- How to change ubuntu’s server date and time via command line?
- 7 Answers 7
- How to Work with Date and Time in Bash Using date Command
- Change Linux System Date and Time
- Formatting Options
- Handling Date in Linux
- Handling Time in Linux
- With –date or -d Flag
- Common Operations
- How To Set or Change Time Zone/Date/Time on Ubuntu
- Using timedatectl to Control the System Time and Date
- Display Current Date and Time with timedatectl
- Sync Time to NIST Atomic Clock
- How to Change the Time
- How to Change the Date
- How to Set a Timezone in Ubuntu
- How to Set Universal Time (UTC) in Ubuntu
- How to Sync Hardware Clock
- Set Hardware Clock to Sync to Local Timezone
- Set the Hardware Clock to Sync with UTC
- Set Time, Date Timezone in Ubuntu Older Versions From Command Line
How to change ubuntu’s server date and time via command line?
The Ubuntu server’s current date and time is different from the time zone date and time. I have tried using:
sudo date "30 Sep 2015 4:43:42" to change it but it did not change the date and time, just printed on terminal the date and time I changed, but when I executed:
The date and time is still the old one. What is the correct way to change date and time of Ubuntu Server?
7 Answers 7
You can set the system date with this command:
sudo date --set="2015-09-30 10:05:59.990" Then when using date , it should be showed correctly.
Now you should also the set hardware clock in the BIOS of the system, that the setting persists over a reboot (dureing the startup the system time is set to the value of the hardware clock). Do that with hwclock :
This gets the system clocks (sys) value and sets the hardware clock (hc). Check it with the hwclock command. Both hwclock and date should now show the same date and time.
To set your timezone, you can use this command:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata BTW: If you use a this machine as a server, I strongly recommend using an NTP-Client to sync the time over network. So you can guarantee that all your servers have the exactly same time set. This will sync the time while the machine runs. If you have applications which are dependent of synced time over server, I recommend the NTP-Daemon. The longer it runs in the background, the more precise is the time.
How to Work with Date and Time in Bash Using date Command
Date command is an external bash program that allows to set or display system date and time. It also provides several formatting options. Date command is installed in all Linux distros by default.
Type date command in terminal which will display current date and time.
Change Linux System Date and Time
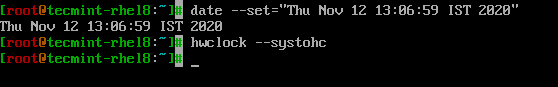
Using date command, system date, time and timezone can be modified and the change has to be synced with the hardware clock.
$ date --set="Thu Nov 12 13:06:59 IST 2020" $ hwclock --systohc
Formatting Options
A good place to get the list of formatting options will be the man page.
Let’s see some of the most common formatting options that we will use.
- To apply formatting use “+ followed by “formatter“.
- To get a list of formatting options for GNU\LINUX take a look at the linked man page.
- To get a list of formatting options for BSD take a look at the linked man page.
The two important parts of the date command is using Format +% and –date option.
Now let’s apply some formatting on the date command. To apply formatting, add plus sign (+) followed by %formatter as shown in examples.
Handling Date in Linux
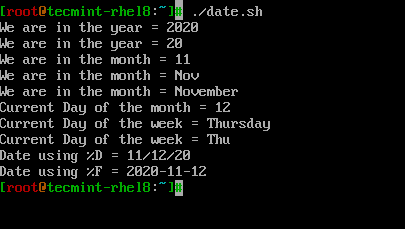
Let’s take a look at how to use date related formatters in a simple shell script called ‘date.sh‘.
# PRINT YEAR,MONTH,DAY AND DATE. echo "We are in the year = $(date +%Y)" echo "We are in the year = $(date +%y)" # Difference between %Y and %y is %Y will print 4 digits while %y will print the last 2 digits of the year. echo "We are in the month = $(date +%m)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%b)" echo "We are in the month = $(date +%B)" # Difference between %B and %b is, %B will print full month name while %b will print abbreviated month name. echo "Current Day of the month = $(date +%d)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%A)" echo "Current Day of the week = $(date +%a)" # Difference between %A and %a is, %A will print full Weekday name while %a will print abbreviated weekday name. # Instead of formatting to get the date, we can use %D which will print the date as %m/%d/%y or %F which prints in %Y-%M-%d format. echo "Date using %D = $(date +%D)" echo "Date using %F = $(date +%F)"
Handling Time in Linux
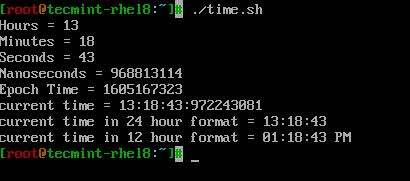
Let’s take a look at how to use time related formatters in a simple shell script called ‘time.sh‘.
# PRINT HOURS, MINS, SECONDS, NANO SECONDS echo Hours = $(date +%H) echo Minutes = $(date +%M) echo Seconds = $(date +%S) echo Nanoseconds = $(date +%N) echo Epoch Time = $(date +%s) echo "current time = $(date +%H:%M:%S:%N)" # can also use %T which displays Time in HH:MM:SS format. echo "current time in 24 hour format = $(date +%T)" # can also use %r to display time in 12 hour format. echo "current time in 12 hour format = $(date +%r)"
With –date or -d Flag
With —date or -d flag input can be passed as string and date command knows to handle it smartly.
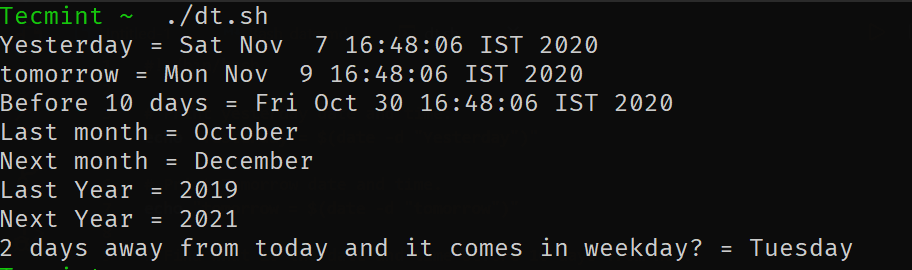
Let’s see some examples to understand how it works.
# Print yesterday's date and time. echo "Yesterday = $(date -d "Yesterday")" # Print Tomorrow date and time. echo "tomorrow = $(date -d "tomorrow")" # Find what is the date and time before 10 days from now. echo "Before 10 days = $(date -d "tomorrow -10 days")" # Find last month and next month echo "Last month = $(date -d "last month" "%B")" echo "Next month = $(date -d "next month" "%B")" # Find last year and next year echo "Last Year = $(date -d "last year" "+%Y")" echo "Next Year = $(date -d "next year" "+%Y")" # Forecast the weekday echo "2 days away from today and it comes on weekdays? = $(date -d "Today +2 days" "+%A")
Common Operations
calculate the number of days between 2 given dates.
$ echo $(( ( $(date -d "2020-11-10" "+%s") - $(date -d "2020-11-01" "+%s") ) / 86400))
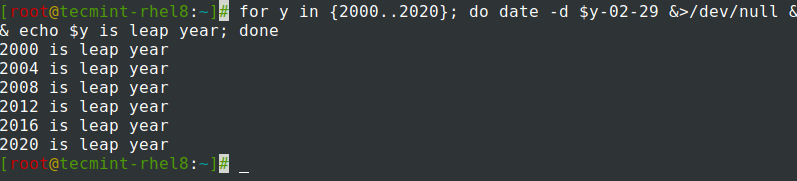
Find the given year is leap year or not.
$ for y in ; do date -d $y-02-29 &>/dev/null && echo $y is leap year; done
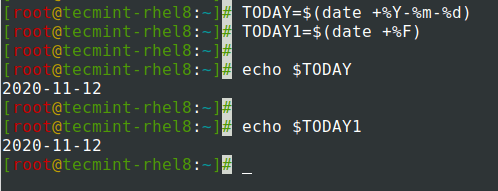
Assigning output of date command to a variable.
$ TODAY=$(date +%Y-%m-%d) OR $ TODAY1=$(date +%F) $ echo $TODAY $ echo $TODAY1
Create log files with the date added to the filename.
Adding date and time while creating log files, backup, or text files is a common operation that we will encounter most often. Let’s take an example, to take a backup, we have created a shell script.
This script will take a backup from 00:00 to 23:59 and scheduled to run daily at 00:00 of the next day. We want to create log files with yesterday’s date format.
CUSTOM_FORMAT=$(date —date «Yesterday» «+%d-%y-%H:%M») LOG_FILE=/var/log/custom_application/application_$.log echo «Script started» >> $ . CODE BLOCKS . echo «Script completed» >> $
That’s it for this article. In this article, we have seen how to use bash date and time in Linux. Let us know your feedback.
How To Set or Change Time Zone/Date/Time on Ubuntu
Modern operating systems detect and synchronize time using NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) time servers. NIST operates an atomic clock that neither gains nor loses a second in 300 million years.
However, you may find that your system needs to be synchronized with NIST time servers properly.
This guide shows you how to check and change Ubuntu’s time, date, and timezone.
- Some operations may require sudo or root privileges
- The command line/terminal window (Ctrl-Alt-T)
Using timedatectl to Control the System Time and Date
Most modern Linux distributions such as Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu, Arch, CentOS v.7.x+, and other Unix-based systems provide the timedatectl utility. This command allows you to control and edit time and date settings using the command line.
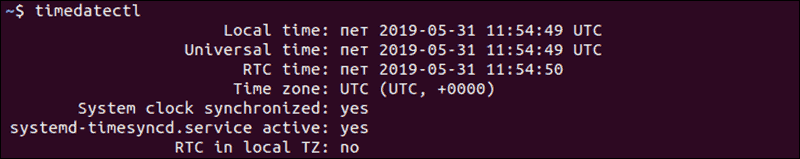
Display Current Date and Time with timedatectl
To display the current time and date information, use the command:
The output provides local time, universal time, and the timezone and informs you if the synchronization process is enabled.
Sync Time to NIST Atomic Clock
Set the Ubuntu system to synchronize to the NIST atomic clock with the following command:
To adjust the time and date manually, turn off NTP synchronizing with:
Note: NTP stands for Network Time Protocol.
How to Change the Time
To set the time to your specifications, use the following command:
timedatectl set-time 21:45:53The time format is HH:MM:SS (Hours, Minutes, Seconds). Ensure the automatic time synchronization is off to enable changes.
How to Change the Date
Use the same command to define the date on the system:
timedatectl set-time 2019-04-10The date format is YYYY-MM-DD (Year, Month, and Day).
How to Set a Timezone in Ubuntu
The timedatectl command additionally allows you to synchronize your systems with a time zone of your choosing. To change the time zone, follow the steps below:
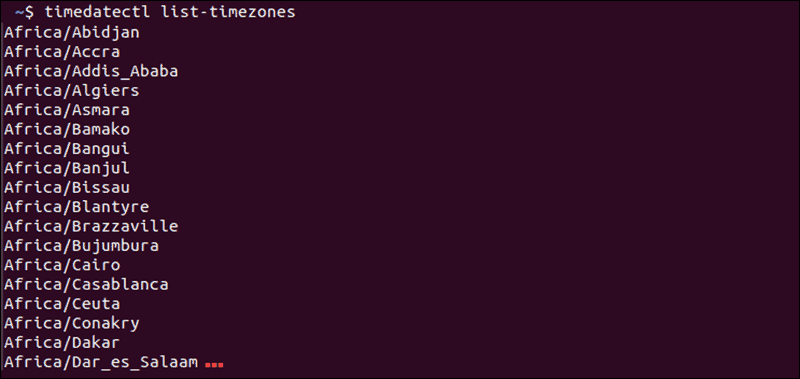
1. To list the names of the time zones, use:
timedatectl list-timezones2. Find the location closest to you, then enter the following:
timedatectl set-timezone Region/Location3. Replace Region/Location with a name from the time zone list.
The time zone list is extensive. Filter the list by keyword by piping the grep command:
timedatectl list-timezones | grep keywordSubstitute keyword for any keyword you wish, such as America , Asia , or New_York . If you get an error, double-check your spelling and make sure that you are using capital letters correctly.
How to Set Universal Time (UTC) in Ubuntu
UTC stands for Coordinated Universal Time and appears in scientific calculations and synchronizing between time zones across the globe. Synchronize your system with the following command:
timedatectl set-timezone UTCThere is no immediate output; however, you can check the applied settings with timedatectl .
Note: GMT and Zulu Time are often used to refer to UTC. They are equivalent terms when fractions of a second are not relevant.
How to Sync Hardware Clock
RTC stands for Real-Time Clock, another name for the hardware clock the computer. The system has a tiny quartz crystal and a battery that keeps time when the system disconnects from a network.
Set Hardware Clock to Sync to Local Timezone
To have the Real-Time Clock synchronize to your local time zone, enter:
timedatectl set-local-rtc 1You may get an error in this mode, since updating the hardware clock to the local time zone is unsupported.
Set the Hardware Clock to Sync with UTC
Set the hardware clock to synchronize with UTC by entering the following command:
timedatectl set-local-rtc 0As with the previous command, there is no confirmation that the change has applied. Verify the change manually with the timedatectl command.
Set Time, Date Timezone in Ubuntu Older Versions From Command Line
Older Ubuntu versions may not support the timedatectl command. Find out how to check the Ubuntu version.
There are alternative commands to display and adjust system time setting from a command line. Use the commands listed below:
sudo date -s "YY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS"Replace YY-MM-DD with Year-Month-Day, and HH:MM:SS with Hour:Minute:Second. You can set just the date or only the time, depending on your needs.
sudo hwclock --show --verboseNote: Some versions may not support the —verbose option, and it may not work on a virtual machine. The hardware clock may not hold the same time as the operating system.
sudo hwclock --set --date "MM/DD/YY HH:MM:SS"This command tells the system to set the HC (hardware clock) to SYS (system):
Use this command to reverse the previous process.
This guide showed you how to set the time, date, and time zone on your Ubuntu system. Setting the system to synchronize with NTP is typically the best course of action.
Vladimir is a resident Tech Writer at phoenixNAP. He has more than 7 years of experience in implementing e-commerce and online payment solutions with various global IT services providers. His articles aim to instill a passion for innovative technologies in others by providing practical advice and using an engaging writing style.
Your server’s MySQL time zone and your own might be out of sync. Read this article to learn 2 ways of editing .
Finding out which Ubuntu version is running on your system can be important when troubleshooting issues or .
In this tutorial, learn the five most commonly used commands to check memory usage in Linux. We also provide .
You have probably noticed your Linux OS slowing down, especially when working harder. Understanding CPU .