- How do I configure my DNS settings in Ubuntu server?
- How to set DNS Nameserver on Ubuntu 20.04
- Change DNS Nameserver via GUI
- Change DNS Nameserver via Config File
- Why Change DNS Nameserver on Ubuntu?
- Change DNS Server Settings in Linux
- When must the DNS Server be Changed?
- Tutorial Change DNS Server Settings in Linux
- How to Change your DNS Server in GNOME
- How to Change DNS settings in Plasma
- Change your DNS Server Using Command line
- Change DNS on Linux Permanently
- Changing systemd configurations
- Use resolvconf
- FAQ
- How to change DNS Server in through an Ethernet cable?
- Conclusion
How do I configure my DNS settings in Ubuntu server?
According to this page it appears to be simple. However, /etc/bind does not exist on the default installation of Ubuntu 12.04.3 LTS server. So, without installing any further software, how can configure DNS and remove dnsmasq on ubuntu server? I am quite familiar with sudo & nano .
Also take a look at help.ubuntu.com/community/Dnsmasq. bind IS a nameserver. If you need nameserver functionality on your server, you must install a nameserver. It would help if you could describe what it is you are trying to achieve.
You were reading a manual to configure a DNS Server, not how to configure the DNS entries in the server. The manual you should have read are this
I don’t have the rep to post a comment on another answer, but in reply to Nullet’s answer on September 17th 2013, this worked for me. I was thinking that there was a problem with my router (a cheap, ISP provided one). I also think it worth mentioning that on the dns-nameservers line, you should use the IP of the public DNS. Don’t use the local address of the DNS, which is most likely on your router. I was connecting to the DNS on my router, which for some unknown reason wasn’t working with my server. Instead, I found out where the DNS on my router was getting its information from, and set dn
I think there is a better answer here unix.stackexchange.com/a/154538/82018 — basically you can override your dhcp settings to «prepend» a server in front of the ones you currently use. This is nice as you don’t have to rely solely on the new server, you just give it precedence for lookups.
How to set DNS Nameserver on Ubuntu 20.04
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates text-based domain names to numeric IP addresses. By default, most networks are configured to work with DNS servers supplied by the internet service provider. However, users are free to change the DNS nameservers.
This tutorial will show you how to change DNS nameservers on your Ubuntu machine using GUI or the command line.
- Ubuntu 20.04 (both methods also work on Ubuntu 18.04 and later)
- Access to the terminal
- Sudo privileges
Change DNS Nameserver via GUI
Use Ubuntu Settings to complete all the steps to change DNS addresses via the graphical user interface.
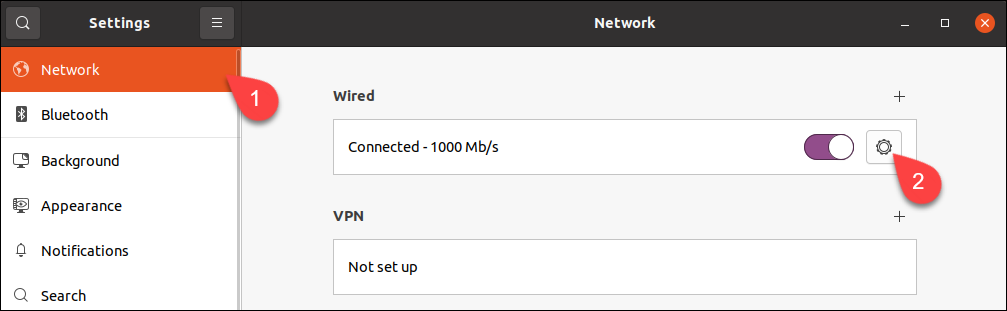
1. Launch Settings and click the Network tab in the menu on the left.
2. Click the cogwheel next to the connection you wish to set up.
Note: To change the settings for a wireless connection, select the Wi-Fi tab, choose a wireless network and proceed with the steps below.
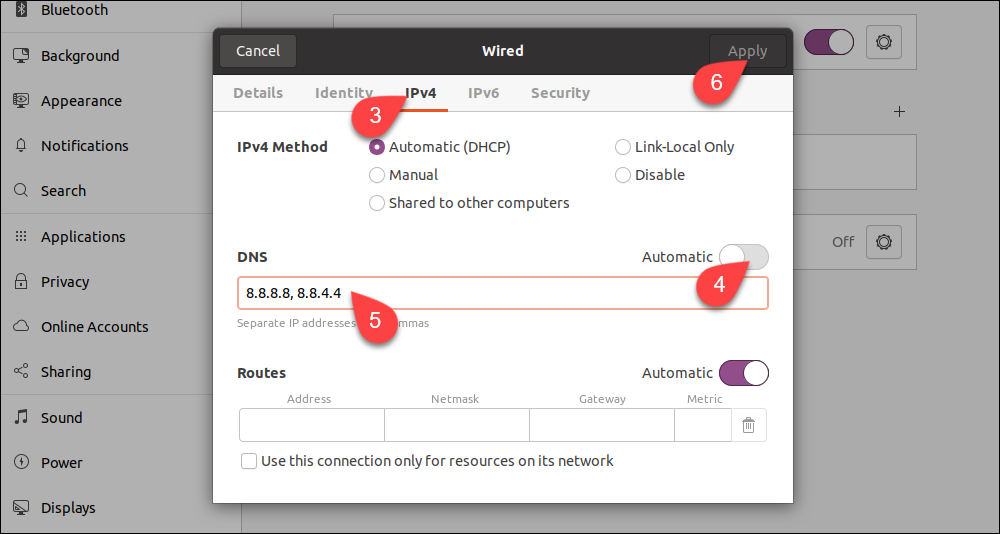
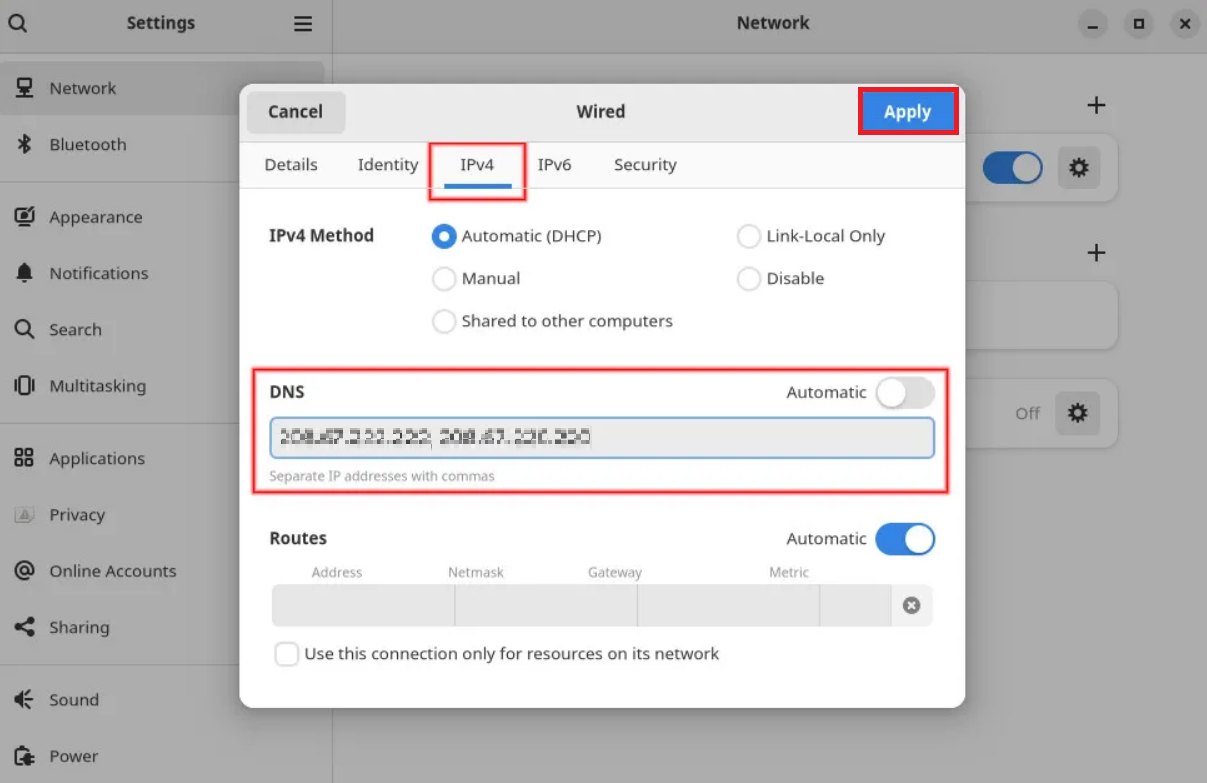
3. Go to the IPv4 tab.
4. Disable automatic DNS configuration by turning off the switch next to the DNS field.
5. Type new DNS addresses in the field. The example shows Google’s public DNS nameservers.
6. Click Apply.
The system is now configured to work with the new DNS servers.
Note: If you wish to set up IPv6 nameservers, go to the IPv6 tab and enter them there. The IPv6 address format is different from IPv4. For example, Google’s IPv6 DNS servers are: 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844 .
Change DNS Nameserver via Config File
If you do not use a GUI, change DNS settings with the command line Netplan tool.
1. Go to the Netplan directory:
2. List the directory contents with ls to see the name of the yaml file containing network configuration.
Open the file in a text editor. Your file may have a different name.
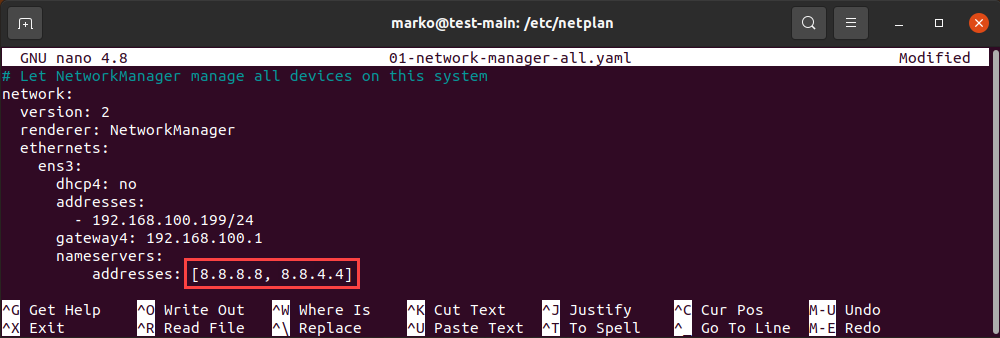
sudo nano 01-network-manager.yamlEthernet connections are listed in the ethernets section of the file. If there are any wireless connections, you can find them in the wifis section. Netplan stores the current DNS configuration parameters in nameservers subsections of each section.
Replace the addresses located in the file with the DNS addresses you want to use. You can enter more than two addresses. Save the changes and exit.
Note: The file on your system may lack the entire ethernets or wifis section. In that case, add the lines that are missing, making sure you respect the indentation provided in the example.
3. Apply the changes you made in the config file:
If the operation is successful, there is no output. To check if the system successfully applied the changes, type:
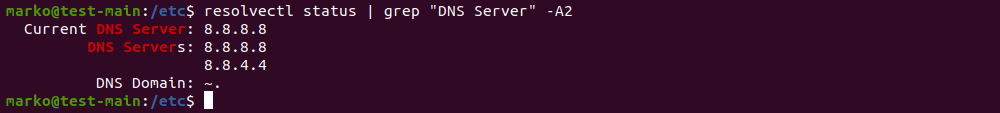
resolvectl status | grep "DNS Server" -A2The output lists your current DNS servers:
Why Change DNS Nameserver on Ubuntu?
In most cases, your default DNS settings offer optimal performance. However, there are scenarios in which you should consider switching to a third-party DNS provider:
- Large companies with better infrastructure are usually more capable of providing uninterrupted DNS service. If your ISP is unreliable and you experience frequent downtimes, switching the DNS provider may be the solution.
- Third-party DNS servers can be faster than those provided to you by your ISP.
Note: Since latency is the primary consideration for DNS, a fast third-party server located far away may provide inferior service to a slower one that is closer to you.
- Some DNS providers offer filters that prevent phishing sites from reaching your computer. The same mechanism is also used to block sensitive content on the internet. Businesses often employ this DNS feature.
- Internet Service Providers sometimes block content on the DNS level, so switching to another DNS nameserver may help you access some geo-restricted websites.
Note: Learn how to install PowerDNS on Ubuntu, a flexible and robust DNS solution.
This tutorial showed you how to set your DNS nameservers on Ubuntu, either using a GUI or CLI.
Change DNS Server Settings in Linux
Domain name server (DNS) translates the internet address to the numeric machine address. A DNS server converts each domain name you enter into your browser into an IP address. The website you want to visit can then be found and connected to using that address by your browser. Since your internet speed is affected by the DNS server you use, this article will teach you how to change DNS server settings in Linux.
After buying Linux VPS, you might need to change the DNS server on Linux whenever you find the servers your internet provider has set are not what you consider. Join us with this article to learn two different methods to change DNS server settings in Linux to troubleshoot the misconfiguration of your device’s DNS.
When must the DNS Server be Changed?
Previously, you have learned all about DNS and Trustable DNS servers were introduced to you. The setup and performance of DNS servers can have a significant impact on your online experience because they are such a fundamental component of internet communication. Every time you attempt to connect to a website, slow DNS servers will result in delays. You may find up on websites you didn’t plan to visit if DNS servers are misconfigured. DNS servers can also be configured to prevent you from viewing particular websites by your internet service provider, the government, or another organization. All of these potential issues can be fixed by switching your DNS servers.
This article will provide step-by-step instructions on how to modify your device’s DNS if it is incorrectly configured or if you want to do so to get around a website block. In the end, you will be able to change your DNS server with any version of Linux you are using fast and easily.
Tutorial Change DNS Server Settings in Linux
In this article, you will learn to change your DNS settings in Desktop and Terminal environments. Regardless of whether you are using Linux or windows, you can test the method of clearing DNS cache to solve some issues like getting 404 error or the problem accessing the site.
Let’s go through this guide by learning how to find the current DNS server on Linux. Simply, open your terminal and run the command below to see the current DNS server(s).
Your current network connections, together with the DNS servers utilized by each, are displayed in the output. Most of the time, only one connection will be active, and DNS information won’t be displayed for other entries.
How to Change your DNS Server in GNOME
Open the system setting app and click on Wi-Fi at the top left to switch to a new DNS server in GNOME. Once the list of available network connections is shown, you can see the network you are connected to at the top of the list (which displays the word Connected). Right beside that, click on the gear icon.
Click on the IPv4 tab in the dialog box that appears. Your preferred DNS servers can be entered in the space provided in the dialog box’s center. There is a toggle switch with the word Automatic right above the box. Just turn off automated settings and type your new DNS servers in the box provided, separating them with commas. After configuring your new DNS server addresses, simply click Apply in the top right corner to save your settings. To make sure the modifications were applied, use the resolvectl status command once more.
How to Change DNS settings in Plasma
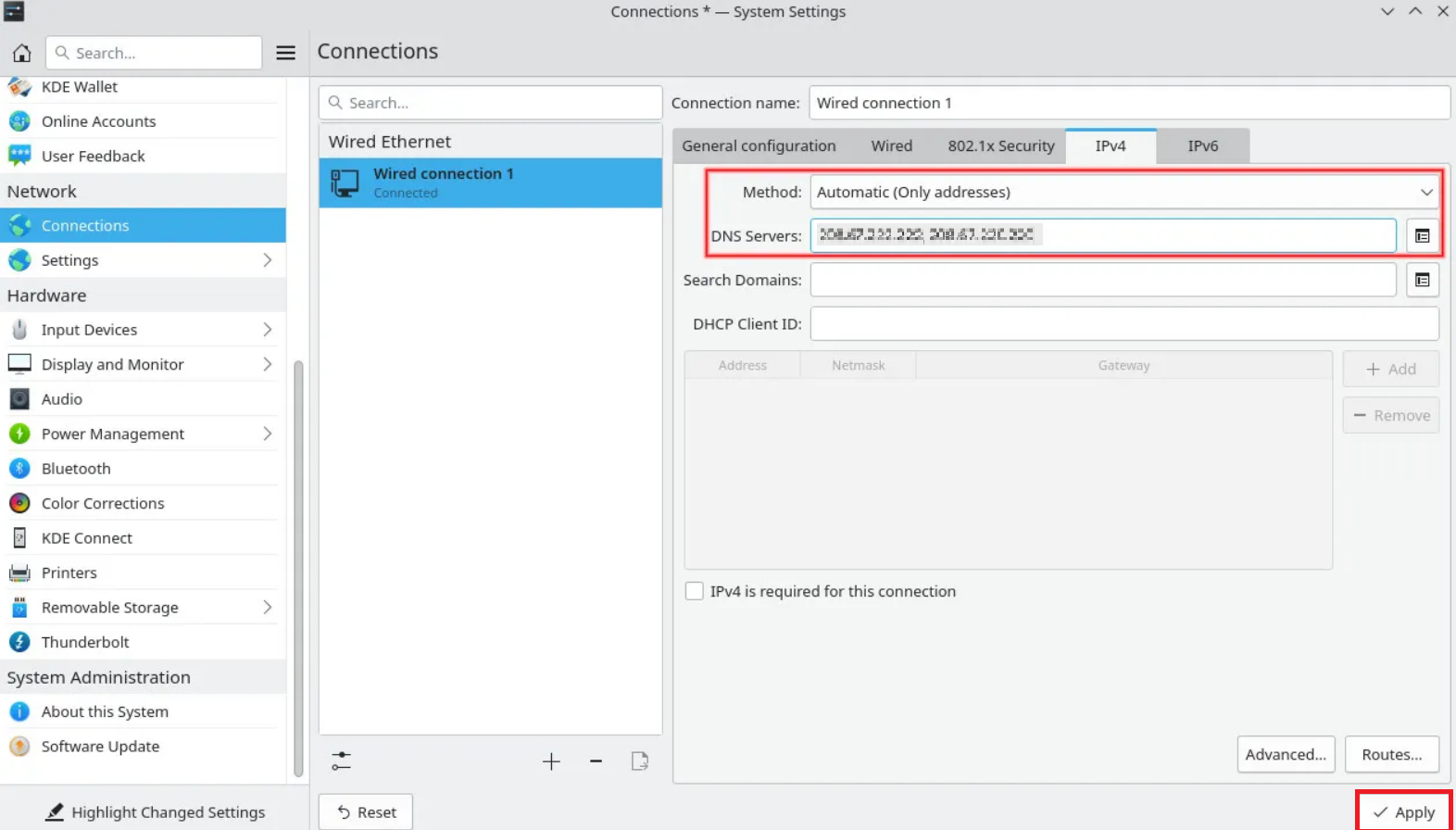
Switching to a new DNS server in KDE Plasma is very similar to the above method. First, open the system settings app and go to the Network section. Choose your current connection from the list of connections by clicking Connections under Network. To access advanced settings, click the IPv4 tab on the right-hand side of the page.
The top two input fields are what you want to modify here. The first one, titled “Method,” will by default read “Automatic.” Select Automatic from the drop-down menu by clicking on it (Only Addresses). Now, enter your DNS server IP addresses in the second field, separated by commas. A minimum of two servers should be entered, though you are free to enter more. Finally, press Apply in the bottom right corner, and your system will begin utilizing the new DNS servers.
Change your DNS Server Using Command line
For any reason, if you are not interested in using your graphical interface to change DNS server settings in Linux, do this at the command line. Since the DNS configurations are stored in a file named resolv.conf, use your favorite text editor to open /etc/resolv.conf with sudo privileges.
Then, add the line for Domain nameservers you consider to use.] Finally, you can save resolv.conf. If you are using the nano text editor, press Crtl + X and then Y to save the file. All these changes are done Temporarily and resolv.conf will be reset when you run dhclient. So, if you need to change DNS server settings in Linux Permanently, continue reading this tutorial.
Change DNS on Linux Permanently
Let’s see what ways you can use to make DNS changes permanent in Linux.
Changing systemd configurations
Firstly, you can use the method of changing systemd configurations to change the DNS changes permanently. To do this, again with sudo privileges open /etc/systemd/resolved.conf.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/resolved.confThen, uncomment the DNS and Fallback DNS lines and add your considered name servers and save the file to change the nameservers.
Use resolvconf
The second way to permanently change DNS on Linux, you can install the resolvconf software to control DNS. Between applications that consume DNS information and programs that provide DNS information, this package serves as a middleman. This package automatically generates DNS settings upon installation and replaces the data in /etc/resolv.conf with its own settings.
Therefore, if we change the program’s default DNS settings, our new, permanent DNS settings will be those that are consistently added to /etc/resolv.conf.
To install resolvconf on Debian/Ubuntu, run:
sudo apt install resolvconfAnd use the following command to install resolvconf on Arch:
Finally, we want to add our DNS to the header file of the automatically created settings. Open /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head and place the nameservers there, just as we did for resolv.conf, to do this.
sudo vim /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/headIn the end, you can check which DNS is in use. In this way, you will view the result of your modifications and verify if the changes have been reflected. To do this, run the command below:
Well done. That was all you could do to change DNS server settings in Linux.
FAQ
How to change DNS Server in through an Ethernet cable?
Open the system settings app, click on Wi-Fi at the top left, and click on Network. The other required steps are the same you reviewed in the article.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to Change DNS Server Settings in Linux. Also, you reviewed how to do this temporarily and permanently. If you follow the above steps properly then you can smoothly install without any errors. If you encounter any problems, please do not hesitate to contact us. Our technical support team will try their best to solve your problems.