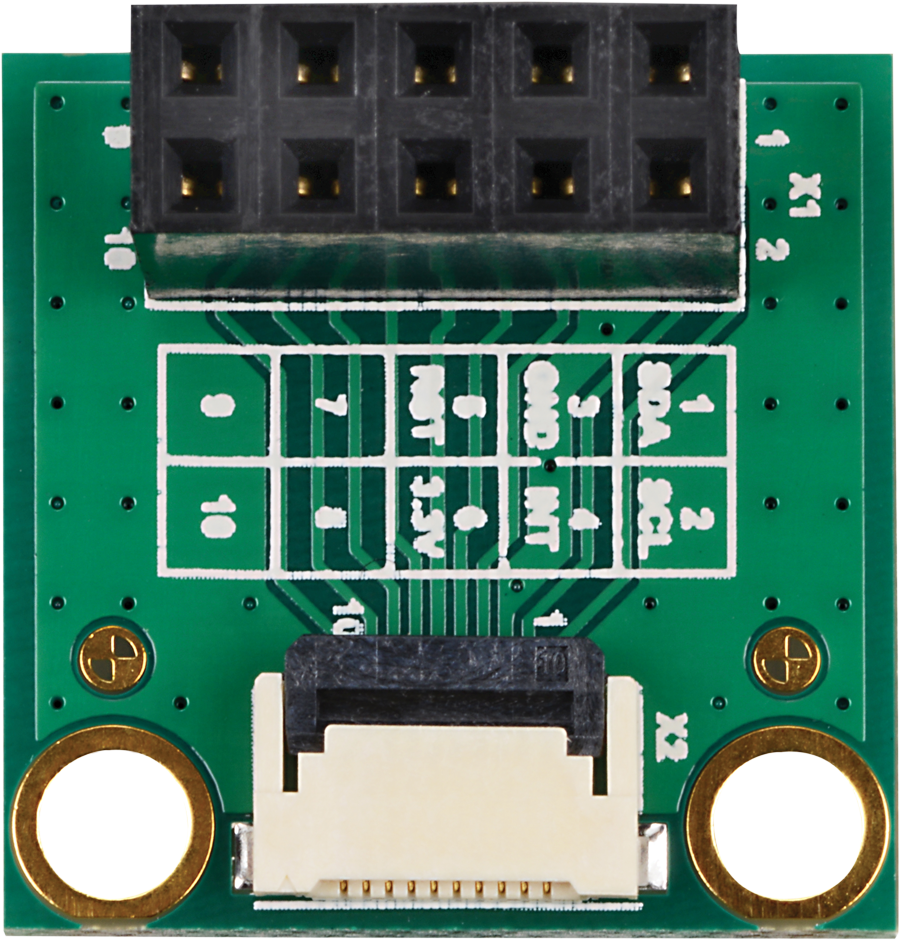
| Capacitive Touch Adapter V1.0 | Apalis Evaluation Board V1.0 / V1.1 | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1, Pin 1: I2C_SDA | X8, Pin 40; X9, Pin A40: MXM3_209 (I2C1_SDA) | ||
| X1, Pin 2: I2C_SCL | X8, Pin 39; X9, Pin A39: MXM3_211 (I2C1_SCL) | ||
| X1, Pin 3: GND | X2/X3/X4, Pin 11: GND | ||
| X1, Pin 4: TOUCH_INT# | X2, Pin 6; X3, Pin A6: MXM3_11 (GPIO5) | ||
| X1, Pin 5: TOUCH_RESET# | X2, Pin 5; X3, Pin A5: MXM3_13 (GPIO6) | ||
| X1, Pin 6: +3.3V | X2/X3/X4, Pin 1: 3.3V_SW | Optional |
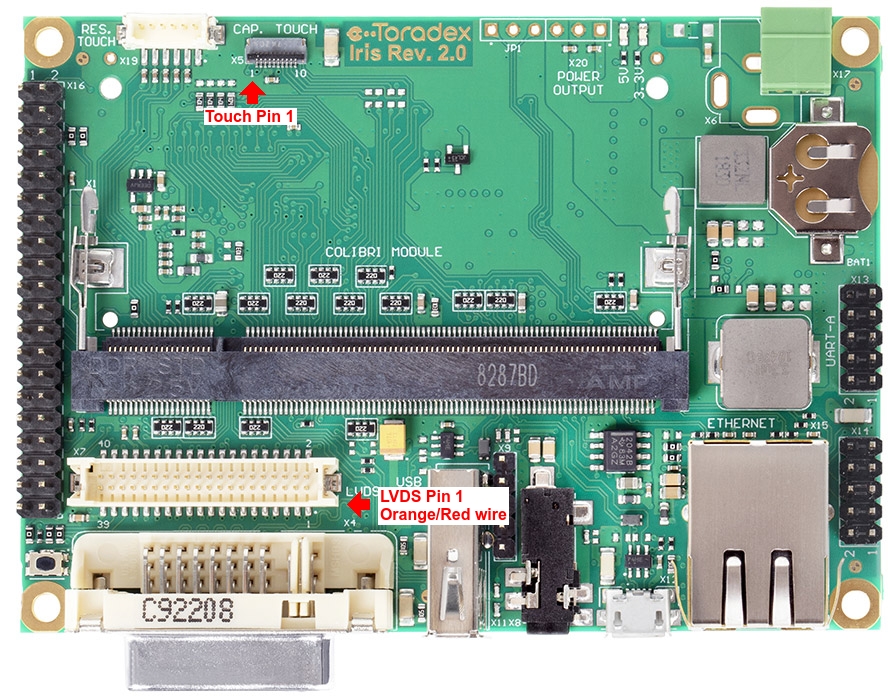
Connections on Iris Carrier Board
Important! The LVDS connector is directly connected to the power input connector. For this reason, use only 12V (+/-10%) power supplies with the board. Otherwise, you can damage the LVDS display or observe a malfunction.
See the picture below for the direct connection from the display to the Iris Carrier Board. Make sure to connect the pin 1 side of both display and touch controller to the respective pin 1 of the carrier board.
Connections on Verdin Development Board
A Verdin DSI to LVDS Adapter is required to use this display on Verdin boards. The Verdin DSI to LVDS Adapter features a touch connector compatible with the Capacitive Touch Display 10.1″ LVDS. Connect both the flat ribbon cable of the touch panel and the LVDS Cable into the adapter. See the indication on the silk mask in the adapter board indicating the correct side of the contacts for the Touch’s flat ribbon cable. 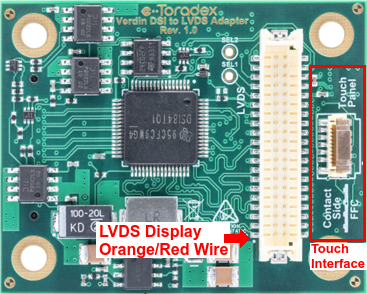
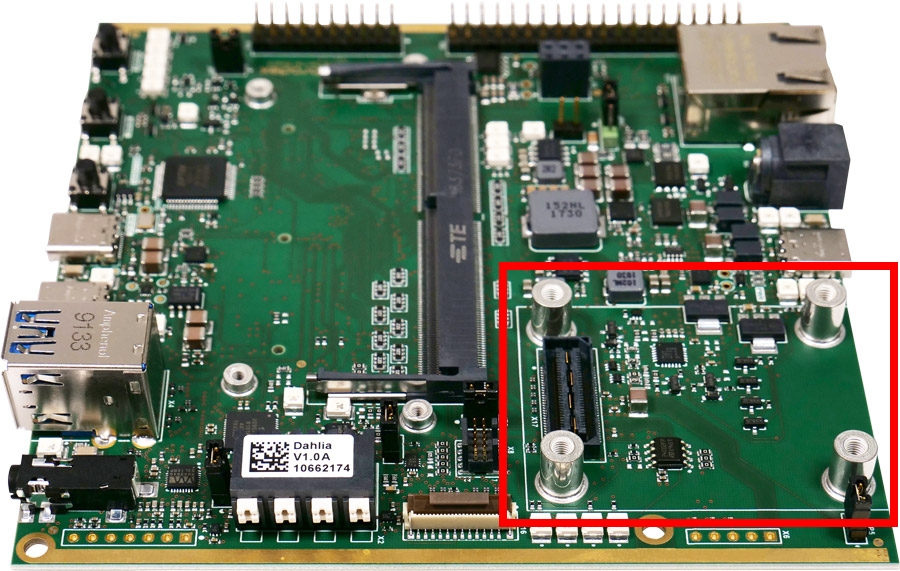
Connections on Dahlia Carrier Board
A Verdin DSI to LVDS Adapter is required to use this display on Verdin boards. The Verdin DSI to LVDS Adapter features a touch connector compatible with the Capacitive Touch Display 10.1″ LVDS. Connect both the flat ribbon cable of the Touch and the LVDS Cable into the adapter. See the indication on the silk mask in the adapter board indicating the correct side of the contacts for the Touch’s flat ribbon cable. 
Installation on Embedded Linux
TorizonCore 5
On TorizonCore 5, Toradex deploys pre-compiled and ready-to-use device tree overlays for this display, inherited from the BSP layers. Enabling them for evaluation can be done with few commands. Learn how to do it on Setting up Displays with Torizon.
Reference Images for Yocto Project 5
On BSP 5, Toradex deploys pre-compiled and ready-to-use device tree overlays for this display. This enables you to evaluate it with few commands and very fast. Learn how to do it on Device Tree Overlays (Linux).
For more advanced use cases, please refer to the article Display Output, Resolution and Timings (Linux).
Adjusting the Brightness
Read the dedicated article Backlight (Linux).
Touch Screen
Resistive touch screen works out-of-the-box in our BSP. To learn more about resistive touch, read the article Resistive Touch Screen (Linux).
Touch Screen Calibration
Read the dedicated articles: