- Cisco IOS Configuration Guide for Autonomous Cisco Aironet Access Points — Release 15.3(3)JE and later
- Book Title
- 1 Overview of Access Point Features
- Results
- Chapter: 1 Overview of Access Point Features
- Overview of Access Point Features
- Radios in Access Points
- New Features and Commands in a Release
- Management Options
- Roaming Client Devices
- Network Configuration Examples
- Root Access Point
- Repeater Access Point
- Bridges
- Workgroup Bridge
- Central Unit in an All-Wireless Network
- Wireless access points
- Wireless reimagined
- Security built in
- IoT-ready
- Above-and-beyond reliability
- The power of partnerships
- Blaze new paths to tomorrow. Your journey, your way.
- Featured Cisco products
- Wi-Fi 6/6E
- Cisco Catalyst 9100 Access Points
- Cisco Meraki wireless
- Cisco DNA Software for Wireless
- Cisco Meraki platform
- Cisco DNA Center
- Outdoor and industrial
- Cisco Catalyst 9124AX Series
- Catalyst IW9167 Series
- Catalyst IW6300 Heavy Duty Access Points
- Cisco 6300 Series Embedded Services Access Points
- Cisco Industrial Wireless 3700 Series
- Wi-Fi 5
- Cisco Aironet 4800 Access Points
- Cisco Aironet 3800 Series Access Points
- Cisco Aironet 2800 Series Access Points
- Small business
- Cisco Business 200 Series
- Cisco Business 100 Series
- Save up to 25% when you bundle a Cisco DNA Center appliance with access devices
Cisco IOS Configuration Guide for Autonomous Cisco Aironet Access Points — Release 15.3(3)JE and later
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Preface
- 1 Overview of Access Point Features
- 2 Using the Web-Browser Interface
- 3 Using the Command-Line Interface
- 4 Configuring the Access Point for the First Time
- 5 Administrating the Access Point
- 6 Configuring Radio Settings
- 7 Configuring Multiple SSIDs
- 8 Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
- 9 Configuring an Access Point as a Local Authenticator
- 10 Configuring WLAN Authentication and Encryption
- 11 Configuring Authentication Types
- 12 Configuring Other Services
- 13 Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+ Servers
- 14 Configuring VLANs
- 15 Configuring QoS
- 16 Configuring Filters
- 17 Configuring CDP
- 18 Configuring SNMP
- 19 Configuring Repeater and Standby Access Points and Workgroup Bridge Mode
- 20 Managing Firmware and Configurations
- 21 Configuring SCEP
- 22 Configuring LLDP
- 23 Configuring L2TPv3 Over UDP/IP
- 24 Configuring Ethernet over GRE
- 25 Configuring System Message Logging
- 26 Troubleshooting
- 27 Miscellaneous AP-Specific Configurations
- APPENDIX A Protocol Filters
- APPENDIX B Supported MIBs
- APPENDIX C Error and Event Messages
Book Title
Cisco IOS Configuration Guide for Autonomous Cisco Aironet Access Points — Release 15.3(3)JE and later
1 Overview of Access Point Features
Results
Chapter: 1 Overview of Access Point Features
Overview of Access Point Features
Cisco Aironet Access Points (hereafter called access points, or abbreviated as APs) provide a secure, affordable, and easy-to-use wireless LAN solution that combines mobility and flexibility with the enterprise-class features required by networking professionals. With a management system based on Cisco IOS software, Cisco Aironet access points are Wi-Fi certified, and depending on the specific model are 802.11a-compliant, 802.11b-compliant, 802.11g-compliant, 802.11n-compliant, and 802.11ac-compliant wireless LAN transceivers.
Note When booting up a 1530, 1700, or a 2700 series AP for the first time, it will boot up with a unified mode software image. To deploy the AP in an autonomous network, use following command from the AP console or telnet to force AP to reboot using autonomous mode software image.
capwap ap autonomous
For more information on software images on the AP, see Working with Software Images.
You can configure and monitor the wireless device using the command-line interface (CLI), the browser-based management system, or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Radios in Access Points
An access point serves as the connection point between wireless and wired networks or as the center point of a stand-alone wireless network. In large installations, wireless users within the radio range of an access point can roam throughout a facility while maintaining seamless, uninterrupted access to the network.
Each access point platform contains one, two, or three radios. For more information on the radios supported by each access point model, see the corresponding Access Point Data Sheet.
New Features and Commands in a Release
For full information on the new features and updates to existing features in a release, see the Release Notes, for the release at the following URL:
Note The proxy Mobile-IP feature is not supported in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(2)JA and later.
Management Options
You can use the wireless device management system through the following interfaces:
- The Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI), which you use through a console port or Telnet session. Use the interface dot11radio global configuration command to place the wireless device into the radio configuration mode. Most of the examples in this manual are taken from the CLI. “Using the Command-Line Interface,” provides a detailed description of the CLI.
- A web-browser interface, which you use through a Web browser. “Using the Web-Browser Interface,” provides a detailed description of the web-browser interface.
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). “Configuring SNMP,” explains how to configure the wireless device for SNMP management.
Roaming Client Devices
If you have more than one wireless device in your wireless LAN, wireless client devices can roam seamlessly from one wireless device to another. The roaming functionality is based on signal quality, not proximity. When signal quality drops from a client, it roams to another access point.
Wireless LAN users are sometimes concerned when a client device stays associated to a distant access point instead of roaming to a closer access point. However, if a client signal to a distant access point remains strong and the signal quality is high, the client will not roam to a closer access point. Checking constantly for closer access points would be inefficient, and the extra radio traffic would slow throughput on the wireless LAN.
Using Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM) or 802.11r, with a device providing wireless distribution system (WDS), client devices can roam from one access point to another so quickly that there is no perceptible delay in voice or other time-sensitive applications.
Network Configuration Examples
This section describes the role of an access point in common wireless network configurations. The access point default configuration is as a root unit connected to a wired LAN or as the central unit in an all-wireless network. Access points can also be configured as repeater access points, bridges, and workgroup bridges. These roles require specific configurations.
Root Access Point
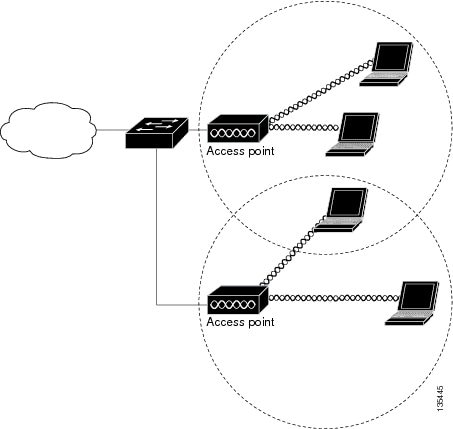
An access point connected directly to a wired LAN provides a connection point for wireless users. If more than one access point is connected to the LAN, users can roam from one area of a facility to another without losing their connection to the network. As users move out of range of one access point, they automatically connect to the network (associate) through another access point. The roaming process is seamless and transparent to the user. Figure 1-1 shows access points acting as root units on a wired LAN.
Figure 1-1 Access Points as Root Units on a Wired LAN
Repeater Access Point
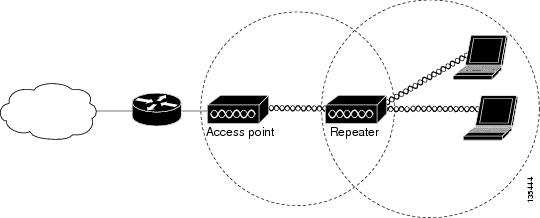
An access point can be configured as a stand-alone repeater to extend the range of your infrastructure or to overcome an obstacle that blocks radio communication. The repeater forwards traffic between wireless users and the wired LAN by sending packets to either another repeater or to an access point connected to the wired LAN. The data is sent through the route that provides the best performance for the client. Figure 1-2 shows an access point acting as a repeater. Consult the “Configuring a Repeater Access Point” for instructions on setting up an access point as a repeater.
Note Non-Cisco client devices might have difficulty communicating with repeater access points.
Figure 1-2 Access Point as Repeater
Bridges
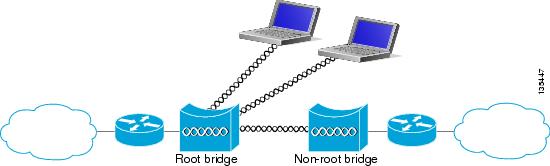
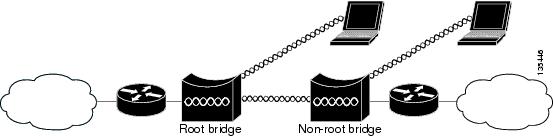
Access points can be configured as root or non-root bridges. In this role, an access point establishes a wireless link with a non-root bridge. Traffic is passed over the link to the wired LAN. Access points in root and non-root bridge roles can be configured to accept associations from clients. Figure 1-3 shows an access point configured as a root bridge with clients. Figure 1-4 shows two access points configured as a root and non-root bridge, both accepting client associations. Consult the “Configuring the Role in Radio Network” section for instructions on setting up an access point as a bridge.
When wireless bridges are used in a point-to-multipoint configuration the throughput is reduced depending on the number of non-root bridges that associate with the root bridge. With a link data rate at 54 Mbps, the maximum throughput is about 25 Mbps in a point-to-point link. The addition of three bridges to form a point-to-multipoint network reduces the throughput to about 12.5 Mbps.
Figure 1-3 Access Point as a Root Bridge with Clients
Figure 1-4 Access Points as Root and Non-root Bridges with Clients
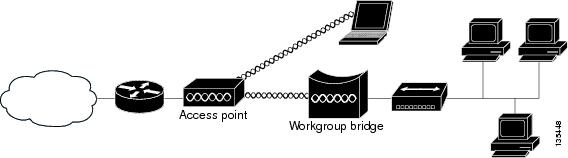
Workgroup Bridge
You can configure access points as workgroup bridges. In workgroup bridge mode, the unit associates to another access point as a client and provides a network connection for the devices connected to its Ethernet port. For example, if you need to provide wireless connectivity for a group of network printers, you can connect the printers to a hub or to a switch, connect the hub or switch to the access point Ethernet port, and configure the access point as a workgroup bridge. The workgroup bridge associates to an access point on your network.
If your access point has multiple radios, either radio can function in workgroup bridge mode..
Figure 1-5 shows an access point configured as a workgroup bridge. Consult the “Understanding Workgroup Bridge Mode” section and the “Configuring Workgroup Bridge Mode” section for information on configuring your access point as a workgroup bridge.
Figure 1-5 Access Point as a Workgroup Bridge
Central Unit in an All-Wireless Network
In an all-wireless network, an access point acts as a stand-alone root unit. The access point is not attached to a wired LAN; it functions as a hub linking all stations together. The access point serves as the focal point for communications, increasing the communication range of wireless users. Figure 1-6 shows an access point in an all-wireless network.
Figure 1-6 Access Point as Central Unit in All-Wireless Network
Wireless access points
Reliable, secure, and built for your organization. Experience all that Wi-Fi 6 and 6E have to offer.
Wireless reimagined
Enjoy superior security and resilience for an exceptional wireless experience.
Security built in
Encrypted threats are the new normal. Design an intelligent network that can detect and help stop them.
IoT-ready
Monitor and manage devices and IoT sensors with a comprehensive on-premises or cloud dashboard.
Above-and-beyond reliability
Go beyond basic connectivity and security. Build a robust Wi-Fi 6/6E network that works for you.
The power of partnerships
Innovation doesn’t happen in a vacuum. Take advantage of integrations with Cisco partners and other tools.
Blaze new paths to tomorrow. Your journey, your way.
Featured Cisco products
Wi-Fi 6/6E
Cisco Catalyst 9100 Access Points
Get the network of the future today with these flexible access points.
Cisco Meraki wireless
Deliver impressive wireless experiences with ease through the cloud-managed Meraki platform.
Cisco DNA Software for Wireless
Boost your network’s intelligence with Cisco DNA Software.
Cisco Meraki platform
Remotely configure and manage your wireless network on the Meraki cloud-first platform.
Cisco DNA Center
Get better performance and spend less time managing your network.
Outdoor and industrial
Cisco Catalyst 9124AX Series
Wi-Fi 6 with a weather-resistant casing for outdoor deployments
Catalyst IW9167 Series
Available in Wi-Fi 6/6E ready or Cisco Ultra-Reliable Wireless Backhaul
Catalyst IW6300 Heavy Duty Access Points
Purpose-built for hazardous locations
Cisco 6300 Series Embedded Services Access Points
Built-in security plus resilient wireless mesh capabilities designed to integrate with your hardware
Cisco Industrial Wireless 3700 Series
802.11ac Wi-Fi for industrial, outdoor environments
Wi-Fi 5
Cisco Aironet 4800 Access Points
Wi-Fi 5 with four radios designed for large enterprise organizations
Cisco Aironet 3800 Series Access Points
Wi-Fi 5 with three radios for midsized to large enterprises requiring mission-critical traffic
Cisco Aironet 2800 Series Access Points
Wi-Fi 5 with three radios designed for midsized to large enterprises requiring advanced features
Small business
Cisco Business 200 Series
Wi-Fi 5 for superior performance and enhanced range in the small business workplace
Cisco Business 100 Series
Wi-Fi 5 for small business workplaces that need a highly secure, reliable wireless connection
Save up to 25% when you bundle a Cisco DNA Center appliance with access devices
Get everything you need to test-drive Cisco DNA Center automation and assurance capabilities in your lab or production environment.
Offer expires on July 29, 2023.