- How to Set the Permission drwxr-xr-x to Folders?
- What are Permissions in Linux?
- What are Different Users in Linux?
- How to Set the Permission drwxr-xr-x to Folders?
- Method 1: Using Alphabetic Representation of Permissions
- Method 2: Using Numeric Values of Permissions
- Conclusion
- Права доступа к файлам Linux
- Примеры форматов
- Права доступа к папке Linux
- Изменение прав доступа
- Примеры изменения прав доступа Linux
How to Set the Permission drwxr-xr-x to Folders?
Linux Operating System (OS) consists of different system files, and only a skilled administrator is authorized to manipulate them. To keep the files/folders secure, Linux allows setting different permissions to various users, groups, etc. This post aims to set the permission drwxr-xr-x to folders in Linux.
We will show you how to grant everything to the main users or admins and remove the right to write anything for the group/other users by discussing the two main topics listed below:
- What are Permissions in Linux?
- How to Set the Permission drwxr-xr-x to Folders?
- Method 1: Using Alphabetic Representation of Permissions
- Method 2: Using Numeric Values of Permissions
Let’s discuss them one by one in more detail.
What are Permissions in Linux?
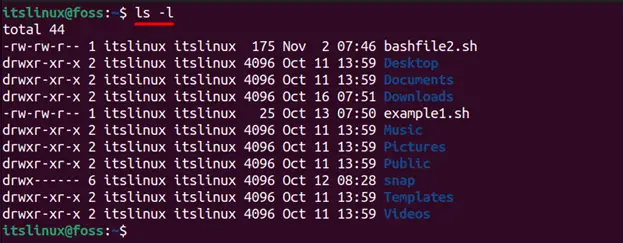
You can see the list of permission of files/directories in PWD by typing the following command in the terminal:
When you look at the above image closely, you will find different characters such as “d”, “r”, “w” and “x” written at the start. A total of 10 dashes are available where “d” stands for the directory, “r” stands for read, “w” stands for write, and “x” stands for execute. Now let’s discuss what these permissions do in detail.
Read: If the “r” is written, then the user has permission to read else the user cannot read. .
Write: You can either have permission to write on a file and do some modifications or you cannot perform any changes on the file/directory.
Execute: Shows the executable permissions of a file/directory by the user.
Also, the letter ‘d’ written at the start stands for the directory.
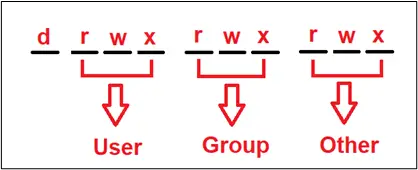
Note: You can give these permissions to a different set of users that belong to three different categories, which are User, Group, and Owner, which will be discussed in the next section. The letter‘ d’ on the first slot represents the directory.
What are Different Users in Linux?
As mentioned earlier, the permissions are granted on three different levels explained below:
User: Linux users are also considered system administrators since they are the primary owners of the operating system. Linux (OS) gives ownership of files to anyone who creates them.
Group: The system administrator might need to give separate rights to each user when several people are accessing the same Linux OS. The right of the group comes second, and an administrator can create groups and assign the same rights to all users in that group.
Other: Others are neither a user nor are they in the group and are considered separate entities and are not usually allowed to create any files. Their permission comes the third place.
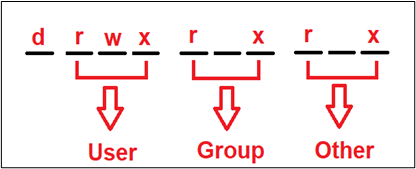
To give you a complete picture of what everything has been discussed till now, please see the below image.
How to Set the Permission drwxr-xr-x to Folders?
Let’s come to the main topic where we need to give ‘drwxr-xr-x’ to any folder. This first letter, “d” means a directory or folder followed by providing the main user’s read, write and execute rights. Now both Group users and other users have only the read and execute rights and cannot modify them by writing anything that can be seen below:
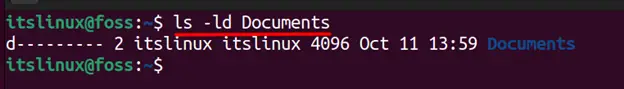
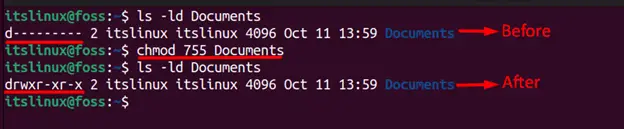
Let’s suppose you want to give these rights to the “Document” folder. Currently, the permissions set to the “Documents” directory can be viewed using the command:
You can see that there is no permission given to any user as all the dash (-) are empty. To give the exact permission for each user, you may use the alphabet or the numeric representation of the permissions. Let’s practice both methods:
Method 1: Using Alphabetic Representation of Permissions
The commands provided below will set the desired permissions to the folder named “Documents”:
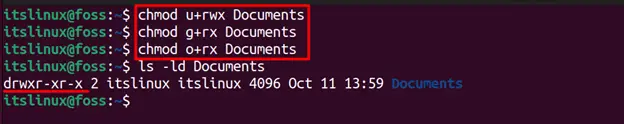
$ chmod u+rwx Documents $ chmod g+rx Documents $ chmod o+rx Documents
- ‘u+rwx’ means that we are giving user permission to read, write and execute.
- ‘g+rx’ means that a group has permission to read and execute.
- The same goes for other users because we also wrote ‘o+rx’ to give them permission to read and execute.
There is another variation where you can set your desired permission by writing a single command mentioned below:
$ chmod u+rwx,g+rx,o+rx Documents
Method 2: Using Numeric Values of Permissions
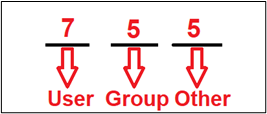
The second method of doing the same thing is by using the numeric value that’s been assigned to them which are mentioned below
Execute → 1
For a user the numeric value would be:
User (Read, Write, Execute) → (4+2+1 = 7)
For Group users the numeric value would be:
Group Users (Read and Execute) → (4+1 = 5)
For other users the numeric value would be:
Other Users(Read and Execute) →(4+1 = 5)
A detailed illustration of what been discussed above is mentioned below:
To give this desired permission (rwxr-xr-x), the command provided below will be executed:
That’s all for this article.
Conclusion
To set the permission “drwxr-xr-x” permissions to the folders, you can utilize the commands “chmod 755 path/of/folder” or chmod u+rwx,g+rx,o+rx path/of/folder. In Linux OS, there are three types of users: users, group users, and others, and they can be granted permission to read, write, and execute a specific file/folder. This post has demonstrated the methods to set the permission of the folders to “drwxr-xr-x”.
Права доступа к файлам Linux
Все пользователи объединяются в группы и идентифицируются по номеру. Чтобы узнать свой UID и GID, то есть уникальный номер пользователя и номер группы, к которой принадлежит пользователь, необходимо ввести команду id, результат должен выглядеть следующим образом:
uid=1000(testk) gid=1000(testk) groups=1000(testk),27(sudo)Просмотреть текущие права доступа к файлам Linux или каталогу можно по команде:
ls -l /etc
Результат выполнения команды выглядит следующим образом:
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Nov 2 11:14 postfix drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 1 22:37 ppp drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Aug 1 22:37 ppp -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 608 Nov 3 13:02 profile drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Oct 26 09:20 profile.d -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2932 Oct 25 2014 protocolsПараметры результата обозначают следующие параметры:
drwxr-xr-x 4 testk testk 4096 Oct 28 11:53 testk формат владелец группа размер_файла дата_последнего_изменения имя_файла
- Первый символ обозначает тип объекта: «—» означает обычный файл, «d» означает папку.
- Три следующих символа rwx означают права доступа владельца файла.
- Далее следует триада rwx означают права доступа группы.
- Последние 3 символа rwx означают права доступа остальных.
Символ r — это сокращение от слова Read (Чтение).
Для обычного файла это разрешение на чтение, позволяет пользователю просматривать содержимое файла.
Для каталога разрешение на чтение позволяет пользователю просматривать имена файлов в каталоге.
Символ w — это сокращение от слова Write (Запись)/
Для файла это разрешение на запись, позволяет пользователю изменять и удалять файл.
Для каталога разрешение на запись позволяет пользователю удалить каталог, изменять его содержимое (создавать, удалять и переименовывать файлы в нем), а также изменять содержимое файлов, которые пользователь может прочитать.
Символ x — это сокращение от слова Execute (Выполнять)
Для файла это разрешение на исполнение, позволяет пользователю выполнять файл (пользователь также должен иметь разрешение на чтение). Таким образом, права на выполнение должны быть установлены для исполняемых программ и скриптов до того, как пользователь запустит их.
Для каталога разрешение на выполнение позволяет пользователю получить доступ к метаданным о файлах в каталоге (информация, которая может быть получена в результате выполнения команды ls -l).
Примеры форматов
- -rw——-: Файл, который доступен только его владельцем.
- -rwxr-хт-х: Файл, который является исполняемым любым пользователем в системе.
- -rw-rw-rw-: Файл, который открыт для модификации каждого пользователя в системе.
- drwxr-хт-х: каталог, что каждый пользователь в системе может читать и доступ.
- drwxrwx —: Каталог, который является изменяемым (включая его содержание) его владельцем и группой.
- drwxr-х —: Каталог, который доступен по своей группе.
Права доступа к папке Linux
- разрешение на чтение папки дает право на просмотр списка имен файлов (не более);
- получение разрешения записи для каталога дает право создавать и удалять файлы в нем, в том числе принадлежащие другим пользователям;
- для получения подробной информации о файлах, находящихся в каталоге нужно иметь доступ на исполнение папки.
Изменение прав доступа
Права пользователя могут быть изменены только владельцем файла или пользователем с правами администратора системы. Для изменения прав используются команды chown, chgrp и chmod.
Рассмотрим подробно аргументы команды chmod:
chmod [ u | g | o | a ] [+ | — | = ] [r | w | x ] name1 [name2 . ]
Выделяют 3 группы, которые могут иметь права доступа к файлам Linux:
owner (u) – владелец файла;
group (g) – группа владельца файла;
others (o) – все остальные;
all (a ) – все вышеперечисленные группы вместе.
и 3 вида прав доступа для каждой группы:
право на чтение ( r);
право на запись (w);
право на исполнение (x).
а также 3 вида операций:
добавить (+);
убрать (-);
присвоить (=).
С помощью команды chmod также происходит управление битами, которые позволяют производить тонкое изменение прав доступа и запускать файл на выполнение с правами владельца или группы (биты SGID и SUID).
Изменять права доступа к файлу может его владелец или суперпользователь (root).
Примеры изменения прав доступа Linux
Команда, добавляющая право записи для группы владельца файла выглядит так:
chmod g+w file
Для добавления права доступа к файлам Linux для совершения записи для владельца и группы владельца:
chmod ug+w file
Дает право чтения файла всем пользователям, кроме владельца:
chmod go=r file
Лишает пользователей не находящихся в группе владельца права исполнения файла:
chmod o-x file
- chmod rw-r—r— или chmod 644 – команда разрешает владельцу чтение и запись файла, а пользователям из группы владельца и всем остальным, только чтение.
- chmod rwxr-xr-x или chmod 755 – команда дает владельцу выполнять любые операции с файлом, а пользователям из группы владельца и всем остальным разрешено чтение и исполнение.
- chmod rwxrxxrxx или chmod 777 – у всех пользователей есть все права.
- chmod r-sr-xr-xfail.pl или chmod 4555 для запуска с правами владельца, где «4» — обозначение бита SUID.
- chmod r-xr-sr-xfail.pl или chmod 2755 для запуска с правами группы, где «2» — обозначение бита SGID.