- How to list all enabled services from systemctl?
- 9 Answers 9
- How to List Services in Linux Using Systemctl
- Using Systemctl Command
- 1. List All the Available Services
- 2. List Only Loaded and Active Services
- 3. List Only the Running Services
- 4. List All Stopped Services
- Other Methods to Display Services in Linux
- List All Available Services using service command
- Display Only Running Services using service command
- Extract Only Stopped Services using Service Command
- Listing /etc/init.d
- Conclusion
- How To Check and List All Services in CentOS/RHEL(6/7/8) Linux
- Check Status of a Service on CentOS 6
- List All Running Services on CentOS 7/8
- Check Status of a Service on CentOS 7/8
- Conclusion
How to list all enabled services from systemctl?
How can I list all enabled services from systemctl ? I know running systemctl command by itself lists all services, but I would like to only get the enabled ones.
Fascinating. The lowest rated answer is the most «correct» answer, even though it is clearly not the best answer. This excellent question (and its answers) is an interesting example of how systemd violates the long-standing (and brilliant) design principles of Unix & Co. @FelipeAlvarez complains that the most-accepted answer assumes systemd follows the unix design philosopy, but systemd/systemctl can do exactly what he wants (most experienced users will just consider that complete bloat). I begin to see more clearly why Linus Torvalds is so vehemently critical of systemd.
If you want to list «templated» services (blabla@instance.service), do not forget to add «—all» — thanks to @rafdouglas below.
9 Answers 9
systemctl list-unit-files | grep enabled will list all enabled ones.
If you want which ones are currently running, you need systemctl | grep running .
Use the one you’re looking for. Enabled, doesn’t mean it’s running. And running doesn’t mean it’s enabled. They are two different things.
Enabled means the system will run the service on the next boot. So if you enable a service, you still need to manually start it, or reboot and it will start.
Running means it’s actually running right now, but if it’s not enabled, it won’t restart when you reboot.
annoying to have to use an external tool (grep) to show this vital information. But thank you for showing us the way 🙂
@FelipeAlvarez Correct. But that’s how Linux works. Many small binaries that work well with each other. systemctl does what is asked, it lists services. There is no filtering command built-in to systemctl because grep already exists and can do that well with any program’s output. It’s how it’s always been 🙂
I agree and so it should be. But, systemd already tries to do SO much that I wonder why it can’t list enabled services?
systemctl | grep running do not list anything to me! Even if something is running is only listed as for his status like: enabled, disabled, masked, static
—state=
The argument should be a comma-separated list of unit LOAD , SUB , or ACTIVE states. When listing units, show only those in the specified states. Use —state=failed to show only failed units.
LOAD : Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded.
ACTIVE : The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB .
SUB : The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
Though you can also use this to only show enabled units with:
systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled If a unit is enabled that means that the system will start it on startup. Though setting something to enabled doesn’t actually also start it so you will need to do that manually, or reboot the system after setting it to enabled .
How to List Services in Linux Using Systemctl
Service is a Linux program that runs continuously in the background. Some of the common examples of Linux services are reverse proxy servers, network, cron, SSH, and the high-performance web server. Linux supports multiple tools and methods to list and manage services. Some services start at the boot time and some services can be started after your system boots up. You can control Linux services with systemctl commands.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to list services in Linux using systemctl.
Using Systemctl Command
The systemctl command-line utility is used for controlling the services on Linux systems. Systemctl is part of the systemd software suite that can list all, enabled, active, stopped, or disabled services. All enabled services start at boot. Systemctl is the primary command for managing system services.
In the following examples, we will show you how to use the systemctl command to list services.
1. List All the Available Services
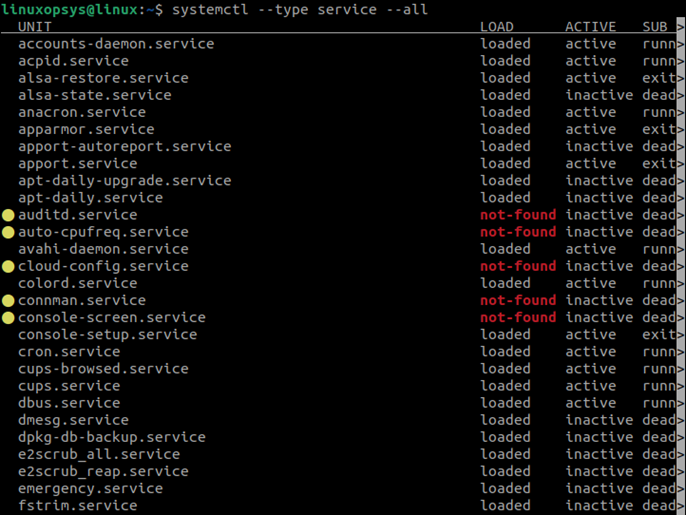
Systemctl provides a wide range of information about all the available services on your Linux systems. To list all available services, use the —all option.
Use the following command to list all active, inactive, failed, running, and stopped services:
systemctl --type service --allLet us describe each column to better understand the output:
- UNIT – Every resource that systemd manages is denoted as a UNIT. It is the name of the service.
- LOAD – Denotes if the specific service was loaded into memory or not after the system boot up.
- ACTIVE – Denotes if the service is currently active or inactive.
- SUB – Denotes the current state of the Linux service units.
- DESCRIPTION – Provides a brief description of each service.
All these columns are available in the systemctl output, whether you display all available services or only the active/loaded units.
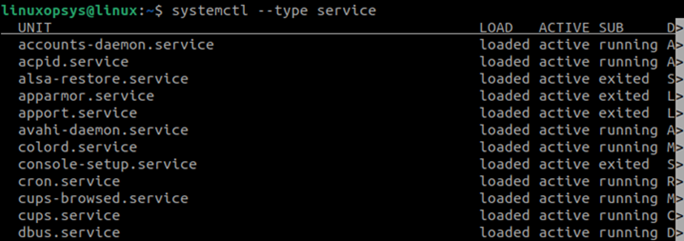
2. List Only Loaded and Active Services
To list only the active or loaded services, do not use the —all option. The following command output includes both running and stopped units, which are still active and loaded.
In this output, we see only the loaded and active services, which is also displayed under the LOAD and ACTIVE columns.
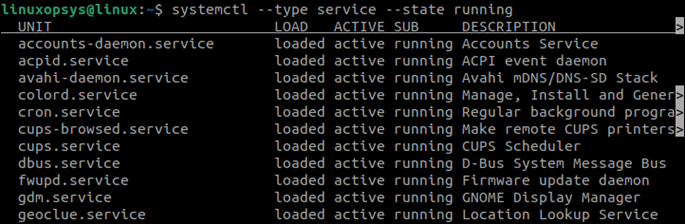
3. List Only the Running Services
Only the loaded and active services can be running, but it does not include all the available services. To list only the units that are running, use the —state option with the value running. For example:
systemctl --type service --state runningThe —state filter can be used to sort out the services based on your requirements.
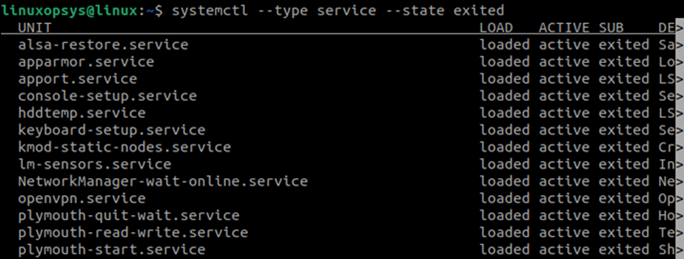
4. List All Stopped Services
Like listing all other services, you can also use systemctl status command to list all the stopped services. Use the —state option with the value exited and you will get a list of the services that were either stopped naturally or were stopped manually:
systemctl --type service --all --state exitedOther Methods to Display Services in Linux
Linux distributions support other options to list services, along with the systemctl. The service command is one such option.
On my Ubuntu 22.04, I am able to use the service command to list services.
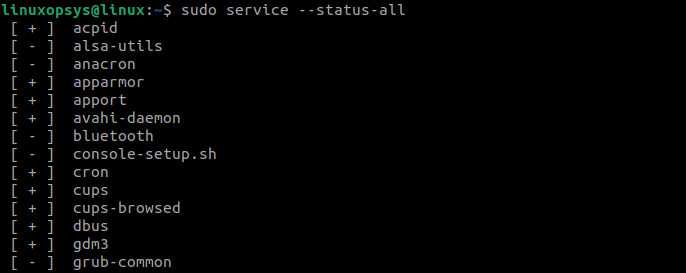
List All Available Services using service command
Use the following command to list all services on your Linux system, including active, inactive, running, or stopped services:
The [ + ] and [ — ] symbols before each service name denotes the service status. The [ + ] symbol denotes that the service is running whereas [ — ] denotes that the service is stopped.
When you run this command for that first time, it may take some time for the output to display on the terminal. The service command collects data from the /etc/init.d/ directory.
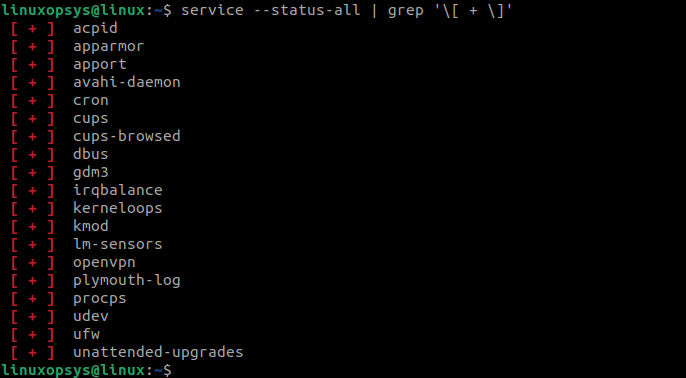
Display Only Running Services using service command
You can also use the service command to run only the running services. Use the [ + ] symbol with the grep command to sort list only the services that are currently running:
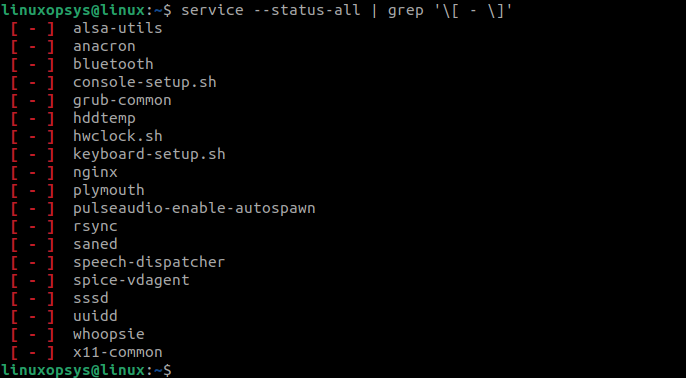
Extract Only Stopped Services using Service Command
Similar to listing Linux services, which are running, using the service command, you can also use the service command to list all stopped services using the [ — ] symbol with the grep command:
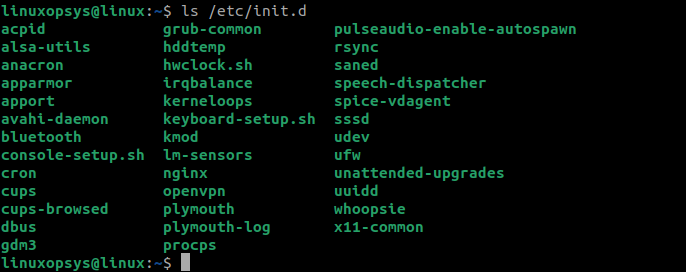
Listing /etc/init.d
The service command retrieves service names and status from the /etc/init.d directory. Thus, you can directly list the units from /etc/init.d using the ls command. This method bypasses the source code execution that is required when you run the service command:
The ls command in this example merely lists the contents of the /etc/init.d directory. However, it does not provide you the status of the services. It just gets a list of all the services even if they are stopped or inactive.
Conclusion
Now almost all Linux distributions have adopted using systemd as its init system. Prefer using systemctl because it gives greater control options. Whereas service command is wrapper script and previously used for /etc/init.d scripts.
On my Ubuntu system, I am successfully able to use both systemctl and service command to list services. Over various versions of Ubuntu, users can reliably use service command to list, status check, start/stop services.
Thanks for reading, please leave your feedback and suggestion in the below comment section.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks
How To Check and List All Services in CentOS/RHEL(6/7/8) Linux
If you want to list all running services on your CentOS /RHEL 6 Linux system, and you can use service command with —status-all option, type:
$ service --status-all $ service --status-all | less
[root@devops ~]# service --status-all| less Stopped cgred is stopped crond (pid 1401) is running. htcacheclean is stopped httpd (pid 20286) is running. Table: filter Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination 1 ACCEPT all ::/0 ::/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED 2 ACCEPT icmpv6 ::/0 ::/0 3 ACCEPT all ::/0 ::/0 4 ACCEPT udp ::/0 fe80::/64 state NEW udp dpt:546 5 ACCEPT tcp ::/0 ::/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22 6 REJECT all ::/0 ::/0 reject-with icmp6-adm-prohibited Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination 1 REJECT all ::/0 ::/0 reject-with icmp6-adm-prohibited Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) num target prot opt source destination . Check Status of a Service on CentOS 6
If you want to check the status of a service (such as: httpd serivce ) in CentOS or RHEL 6 Linux,you can use one of the following command:
[root@devops ~]# service httpd status httpd (pid 20286) is running. [root@devops ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd status httpd (pid 20286) is running.
List All Running Services on CentOS 7/8
If you want to list all running services in CentOS 7 or CentOS 8 system, and you can use the below systemctl command, type:
$ systemctl list-units --type=service
[devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl list-units --type=service UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION accounts-daemon.service loaded active running Accounts Service alsa-state.service loaded active running Manage Sound Card State (restore and> atd.service loaded active running Job spooling tools auditd.service loaded active running Security Auditing Service avahi-daemon.service loaded active running Avahi mDNS/DNS-SD Stack bolt.service loaded active running Thunderbolt system service chronyd.service loaded active running NTP client/server colord.service loaded active running Manage, Install and Generate Color P> crond.service loaded active running Command Scheduler . [devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl list-units --type=service | wc -l 71
To list all services in your system, you can type the following command:
[devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl list-unit-files |less UNIT FILE STATE proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.automount static -.mount generated boot.mount generated dev-hugepages.mount static dev-mqueue.mount static home.mount generated proc-fs-nfsd.mount static proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount static sys-fs-fuse-connections.mount static sys-kernel-config.mount static . [devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl list-unit-files | wc -l 414
Check Status of a Service on CentOS 7/8
If you want to check the status of a service named httpd in your CentOS or RHEL 7/8 Linux system, just run the following command:
$ systemctl status httpd.service
[devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl status httpd.service httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Sat 2019-10-12 06:23:25 EDT; 2s ago Docs: man:httpd.service(8) Main PID: 3199 (httpd) Status: "Started, listening on: port 80" Tasks: 213 (limit: 8297) Memory: 29.4M CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service ├─3199 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─3208 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─3209 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─3210 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND └─3211 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND Oct 12 06:23:24 mydevops.com systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server. Oct 12 06:23:25 mydevops.com httpd[3199]: AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using mydevops.com.> Oct 12 06:23:25 mydevops.com httpd[3199]: Server configured, listening on: port 80 Oct 12 06:23:25 mydevops.com systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
To check a service named httpd if it is running or enabled in your system, and you can use the below commands:
$ systemctl is-active httpd $ systemctl is-enabled httpd
[devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl is-active httpd active [devops@mydevops ~]$ systemctl is-enabled httpd disabled
Conclusion
You should know that how to list all running services or check the stauts of a given service in your CentOS/RHEL/ 6/7/8 Linux.