- How to add an alias to a command in terminal?
- 8 Answers 8
- Aliases’ File
- Alias Help
- Linux alias Command: How to Use It With Examples
- What Is an Alias in Linux?
- Linux Alias Syntax
- Create Aliases in Linux
- Create a Temporary Alias in Linux
- Create a Permanent Alias in Linux
- List All Aliases in Linux
- Remove Aliases in Linux
How to add an alias to a command in terminal?
By typing a manually specified command in terminal I want to execute some other command. How could add an alias to a command? Can i do that with the help of the terminal or should I edit some kind of file?
8 Answers 8
alias new_name='old command' To create a permanent alias you have to edit the .bashrc file in your home directory.
There is no manual entry for alias. It is a built-in command. You must look at the man page for the shell.
On the bash command line it is simply a case of typing:
alias my_command="Command to run" For example to create a short command run a long listing you could do:
The quotes are not required if you are not adding switches to the aliased command.
To make permanent changes you can put your aliases separetely in ~/.bash_aliases
You can either use the alias built-in command in the shell you’re using, or you can write a script which does what you want. Assuming you are using bash as the shell (which is the default), you can type man bash and skip down to the ALIASES section, for documentation on aliases in bash.
I write a GUI for adding/editing alias commands. You can also use it from commandline like this:
addalias -add "sinstall" "sudo apt-get install" To make the changes permanent (i.e. to be read everytime you start a shell) add the alias commands you typed in the terminal to the file ~/.bashrc file.
This has been flagged for deletion. Can I suggest you add the relevant bits of the link into the answer to make it self contained?
You can directly create a file in your home for collecting all the aliases .bash_profile by writing nano ~.bash_profile and simply write on the file the commands/shortcuts you want to create, for example:
alias edbp='nano ~/.bash_profile' and then validate it sourcing the file, so running
Remember that every time you modify your document you have to run again source ~.bash_profile
Aliases’ File
Add aliases to the file ~/.bash_aliases and create it if it doesn’t exist. For example, I have:
$ more ~/.bash_aliases alias trop='tree --dirsfirst -L 1' (. ) Alias Help
$ alias --help alias: alias [-p] [name[=value] . ] Define or display aliases. Without arguments, `alias' prints the list of aliases in the reusable form `alias NAME=VALUE' on standard output. Otherwise, an alias is defined for each NAME whose VALUE is given. A trailing space in VALUE causes the next word to be checked for alias substitution when the alias is expanded. Options: -p print all defined aliases in a reusable format Exit Status: alias returns true unless a NAME is supplied for which no alias has been defined. Linux alias Command: How to Use It With Examples
Depending on the type of work you do on your Linux system, you may need to enter the same long and complicated commands frequently. The alias command lets you create shortcuts for these commands, making them easier to remember and use.
In this tutorial, we will show you how you can create, review, and remove command aliases in Linux.
- A system running a Linux distribution
- An account with sudo privileges
- Access to the terminal window or command line
- A text editor, such as Vim or nano
What Is an Alias in Linux?
In Linux, an alias is a shortcut that references a command. An alias replaces a string that invokes a command in the Linux shell with another user-defined string.
Aliases are mostly used to replace long commands, improving efficiency and avoiding potential spelling errors. Aliases can also replace commands with additional options, making them easier to use.
Linux Alias Syntax
The alias command uses the following syntax:
The different elements of the alias command syntax are:
- alias : Invokes the alias command.
- [option] : Allows the command to list all current aliases.
- [name] : Defines the new shortcut that references a command. A name is a user-defined string, excluding special characters and ‘alias’ and ‘unalias’, which cannot be used as names.
- [value] : Specifies the command the alias references. Commands can also include options, arguments, and variables. A value can also be a path to a script you want to execute.
Note: Enclosing the value in single quotation marks (‘) will not expand any variables used with the command. To expand the variables, use double quotation marks («).
Create Aliases in Linux
There are two types of aliases to create in Linux:
- Temporary. Add them using the alias command.
- Permanent. These require to edit system files.
Create a Temporary Alias in Linux
Use the alias command to create a temporary alias that lasts until the end of the current terminal session. For instance, creating c as an alias for the clear command:
Note: The alias command allows you to include multiple commands as the value by dividing them with the pipe symbol (|).
If you want to reference any additional command options when creating an alias, include them as a part of the value. For example, adding move as an alias for the mv command with the option of asking for confirmation before overwriting:
Note: Learn more about the mv command in our guide to moving directories in Linux.
Another use for aliases is to create a shortcut for running scripts. To do this, provide the absolute path to the script as the value:
alias frename='Example/Test/file_rename.sh'In this example, using frename as a command runs the file_rename.sh bash script.
Create a Permanent Alias in Linux
To make an alias permanent, you need to add it to your shell configuration file. Depending on the type of shell you are using, use:
Start by opening the shell configuration file in a text editor. In this example, we are using the Bash shell and nano text editor:
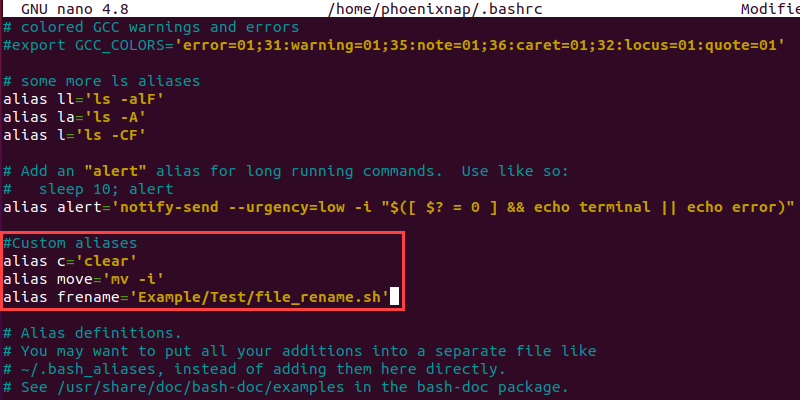
Scroll down until you find a section that lists default system aliases. For ease of use, create a separate section with a descriptive comment and add your aliases using the alias command syntax.
#Custom aliases alias c='clear' alias move='mv -i' alias frename='Example/Test/file_rename.sh' Once you add all of the new alises, press Ctrl+X, type Y and press Enter to save the changes to the configuration file.
The new aliases automatically load in the next terminal session. If you want to use them in the current session, load the configuration file using the source command:
List All Aliases in Linux
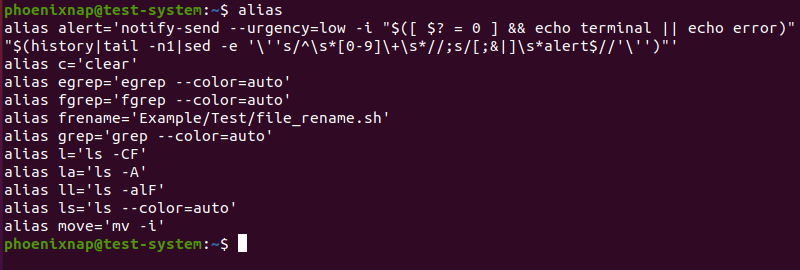
Using the alias command on its own displays a list of all currently set aliases:
Another method is to add the -p flag. This option displays the list in a format suitable for input to the shell:
Remove Aliases in Linux
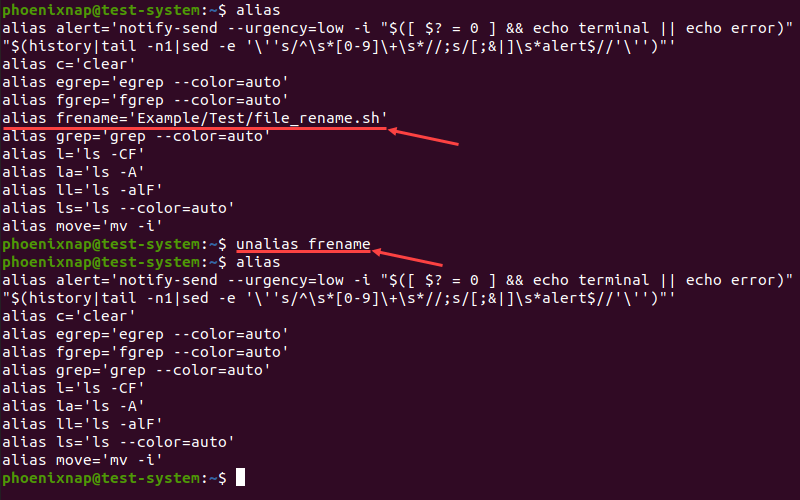
To remove an alias, use the unalias command with the following syntax:
For instance, to remove the frename alias:
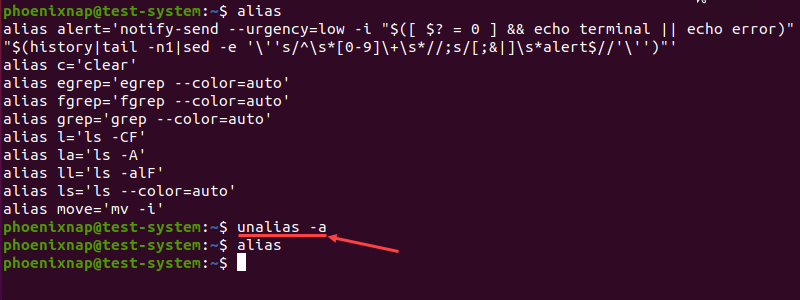
Adding the -a option allows you to remove all aliases:
The example above shows how alias does not return any results after the unalias -a command.
After reading this tutorial, you should be able to use the alias command to create and manage aliases on your Linux system. This will help streamline your work and make terminal commands easier to use.
To learn more about other commands in Linux, check out our Linux commands cheat sheet.