- How do you close a file in Linux?
- How do you close a file in Linux terminal?
- How do you close a file?
- How do I close all open files in Linux?
- How do you end in Linux?
- How do you close a file in Unix?
- How do I open a file in Linux command line?
- What is closing a file?
- What are the two ways to close a file?
- Which function is used to close a file?
- How do I see open files in Linux?
- What is a file descriptor in Linux?
- What is LSOF command in Linux?
- How do I start a process in Linux?
- What is end command?
- How do you kill a process in Unix?
- Close all file descriptors in bash
- 7 Answers 7
- Update
- How do I close open files in Linux?
- How do you close a file in Linux?
- How do I close an open file?
- How do you close a file in Terminal?
- What is list of open files in Linux?
- How do I see open limits in Linux?
- How do you open a file in Linux?
- What is the file command in Linux?
- How do I close a file that is open by another user?
- What is used to close the file?
- Can’t delete because the file is open in system?
- Which command is used to terminate a process?
- How do I close and save a file in Linux terminal?
- Which is called end of file command in Linux?
How do you close a file in Linux?
To close a file to which no changes have been made, hit ESC (the Esc key, which is located in the upper left hand corner of the keyboard), then type :q (a colon followed by a lower case “q”) and finally press ENTER.
How do you close a file in Linux terminal?
Press the [Esc] key and type Shift + Z Z to save and exit or type Shift+ Z Q to exit without saving the changes made to the file.
How do you close a file?
When you want to close a file quickly, click on the close icon in the document tab. You may also use the Close icon in the main tool bar, or the File → Close (Ctrl-W) menu item. If the file is unchanged, it is merely closed.
How do I close all open files in Linux?
If you want to find only close the open file descriptors, you can use the proc filesystem on systems where it exists. E.g. on Linux, /proc/self/fd will list all open file descriptors. Iterate over that directory, and close everything >2, excluding the file descriptor that denotes the directory you are iterating over.
How do you end in Linux?
You typically can use the arrow keys to scroll up or down, and can exit by pressing q .
How do you close a file in Unix?
To close a file to which no changes have been made, hit ESC (the Esc key, which is located in the upper left hand corner of the keyboard), then type :q (a colon followed by a lower case “q”) and finally press ENTER.
How do I open a file in Linux command line?
Following are some useful ways to open a file from the terminal: Open the file using cat command.
…
Open the file using tail command.
- Open File Using cat Command. …
- Open File Using less Command. …
- Open File Using more Command. …
- Open File Using nl Command.
What is closing a file?
Closing a file removes the association between the file and its unit number, thus freeing the unit number for use with a different file. There is usually an operating system-imposed limit on the number of files a user may have open at once. … In any event, it is good style to only keep needed files open.
What are the two ways to close a file?
There are two ways to close a document:
- • close your document without exiting the software; or.
- • …
- Choose File > Close to close your document without exiting.
- If you have modified your document since the last time you saved, you are prompted to save the changes.
Which function is used to close a file?
Closing a file is performed using the fclose() function. fclose(fptr); Here, fptr is a file pointer associated with the file to be closed.
How do I see open files in Linux?
You can run lsof command on Linux filesystem and the output identifies the owner and process information for processes using the file as shown in the following output.
- $ lsof /dev/null. List of All Opened Files in Linux. …
- $ lsof -u tecmint. List of Files Opened by User. …
- $ sudo lsof -i TCP:80. Find Out Process Listening Port.
What is a file descriptor in Linux?
In Unix and related computer operating systems, a file descriptor (FD, less frequently fildes) is an abstract indicator (handle) used to access a file or other input/output resource, such as a pipe or network socket.
What is LSOF command in Linux?
lsof meaning ‘LiSt Open Files’ is used to find out which files are open by which process. As we all know Linux/Unix considers everything as a files (pipes, sockets, directories, devices etc). One of the reason to use lsof command is when a disk cannot be unmounted as it says the files are being used.
How do I start a process in Linux?
The easiest way to start a process is to type its name at the command line and press Enter. If you want to start an Nginx web server, type nginx.
What is end command?
The end command terminates a process on another port, or the current port if a port number is not specified. The end command clears an active list and requires a sys2 privilege level. … NOTE. If the port number and user-ID are not specified, the end command stops the process on the current line.
How do you kill a process in Unix?
Control sequences. The most obvious way to kill a process is probably to type Ctrl-C. This assumes, of course, that you’ve just started running it and that you’re still on the command line with the process running in the foreground. There are other control sequence options as well.
Close all file descriptors in bash
Is there a way to close all the open file descriptors, without having an explicit list of them beforehand?
What are «all the open file descriptors»? 0, 1, and 2? Or do you have many more? If so, where did they come from?
This is useful to know for the situation when you fork a shell-script, and thus need to close all the parents sockets.
7 Answers 7
To answer literally, to close all open file descriptors for bash :
for fd in $(ls /proc/$$/fd); do eval "exec $fd>&-" done However this really isn’t a good idea since it will close the basic file descriptors the shell needs for input and output. If you do this, none of the programs you run will have their output displayed on the terminal (unless they write to the tty device directly). If fact in my tests closing stdin ( exec 0>&- ) just causes an interactive shell to exit.
What you may actually be looking to do is rather to close all file descriptors that are not part of the shell’s basic operation. These are 0 for stdin , 1 for stdout and 2 for stderr . On top of this some shells also seem to have other file descriptors open by default. In bash , for example, you have 255 (also for terminal I/O) and in dash I have 10, which points to /dev/tty rather than the specific tty / pts device the terminal is using. To close everything apart from 0, 1, 2 and 255 in bash :
for fd in $(ls /proc/$$/fd); do case "$fd" in 0|1|2|255) ;; *) eval "exec $fd>&-" ;; esac done Note also that eval is required when redirecting the file descriptor contained in a variable, if not bash will expand the variable but consider it part of the command (in this case it would try to exec the command 0 or 1 or whichever file descriptor you are trying to close).
NOTE: Also using a glob instead of ls (eg /proc/$$/fd/* ) seems to open an extra file descriptor for the glob, so ls seems the best solution here.
Update
For further information on the portability of /proc/$$/fd , please see Portability of file descriptor links. If /proc/$$/fd is unavailable, then a drop in replacement for the $(ls /proc/$$/fd) , using lsof (if that is available) would be $(lsof -p $$ -Ff | grep f6 | cut -c 2-) .
How do I close open files in Linux?
If you want to find only close the open file descriptors, you can use the proc filesystem on systems where it exists. E.g. on Linux, /proc/self/fd will list all open file descriptors. Iterate over that directory, and close everything >2, excluding the file descriptor that denotes the directory you are iterating over.
How do you close a file in Linux?
How do you close a file in Linux? Press the [Esc] key and type Shift + Z Z to save and exit or type Shift+ Z Q to exit without saving the changes made to the file.
How do I close an open file?
To disconnect multiple open files or folders, press the CTRL key while clicking the file or folder names, right-click any one of the selected files or folders, and then click Close Open File. This closes the selected files or folders.

How do you close a file in Terminal?
Press the [Esc] key and type Shift + Z Z to save and exit or type Shift+ Z Q to exit without saving the changes made to the file.
What is list of open files in Linux?
You can run lsof command on Linux filesystem and the output identifies the owner and process information for processes using the file as shown in the following output.
- $ lsof /dev/null. List of All Opened Files in Linux. …
- $ lsof -u tecmint. List of Files Opened by User. …
- $ sudo lsof -i TCP:80. Find Out Process Listening Port.
How do I see open limits in Linux?
To display the individual resource limit then pass the individual parameter in ulimit command, some of parameters are listed below:
- ulimit -n –> It will display number of open files limit.
- ulimit -c –> It display the size of core file.
- umilit -u –> It will display the maximum user process limit for the logged in user.
How do you open a file in Linux?
Following are some useful ways to open a file from the terminal:
- Open the file using cat command.
- Open the file using less command.
- Open the file using more command.
- Open the file using nl command.
- Open the file using gnome-open command.
- Open the file using head command.
- Open the file using tail command.

What is the file command in Linux?
The file command determines the file type of a file. It reports the file type in human readable format (e.g. ‘ASCII text’) or MIME type (e.g. ‘text/plain; charset=us-ascii’). As filenames in UNIX can be entirely independent of file type file can be a useful command to determine how to view or work with a file.
How do I close a file that is open by another user?
To disconnect multiple open files or folders, press the CTRL key while clicking the file or folder names, right-click any one of the selected files or folders, and then click Close Open File. This closes the selected files or folders.
What is used to close the file?
FILE menu is used to close the file.
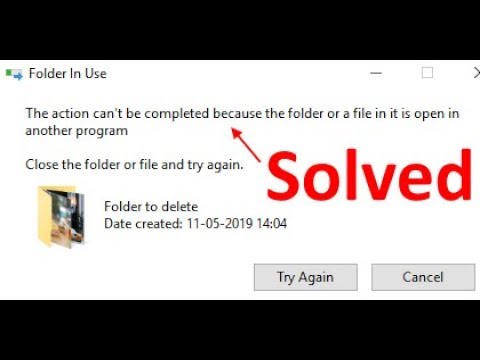
Can’t delete because the file is open in system?
End the Application via the Task Manager
This is the most successful method to fix the “file is open in another program” error. Click Ctrl + Shift + ESC to open the Task Manager. Alternatively, you can right-click the Taskbar or click Ctrl + Alt + Del anywhere in Windows and select Task Manager.
Which command is used to terminate a process?
When no signal is included in the kill command-line syntax, the default signal that is used is –15 (SIGKILL). Using the –9 signal (SIGTERM) with the kill command ensures that the process terminates promptly.
How do I close and save a file in Linux terminal?
To save a file, you must first be in Command mode. Press Esc to enter Command mode, and then type :wq to write and quit the file. The other, quicker option is to use the keyboard shortcut ZZ to write and quit. To the non-vi initiated, write means save, and quit means exit vi.
Which is called end of file command in Linux?
The tail command by default shows the last 10 lines of a file.
