- Change Permissions Linux Changing Permissions in Linux System
- File Permissions in Linux / Unix: How to Read, Write & Change?
- Linux File Ownership
- User
- Group
- Other
- Linux File Permissions
- Changing file/directory permissions in Linux Using ‘chmod’ command
- Absolute(Numeric) Mode in Linux
- Symbolic Mode in Linux
- Changing Ownership and Group in Linux
- Tip
- Summary:
Change Permissions Linux Changing Permissions in Linux System
In Absolute mode, we use the Octal Number to represents Permissions for Owner, Group, and Others.
Okay, but what do you mean by Octal Number?
Octal is a number system that is used to represent numbers on a computer.
In Octal, counting is done with numbers from 0 to 7
| Octal Number | Type of Permission | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No Permission | — |
| 1 | Execute Only | —x |
| 2 | Write Only | -w- |
| 3 | Write and Execute | -wx |
| 4 | Read Only | r— |
| 5 | Read and Execute | r-x |
| 6 | Read and Write | rw- |
| 7 | Read, Write and Execute | rwx |
Let’s look at the syntax for chmod
To change the mode of a file/directory we just use chmod along with one of the modes from the above table and files/directories.
In the above example, we used the command ls -l hello.txt to check the current permissions for owner, group, and others and found that the owner had read and write (rw-) permission, group also had read and write (rw-) permission and other had read-only permission (r—)
What if to make it more secure we wanted to change the permission for the group to read-only and keep the rest as is
we used the command chmod 644 hello.txt where
chmod represents the command change mode
644 represents read-write, read-only and read-only permissions
hello.txt represents name of the file we want to change permissions for.
Now that we know how to use chmod command let’s look at what are some most used modes
| Mode | File Attributes | Meaning of mode |
|---|---|---|
| 777 | rwxrwxrwx | No restrictions on permissions. Generally, not a good setting as anyone can change and execute your file |
| 700 | rwx—— | The owner has full access. Nobody else has any rights. This setting is useful if we want to keep our files and directories private. Similarly we can use 600 for non-executable file |
| 644 | rw-r—r— | The owner may read and write a file, while all others may only read the file. This setting is useful if the owner should be the only one to change the file |
| 666 | rw-rw-rw- | All users may read and write the file. This setting is useful if you have some common file |
Now, let’s move on the 2nd way we can change mode
Symbolic Notation
The Symbolic notation is divided into three parts
Unlike Absolute mode in Symbolic notation, we can actually specify who should be affected by the change
u represents user(Owner)
g represents group
o represents others
a represents all(i.e. u , g and o )
+ represents an operation to add a permission
— represents an operation to remove a permission
= represents an operation to set permission and replace the previous one
r represents read permission
w represents write permission
x represents execute permission
Let’s take an example of each operation
In the above example, we used the command chmod u+x hello.txt to add executable permission to the Owner where
chmod represents the command to change mode
u represents user(Owner)
+ represents the addition of permission
x represents executable permission
In the above example, we used the command chmod o-r hello.txt to remove the read-only permission from Other where
chmod represents the command to change mode
o represents other
— represents the removal of permission
r represents read permission
In the above example, we used the command chmod g=wr hello.txt to assign the read and write permission to group where
chmod represents the command to change mode
g represents group
= represents the assignment of permission
wr represents read and write permission
Note: If we don’t specify who will be affected, it is by default taken as all
This was all about changing permissions of a file/directory.
Now, let’s look at how to change ownership and group of a file/directory.
chown Command
The chown command is used to change the owner/group of a file.
In the example, we can see that the owner and group of the file hello.txt is «yash».
Let’s try and change the owner of the file to «root».
Since we are changing the ownership of the file this operation will require the root access
In the above example, we first tried changing the ownership without using root privileges and it gave us an error.
Then we used the command sudo chown root hello.txt command where
sudo for executing as a superuser
chown represents the change ownership command
root represents the new owner
hello.txt represents the file to be affected
Let’s take another example where we change our owner back to «yash» but change our group to «root»
In the above example, we used the command sudo chown yash:root hello.txt where
sudo for executing as a superuser
chown represents the change ownership command
yash represents the new owner
root represents the new group
hello.txt represents the file to be affected
What if we just wanted to change our group?
chgrp Command
To change the group using chgrp command we just use chgrp newGroupName fileName
Let’s take an example, we recently changed the group of our file «hello.txt» from «yash» to «root».
In the above example, we used the command chgrp yash hello.txt where
chgrp represents the change group command
yash represents the new group
hello.txt represents the file to be affected
So, this was all about Changing Permissions in Linux System. Hope you understood.
Please let me know if there are any queries and suggestions.
See you in the funny papers 🚀
File Permissions in Linux / Unix: How to Read, Write & Change?
Linux is a clone of UNIX, the multi-user operating system which can be accessed by many users simultaneously. Linux can also be used in mainframes and servers without any modifications. But this raises security concerns as an unsolicited or malign user can corrupt, change or remove crucial data. For effective security, Linux divides authorization into 2 levels.
In this Linux file commands tutorial, you will learn-
The concept of Linux File permission and ownership is crucial in Linux. Here, we will explain Linux permissions and ownership and will discuss both of them. Let us start with the Ownership.
Click here if the video is not accessible
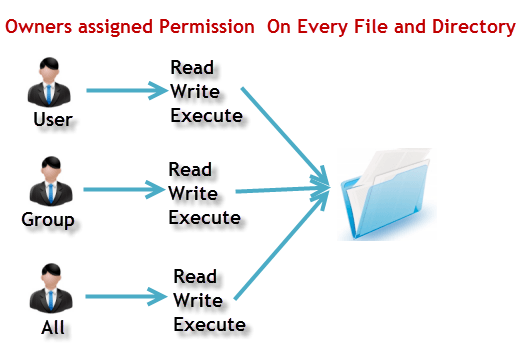
Linux File Ownership
Every file and directory on your Unix/Linux system is assigned 3 types of owner, given below.
User
A user is the owner of the file. By default, the person who created a file becomes its owner. Hence, a user is also sometimes called an owner.
Group
A user- group can contain multiple users. All users belonging to a group will have the same Linux group permissions access to the file. Suppose you have a project where a number of people require access to a file. Instead of manually assigning permissions to each user, you could add all users to a group, and assign group permission to file such that only this group members and no one else can read or modify the files.
Other
Any other user who has access to a file. This person has neither created the file, nor he belongs to a usergroup who could own the file. Practically, it means everybody else. Hence, when you set the permission for others, it is also referred as set permissions for the world.
Now, the big question arises how does Linux distinguish between these three user types so that a user ‘A’ cannot affect a file which contains some other user ‘B’s’ vital information/data. It is like you do not want your colleague, who works on your Linux computer, to view your images. This is where Permissions set in, and they define user behavior.
Let us understand the Permission system on Linux.
Linux File Permissions
Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners discussed above.
- Read: This permission give you the authority to open and read a file. Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content.
- Write: The write permission gives you the authority to modify the contents of a file. The write permission on a directory gives you the authority to add, remove and rename files stored in the directory. Consider a scenario where you have to write permission on file but do not have write permission on the directory where the file is stored. You will be able to modify the file contents. But you will not be able to rename, move or remove the file from the directory.
- Execute: In Windows, an executable program usually has an extension “.exe” and which you can easily run. In Unix/Linux, you cannot run a program unless the execute permission is set. If the execute permission is not set, you might still be able to see/modify the program code(provided read & write permissions are set), but not run it.
Let’s see file permissions in Linux with examples:
ls – l on terminal gives
Here, we have highlighted ‘-rw-rw-r–‘and this weird looking code is the one that tells us about the Unix permissions given to the owner, user group and the world.
Here, the first ‘–‘ implies that we have selected a file.p>
Else, if it were a directory, d would have been shown.
The characters are pretty easy to remember.
r = read permission
w = write permission
x = execute permission
– = no permission
Let us look at it this way.
The first part of the code is ‘rw-‘. This suggests that the owner ‘Home’ can:
- Read the file
- Write or edit the file
- He cannot execute the file since the execute bit is set to ‘-‘.
By design, many Linux distributions like Fedora, CentOS, Ubuntu, etc. will add users to a group of the same group name as the user name. Thus, a user ‘tom’ is added to a group named ‘tom’.
The second part is ‘rw-‘. It for the user group ‘Home’ and group-members can:
The third part is for the world which means any user. It says ‘r–‘. This means the user can only:
Changing file/directory permissions in Linux Using ‘chmod’ command
Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images. This can be achieved by changing file permissions.
We can use the ‘chmod’ command which stands for ‘change mode’. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and the world.
chmod permissions filename
There are 2 ways to use the command –
Absolute(Numeric) Mode in Linux
In this mode, file permissions are not represented as characters but a three-digit octal number.
The table below gives numbers for all for permissions types.
| Number | Permission Type | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No Permission | — |
| 1 | Execute | –x |
| 2 | Write | -w- |
| 3 | Execute + Write | -wx |
| 4 | Read | r– |
| 5 | Read + Execute | r-x |
| 6 | Read +Write | rw- |
| 7 | Read + Write +Execute | rwx |
Let’s see the chmod permissions command in action.
In the above-given terminal window, we have changed the permissions of the file ‘sample to ‘764’.
‘764’ absolute code says the following:
- Owner can read, write and execute
- Usergroup can read and write
- World can only read
This is shown as ‘-rwxrw-r–
This is how you can change user permissions in Linux on file by assigning an absolute number.
Symbolic Mode in Linux
In the Absolute mode, you change permissions for all 3 owners. In the symbolic mode, you can modify permissions of a specific owner. It makes use of mathematical symbols to modify the Unix file permissions.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Adds a permission to a file or directory |
| – | Removes the permission |
| = | Sets the permission and overrides the permissions set earlier. |
The various owners are represented as –
| User Denotations | |
|---|---|
| u | user/owner |
| g | group |
| o | other |
| a | all |
We will not be using permissions in numbers like 755 but characters like rwx. Let’s look into an example
Changing Ownership and Group in Linux
For changing the ownership of a file/directory, you can use the following command:
In case you want to change the user as well as group for a file or directory use the command
In case you want to change group-owner only, use the command
chgrp group_name filename
‘chgrp’ stands for change group.
Tip
- The file /etc/group contains all the groups defined in the system
- You can use the command “groups” to find all the groups you are a member of
Summary:
- Linux being a multi-user system uses permissions and ownership for security.
- There are three user types on a Linux system viz. User, Group and Other
- Linux divides the file permissions into read, write and execute denoted by r,w, and x
- The permissions on a file can be changed by ‘chmod’ command which can be further divided into Absolute and Symbolic mode
- The ‘chown’ command can change the ownership of a file/directory. Use the following commands: chown user file or chown user:group file
- The ‘chgrp’ command can change the group ownership chrgrp group filename
- What does x – eXecuting a directory mean? A: Being allowed to “enter” a dir and gain possible access to sub-dirs.












.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


