- LFCA: Learn to Manage Time and Date in Linux – Part 6
- Check Time and Date On a Linux System
- How to Set a Timezone on a Linux System
- Set Date and Time on a Linux System
- Set Automatic Time Synchronization using NTP Server
- Related Posts
- 1 thought on “LFCA: Learn to Manage Time and Date in Linux – Part 6”
- How to Use Ubuntu Timedatectl
- Hardware Clock
- Software Clock
- How to check and edit time/date on Ubuntu 20.04
- How to check current time and date using timedatectl
- How to Change the time or date using timedatectl
- How to Change the time zone using timedatectl
- How to Synchronize Real Time Clock using timedatectl
- Conclusion
LFCA: Learn to Manage Time and Date in Linux – Part 6
This article is Part 6 of the LFCA series, here in this part, you will acquaint yourself with the general system administration commands to manage time and date settings in the Linux system.
Time is crucial in any Linux system. Multiple services such as crontab, anacron, backup and restore services depend on accurate time to carry out their tasks as expected.
Linux has 2 types of clocks:
- Hardware clock – This is the battery-powered clock also referred to as the CMOS clock or RTC ( Real Time Clock). The clock runs independently of the operating system & keeps running even when the system is powered off provided the CMOS battery is present.
- System clock ( Software clock ) – This is also referred to as the kernel clock. At boot time, the system clock is initialized from the hardware clock and takes over from there.
Usually, there exists a time difference between the two clocks such that they gradually drift from each other. We will come to this later and show you how you can sync these clocks.
For now, we will see how you can check time and date on a Linux system.
Check Time and Date On a Linux System
There are two main utilities used to check time and date on a Linux system. The first is the date command. Without any arguments, it provides quite a bit of information shown
$ date Friday 26 March 2021 11:15:39 AM IST
To view the date in dd-mm-yy time format only, execute the command:
$ date +"%d-%m-%y" 26-03-21
If you just want to view the current time only and nothing else, use the command:
$ date "+%T" 11:17:11
The timedatectl command is a new utility used in modern Linux systems such as Ubuntu 18.04, RHEL 8 & CentOS 8. It’s a replacement of the date command which was prominent in the old SysVinit systems. It can be used to query and adjust the time on a Linux system.
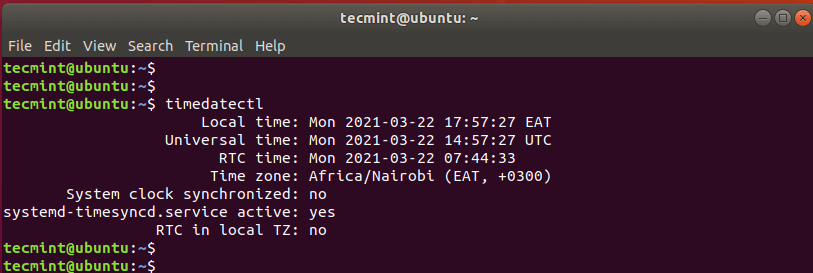
Without any options, the timedatectl command prints out an array of information such as the local time, UTC time, RTC time, and the timezone to mention a few.
How to Set a Timezone on a Linux System
On a Linux system, time is dependent on the timezone that is set. To check the timezone that is configured on your system, issue the command:
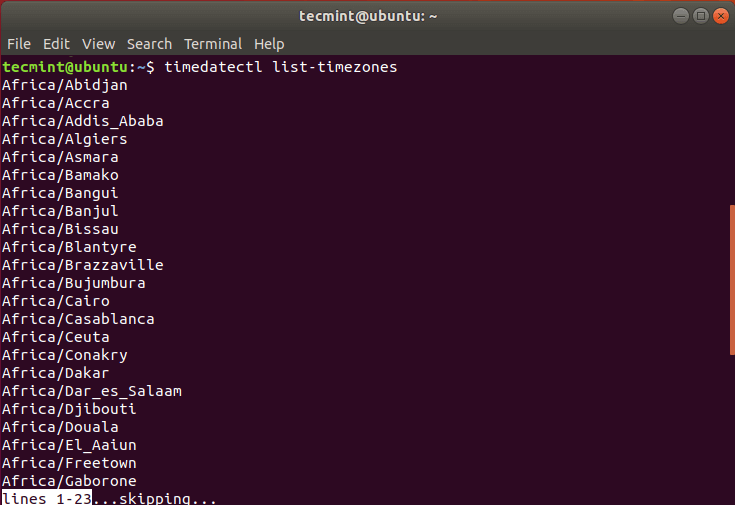
From the output in the snippet above, I am in the Africa/Nairobi timezone. To view the available timezones, run the command:
$ timedatectl list-timezones
Press ENTER to scroll through the whole list of the possible time zones that are available.
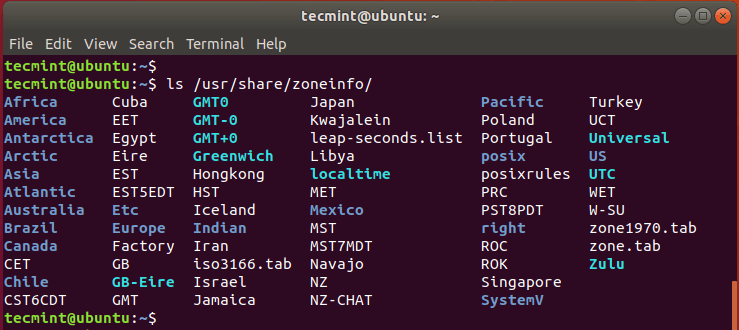
Timezones are also defined in the /usr/share/zoneinfo/ path as shown.
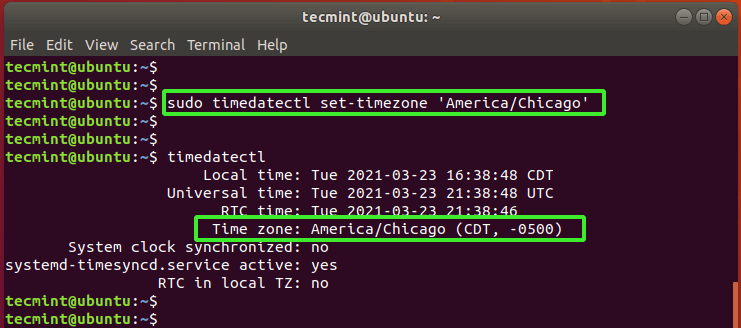
There are a couple of ways that you can use to configure the timezone. Using the timedatectl command, you can set the timezone, for instance, to America/Chicago, using the syntax shown.
$ timedatectl set-timezone 'America/Chicago'
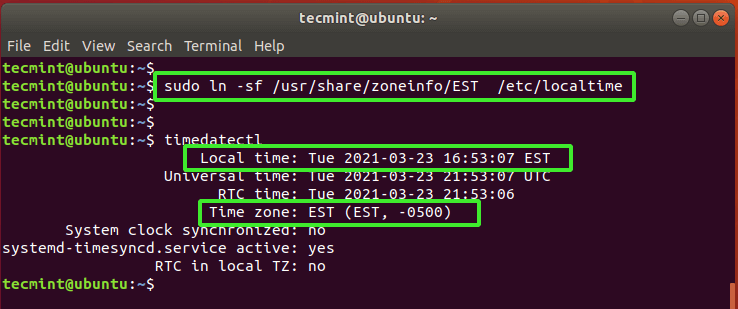
The other way you can set the timezone is to create a symbolic link from a timezone file in the /usr/share/zoneinfo path to /etc/localtime. For example, to set the local time zone to EST (Eastern Standard Time), issue the command:
$ sudo ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/EST /etc/localtime
Set Date and Time on a Linux System
To set time only on a Linux system using the format HH:MM:SS (Hour: Minute: Second ), use the syntax below
$ timedatectl set-time 18:30:45
To set the date only in YY-MM-DD (Year: Month: Day) format, use the syntax:
$ timedatectl set-time 20201020
To set both date and time, run:
$ timedatectl set-time '2020-10-20 18:30:45'
NOTE: Manually setting time and date in this manner is not recommended since you are likely to configure inaccurate time and date settings. In fact, by default, automatic time synchronization is turned on to prevent you from making manual time and date settings.
The most recommended way to set time is by either specifying the time zone that you are in as shown earlier or turning on automatic time synchronization with a remote NTP server.
Set Automatic Time Synchronization using NTP Server
NTP is short for Network Time Protocol, which is an internet protocol that is used to automatically synchronize the system’s time clock with a pool on online NTP servers.
Using the timedatectl command, you can set automatic time synchronization as follows:
To disable automatic NTP time synchronization, execute:
Conclusion
The timedatectl and date commands are handy command-line tools that can help you check and adjust your time on Linux.
This is James, a certified Linux administrator and a tech enthusiast who loves keeping in touch with emerging trends in the tech world. When I’m not running commands on the terminal, I’m taking listening to some cool music. taking a casual stroll or watching a nice movie.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
1 thought on “LFCA: Learn to Manage Time and Date in Linux – Part 6”
“The timedatectl command is a new utility used in MODERN Linux systems such as Ubuntu 18.04, RHEL 8 & CentOS 8. It’s a replacement of the date command which was prominent in the OLD SysVinit systems.” (emphases mine) That statement insinuates that systemd is the new standard and SysVinit, and other non-systemd inits, are totally deprecated, which is very far from the truth. Whether a Linux distro is Modern or OLD is determined by the kernel version it uses, not the version of any of the distro’s components, even if it is the init. There still are many MODERN Linux systems, such as Gentoo, PCLinuxOS, Devuan, Artix, and others that use SysVinit, runit, or other inits rather than systemd. BTW – Ubuntu 18.04 can in no way be considered MODERN as Ubuntu 21.04 has been already released. “There are two main utilities used to check time and date on a Linux system.” You should differentiate right up front which command is used by distros using systemd as init and which command is used by distros using non-systemd inits. Somehow you did not provide the “date” command options for setting time zone, date & time, and how to sync with NTP servers. Reply
How to Use Ubuntu Timedatectl
Every computing device has time and date as the very basic service provided by them. Date/time and time zone are interlinked phenomena in computing devices as date/time depends on the time zone selected by the user. The date and time are automatically fetched according to the time zone; however, the users can also change them manually.
The Linux computer manages two types of clocks:
Hardware Clock
It is also known as Real-Time Clock (RTC) and keeps on tracking the time and date even if the system is turned off. There is a small battery backup available for RTC that enables it to keep on running the clock.
Software Clock
Contrary to RTC, this clock has no power back up; thus, it does not keep the time when the system is powered off or on low power. However, when the system is turned ON, it gets help from the hardware clock and fetches the correct date/time. A software clock can also be referred to as a system clock.
In this article, we will provide a detailed usage of a well-known timedatectl command; so, let’s start:
How to check and edit time/date on Ubuntu 20.04
This section explains the process of checking and editing the time/date on Ubuntu 20.04.
The syntax timedatectl command is given below:
How to check current time and date using timedatectl
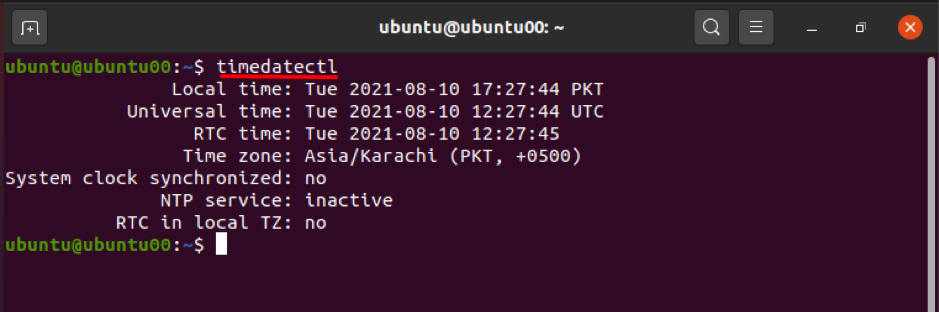
The primary use of this command is to show you current date and time; execute the command mentioned below to get the print of time and date:
After getting the result of the above command; you may notice detailed information such as your local time and date, universal time, time zone, etc.:
How to Change the time or date using timedatectl
The timedatectl command can be used to change the time or date of the system. To change the date or time, following syntax is used:
Moreover, the following command will change the local time to 11:11:11(HH:MM:SS); it is observed that the universal time and RTC are also adjusted according to local time:
To verify the changes, you must execute the following command:
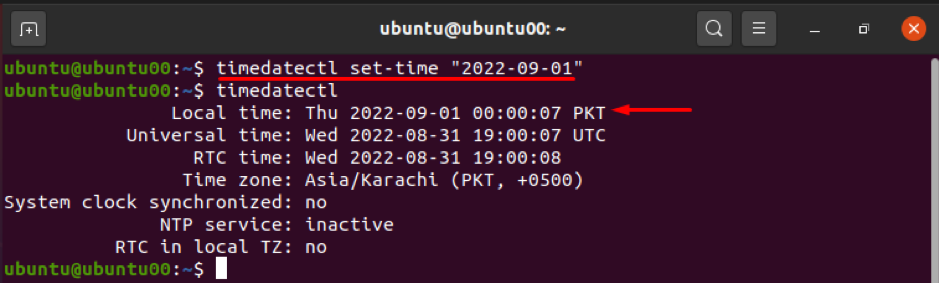
Similarly, one can change the current date of the system using the same command as above:
The syntax to change the date of the system is given below:
Where “Y”, “M” and “D” represent the year, month, and day respectively.
For instance, the command given below changes the date to 2022-09-01(YYY-MM-DD): it is noted that time will also be reset to 00:00:00 :
How to Change the time zone using timedatectl
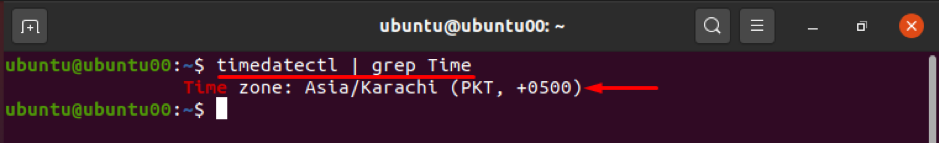
Firstly, you must know the time zone in which you are operating; you can check your time zone using the following command:
Or simple timedatectl command can also give you the required result, as shown in the screenshot below:
The timedatectl can be used to change the current time zone; firstly, you must know the time zones supported by your system; to check the list of available time zones, execute the following command.
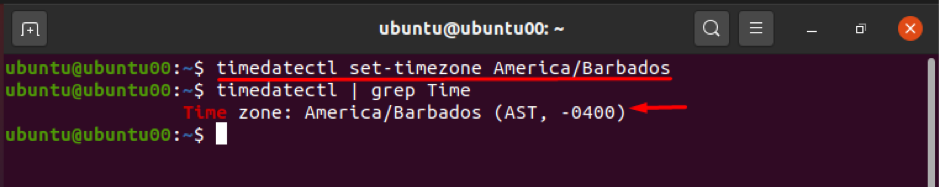
In case you want to change the time zone to other available time zones, the above list would be helpful to you in this regard. You can set the timezone by following the syntax described below:
For instance, the following command will help to change the time zone to “America/Barbados”:
Moreover, if you want to set the time zone to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), then execute the command given below: it is recommended to keep the settings of the clock in UTC:
How to Synchronize Real Time Clock using timedatectl
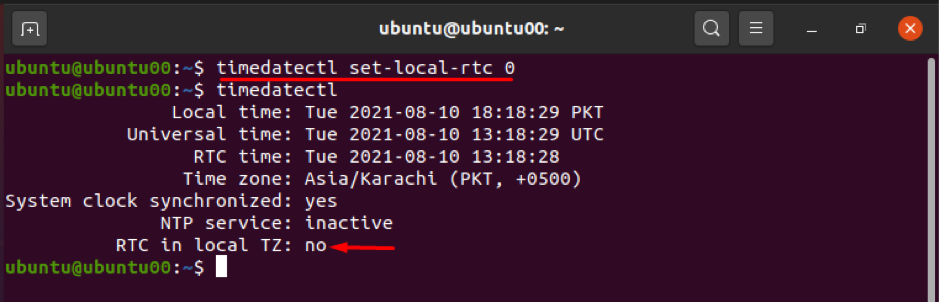
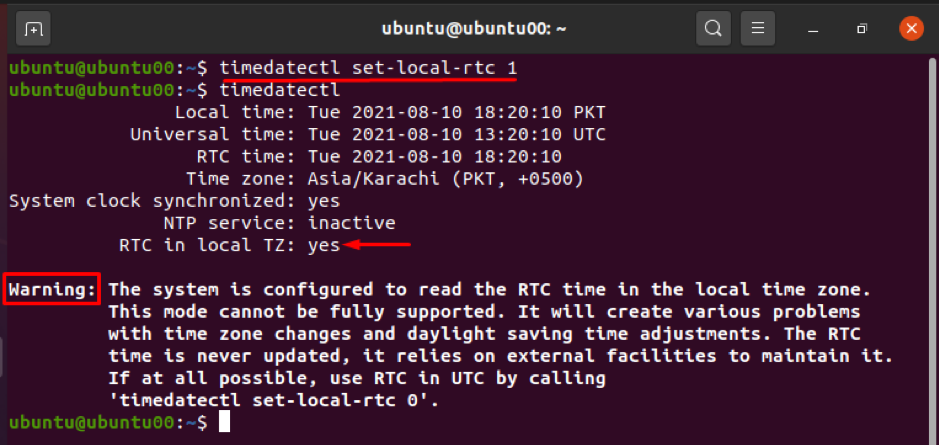
The hardware clock (also known as a real-time clock) of the system can be synchronized with your local time zone or UTC, using the timedatectl command. It passes binary numbers (0,1) to the command, which refers to the local time zone or UTC.
The binary number (0) is used to sync the hardware clock with the local time zone, and you can execute the following command to synchronize the Real-Time Clock to UTC:
Alternatively, you can synchronize RTC to the local time zone by using the command given below. This command will show the warning that changing the RTC to a local time zone can cause problems.
Referring to the syntax of timedatectl, it contains option keywords between timedatectl and command keywords. The timedatectl supports various options that can be considered to perform specific tasks, such as:
–h shows the help information
To check the version of the timedatectl; —version option is used.
—no–ask–password option will allow the user to bypass the authentication process
Conclusion
Ubuntu being the famous distro of Linux, allows a variety of commands to perform several operations. Among them, the timedatectl command is used to facilitate the command line users regarding the time zone, date, and time of your system. This guide provides brief information related to the timedatectl command of Ubuntu. The users can edit time, date, and time zone using the command line terminal. Moreover, it allows synchronization of the Real-Time Clock with local time zone or UTC, but it is better to practice keeping the RTC synchronized with UTC.