- How do I determine the total size of a directory (folder) from the command line?
- How to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
- Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
- Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
- Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
- 5 Commands to Check Folder Size in Linux and Best Practices
- Using the du command
- Using the df command
- How to Get Directory Size in Linux with du Command
- Using the ls command
- Using the tree command
- Using the ncdu command
- Other helpful command examples to check folder size in Linux
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions — FAQs
- How do I check the size of a folder in Linux using du command?
- Can I exclude certain files or folders while checking folder size in Linux using du command?
- How do I use the ls command to check folder size in Linux?
- Can I see the size of hidden files and folders using the tree command in Linux?
- What is the advantage of using the ncdu command to check folder size in Linux?
- How can I visualize file and folder sizes using the tree command in Linux?
How do I determine the total size of a directory (folder) from the command line?
The -h flag on sort will consider «Human Readable» size values.
If want to avoid recursively listing all files and directories, you can supply the —max-depth parameter to limit how many items are displayed. Most commonly, —max-depth=1
du -h --max-depth=1 /path/to/directory I use du -sh or DOOSH as a way to remember it (NOTE: the command is the same, just the organization of commandline flags for memory purposes)
There is a useful option to du called the —apparent-size. It can be used to find the actual size of a file or directory (as opposed to its footprint on the disk) eg, a text file with just 4 characters will occupy about 6 bytes, but will still show up as taking up ~4K in a regular du -sh output. However, if you pass the —apparent-size option, the output will be 6. man du says: —apparent-size print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in (‘sparse’) files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks
This works for OS X too! Thanks, I was really looking for a way to clear up files, both on my local machine, and my server, but automated methods seemed not to work. So, I ran du -hs * and went into the largest directory and found out which files were so large. This is such a good method, and the best part is you don’t have to install anything! Definitely deserved my upvote
@BandaMuhammadAlHelal I think there are two reasons: rounding ( du has somewhat peculiar rounding, showing no decimals if the value has more than one digit in the chosen unit), and the classical 1024 vs. 1000 prefix issue. du has an option -B (or —block-size ) to change the units in which it displays values, or you could use -b instead of -h to get the «raw» value in bytes.
How to Get the Size of a Directory in Linux
Many users run Linux from the command line. However, the command line — sometimes known as the terminal — doesn’t have an intuitive interface for checking disk space in Linux.
This guide shows you how to find the size of a specific directory in Linux from the command line.
- A system running Linux
- A command line / terminal window (available by clicking Search, then typing terminal)
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
Note: In Linux, a directory is the equivalent of a folder in Windows. A directory may have directories inside (called subdirectories), or it may only contain files.
Option 1: Display the Size of a Directory Using the du Command
The du command stands for disk usage. This command is included by default in most Linux distributions.
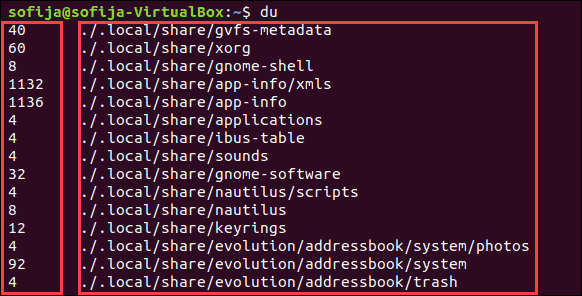
You can display the size of your current directory by typing du in the command line:
The system should display a list of the contents of your home directory, with a number to the left. That number is the size of the object in kilobytes.
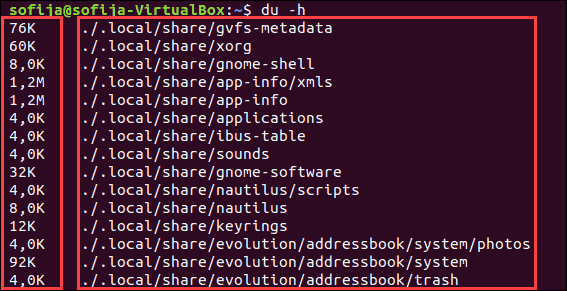
You can add the -h option to make the output more readable:
Each entry will start with a number and a letter. The number is the amount of space used, and the letter (usually K, M, or G) indicates Kilobytes, Megabytes, or Gigabytes. For example:
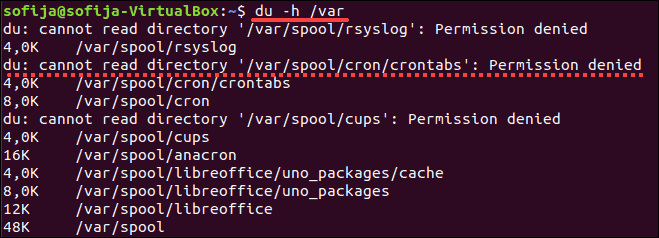
400K – 400 kilobytes 7.3M – 7.3 megabytes 2.2G – 2.2 gigabytesTo find the size of a specific directory different from your current working directory. The du command allows you to specify a directory to examine:
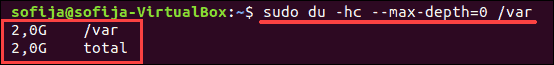
This displays the size of the contents of the /var directory. You may see some entries with an error, as in the image below.
This happens when your user account does not have permission to access a particular directory. Use the sudo or su command to get access privileges:
Note: Some versions of Linux don’t enable sudo by default. You can use the su command to switch to the root user account instead.
To display total disk usage of a particular directory, use the -c command:
Options can be combined. If you wanted to repeat the previous command in human-readable format, enter the following:
You can limit the scan to a certain level of subdirectory by using the max-depth option. For example, to scan only the size of the top directory, use —max-depth=0 :
If you wanted to list only the top directory and the first layer of subdirectories, change —max-depth=1 :
If you run into trouble or want to explore more options for the du command, enter the following command to display the help file:
Option 2: Get Size of Directory in Linux Using tree Command
By default, the tree command is not included in some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
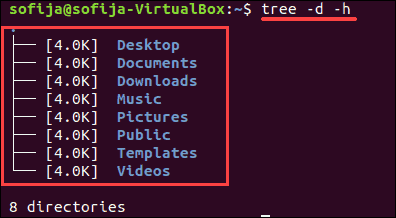
The tree command displays a visual representation of your directories. It uses lines to indicate which subdirectories belong where, and it uses colors to indicate directories and files.
tree can also be used with options. To display a human-readable size of the current directory’s subdirectories, enter the following:
Like the du command, tree can target a specific directory:
This command takes a few moments since the /var directory has many entries.
The tree command also has a help file, which you can access by entering:
Option 3: Find the Size of a Linux Directory Using ncdu Command
The ncdu tool stands for NCurses Disk Usage. Like the tree command, it is not installed by default on some versions of Linux. To install it, enter the following:
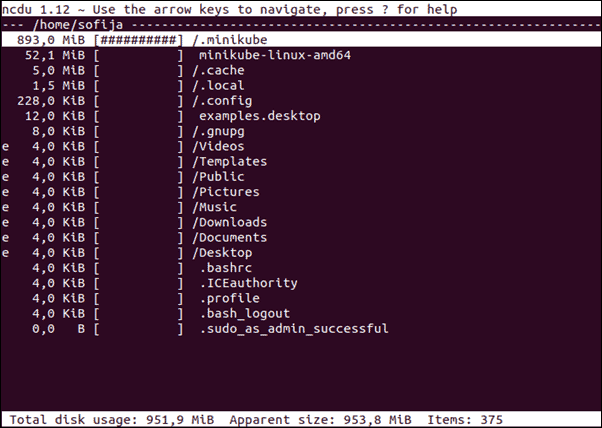
The ncdu utility is an interactive display of your disk usage. For example, enter the following:
In the upper left corner, it displays the current directory being scanned. A column on the left displays the numerical size, a graph of #- signs to indicate the relative size, and the file or directory.
Use the up and down arrows to select different lines. The right arrow will browse into a directory, and the left arrow will take you back.
ncdu can be used to target a specific directory, for example:
For help, press the ? key inside the ncdu interface. To quit, press the letter q .
Note: Learn how to move directories in Linux using the GUI or system commands.
You now have three different options to find the size of a directory in Linux operating systems.
If you want to learn more about directories in Linux, read our article how to rename directories in Linux.
5 Commands to Check Folder Size in Linux and Best Practices
Learn how to check folder size in Linux using commands such as du, df, ls, tree, and ncdu. Discover their advantages, disadvantages, and best practices for efficient disk space management.
- Using the du command
- Using the df command
- How to Get Directory Size in Linux with du Command
- Using the ls command
- Using the tree command
- Using the ncdu command
- Other helpful command examples to check folder size in Linux
- Conclusion
- How to check folder size on Linux?
- How do I check the size of a folder?
- What is size command in Linux?
- How to check size in Linux?
As a Linux user, managing disk space is essential to keep your system running smoothly. Checking folder size can help you identify large files or directories that are taking up too much space and causing your system to slow down or crash. Fortunately, Linux offers various ways to check the size of a folder using command line tools such as du , df , ls , tree , and ncdu . In this blog post, we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and best practices of each command.
Using the du command
The du command is a disk usage utility that estimates the space used by files and directories in the present working directory. It is a versatile command that provides a summary of file and folder sizes. You can use the -s option to get results in “Human Readable Format”, which displays sizes in KB, MB, or GB. Additionally, the —apparent-size option can be used to find the apparent size of a directory , which is the amount of space used by the directory entries themselves.
One advantage of using the du command is the ability to summarize the disk usage of files and directories in your system. This can be useful for identifying large files or directories that are taking up too much space. However, the time it takes to scan large directories can be a disadvantage of this command. To overcome this, you can use options such as —exclude and —threshold to exclude certain files or set a minimum threshold for file sizes.
Using the df command
The df command shows the amount of disk space used and available on a file system. It is a quick and straightforward way to check disk space usage. You can use the df command to know the free space in the filesystem containing the directory. One advantage of using the df command is the speed of the command in checking disk space usage. However, the df command does not show the size of individual files or folders, which is a disadvantage.
How to Get Directory Size in Linux with du Command
You may use ls -h to get the size of files but you won’t get the directory size. To check the Duration: 3:20
Using the ls command
The ls command is a simple and easy-to-use command that lists all files and directories in the current directory. It can be used to check the size of individual files or folders. The -h flag can be used to format the sizes in KB, MB, and GB for you. This command is useful for quick and easy checks of file and folder sizes. However, the ls command does not show the size of hidden files, which is a disadvantage.
Using the tree command
The tree command lists the contents of a directory in a tree-like format. It is a useful command that provides an easy visualization of file and folder sizes. You can use the -h flag to show file and folder sizes in “human-readable” format. However, the tree command does not show the size of hidden files, which is a disadvantage.
Using the ncdu command
The ncdu command is a disk usage analyzer with an ncurses interface. It provides a detailed summary of disk usage, including individual file and folder sizes. One advantage of using the ncdu command is the user-friendly interface and detailed information on disk usage. However, the ncdu command can take up system resources while scanning large directories, which is a disadvantage.
Other helpful command examples to check folder size in Linux
In shell, how to check folder size in linux code example
# show all folder size in the current directory du -h --max-depth=1In shell, command to check size of folder in linux code example
du -lh --max-depth=1 --block-size=M | sort -nrIn shell, size of folder linux code example
In shell, get folder size linux code example
#This shows you the folder size in human readable formatsudo du -sh /folderIn shell, find folder size in linux code example
In shell, how to check directory size in linux code example
du -h --max-depth=1 /directory du -sh * du -sh /directory du -shx /directoryConclusion
Checking folder size in Linux is essential for managing disk space and preventing system crashes or data loss. There are various commands such as du , df , ls , tree , and ncdu that can be used to check folder size in Linux. Knowing the advantages, disadvantages, and best practices of each command can help you choose the most efficient way to check folder size in Linux. By mastering these commands, you can keep your system running smoothly and avoid running out of disk space.
Frequently Asked Questions — FAQs
How do I check the size of a folder in Linux using du command?
To check the size of a folder in Linux using the du command, open your terminal and type «du -sh foldername». This will display the size of the folder in a human-readable format.
Can I exclude certain files or folders while checking folder size in Linux using du command?
Yes, you can exclude certain files or folders while checking folder size in Linux using the du command. Use the «—exclude» option followed by the file or folder name you want to exclude. For example, «du -sh —exclude=foldername» will exclude the folder named «foldername» from the size calculation.
How do I use the ls command to check folder size in Linux?
To use the ls command to check folder size in Linux, open your terminal and navigate to the folder you want to check. Then, type «ls -sh» to display the size of all files and folders in the current directory.
Can I see the size of hidden files and folders using the tree command in Linux?
What is the advantage of using the ncdu command to check folder size in Linux?
The ncdu command provides a user-friendly interface and detailed information on disk usage, including individual file and folder sizes.
How can I visualize file and folder sizes using the tree command in Linux?
To visualize file and folder sizes using the tree command in Linux, open your terminal and navigate to the folder you want to check. Then, type «tree -h» to display the size of all files and folders in a tree-like format.