- 5 Ways to check laptop Battery status and Level from Linux Terminal
- Following Utilities are available in Linux to Check Battery Status.
- How to check Laptop Battery status using upower Command?
- How to check Laptop Battery status using TLP command?
- How to check Laptop Battery status using ACPI Command?
- How to check Laptop Battery status using Batstat Command?
- How to check Laptop Battery status using sysfs filesystem?
- 3 Tools To Display Linux Laptop Battery Information From the Command Line
5 Ways to check laptop Battery status and Level from Linux Terminal
We can easily check the battery status through GUI such as current battery percentage, whether it’s charging or not and how long it will be usable without charging, but we can’t check the battery health and other related information.
Yes, we have few utilities available for this in Linux and it can be achieved through command line.
We are going to discuss more this topic today through this article and I will try to cover most possible information we can.
Checking your battery health monthly once is a good practice. It will help you to identify whether we are facing any issues related to battery life or charge.Also, we can see battery model name, power source, vendor and battery technology, etc,.
Power management is a feature that turns off the power or switches system’s components to a low-power state when inactive.
Following Utilities are available in Linux to Check Battery Status.
- upower : upower is a command line tool which provides an interface to enumerate power sources on the system.
- acpi : acpi Shows information from the /proc or the /sys filesystem, such as battery status or thermal information.
- batstat : batstat is a command line tool to print battery status for linux.
- tlp : TLP brings you the benefits of advanced power management for Linux without changing any configuration.
- class file : The sysfs filesystem is a pseudo-filesystem which provides an interface to kernel data structures.
How to check Laptop Battery status using upower Command?
upower is a command line tool that provides an interface to enumerate power sources on the system. It control the latency of different operations on your computer, which enables you to save significant amounts of power.
Just run the following command to get the battery and it’s related information on Linux.
$ upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0 native-path: BAT0 vendor: SMP model: L14M4P23 serial: 756 power supply: yes updated: Monday 03 December 2018 07:56:18 PM IST (95 seconds ago) has history: yes has statistics: yes battery present: yes rechargeable: yes state: discharging warning-level: none energy: 28.23 Wh energy-empty: 0 Wh energy-full: 52.26 Wh energy-full-design: 60 Wh energy-rate: 10.714 W voltage: 14.819 V time to empty: 2.6 hours percentage: 54% capacity: 87.1% technology: lithium-ion icon-name: 'battery-good-symbolic' History (charge): 1543847178 54.000 discharging History (rate): 1543847178 10.714 discharging
To check the specific information about battery, use the following format.
$ upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0 | grep -i "state\|percentage\|time to empty" state: discharging time to empty: 2.1 hours percentage: 43%
It’s same as above, but it’s taken after power cable plugged in, that’s why the state showing charging.
$ upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0 | grep -i "state\|percentage\|time to empty" state: charging percentage: 41%
How to check Laptop Battery status using TLP command?
TLP is a free opensource feature-rich command line tool which optimize laptop battery without making any configuration change.
TLP brings you the benefits of advanced power management for Linux without the need to understand every technical detail. TLP comes with a default configuration already optimized for battery life, so you may just install and forget it. Nevertheless TLP is highly customizable to fulfil your specific requirements.
TLP package is available in most of the Linux distribution official repository such as Arch, Debian, Fedora, Gentoo, openSUSE, etc. Use your distribution Package Manager to install the TLP utility.
Just run the following command to get the battery and it’s related information on Linux.
$ sudo tlp-stat -b --- TLP 1.1 -------------------------------------------- +++ Battery Status /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/manufacturer = SMP /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/model_name = L14M4P23 /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/cycle_count = (not supported) /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/energy_full_design = 60000 [mWh] /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/energy_full = 52260 [mWh] /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/energy_now = 21950 [mWh] /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/power_now = 10923 [mW] /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/status = Discharging Charge = 42.0 [%] Capacity = 87.1 [%]
To see other information as well.
$ sudo tlp-stat -s --- TLP 1.1 -------------------------------------------- +++ System Info System = LENOVO Lenovo ideapad Y700-15ISK 80NV BIOS = CDCN35WW Release = "Manjaro Linux" Kernel = 4.19.6-1-MANJARO #1 SMP PREEMPT Sat Dec 1 12:21:26 UTC 2018 x86_64 /proc/cmdline = BOOT_IMAGE=/boot/vmlinuz-4.19-x86_64 root=UUID=69d9dd18-36be-4631-9ebb-78f05fe3217f rw quiet resume=UUID=a2092b92-af29-4760-8e68-7a201922573b Init system = systemd Boot mode = BIOS (CSM, Legacy) +++ TLP Status State = enabled Last run = 07:16:12 IST, 4362 sec(s) ago Mode = battery Power source = battery
How to check Laptop Battery status using ACPI Command?
ACPI stands for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface modules are kernel modules for different ACPI parts. They enable special ACPI functions or add information to /proc or /sys. These information can be parsed by acpid for events or other monitoring applications.
$ acpi Battery 0: Charging, 43%, 01:05:11 until charged
$ acpi -i Battery 0: Charging, 43%, 01:05:07 until charged Battery 0: design capacity 3817 mAh, last full capacity 3324 mAh = 87% To see more details about battery and related information.
$ acpi -V Battery 0: Charging, 43%, 01:05:07 until charged Battery 0: design capacity 3815 mAh, last full capacity 3323 mAh = 87% Adapter 0: on-line Cooling 0: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 1: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 2: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 3: iwlwifi 0 of 19 Cooling 4: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 5: iwlwifi no state information available Cooling 6: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 7: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 8: Processor 0 of 10 Cooling 9: intel_powerclamp no state information available Cooling 10: x86_pkg_temp no state information available Cooling 11: Processor 0 of 10
How to check Laptop Battery status using Batstat Command?
batstat is a command line tool to print battery status in linux terminal.
Status: Charging Max energy: 50.00 Wh Energy left: 24.50 Wh Power Consumption: 26.40 W Percentage left: 49.00% Average power Consumption: 0.00 W Time elapsed: 0: 0:12 since 49.00% = Time ======== Percent ============================================ 0: 0: 0 49.00%
How to check Laptop Battery status using sysfs filesystem?
The sysfs filesystem is a pseudo-filesystem which provides an interface to kernel data structures. The files under sysfs provide information about devices, kernel modules, filesystems, and other kernel components.
The sysfs filesystem is commonly mounted at /sys. Typically, it is mounted automatically by the system, but it can also be mounted manually using a command such as mount -t sysfs sysfs /sys
Many of the files in the sysfs filesystem are read-only, but some files are writable, allowing kernel variables to be changed. To avoid redundancy, symbolic links are heavily used to connect entries across the filesystem tree.
$ cat /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/* 0 51 Normal 0 cat: /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/device: Is a directory 52260000 60000000 26660000 SMP L14M4P23 cat: /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/power: Is a directory 27656000 1 756 Charging cat: /sys/class/power_supply/BAT0/subsystem: Is a directory Li-ion Battery POWER_SUPPLY_NAME=BAT0 POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS=Charging POWER_SUPPLY_PRESENT=1 POWER_SUPPLY_TECHNOLOGY=Li-ion POWER_SUPPLY_CYCLE_COUNT=0 POWER_SUPPLY_VOLTAGE_MIN_DESIGN=14800000 POWER_SUPPLY_VOLTAGE_NOW=15840000 POWER_SUPPLY_POWER_NOW=27656000 POWER_SUPPLY_ENERGY_FULL_DESIGN=60000000 POWER_SUPPLY_ENERGY_FULL=52260000 POWER_SUPPLY_ENERGY_NOW=26660000 POWER_SUPPLY_CAPACITY=51 POWER_SUPPLY_CAPACITY_LEVEL=Normal POWER_SUPPLY_MODEL_NAME=L14M4P23 POWER_SUPPLY_MANUFACTURER=SMP POWER_SUPPLY_SERIAL_NUMBER= 756 14800000 15840000
3 Tools To Display Linux Laptop Battery Information From the Command Line
This article explains how to display Linux laptop battery information from the command line. Using the tools below, you’ll be able to check the current battery discharging rate, the battery capacity (current, full and design), current battery voltage, temperature, and more.
1. Get laptop battery information from the command line using battop.
battop, or rust-battop is an interactive viewer similar to top, htop and other such utilities, but for battery information / statistics.
The tool runs on Linux, macOS, FreeBSD and DragonflyBSD (no Windows support yet) and it supports multiple batteries. As for the information it can display, this includes charge state, voltage, battery discharging rate, temperature (this didn’t work for my laptop though), battery capacity information (current, when full, and full design), time to full / empty, charge cycles count, and more.
To install battop, grab the binary from the tool’s GitHub releases page, and place it in your home folder. Next, use the following command to install it to /usr/local/bin :
sudo install battop-* /usr/local/bin/battopYou can also install battop from AUR on Arch Linux Manjaro, and from source, using cargo. See this page for details.
Once installed, to view your battery status and various info simply type battop in a terminal.
2. Get Linux laptop battery information using UPower.
UPower is an abstraction for enumerating power devices, listening to device events and querying history and statistics. It comes with a command line tool (also called upower) that, among others, allows querying the battery history and statistics.
To use the UPower command line tool to get information / statistics about your Linux laptop battery, the first thing you need to do is figure out the battery path. This can be done with the UPower —enumerate ( -e ) command line flag, which enumerates object paths for devices:
Here’s the command with output from my ASUS laptop:
$ upower -e
/org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/line_power_AC0
/org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0
/org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/DisplayDeviceThe path you’re looking for is the one that contains BAT at the end (it can be BAT0, BAT1, BATT, etc.) In this case, the battery path is /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0 .
Now that we know the battery path, we can use the UPower command line tool to display information about the laptop battery (replace the path below with your battery’s path, as explained above):
upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0This is how the output of this command looks for my ASUS laptop:
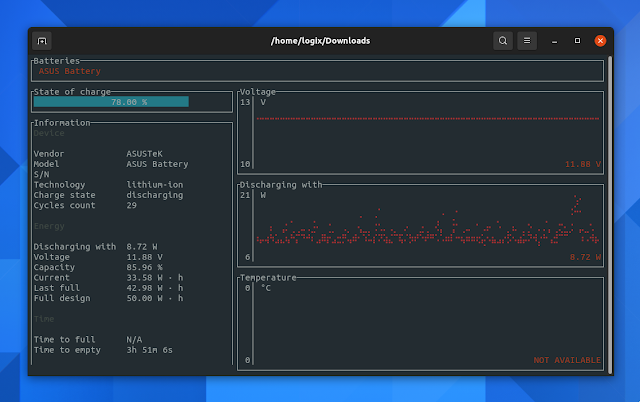
$ upower -i /org/freedesktop/UPower/devices/battery_BAT0
native-path: BAT0
vendor: ASUSTeK
model: ASUS Battery
power supply: yes
updated: Wed 19 May 2021 11:13:41 (35 seconds ago)
has history: yes
has statistics: yes
battery
present: yes
rechargeable: yes
state: discharging
warning-level: none
energy: 36.509 Wh
energy-empty: 0 Wh
energy-full: 42.982 Wh
energy-full-design: 50.002 Wh
energy-rate: 12.969 W
voltage: 11.877 V
time to empty: 2.8 hours
percentage: 84%
capacity: 85.8426%
technology: lithium-ion
icon-name: 'battery-full-symbolic'
History (charge):
1621412021 84.000 discharging
History (rate):
1621412021 12.969 discharging3. Get battery information from the command line using ACPI.
Another way of displaying the battery status from the command line on Linux is to use ACPI. This shows information from the /proc or the /sys filesystem, such as battery status or thermal information.
To show all the battery information available via ACPI, run:
This is the command with output from my laptop:
$ acpi -V
Battery 0: Discharging, 81%, 02:35:35 remaining
Battery 0: design capacity 4209 mAh, last full capacity 3618 mAh = 85%
Adapter 0: off-line
Thermal 0: ok, 48.0 degrees C
Thermal 0: trip point 0 switches to mode critical at temperature 103.0 degrees C
Cooling 0: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 1: SEN3 no state information available
Cooling 2: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 3: pch_cannonlake no state information available
Cooling 4: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 5: x86_pkg_temp no state information available
Cooling 6: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 7: INT3400 Thermal no state information available
Cooling 8: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 9: SEN2 no state information available
Cooling 10: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 11: SEN4 no state information available
Cooling 12: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 13: B0D4 no state information available
Cooling 14: intel_powerclamp no state information available
Cooling 15: iwlwifi_1 no state information available
Cooling 16: Processor 0 of 3
Cooling 17: SEN1 no state information availableOr you could only use acpi to show the current battery status, charge level, design and full capacity, using acpi -i . Example with output:
$ acpi -i
Battery 0: Discharging, 68%, 03:42:57 remaining
Battery 0: design capacity 4209 mAh, last full capacity 3618 mAh = 85%You can also query ACPI for specific info, e.g. to show battery information only use -b , to show thermal information use -t , etc. See the ACPI help for details ( acpi -h and man acpi ).