- How to Check Services Running in Linux
- Method 1: How to Check Services Running in Linux Using “systemctl” Utility?
- Method 2: How to Check Services Running on Linux Using “service” Command?
- Conclusion
- How can I see all services in Ubuntu?
- How to list all services in Ubuntu?
- List all services using the systemctl command
- How to list systemd unit files?
- How to list systemd service unit files using states?
- List all active or running services
- List all excited services
- List all stopped or dead services
- Managing systemd services using systemctl
- View service status using systemctl command
- More commands to list services in Ubuntu
- Use of pstree command
- List firewall services
- List top control groups with resource utilization
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Samreena Aslam
- How to List Services in Ubuntu Server / Desktop
- List Ubuntu Services with Service command
- List Services with systemctl command
How to Check Services Running in Linux
Different operations are running in the background of Ubuntu and are not visible to the users. These services run for specific purposes and can only be managed by some utilities. One of these utilities is “systemctl” to start/stop services. These services make the processing unit of the computer busy, which consumes the battery health as well as slows down other programs.
Considering the importance of services, this post will provide the methods to check services on Linux. The outcomes of this article are:
Method 1: How to Check Services Running in Linux Using “systemctl” Utility?
As discussed earlier, the “systemctl‘ utility is the most used to manage the services on Linux-based systems. Let’s see how it can be used to list down services:
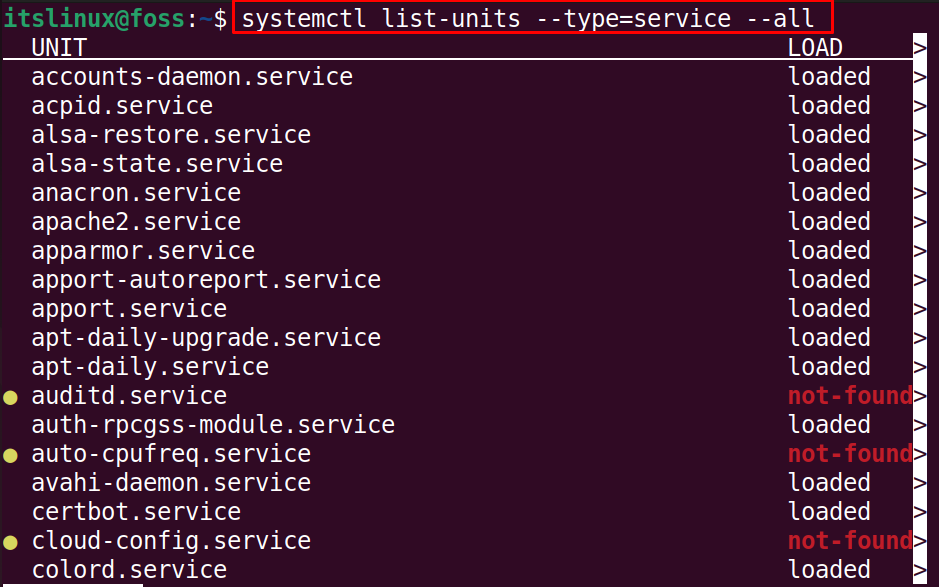
List Down Machine Services
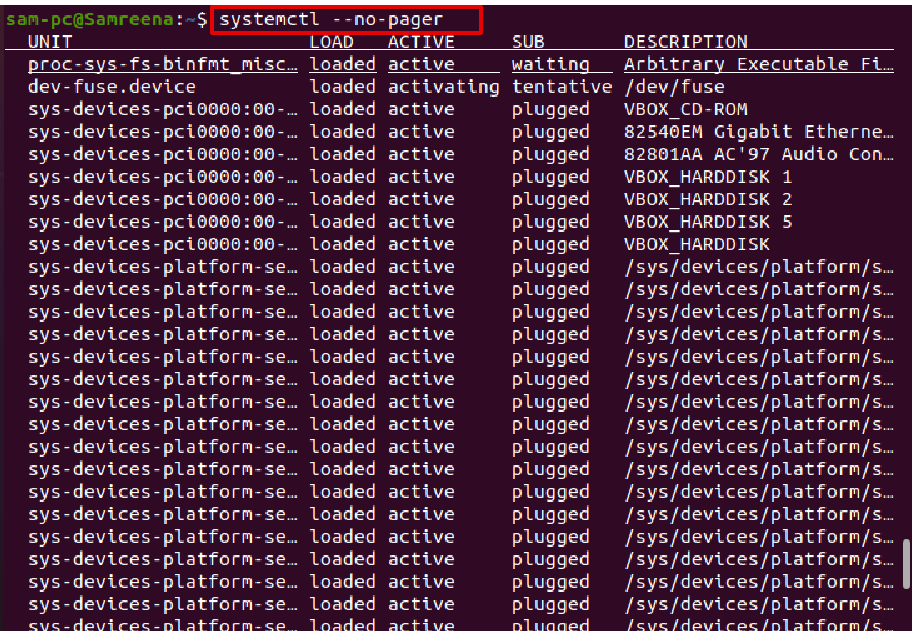
First of all, we are supposed to list down all the machine services using the systemctl command:
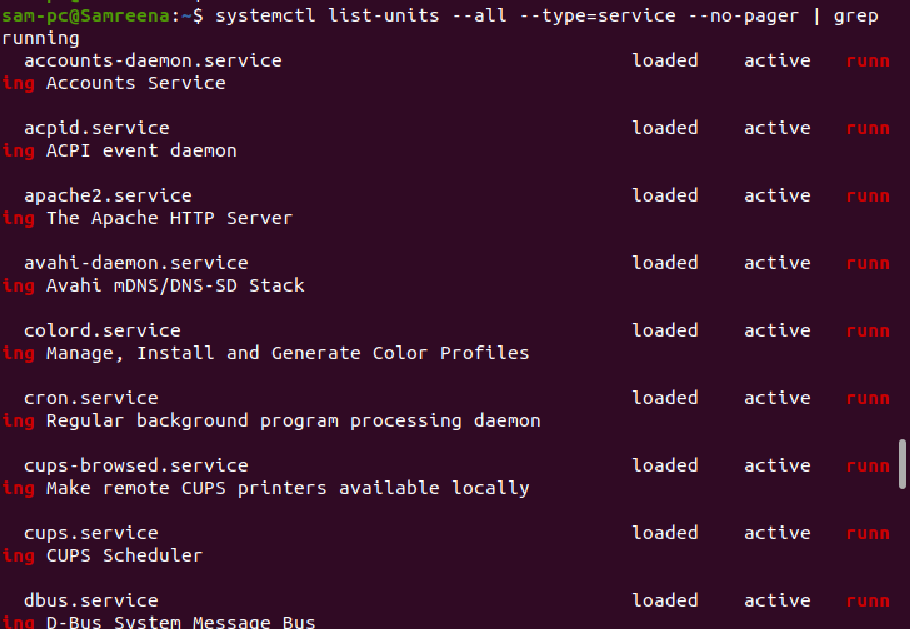
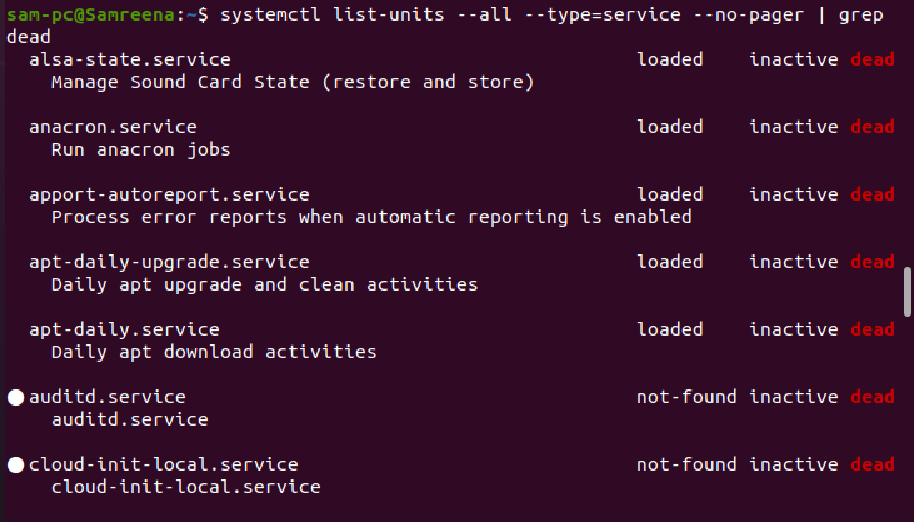
$ systemctl list-units --type=service --all
There are different states of the services, these can be loaded, running, or not found.
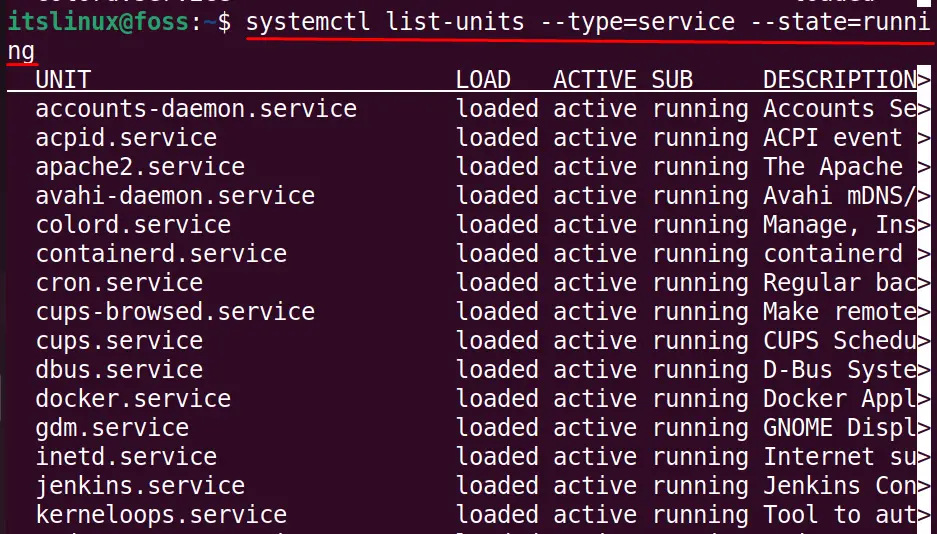
Check Running Services
To display all the running services, use the command:
$ systemctl list-units --type=service --state=running
All the services in a running state will be displayed on the screen.
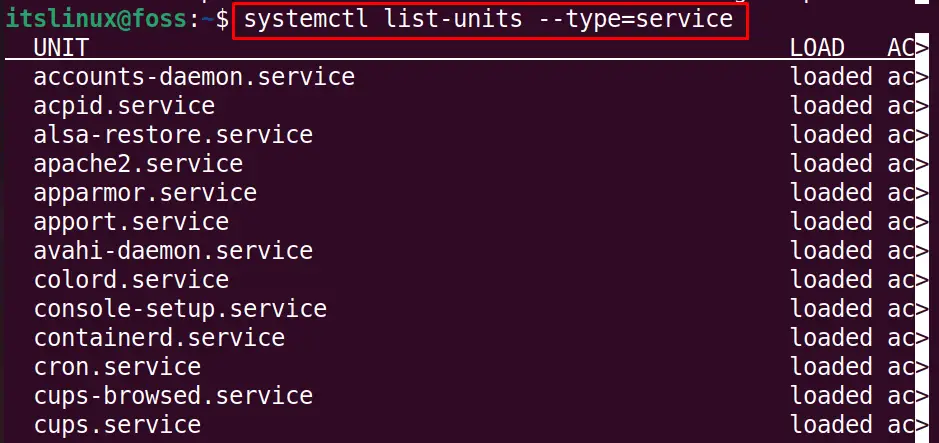
List Down the Loaded Services
Similarly, to display all the loaded services, simply use the command:
$ systemctl list-units --type=service
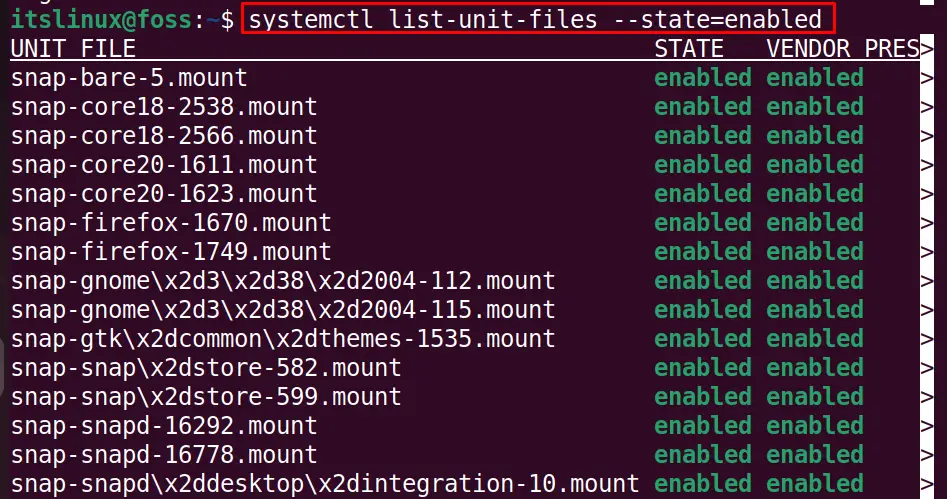
Show the Enabled Services
Likewise, to display the enabled services, use the command:
$ systemctl list-unit-files --state=enabled
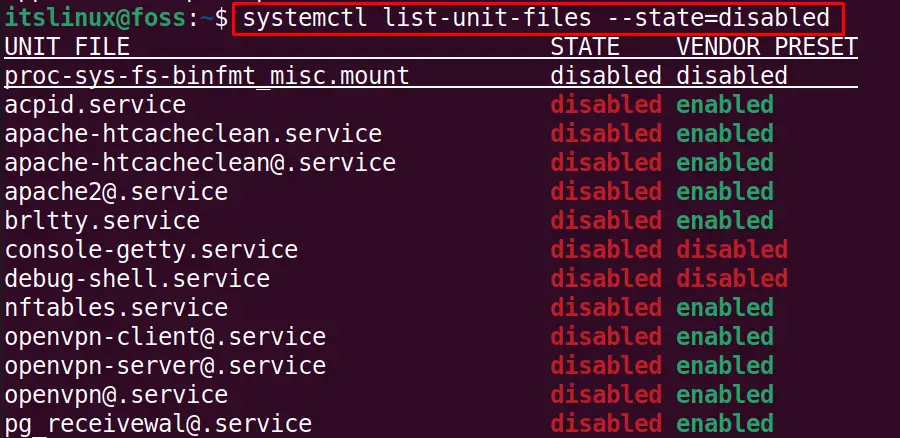
List Down Disabled Services
To display the disabled services, change the state in the above command:
$ systemctl list-unit-files --state=disabled
These are the different commands that can be used to display the status of the services using the systemctl utility.
Method 2: How to Check Services Running on Linux Using “service” Command?
Apart from the “systemctl” utility, another utility named “service” can also provide the list of services running in Linux.
List Down All Services
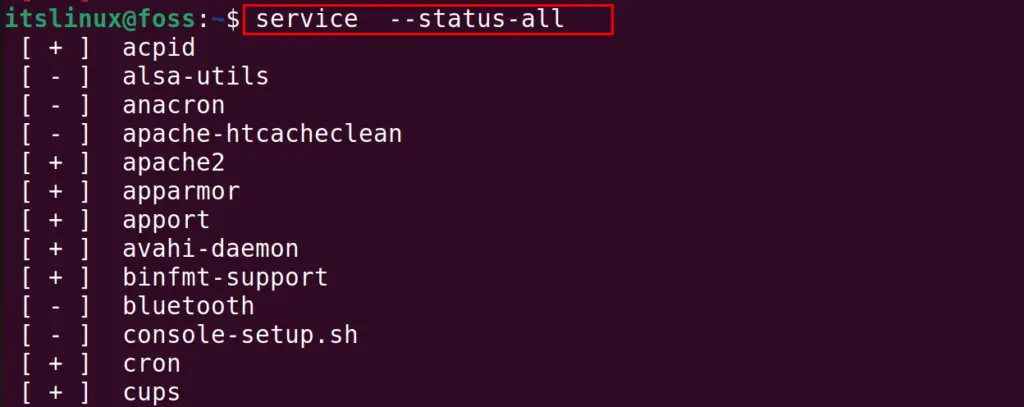
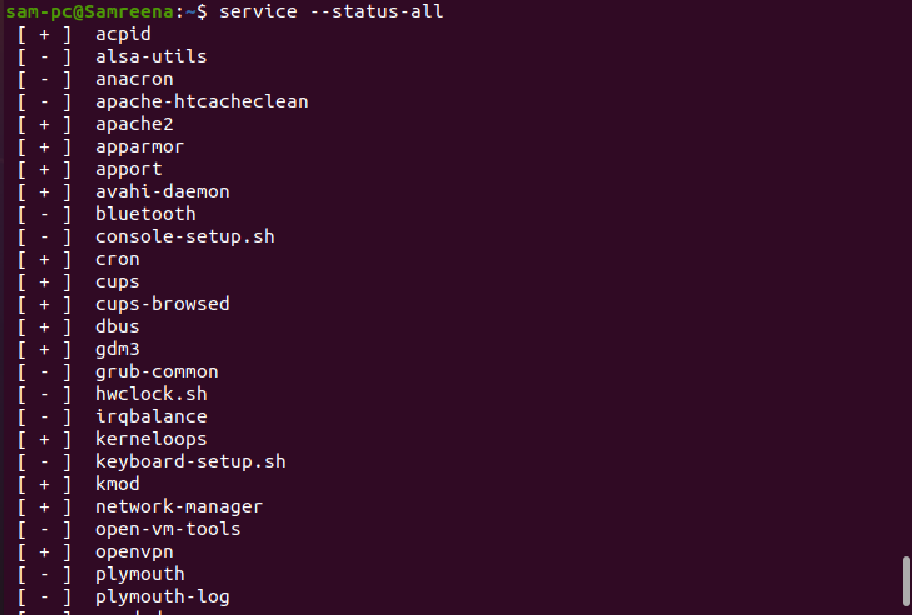
The following “service” command will list down all the services on the Linux system:
In the above figure, the services with the “+” sign are running on the system where the services with the “-” sign are not running on the system.
Check Running Services
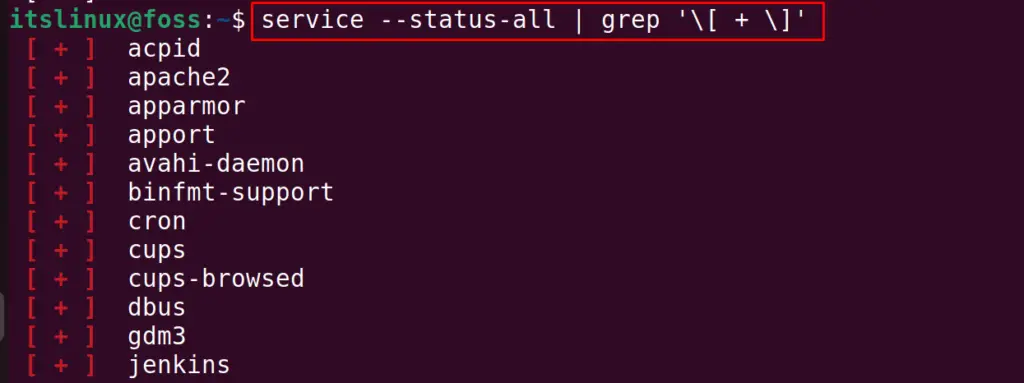
To list down only the running services, use the command:
Check Only Stopped Services
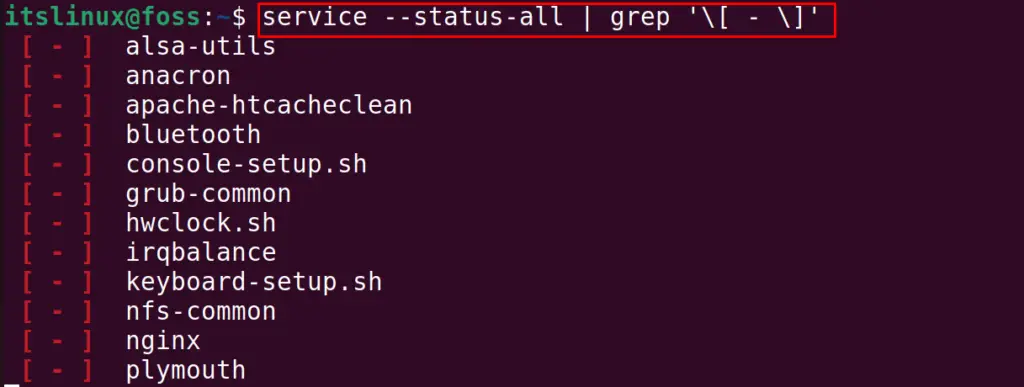
Likewise, to display the services which are not running but are installed on the system, use the command:
In these ways, the running services can be checked on Ubuntu.
That’s all from this guide!
Conclusion
To check the services running on Linux, open the terminal and run the command “systemctl list-units –type=service –state=running”. The service command “service –status-all | grep ‘\[ + \]’” can also list all the running services on Linux. Apart from the running services, the “systemctl” utility and “service” command can also be used to list the stopped or all services. This post has provided all the possible commands to check services running in Linux.
TUTORIALS ON LINUX, PROGRAMMING & TECHNOLOGY
How can I see all services in Ubuntu?
System services are the processes or system programs known as ‘daemons’ that continuously run in the background. These services wait for client requests and are responsible for how the system works and how it communicates with other programs. When working in a Linux environment, including Ubuntu, you can easily manage all system services (start, stop, restart, enable at system boot, etc.) through a service manager. Most of the modern Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, now use a process manager known as ‘systemd’. The systemd is a service manager in the Ubuntu system and used to replace the ‘init’ process. The systemd services manager is controlled by the primary command-line tool ‘systemctl’ command.
We will show you the various techniques in this tutorial related to listing or viewing all services in the Ubuntu 20.04 system.
How to list all services in Ubuntu?
Various services are running in the background of your Ubuntu Linux distribution. While working as a system administrator, you must know how to view all services, including system services such as (login, process management, syslog, cron jobs). You must have the knowledge to view all network services (remote login, web hosting, file transfer, DNS and DHCP, etc.) using the systemctl command and other ways you can control or manage all Linux services. We will also discuss this in this article.
List all services using the systemctl command
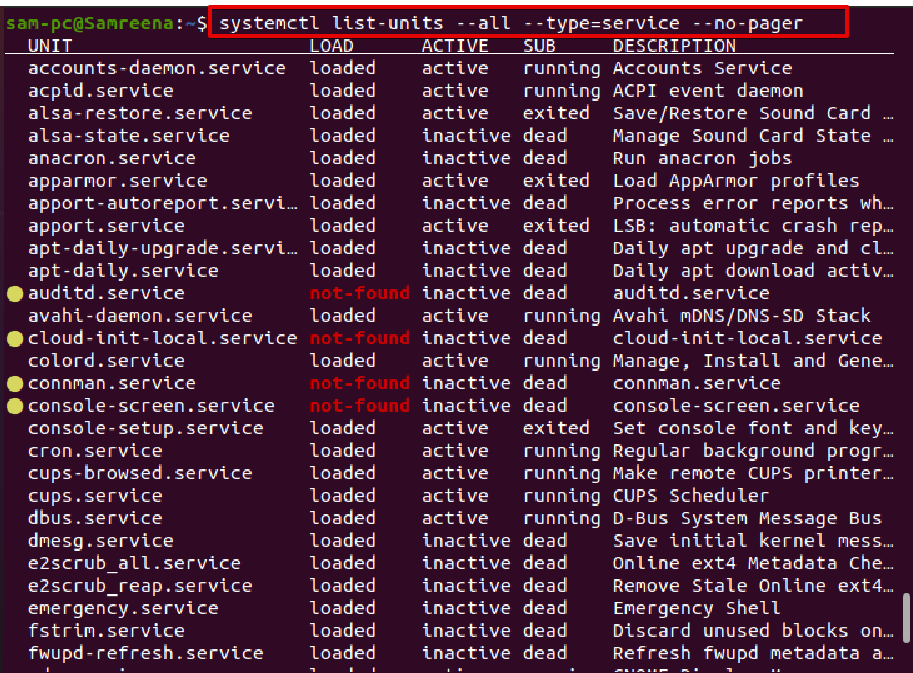
When the systemctl command is used without any arguments, in this case, it displays the list of loaded systemd units, including services either these are active or not.
The following command will also display all services unit files:
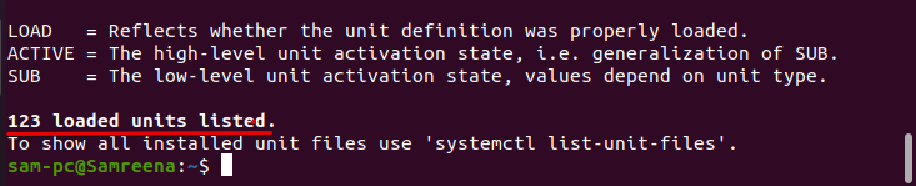
In the output, the details about UNIT, LOAD, ACTIVE, SUB, and service Description displays in the form of columns as follows:
- UNIT This column shows the corresponding details about the systemd unit name.
- LOAD The column displays the information about the unit, either currently loaded in the memory or not.
- Active This column shows whether the systemd unit is active or not.
- SUB This column shows the running state of the systemd unit.
- DESCRIPTION This column displays the short details about the unit.
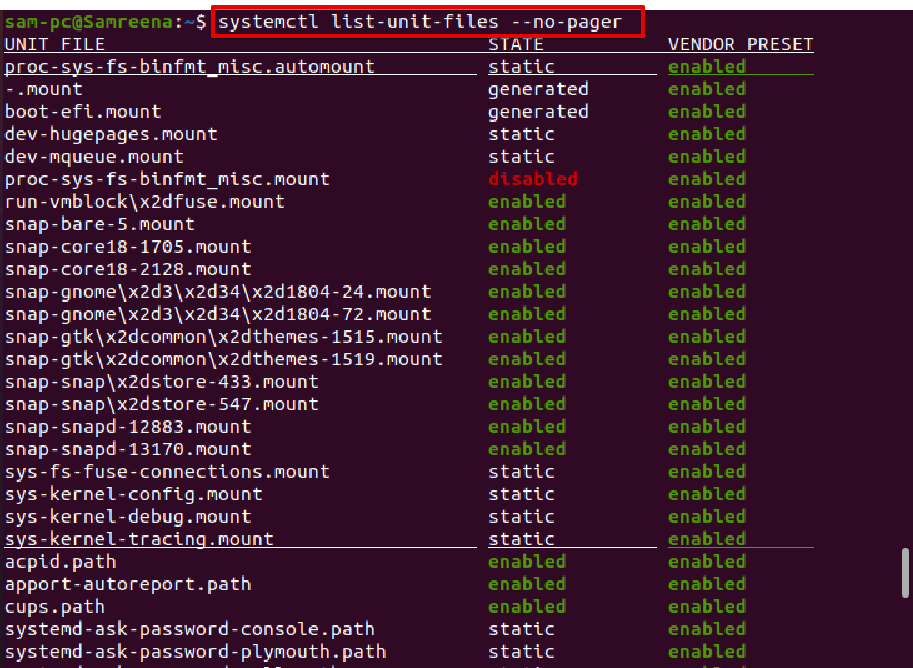
How to list systemd unit files?
The below-mentioned will show the all available systemd unit files rather than their type and running status info:
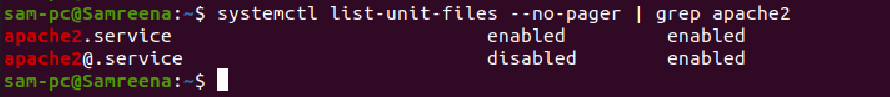
Use the grep command in case you are searching for a specific unit file. For example, the below command will search for an apache2 unit file:
If you want to search for a specific unit file, you can also perform this action using the grep command.
For example, we want to search an apache2 service unit file by using the grep command as follows:
The above command will retrieve all unit files related to the apache2 service that you can see in the following screenshot:
How to list systemd service unit files using states?
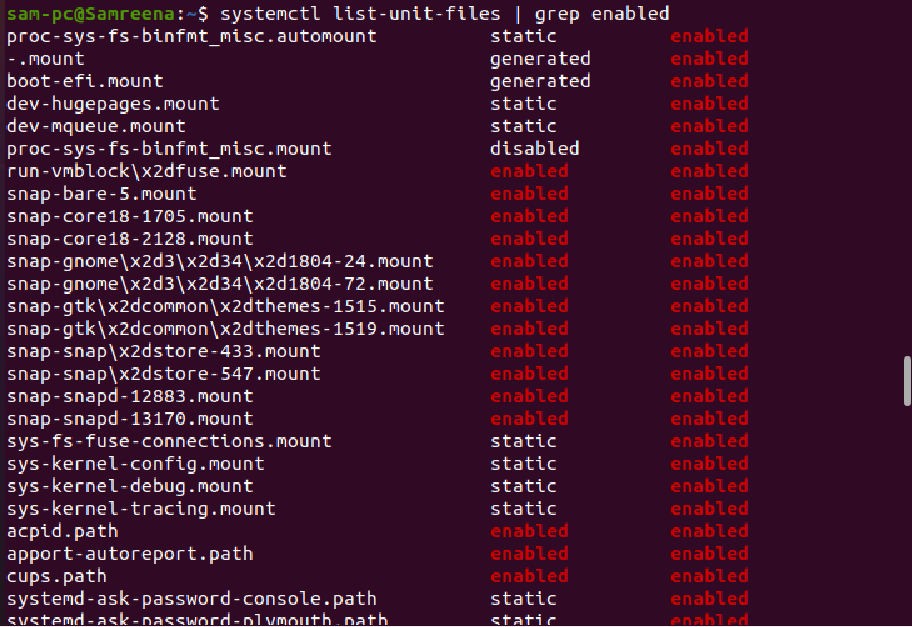
The following systemctl command will show you the information about all enabled systemd unit files on Ubuntu 20.04 system:
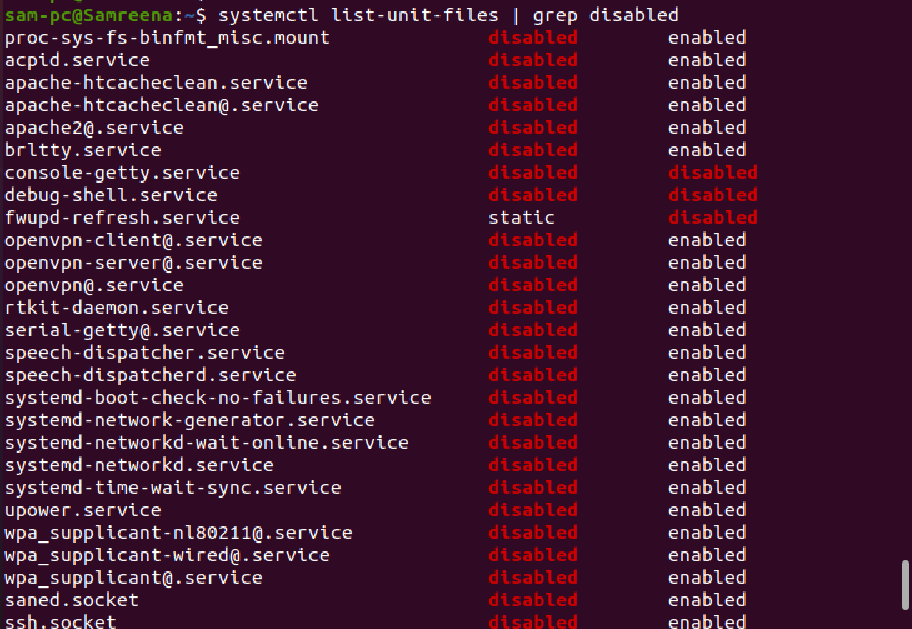
To display all disabled systemd unit files, run the below-mentioned command:
The services that are enabled on your system automatically start on system reboot.
List all active or running services
Using the ‘systemctl’ command, you can filter active or running services from the all services list as follows:
List all excited services
By running the below-given command, you can easily list all services with the excited state:
List all stopped or dead services
With the help of the following command, you can easily list all disabled services on the terminal window:
Managing systemd services using systemctl
The systemctl is the most commonly used command to manage the systemd unit files and services in Ubuntu 20.04 distribution. Users can enable, disable, start and stop services using the following commands respectively.
$ sudo systemctl enable service-name
$ sudo systemctl disable service_name
$ sudo systemctl start service_name
$ sudo systemctl disable service-name
Using the above commands, you can control each service state based on your requirements.
View service status using systemctl command
To view the detailed information about a particular service, use the below-mentioned command:
For example, we want to check the complete status of the ‘ssh’ service. In this case, by running the following command, you can display the complete status of the ssh service as follows:
More commands to list services in Ubuntu
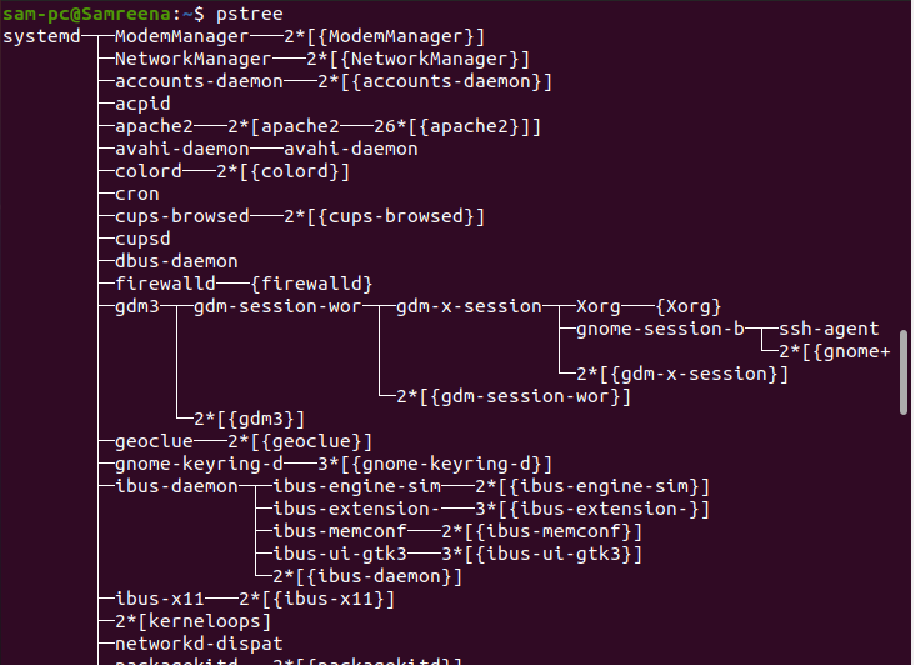
Use of pstree command
Using the ‘pstree’ command, you can list all running Ubuntu services in the form of the tree structure as follows:
List firewall services
By running the following command, the user can easily list firewall services and ports:
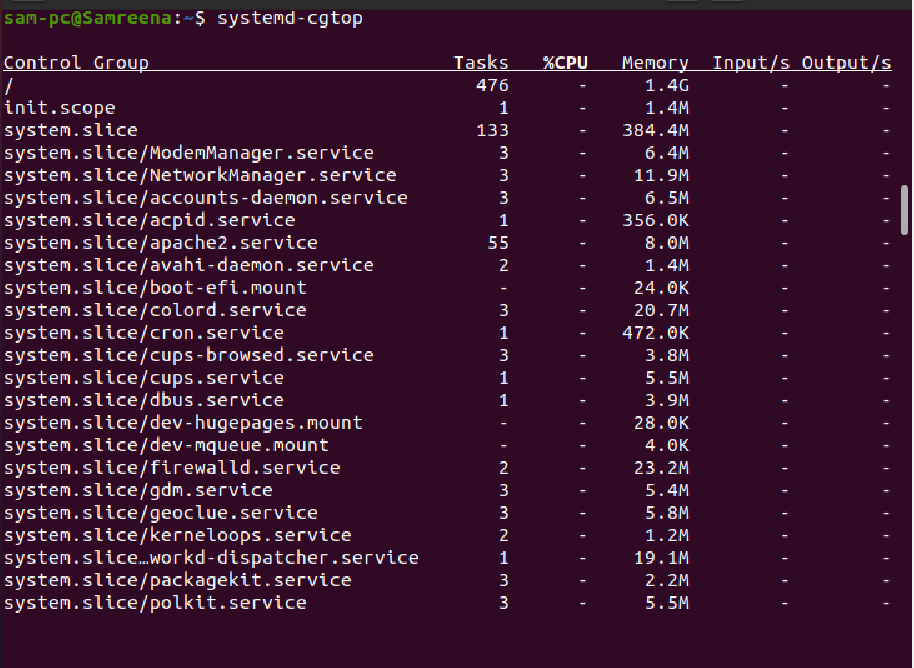
List top control groups with resource utilization
The ‘systemd-cgtop’ command is used to display the top control groups by their resource utilization as follows:
The previous Ubuntu distributions use the ‘service’ command to list all system services as follows:
You can also view all services by directly listing the /etc/init.d directory in older Ubuntu systems as follows:
Conclusion
We learned how to list all services in Ubuntu 20.04 system using the systemctl command. We have also experienced various commands that are also helpful in listing all Ubuntu services. Most of the commands, like the service command, are obsolete now. In the latest Ubuntu distribution, system administrators use ‘systemctl’ to get the details about all systemd services. The systemctl command also offers advanced features and is quite more useful as compared to the other service listing commands.
About the author
Samreena Aslam
Samreena Aslam holds a master’s degree in Software Engineering. Currently, she’s working as a Freelancer & Technical writer. She’s a Linux enthusiast and has written various articles on Computer programming, different Linux flavors including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, and Mint.
How to List Services in Ubuntu Server / Desktop
In this tutorial we are going to learn how to list services in Ubuntu using the command line interface. We will see how we can list running services and services that are not running.
List Ubuntu Services with Service command
The service —status-all command will list all services on your Ubuntu Server (Both running services and Not running Services).
This will show all available services on your Ubuntu System. The status is [ + ] for running services, [ — ] for stopped services.
Using the grep command, we can filter the output to show only the running services.
To list ubuntu services that are not running, Type,
The service command can be used to list services in all Ubuntu releases, including (Ubuntu 17, 16.04, and 14.04).
List Services with systemctl command
Since Ubuntu 15, the services are managed by the systemd. With systemd we can use systemctl command to get information about running services in our Ubuntu system.
To list all running services on Ubuntu, Type:
The output of the command will look something like this:
UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION apache2.service loaded active running LSB: Apache2 web server apparmor.service loaded active exited LSB: AppArmor initialization cron.service loaded active running Regular networking.service loaded active exited Raise network interfaces nmbd.service loaded active running LSB: start Samba NetBIOS nameserver (nmbd) smbd.service loaded active running LSB: start Samba SMB/CIFS daemon (smbd) ssh.service loaded active running OpenBSD LOAD = Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded. ACTIVE = The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB. SUB = The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type. To list all services, including inactive units, Type:
To List inactive unit, Type:
systemctl list-units -a --state=inactiveThe systemctl command does not work for Ubuntu 14.04 and earlier releases, instead use the service —status-all command mentioned above.