Check point endpoint security vpn linux
Если у вас не работает один из способов авторизации, сконвертируйте свой аккаунт по ссылке
Авторизуясь в LiveJournal с помощью стороннего сервиса вы принимаете условия Пользовательского соглашения LiveJournal
После нескольких лет экспериментов мне таки удалось их соединить. Вообще-то Checkpoint использует IPSec, но, как водится, с некоторыми расширениями, делающими его несовместимыми с другими реализациями.
Родной клиент под линукс у Checkpoint’а когда-то был, но последняя версия была под RedHat 5 (не путать с RHEL5!). RH5 — это примерно 1997-98 год. С тех пор Checkpoint на линукс забил, а желающим рекомендует использовать SSL Network Extender, работающий через Java-плагин в браузере. Точнее, в моём случае не работающий, поскольку гейт по HTTPS вообще не отвечает.
Но добрые люди из компании Shrew Soft написали универсальный клиент, который умеет разговаривать на многих диалектах IPSec, включая CheckPoint’овский. Готового пакета под линукс у них самих нет, но из исходников собралось влёт. В некоторых дистрибутивах, типа убунты, говорят, есть уже готовое.
Остались сущие мелочи: настроить. В родной инструкции сказано, что клиенту нужен сертификат, который предлагается экспортировать из сервера. Но у меня нет доступа к серверу. Виндовый клиент этот сертификат скачивает при первом соединении с сервером и сохраняет у себя (способ небезопасный, но уж какой есть). Вот только сохраняет он его таким хитровывернутым способом…
Итак,
1) в Program Files\CheckPoint\SecuRemote\database\ находим файлик userc.C, в котором лежит конфигурация клиента. Файлик, к счастью, текстовый. Находим в нём параметр :cert, представляющий собой длинную строку из шестнадцатиричных цифр. И сохраняем эту строку в другой файлик, скажем, cert.hex
2) Конвертируем в бинарный вид: xxd -p -r cert.hex > cert.bin
3) Переставляем байты в обратном порядке… cat cert.bin | perl -0777e ‘print scalar reverse <>‘ > cert.der
4) Полученный файл представляет собой серверный сертификат в формате DER. Конвертируем в PEM: openssl x509 -inform DER -in cert.der -outform PEM -out cert.pem
Это Страшное Колдунство найдено тут.
Так, с сертификатом разобрались. Переходим к настройке параметров соединения..
Запускаем qikea, тыкаем в кнопочку Add. В полученном диалоге вбиваем следующие настройки:
General:
указываем IP-адрес гейта, порт 500.
Auto configuration: ike config pullю
Local Host Address method: Use a virtual adapter and assigned address и Obtain automatically.
MTU оставляем 1380.
Client:
NAT traversal: disable. Несмотря на это, оно успешно работает из-за NAT’а. Вероятно, эта настройка относится к собственно IPSec’овому NAT-T, а здесь он инкапсулируется в UDP, и NAT проходит на этом уровне. И в инструкции всё равно написано, что Shrew не поддерживает CheckPoint’овский NAT-T.
IKE fragmentation: enable, Max packet size: 540.
Остальные три галки (Enable Dead Peer Detection, Enable ISAKMP Failure Notifications, Enable Client Login Banner) оставляем как есть, то есть, включёнными.
Name resolution: оставляем по умолчанию:
Enable DNS, Obtain automatically. DNS suffix тоже Obtain automatically.
Учтите, что это приведёт к добавлению записей в /etc/resolv.conf при поднятии туннеля, если это нежелательно, можно выключить.
Authentication:
Authentication method: Hybrid RSA+XAuth.
Local Identity: User FQDN, UFQDN string оставляем пустой. В инструкции написано, что надо использовать FQDN, но у меня оно с такой настройкой не работает, только с UFQDN.
Remote Identity: Identification Type: any. В инструкции написано, что можно ещё IP address, я не пробовал.
Credentials: Server Certificate Authority File: вот тут надо указать файл с сертификатом, выковырянный на первом этапе. Сам файл больше уже не понадобится, он тут импортируется и целиком сохраняется в конфиге.
Phase1:
Exchange type: main. Agressive не работает.
DH Exchnage: group 2. Остальные варианты, включая auto, у меня не работают.
Cipher algorithm: AES, Key length: 256 bit. Auto не работает.
Hash algorithm: sha1. Auto не работает.
Key Life Time Limit: оставляем как есть: 86400 sec, data limit: 0 (в смысле, отключено).
Не забыть поставить галку Enable Check Point Compatible Vendor ID, без неё точно не заработает.
Phase2: всё про умолчанию:
Transfer algorithm: auto
HMAC Algorithm: auto
PFS Exchange: disabled
Compression algotithm: disabled
Key life time limit: 3600 sec, data limit: 0.
Policy:
Policy generation level: auto
Maintain persistent Security Associations: у меня выключено, в принципе, можно и включить, если кому надо.
Obtain Topology Automatically or Tunnel All: у меня выключено в связи с идиотской политикой, выдаваемой сервером. Он выдаёт маршрут в VPN для внешнего IP-адреса гейта. Причём в Windows этот идиотизм как-то работает, но в линуксе однозначно не будет. Поэтому все нужные маршруты далее вбить вручную. Тем более, что в инструкции написано, что автоматическое получение маршрутов из CheckPoint’а всё равно не работает.
Вот, собственно, и всё. Сохраняем, запускаем, вводим логин и пароль, и надеемся, что заработает..
Оригинал этой записи в личном блоге.
Любые материалы из этого блога запрещается использовать на сайте livejournal.ru в любой форме и любом объёме.
Check point endpoint security vpn linux
G_W_Albrecht
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
@PhoneBoy Thank you. I read in other posts that SNX client is not working with recent Ubuntu versions, nor with MFA. I don’t know really is what is. From what I read on this site, it is something that the Endpoint admin has to setup, but unfortunatelly I doubt they will do it.
@G_W_Albrecht Thank you for your reply. It’s R84.30 or newer. I tried to follow and adapt the tutorials of @Soeren_Rothe on this site (on Ubuntu desktops 22.04 and 21.10), but it didn’t work for me because I didn’t know how to adapt to the differences (Soeren is using pre-shared secret; our server seems to use a certificate).
In the Windows client, I just create a new connection (by entering the host name), confirm the server certificate fingerprint (because its root CA is self-signed) and then it’s ready to use (I just enter username/password and confirm in Authenticator App).
By reading the Windows client extended logs, I saw that our config uses username+password authentication, but I didn’t find info about the server certificate (I do have the root CA certificate).
G_W_Albrecht
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
How to install Check Point VPN client in Linux
How to install Check Point VPN client in Linux? How to do this? This article will show you how to connect Check Point VPN from a Linux computer.
If your company is using Check Point firewall device and you are using a Linux computer, you will have a small problem.
Check Point client supports very well for Windows and MacOS, mobile. However, with Linux, that is a problem. Check Point currently only supports SSL VPN for Linux devices, so it will have a slightly different connection.
Access to Check Point SSL server
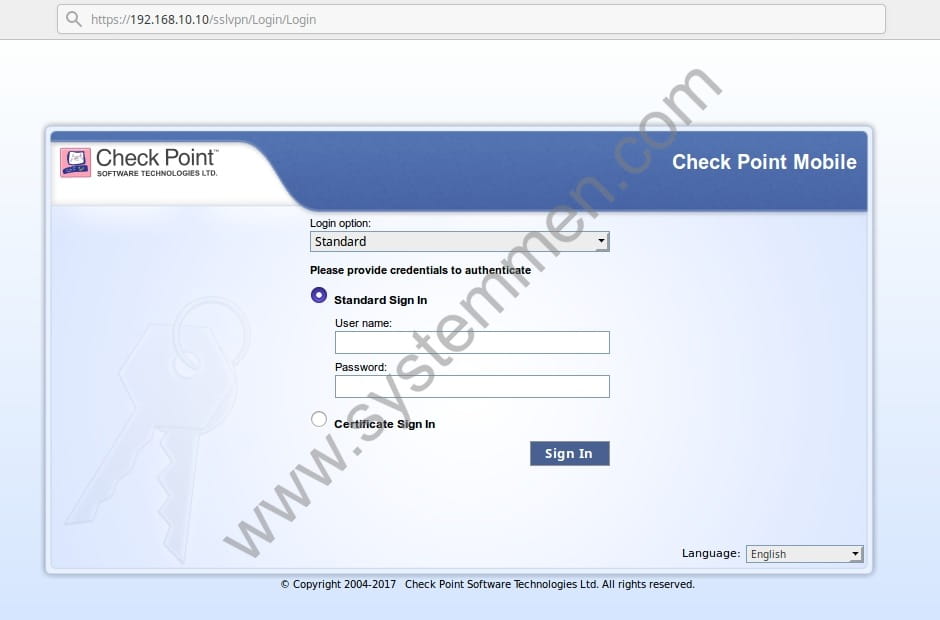
For Windows computers, you have a client application under your computer. You use it to connect to the vpn server. As for Linux, you access it through the browser.
Open the browser and type the IP (or domain) of the vpn server with the URI configuration ssl of Check Point. The example here is https://192.168.10.10/sslvpn .
Access to Check Point SSL server via browser.
You log in with your vpn account. The main window will appear.
Here, if you click the Connect button, you will definitely connect the vpn to failure. You need to click the Settings button that I highlighted in the image below.
Click Settings button in the main window.
In the Settings window, you need to download 2 installation script files that I highlighted in the image below.
You must install both, then you can connect vpn successfully.
Download 2 installation script files to your computer.
Install Check Point agent on Linux computer
The 2 script files you downloaded above are: cshell_install.sh and snx_install.sh .
Now, we will install these 2 scripts. Note, you need root access (or sudo) to install.
First, we will install the script cshell_install.sh . You need to install the dependency package for it before installing it.
# apt-get install libnss3-tools -y
Then install cshell_install.sh .
# bash cshell_install.sh Start Check Point Mobile Access Portal Agent installation Extracting Mobile Access Portal Agent. Done Installing Mobile Access Portal Agent. Done Installing certificate. Done Starting Mobile Access Portal Agent. Done Installation complete
Next, we will install script snx_install.sh and its dependencies.
# apt-get install libstdc++5:i386 libpam0g:i386 -y
# bash snx_install.sh Installation successfull
After installation is complete, now press the Connect button on the Check Point VPN main window on the browser.
Another window will display your VPN information. And on the main window, the VPN state will look like the image below.
Status of connecting Check Point SSL VPN on Linux.
Conclusion
So I showed you how to install Check Point VPN client in Linux successfully.
For longtime Linux users, I think you can solve the problem yourself. However, with less experience users. I hope this article will help you.
(This is an article from my old blog that has been inactive for a long time, I don’t want to throw it away so I will keep it and hope it helps someone).