- How to check Oracle Java version if multiple versions of Java installed on Ubuntu
- 5 Answers 5
- How to Check Java Version Installed on Linux
- Method 1: Check the Java Version On Linux
- Method 2: Find Version by Checking Path Where Java is Installed
- Method 3: Search for Java in the Installed Packages List
- Verify JAVA Installation on Ubuntu and Check the Installed version (if any)
- Method 1: Checking the Java version
- Method 2: By checking the path where Java is installed
- Method3: Search for Java in the Installed Packages list
- How can I tell what version of Java I have installed?
- 4 Answers 4
How to check Oracle Java version if multiple versions of Java installed on Ubuntu
I have both OpenJDK and Oracle Java installed on my Ubuntu. If the activated java is OpenJDK, is there a way to check the version of Oracle java in bash shell?
yes, you need to know the install path of the oracle one. then /path/to/there/bin/java -version . Assume that the openjdk one is your default java.
5 Answers 5
update-java-alternatives -l will list all the java versions installed via the alternatives system.
For instance on one of my systems it will display the version and the path:
java-1.6.0-openjdk-amd64 1061 /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.6.0-openjdk-amd64 java-7-oracle 1069 /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-oracle If you want the oracle one then I guess you could do:
update-java-alternatives -l | grep oracle | awk '< print $1 >' This would alternatively find all oracle versions and issue the -version command against each one in the list:
update-java-alternatives -l | grep oracle | awk '' Output may look something like this:
java version "1.7.0_67" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_67-b01) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.65-b04, mixed mode) One step further would be to parse out the java version from the -version command and simply display it:
(update-java-alternatives -l | grep oracle | awk '&1 | grep \"java version\"")>') | awk -F\" '' The 2>&1 is needed because Java will display version to standard error. The output would simply look like this (and could be easily assigned to a bash variable if you needed it that way):
If you had multiple oracle instances this would display the version for each one. If you wanted to find all the versions for every Java you could simply remove the | grep oracle
How to Check Java Version Installed on Linux
How do I check my current Java version? There are several ways to check if Java is installed and which version is running on your system.
In this tutorial, learn how to check the Java version installed on Linux distros, including Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian.
- A user account with sudo privileges
- Access to the command-line/terminal window
- A version of Java
Method 1: Check the Java Version On Linux
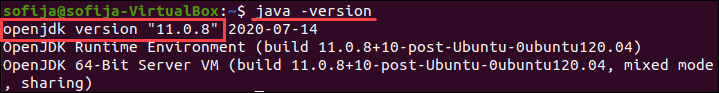
To check the Java version on Linux Ubuntu/Debian/CentOS:
2. Run the following command:
3. The output should display the version of the Java package installed on your system. In the example below, OpenJDK version 11 is installed.
Note: If the output indicates there is no such package on the system, you can install it with the help of one of our guides – How to install Java on Ubuntu or How to Install Java on CentOS.
You can also check the version of the primary Java compiler – javac (pronounced “java-see”) with the command:
Method 2: Find Version by Checking Path Where Java is Installed
There are two ways to find the path of the Java directory.
The first option includes running a single command:
update-alternatives --list javaThe system should respond with the path where Java is installed.
Note: This option may not work on CentOS systems. If you have issues finding the path of the Java directory with the command above, use the alternative outlined below.
Alternatively, you can use the whereis command and follow the symbolic links to find the Java path.
The output tells you that Java is located in /usr/bin/java.
2. List the content of the /usr/bin/java directory:
Inspecting the directory shows that /usr/bin/java is only a symbolic link for /etc/alternatives/java.
3. Just like in the previous step, list the content of the provided path by running:
Finally, the output displays /etc/alternatives/java is another symbolic link and that the real path of the Java directory is /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java.
Method 3: Search for Java in the Installed Packages List
You can also prompt the system to list installed packages and search for Java, with its version number.
Find Java by listing all installed packages.
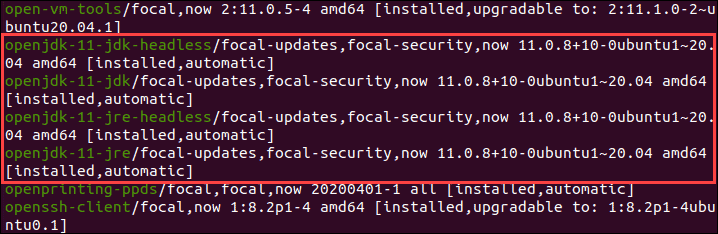
1. To generate a list of all installed packages, use the command:
2. Scroll up/down until you find the Java packages as shown in this example.
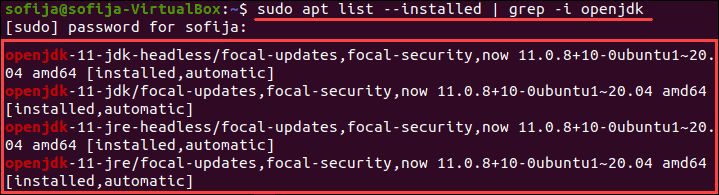
To avoid searching through all installed packages, list Java packages only. Prompt the system to list a specific software package. In this case, the package name is openjdk:
sudo apt list --installed | grep -i openjdkNote: CentOS users need to modify the commands for listing installed packages for their package manager. Use the commands: sudo yum list installed and sudo yum list installed | grep -i openjdk instead.
With this article, you have successfully checked the Java version installed on Linux. We also covered checking the Java path and searching for Java among the installed packages.
Once the Java version is confirmed, you can start developing anything from lightweight mobile to desktop applications.
Verify JAVA Installation on Ubuntu and Check the Installed version (if any)
Certain applications in Ubuntu require that Java Runtime Library is installed on your system. It does not come by default with most Ubuntu versions, as security is a concern when Java is installed on your system. Time and again, a regular Ubuntu user might need to verify if Java is installed on the system at the moment and also if it is installed, which version the system is currently using.
This article describes how you can quickly check your installed Java version on your Ubuntu system. We have tested the commands and procedures mentioned in this article on Ubuntu versions between 18.04 and 22.04.
We will use the Ubuntu command line, the Terminal, to run all the mentioned commands. You can open the Terminal application through Ubuntu Dash or the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut.
Method 1: Checking the Java version
Once you have opened the Terminal, enter one of the following Java commands to check its version:
This will ensure whether Java Runtime Environment is already installed on your system. If yes, it will also let you know which version of Java you have on your system.
In my case, the output shows that I do not have Java currently installed on my system yet.
If you have any version of Java installed on your system, the output will display Java OpenJDK and JRE version information as follows:
Method 2: By checking the path where Java is installed
Enter the following command to check the directory in which Java is installed:
This command will print no output if Java is not installed on your system:
However, if Java is installed on your system, this command will show the exact path where Java is installed:
Method3: Search for Java in the Installed Packages list
You can check if a software package is installed on your system by using the following command syntax:
$ sudo aptitude search PackageName
We can use this command to see if any JDK package is installed on our system or not:
This command will list all the JDK packages available in the Ubuntu repositories.
Please note the prefix with each entry.
Only the packages with the ‘i’ prefix are installed on your system.
In the above output, you can see that Java OpenJDK 11 JRE is installed on my system. Java is not installed on your system if you do not see the ‘i’ prefix with any of the JDK entries. A more in-depth guide on finding installed packages can be found here.
Through these simple ways, you can verify whether Java is installed on your system. You can also view which Java installation you have on your system if it is indeed installed.
How can I tell what version of Java I have installed?
I want to start toying around with java (eventually getting to the point where I can write basic little programs for android or web), but I’ve managed to have java messed up on my computer (from past experiments). I’m not sure which version of java I have, and would like to know if there is a command to see the version of java that is installed and active. Also, which version works best? All this on 32bit Ubuntu 12.04 EDIT:
Ok, so it seems like I have both openjdk 6 and 7, with openjdk 7 in use. I want to use openjdk 7, so how do I uninstall openjdk 6? Is just via USC good enough or is there a command that should be run?
4 Answers 4
update-java-alternatives -l shows you all the Java versions you have installed.
java -version shows you the Java version you are using.
java -showversion shows you the Java version you are using and help.
Normally it would be OpenJDK.
This command should tell you what is currently providing the Java virtual machine ( java ) and the Java compiler ( javac ):
file /etc/alternatives/java /etc/alternatives/javac This assumes the «alternatives» system is working properly, which might not be the case, depending on how Java has been «messed up» in the past. To check this, run:
If the alternatives system is working correctly and being used by Java, then you should see:
/usr/bin/java: symbolic link to `/etc/alternatives/java' /usr/bin/javac: symbolic link to `/etc/alternatives/javac' Otherwise please edit your question to provide details. Then it should be possible to give a more specific answer.
You can remove openjdk-6 with the Software Center. There are multiple packages associated with it, so you may need to remove more than one packages. (All the `openjdk-6 packages are listed here.)
Or you can use the command-line:
sudo apt-get remove openjdk-6-\* icedtea-6-\* However, whichever method you use, you may want to check first to see what depends on these packages—you might have software installed that specifically needs version 6. (Probably not, but possibly.)
You can check for this by simulating the removal operation on the command-line:
apt-get -s remove openjdk-6-\* icedtea-6-\* This will show you the effects of removing those packages, including what other packages would be removed as well. (You’ll notice that since this is a simulation, you don’t need sudo .)
If you want to be able to continue using Java content online in your web browser (this is not the same thing as JavaScript), then before you remove any icedtea-6- or openjdk-6- packages (except perhaps openjdk-6-jdk ), you should make sure you have icedtea-7- packages installed corresponding to whatever icedtea-6- packages are installed.