- DataGinger.com
- Linux – How to Change Group and User Ownership of a Directory – using chown & chgrp
- Команда chgrp в Linux
- Команда chgrp Linux
- Синтаксис и опции chgrp
- Использование команды chgrp
- Выводы
- 5 Practical Examples of chgrp command in Linux
- What is chgrp command in Linux?
- 5 Practical examples of chgrp command in Linux
- 1. Change group of files/directories
- 2. Use chgrp recursively to change group all the files and sub-directories
- 3. Know if you managed to change the group
- 4. Change the group ownership the same as a reference file
- 5. Using chgrp with symbolic links
- Why use chgrp when you can use chown for changing group?
DataGinger.com
Linux – How to Change Group and User Ownership of a Directory – using chown & chgrp
In this post, let’s learn how to use chgrp and chown commands to change group and user ownership of a directory
On a Linux server, by default, the group owner of a file or directory is the primary group of the user who created the file directory. And it is highly likely in most cases the primary group and the user share the same name
Let’s say we need to change the group and user ownership of the directory /home/chris/mars to root user, below are the steps we need to execute
Step1: Switch to root user
#switch to the root user su - root
Note: In order to change the group owner of a file or directory, one must be the user owner of the file AND be a member of the group to which we are changing ownership or else be the root user. Also, remember that only the root user can change the user ownership of a file or directory.
Step2: Use chgrp to change the group owner and chown to change the user owner
#Using chgrp to change the group owner chgrp root /home/chris/mars #Using chown to change the user owner chown root /home/chris/mars
OR
Step3: Use chown to change both group owner and user owner at the same time
#using chown to change both group and user owner at the same time chown root:root /home/chris/mars
Here’s a bonus tip for you: The process to change group and user ownership on a file is the same as performing the commands on a directory, making our job easy!
Команда chgrp в Linux
При домашнем использовании операционной системы Linux мы редко задумываемся о том, кто является владельцем файла. Если же говорить о запуске сервера, то расклад меняетя. Для того, чтобы повысить безопасность, сервер получает собственного пользователя и группу. Нередко серверы используют одну и ту же группу, вроде www-data.
Мы изучим то, как работает команда chgrp с файлами и каталогами. Особое внимание уделим символическим ссылкам, так как они могут создать проблемы при использовании небезопасных параметров.
Команда chgrp Linux
Стандарт прав файлов пришёл в Linux из Unix. У каждого файла есть владелец (user) и группа (group), помимо этого описываются права остальных пользователей (other). Права состоят из трёх пунктов: чтение (read), запись (write), выполнение (execute). Для изменения прав используется команда umask, но для изменения непосредственно владельца и группы используются команды chown и chgrp. Для просмотра текущих прав можно использовать команду ls.
Синтаксис и опции chgrp
$ chgrp [параметры] новая_группа имя_файла
Список распространённых параметров команды chgrp:
- -h – работать непосредственно с самими символьными ссылками, а не с файлами, на которые они ссылаются;
- —dereference – работать с файлами, а не самими символьными ссылками. Используется по умолчанию;
- -R – рекурсивная обработка каталога со всем его содержимым;
- -H – перейти по символической ссылке и изменить атрибуты файла/каталога. Сама ссылка остаётся без изменений. Используется вместе с параметром -R;
- -L — перейти по символической ссылке и продолжить рекурсивную обработку. Сама ссылка остаётся без изменений. Используется вместе с параметром -R;
- -P – при встрече с символьной ссылкой обрабатывать только её. Используется вместе с параметром -R, является значением по умолчанию;
- —reference=имя_образца – использовать группу образца. Используется вместо новая_группа;
- -c – при обработке выводить только изменения;
- -v – выводить информацию о каждом обработанном файле.
Использование команды chgrp
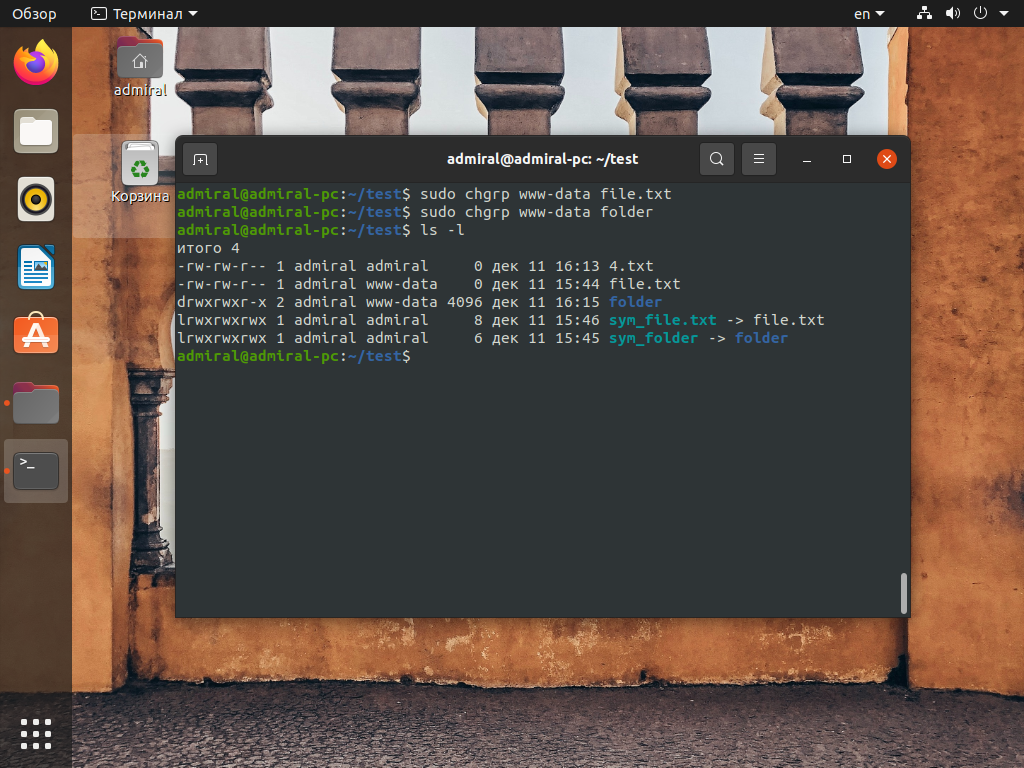
Рассмотрим сразу несколько случаев использования, с реальным файлом и каталогом, а затем с символическими ссылками на них. Простейший пример использования команды chgrp без параметров. Следующая команда меняет группу на www-data для файла file в текущей папке:
sudo chgrp www-data file.txt
А эта меняет группу на www-data для папки folder:
sudo chgrp www-data folder
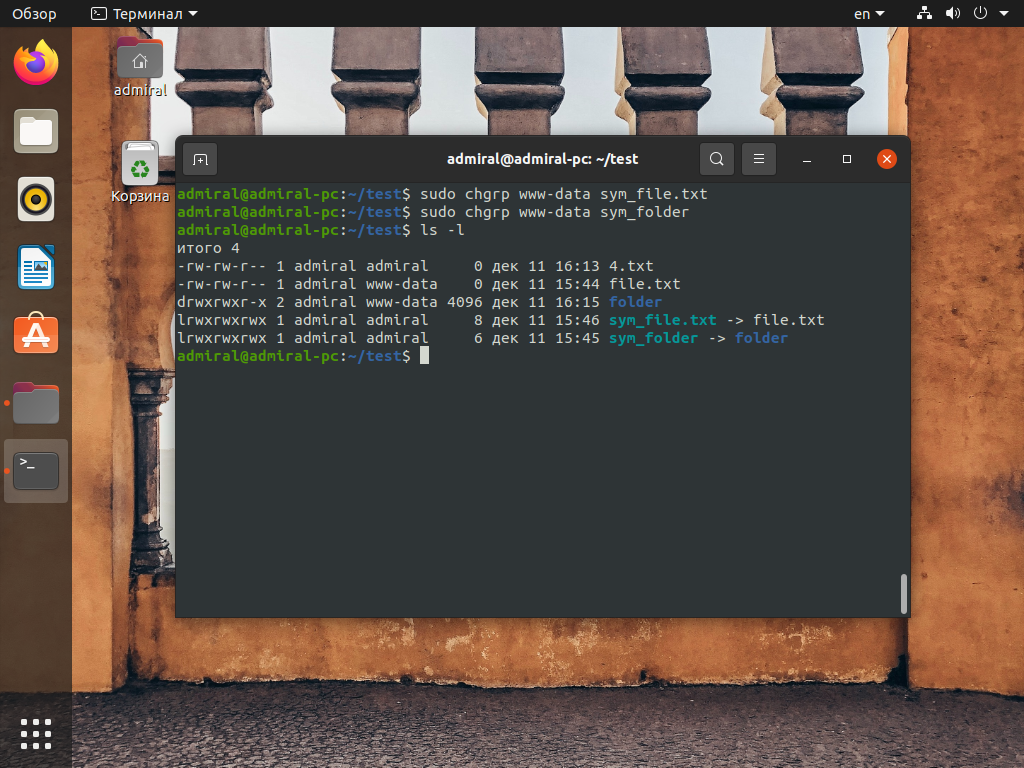
С реальными файлами и каталогами команда работает весьма предсказуемо, меняя их группу. Файлы в папке остаются неизменными. Если же обрабатывать символические ссылки, то их атрибуты останутся неизменными, а файлы получат новую группу. Такое поведение аналогично работе с параметром —dereference. Например, эти команды, применённые к символическим ссылкам, отработают как показано на снимке:
sudo chgrp www-data sym_file.txt
sudo chgrp www-data sym_folder
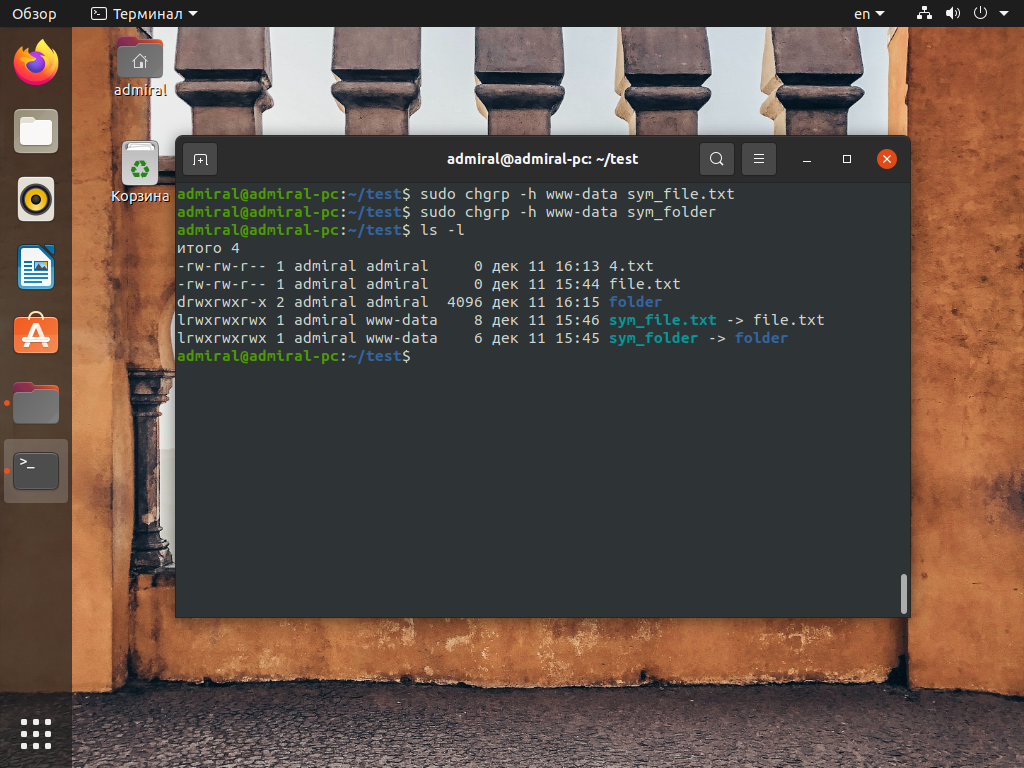
Теперь посмотрим на то, как будет работать параметр -h, меняющий атрибуты символической ссылки:
sudo chgrp -h www-data sym_file
С параметром -h изменились только атрибуты ссылок, а не сами файлы. Теперь рассмотрим работу c параметром -R, предназначенным для рекурсивной обработки каталогов:
sudo chgrp -R www-data folder
Новая группа была задана не только каталогу, но и всем файлам внутри. Обратите внимание на то, что поведение изменилось, теперь при обработке символической ссылки атрибуты выставляются для самой ссылки, а не файла.
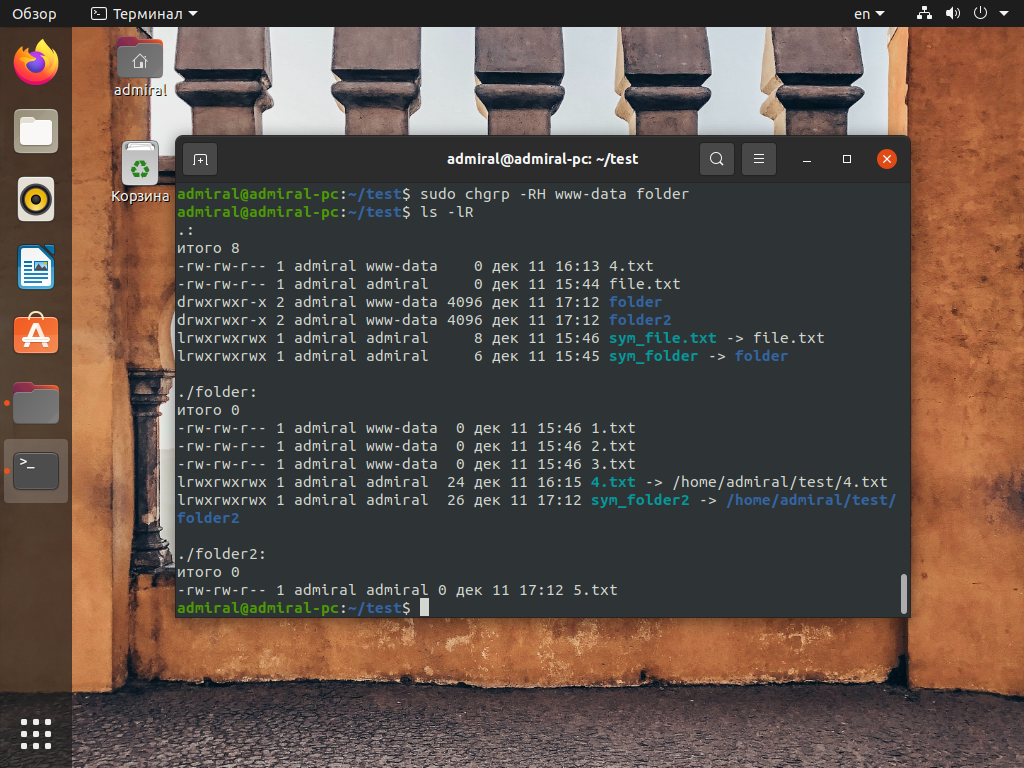
Чтобы увидеть разницу между параметрами -H и -L, рассмотрим ещё пару примеров. Напомним, что их надо использовать совместно с параметром -R:
sudo chgrp -RH www-data folder
С использованием параметра -H поведение при обработке символических ссылок изменилось, теперь они обрабатываются так, как будто команды выполняются по отдельности. Атрибуты ссылок не меняются, меняются атрибуты самих файлов, при переходе на каталог рекурсивная обработка прекращается.
sudo chgrp -RL www-data folder
С использованием параметра -L при переходе к папке по символической ссылке рекурсивная обработка не прекращается. Обращаем ваше внимание на то, что параметры -H и -L использовать небезопасно, они могут дойти до системных файлов.
Выводы
Команда chgrp Linux выполняет одну функцию – меняет группу у файлов и каталогов. При обработке символических ссылок надо быть предельно осторожным, чтобы не навредить системе, поэтому параметр -R не рекомендуется дополнять другими. Также вы можете менять пользователя и группу одновременно с помощью команды chown.
Как вы могли заметить, программа chgrp задаёт только одну группу, на деле же списки управления доступом (ACL) позволяют назначать несколько групп. Для работы с ними можно использовать утилиты setfacl и getfacl, также имеется утилита с графическим интерфейсом eiciel (в репозиториях Debian 10 и Ubuntu 20.04 лежит устаревшая версия, последняя (0.9.13) умеет задавать права рекурсивно).
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
5 Practical Examples of chgrp command in Linux
chgrp command is used for changing the group of a file or directory in Linux. This guide shows you how to use chgrp command in Linux with practical examples.
What is chgrp command in Linux?
If you used our chmod calculator, you are aware of file permissions in Linux, you are probably aware of the group ownership.
chgrp command in Linux is used for changing the group of a file or directory. It stands for ‘change group’.
The syntax for the chgrp command is:
chgrp [options] groupname file5 Practical examples of chgrp command in Linux
Let’s see how to use chgrp command with these useful examples.
1. Change group of files/directories
This is the simplest and perhaps the most prominent use of the chgrp. To change the group ownership of a file or directory, you can use the chgrp command in the following manner:
chgrp group_name file_nameYou can also change the group for multiple files at once:
chgrp group_name file1 file2 file3You don’t have to be in the same directory as the file. You can provide the absolute or relative path as well.
Your current privileges matter. If you try to change the groups to admin or root, you might need super user privileges. You should see a ‘operation not permitted’ error in such cases.
chgrp supports tab completion. Just type a few letters for the group name and hit tab to see what groups exist with those letters.
2. Use chgrp recursively to change group all the files and sub-directories
By default, if you use chgrp with a directory, it only changes the group of the directory. The files and sub-directories remain the same.
If you want to change the group of all the files in the directories and in the sub-directories, you can use the recursive option -R.
chgrp -R group_name path_to_directory3. Know if you managed to change the group
You can figure out if the group has been changed by using the ‘ls -l’ command. But what if you changed the group for several files at once like using the recursive option you saw in the previous section?
chgrp provides a verbose mode that tells you what operations your chgrp command performed. You can use the option -v to run chgrp command in verbose mode.
chgrp -vR abhishek samplechanged group of 'sample/agatha.txt' from sudo to abhishek group of 'sample/a.text' retained as abhishek changed group of 'sample/text/sherlock.txt' from sudo to abhishek changed group of 'sample/text' from sudo to abhishek changed group of 'sample' from sudo to abhishekYou may notice that the verbose mode also tells if the group of a file remained the same. If you want to see this information only for the files for which there were actually a change in group ownership, you can use option -c.
Tip: You can use chgrp to give execute permission to a command (in bin or in init) or so that the command can be executed by all users belonging to a specific group (instead of root).
4. Change the group ownership the same as a reference file
Imagine that you want to change the group of file A the same as file B. How would you do that? You can look for the group of file B and then use the chgrp command with the group name of file B.
Well, that’s one way of doing it. However, chgrp provides a dedicated way of changing the group based on a reference file instead of using the name of the group explicitly.
chgrp --reference=file2 file1This is particularly helpful if you are writing a script where the group owners of files need to be changed as a reference file.
5. Using chgrp with symbolic links
By default, if you use the chgrp command with a symbolic link, it’s the group owner of the referenced file that gets changed while the group of symbolic link remains as it is.
For example, this is the sate of the link and its referenced file:
ls -l agatha.txt link.txt -r--r--rw- 1 abhishek abhishek 457 Aug 10 11:55 agatha.txt lrwxrwxrwx 1 abhishek abhishek 10 Aug 19 10:19 link.txt -> agatha.txtNow if you change the group of the symbolic link like this:
The group of symbolic link will remain the same while the group of the referenced file will be changed.
ls -l agatha.txt link.txt -r--r--rw- 1 abhishek sudo 457 Aug 10 11:55 agatha.txt lrwxrwxrwx 1 abhishek abhishek 10 Aug 19 10:19 link.txt -> agatha.txtIf you want to change just the group ownership of the symbolic link and not the referenced file itself, you can use the -h option.
However, I won’t suggest it because in Linux, link permissions don’t have meaning. The referenced file is what matters here.
Why use chgrp when you can use chown for changing group?
You can also use chown command for changing the group of a file but changing only the group through chown command is not standard. Also, it could be confusing to use chown for this purpose. chgrp is pretty straightforward and it is recommended to use chgrp command for changing the group of a file or directory.
I hope you liked the chgrp command examples. If you have questions or suggestions or a simple thanks, please use the comment box below.