- How to Use Linux Cat Command (With Examples)
- cat Command Syntax
- Linux Cat Command Examples
- 1. Create a New File
- 2. Display Contents of a Single File
- 3. Display Contents of Multiple Files
- 4. Redirect Contents of a Single File
- 5. Redirect Contents of Multiple Files
- 6. Display the Contents in Reverse Order
- 7. Append File Contents to Another File
- 8. Append Text to Existing File
- 9. Combine Operations
- 10. More and Less Options (Manage Large Files)
- 11. Show Line Numbering
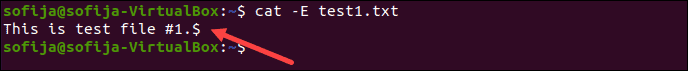
- 12. Show the End of Line
- 13. Show TAB Separated Lines
- 14. Remove Blank Lines
- 15. List All CAT Commands
- Команда cat Linux
- Команда cat
- Использование cat в Linux
- Выводы
How to Use Linux Cat Command (With Examples)
If you have worked in Linux, you surely have seen a code snippet that uses the cat command. Cat is short for concatenate. This command displays the contents of one or more files without having to open the file for editing.
In this article, learn how to use the cat command in Linux.
cat Command Syntax
To use the cat command, follow the format:
[options] – This lets you issue additional instructions to the cat command. For example, to display the contents of a file with each line numbered, use the –n option:
filename(s) – Specify the name of the file (or files) that you want to display. If you use more than one filename, each file will be displayed.
Linux Cat Command Examples
This article includes 15 cat commands and examples of how to use them. To try out the commands, create a couple of sample files, and test the cat commands listed below.
1. Create a New File
You can create new files and add content to them using the cat command.
Create test1.txt and test2.txt, which you can use as sample files to test out the other commands.
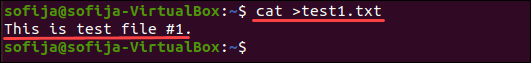
1. Open a terminal window and create the first file:
2. The cursor moves to a new line where you can add the wanted text. Type a simple sentence such as:
3. To exit the prompt and write the changes to the file, hold the Ctrl key and press d.
4. Repeat the process to create test2.txt. Run:
6. Press Ctrl+d.
2. Display Contents of a Single File
To display the contents of test1.txt using the cat command run:
The output displays the content as in the image below.
3. Display Contents of Multiple Files
To display the contents of both files, run the command:
4. Redirect Contents of a Single File
Instead of displaying the contents of a file on the screen, cat can put them in a file.
If the destination filename doesn’t exist, it will be created. If you run cat on test3.txt, you should see the contents from test1.txt:
If a file is exported that already exists, this will overwrite the contents of the file:
The test3.txt file now has the following content:
5. Redirect Contents of Multiple Files
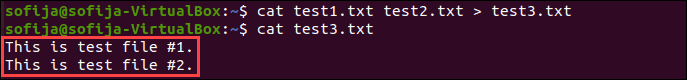
You can redirect the contents of multiple file into one single file:
cat test1.txt test2.txt > test3.txtDisplay the content of test3.txt with:
The output shows the contents of both files, as in the image below.
6. Display the Contents in Reverse Order
The cat command can display the content of a file in reverse order (by lines). To do this, use tac (cat in reverse):
7. Append File Contents to Another File
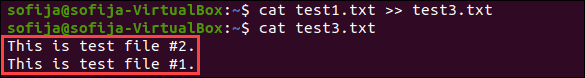
The cat command can add the contents of a file to the end of another file. Instead of using a single > sign, use a double >> sign:
Open the test3 file by running:
The content of test3 followed by test1 should display.
Note: If you want to remove the sample files, take a look at how to remove files and directories using the Linux command line.
8. Append Text to Existing File
You can use a similar command to append text to an existing file:
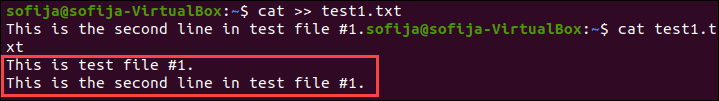
Add a new line to the file:
This is the second line in test file #1.Hold Ctrl and hit d.
Check the content of the test1.txt file:
9. Combine Operations
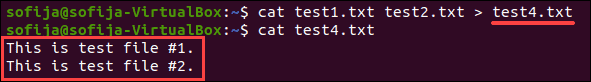
The functions of the cat command can be combined. For example, to combine the output of two files, and store the result in a new file:
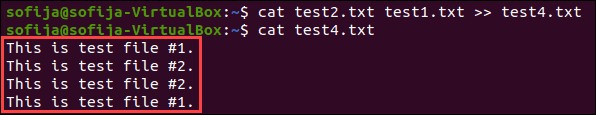
cat test1.txt test2.txt > test4.txtAlternately, you can append multiple files to the end of an existing file:
cat test2.txt test1.txt >> test4.txtNote that the order specified is the order the files in which they are added to the destination file.
Note: Once you have created multiple files, you may want to group them in a single directory. Take a look at how to use mkdir command to make or create a Linux directory.
10. More and Less Options (Manage Large Files)
If you use cat on a very large file, you’ll end up with a huge string of data that’s hard to read. You can break it into pages using | more :
This displays a single page of the file. When you press a key, it will scroll to the next page.
If you’d like the ability to scroll forward and backward through the display, use | less .
Note: Learn how to use the Linux split command to easily manage text files with many lines.
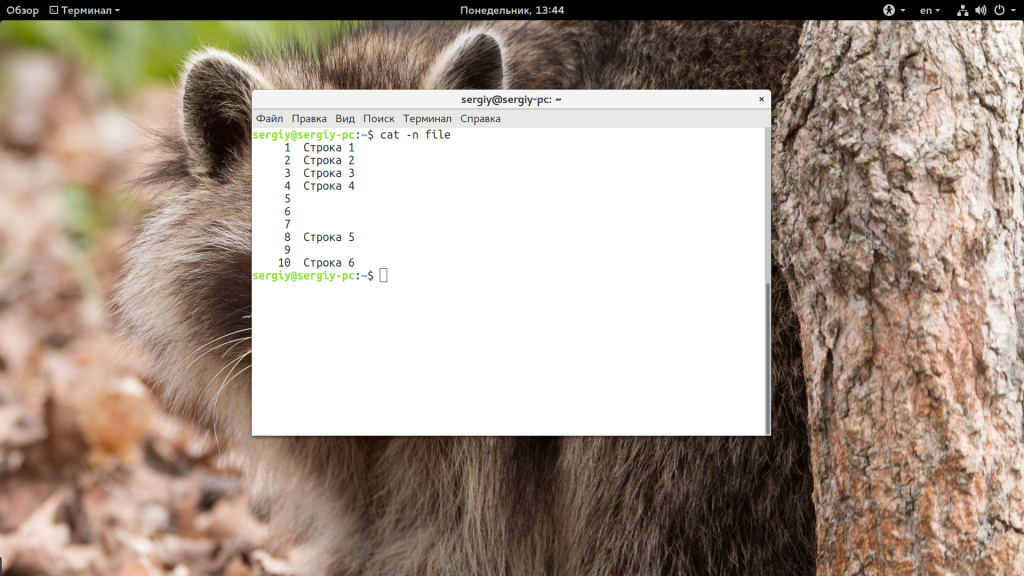
11. Show Line Numbering
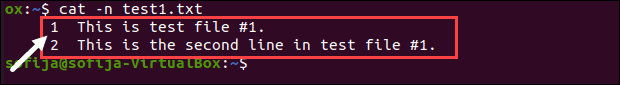
You may find it useful to have line numbers in the output, especially for large files. To enable line numbering, add the -n option to the cat command:
The output should appear as in the image below:
12. Show the End of Line
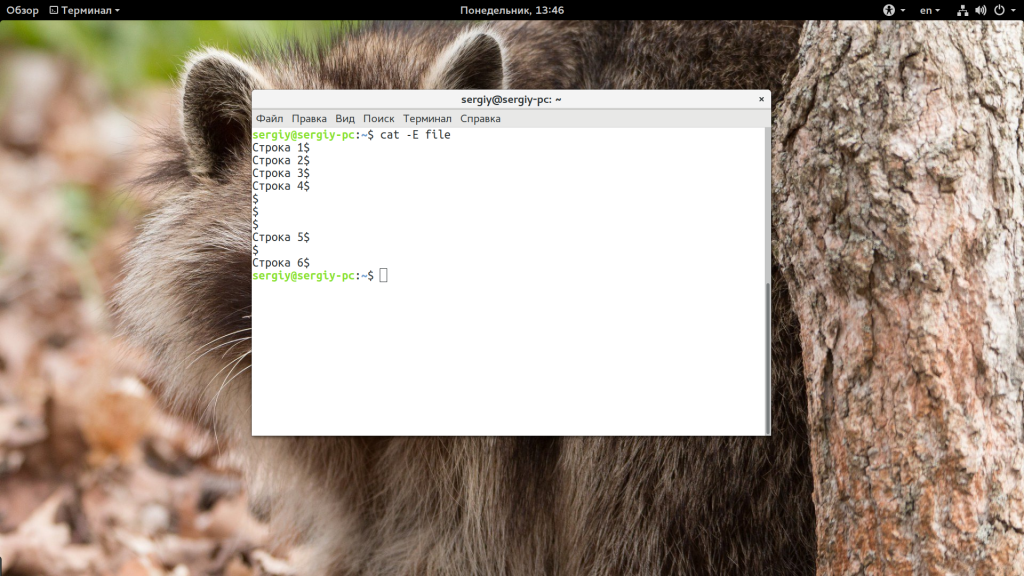
You can instruct cat to highlight the end of each line and spaces between lines with $.
Since the sample file test1.txt has only one line, the output shows one $ at the end of it.
13. Show TAB Separated Lines
The cat command has the option of displaying the file content along with the tab space within the text.
To show tab separated lines for a sample run:
The tab space within the text is represented by ^I.
14. Remove Blank Lines
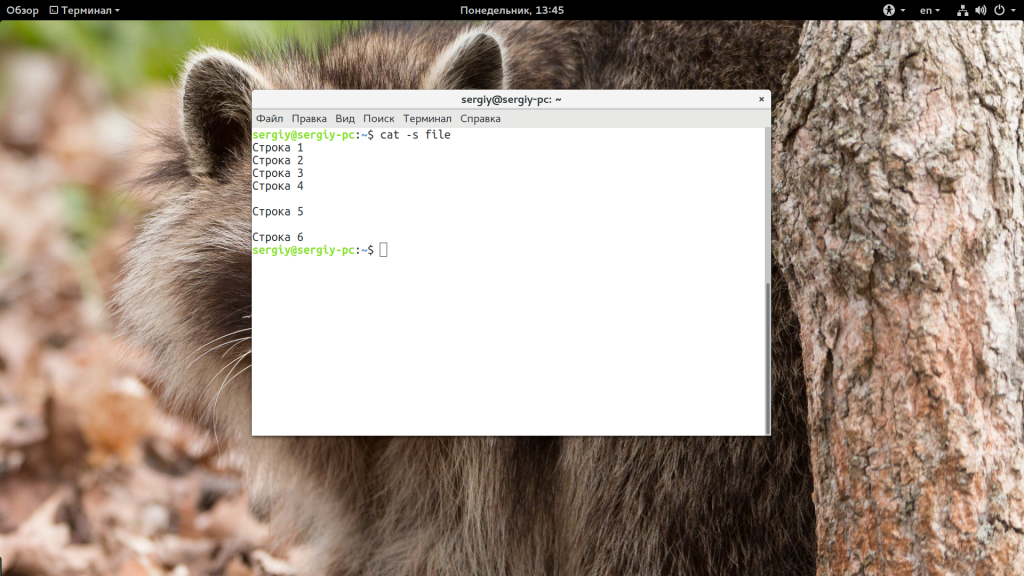
To omit blank lines from the output of cat with the –s option:
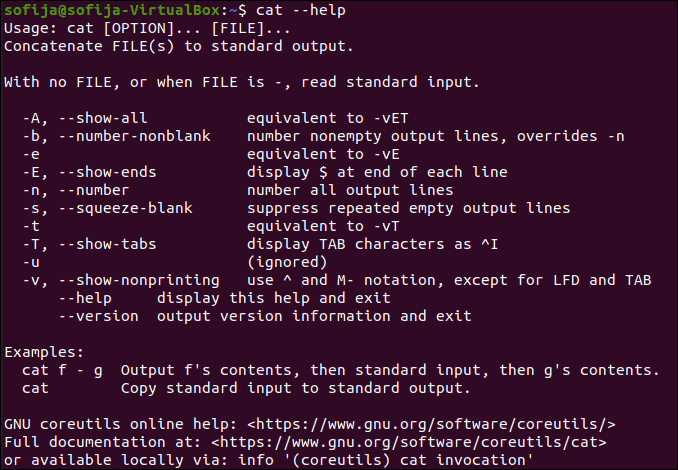
15. List All CAT Commands
If you have trouble remembering the options, use the —help command:
You should now have a good understanding of how to use the cat command in Linux.
Want to master more Linux commands? Check out our list of Linux Commands All Users Should Know.
Sofija Simic is an experienced Technical Writer. Alongside her educational background in teaching and writing, she has had a lifelong passion for information technology. She is committed to unscrambling confusing IT concepts and streamlining intricate software installations.
This guide details the most useful grep commands for Linux / Unix systems. After going through all the.
This article shows which commands best to use when compressing and decompressing files from the command line.
Creating a file in Linux might seem straightforward, but there are some surprising and clever techniques. In.
A text editor is an application that lets you type text. All Linux distributions come with built-in editors.
Команда cat Linux
Команда cat — это одна из самых часто используемых команд Linux. Она часто применяется опытными пользователями во время работы с терминалом. С помощью этой команды можно очень просто посмотреть содержимое небольшого файла, склеить несколько файлов и многое другое.
Несмотря на то что утилита очень проста и решает только одну задачу в лучшем стиле Unix, она будет очень полезной. А знать о ее дополнительных возможностях вам точно не помешает. В этой статье будет рассмотрена команда cat linux, ее синтаксис, опции и возможности.
Команда cat
Название команды — это сокращения от слова catenate. По сути, задача команды cat очень проста — она читает данные из файла или стандартного ввода и выводит их на экран. Это все, чем занимается утилита. Но с помощью ее опций и операторов перенаправления вывода можно сделать очень многое. Сначала рассмотрим синтаксис утилиты:
$ cat опции файл1 файл2 .
Вы можете передать утилите несколько файлов и тогда их содержимое будет выведено поочередно, без разделителей. Опции позволяют очень сильно видоизменить вывод и сделать именно то, что вам нужно. Рассмотрим основные опции:
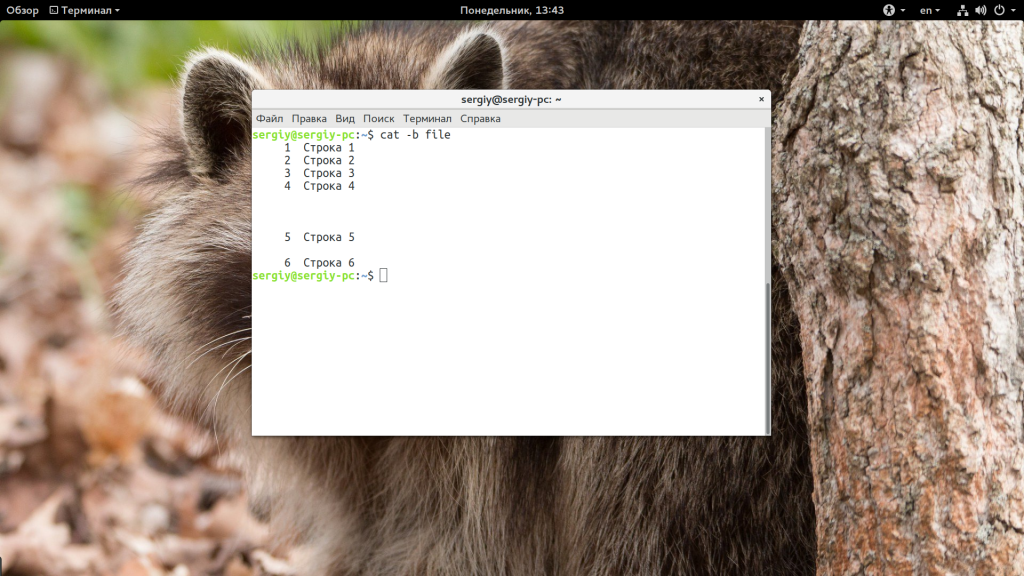
- -b — нумеровать только непустые строки;
- -E — показывать символ $ в конце каждой строки;
- -n — нумеровать все строки;
- -s — удалять пустые повторяющиеся строки;
- -T — отображать табуляции в виде ^I;
- -h — отобразить справку;
- -v — версия утилиты.
Это было все описание linux cat, которое вам следует знать, далее рассмотрим примеры cat linux.
Использование cat в Linux
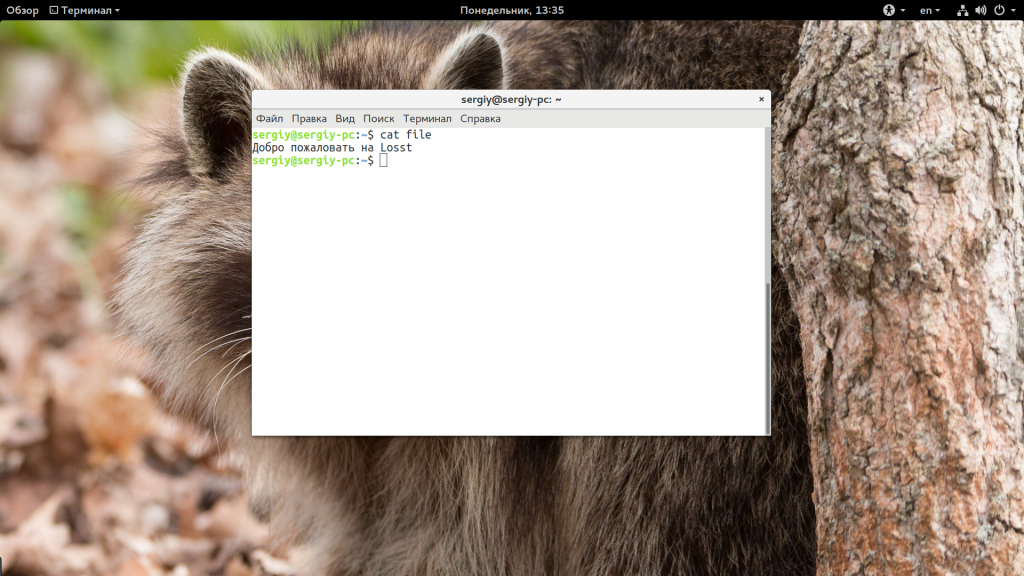
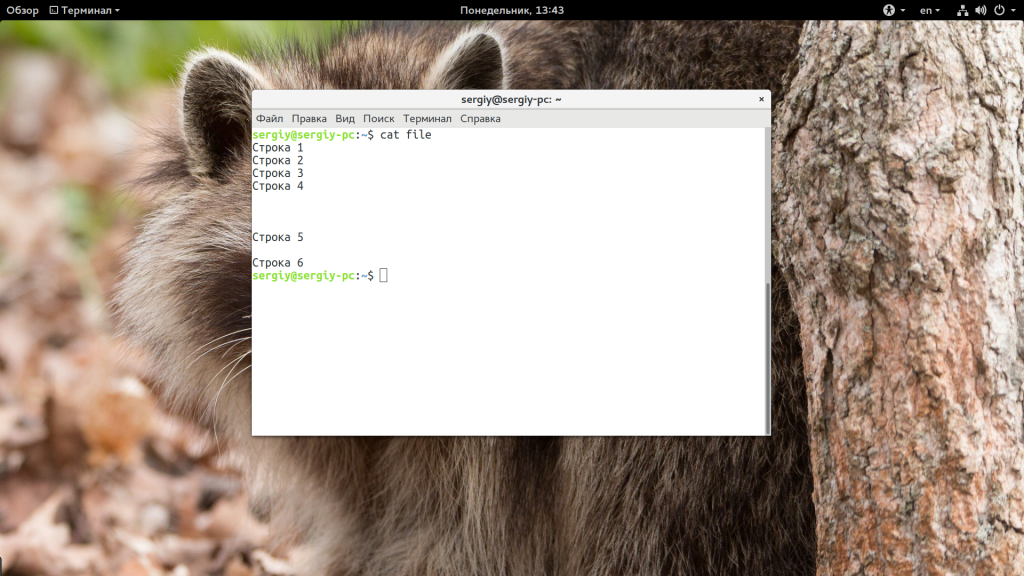
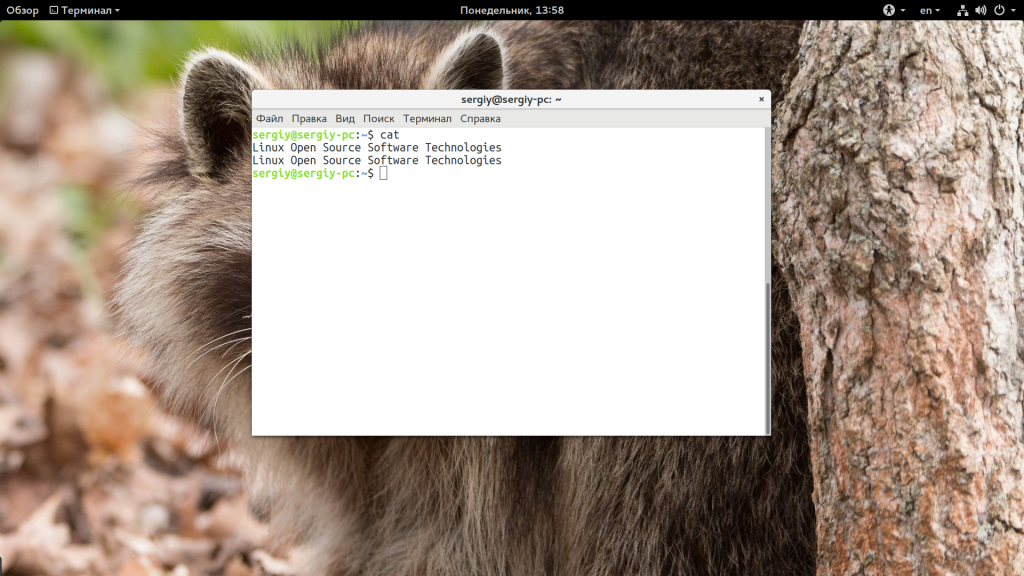
Самое простое и очевидное действие, где используется команда cat linux — это просмотр содержимого файла, например:
Команда просто выведет все, что есть в файле. Чтобы вывести несколько файлов достаточно просто передать их в параметрах:
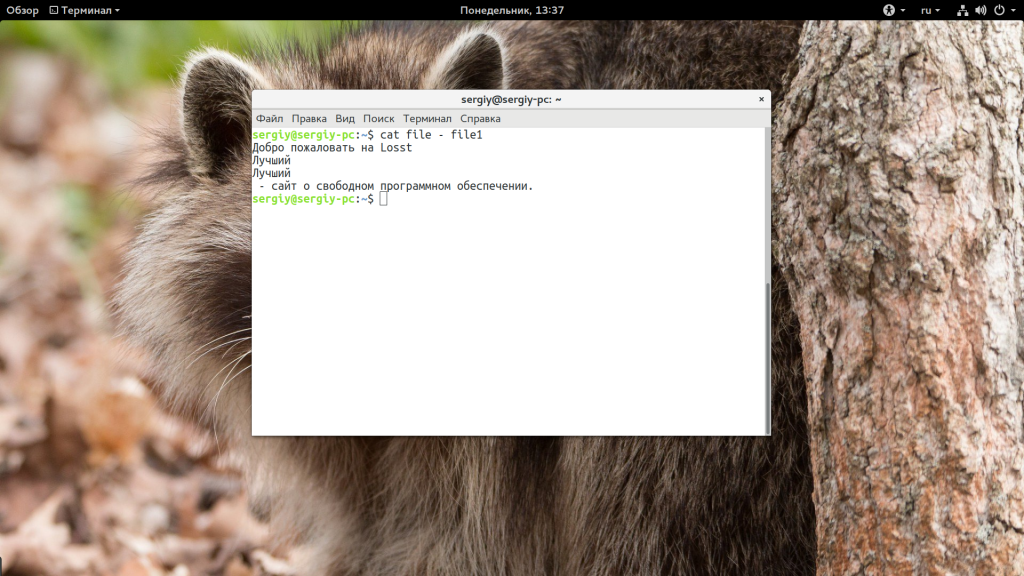
Как вы знаете, в большинстве команд Linux стандартный поток ввода можно обозначить с помощью символа «-«. Поэтому мы можем комбинировать вывод текста из файла, а также стандартного ввода:
Теперь перейдем к примерам с использованием ранее рассмотренных опций, чтобы нумеровать только непустые строки используйте:
Также вы можете нумеровать все строки в файле:
Опция -s позволяет удалить повторяющиеся пустые строки:
А с помощью -E можно сообщить утилите, что нужно отображать символ $ в конце каждой строки:
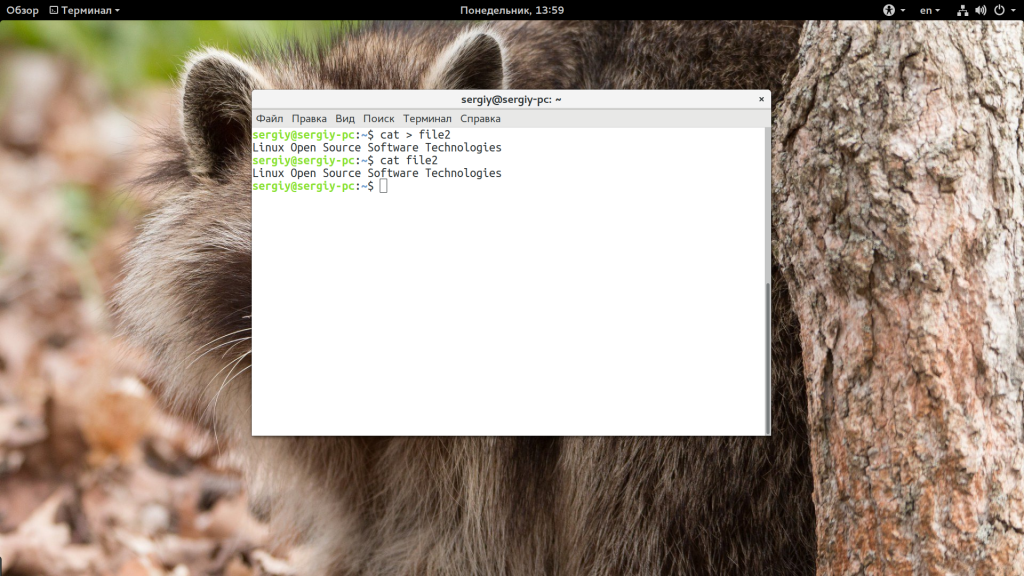
Если вы не передадите никакого файла в параметрах утилите, то она будет пытаться читать данные из стандартного ввода:
Для завершения записи нажмите Ctrl+D. Таким образом можно получить очень примитивный текстовый редактор — прочитаем ввод и перенаправим его вместо вывода на экран в файл:
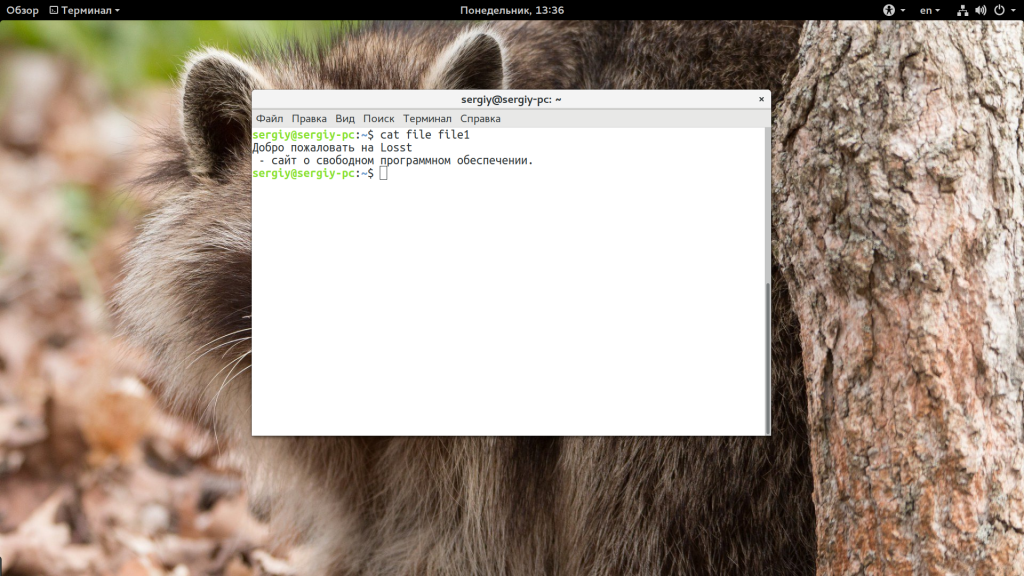
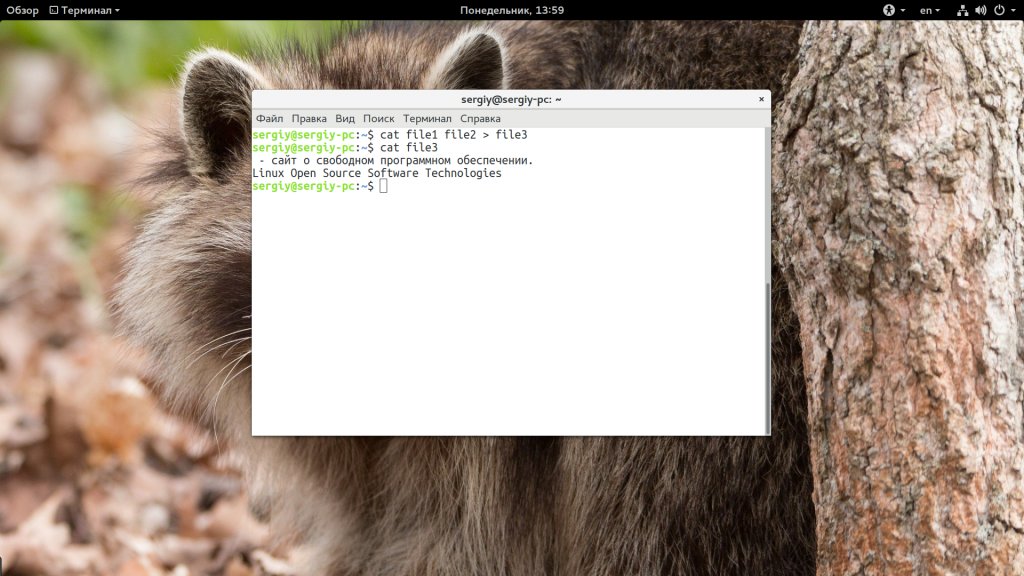
Возможность объединения нескольких файлов не была бы настолько полезна, если бы нельзя было записать все в один:
cat file1 file2 > file3
$ cat file3
Вот, собственно, и все возможности команды cat, которые могут быть полезны для вас.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели что представляет из себя команда cat linux и как ею пользоваться. Надеюсь, эта информация была полезной для вас. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.