- How to Clear Command History in Linux?
- Why Do You Need to Clear Command History?
- How to Display Commands History in Linux?
- How to Clear the Command History of the Current Session?
- How to Clear the Command History of All Terminal Sessions?
- How to Clear the History From Previous Sessions?
- Conclusion
- How to clear command history in Linux
- Why should we remove the Linux Command line History?
- Removing the Linux Command line history
- Remove a Line from the bash history
- Remove or Clear all commands from the bash history
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
- How to Clear BASH Command Line History in Linux
- How to Delete History in Linux Easily
- 1. Delete History List Command Line
- 2. Delete specific command from history
- 3. Delete history without a trace
- 4. Turn off bash history
- 5. Delete History Range
- Conclusion
- About The Author
- Bobbin Zachariah
How to Clear Command History in Linux?
In Linux, the history command is a utility that allows you to view a list of previously entered commands in the terminal. It is a useful utility to overlook the commands and then reuse them easily.
While using too many terminal commands, Linux administrators recommend clearing the terminal’s history regularly. In this post, we will list the possible ways to clear the command history in Linux.
- Why Do You Need to Clear Command History?
- Display Current History in Linux
- Clear Current Session’s Command History
- Clear the Command History All Terminal Sessions
- Clear the History from Previous Sessions
Let’s start the article with the importance of clear command history.
Why Do You Need to Clear Command History?
There are several reasons you might want to clear the command history in Linux:
- Privacy: The command history is stored in a file on your computer, and it can be accessed by anyone who has access to that file. Clearing the command history can help to protect your privacy by preventing others from seeing the commands you have typed.
- Security: If you have typed sensitive information, such as passwords or confidential data, into the terminal, clearing the command history can help to protect that information from being accessed by others.
- Convenience: The command history can become cluttered over time, making it difficult to find specific commands. Clearing the command history can help clean up the list and make it easier to find the commands you need.
- Debugging: If you are having problems with your terminal or with a specific command, clearing the command history can help to resolve those issues.
How to Display Commands History in Linux?
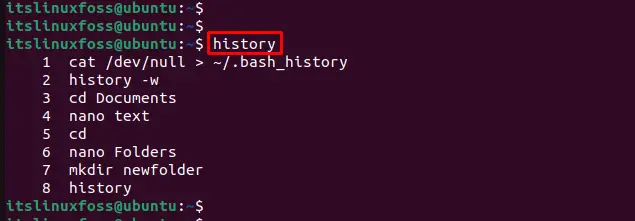
To display the current history in Linux, the “history” command is utilized in the terminal below:
The output displays all the previous history in this terminal.
How to Clear the Command History of the Current Session?
For clearing the command history in Linux, utilize the history command followed by the “-c” option. This will clear the current session’s command history.
To clear the command history, you can use the following command:
Note that this will only clear the command history for the current terminal session.
How to Clear the Command History of All Terminal Sessions?
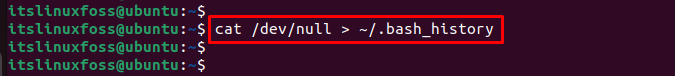
The “.bash_history” file contains the commands run on all terminal sessions. To clear the command history for all terminal sessions, run the below script:
$ cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history
This will overwrite the “bash_history” file with an empty file.
How to Clear the History From Previous Sessions?
Use the history command with the -w option for writing the current history to the .bash_history file and overwrite it with the current session’s commands:
This can be useful if you want to preserve the current session’s command history but clear the history from previous sessions.
That is how clear the command history
Conclusion
Linux offers the “history” utility with the “-c” option to clear the command history. It clears the current sessions. Additionally, the “-w” option is helpful to clear all previous sessions of command history by maintaining the current session history. It is a useful way to manage and maintain your terminal environment. This article has demonstrated all multiple methods to clear the command history in Linux.
How to clear command history in Linux
The bash history stores the records of all terminal commands which are executed by a user on the command-line Linux system. Using the history feature, you can easily locate the previously executed commands on your Linux system through the arrow keys navigation.
Why should we remove the Linux Command line History?
Most of the time, we don’t want to reveal the terminal history of other users on your Linux system. For example, if you are giving classes to your students on a Lab computer and you might have taught some harmful commands and are not recommended to use on our system. But most of the students don’t have an idea about the side effects of these critical commands. A curious student may search about the command-line history and test them to check the working of each command. It may crash your system many times. However, you can repair or re-install your system in a quick way. But, it is not a good practice. So, in this case, we want to prefer to clear the command line history after working on it. Especially when you have shared access with your friends or colleagues. We have just elaborated it with just a simple example; there could be other problems through which you want to clear the Linux command line history. In this article, we will give you a demo of how you can clear the command line history in the Linux system.
We have executed all the commands on Ubuntu 20.04 terminal application in this article. Therefore, it is necessary to open the terminal window on your system. Click on the ‘Activities’ located at the left corner on your system’s desktop, and then using the application search bar, you will search the ‘terminal’ keyword. After completing the search, click on the terminal icon and launch it.
Removing the Linux Command line history
If you want to view the history of your terminal command then, type the following command on the terminal:
Normally, the command line history stores in a file named ‘bash_history’. This file you may locate in a particular user’s home directory /home/username/.bash_history. Execute the below-given command to locate the bash_history file:
Note: A root user can observe the command history of all user’s on your system. But, the standard user can only view their own command line history.
Remove a Line from the bash history
If you want to remove just a single line from the bash history file, then you can use the -d option with history command and enter the targeted line number, which you want to remove.
For example, we want to clear a command that contains your password where you have entered a password in a plain text; you can easily find the line number in the history file and clear it by executing the following command:
Remove or Clear all commands from the bash history
You can also clear or delete all entries from the bash history file. So, use the option -c with the history command. You can run the following command on the terminal to clear or delete the all bash history:
Alternatively, by running the following command, you can remove or delete all history of last executed commands in the bash history file permanently.
Conclusion
In this article, we have presented a better understanding of the history command and why we need to clear it. From the above all mentioned command, I hope now can clear the history of your system easily. But, always remember that what you perform on the terminal all commands recorded in a bash history file, so it is recommended that you never use passwords in a plain-text format on the Linux command line. If you have any queries and thoughts related to this article then, please share your ideas with us.
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
How to Clear BASH Command Line History in Linux
The bash history keeps a record of all commands executed by a user on the Linux command line. This allows you to easily run previously executed commands by using the “up arrow” or “down arrow” keys to scroll through the command history file.
In this article, we will show you two simple ways to clear your command-line history on a Linux system.
The major reason for removing command-line history from the Linux terminal is to prevent another user, who could be using the same account.
For instance if you have typed a command that contained a password in plain-text and you don’t want another system user or an attacker to see this password, you need to delete or clear the history file.
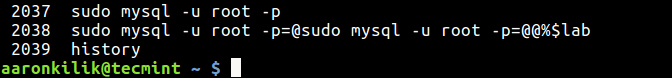
Take a look at the command below, here the user aaronkilik has typed the database server password on the command line.
If you look into th bash history file towards the end, you will see the password typed above in there.
The bash_history file is normally located in a user’s home directory /home/username/.bash_history.
$ ls -l /home/aaronkilik/.bash_history
To remove a single line from the history file, use the -d option. For example, if you want to clear a command where you entered clear-text password as in the scenario above, find the line number in the history file and run this command.
To delete or clear all the entries from bash history, use the history command below with the -c option.
Alternatively, you can use the command below to delete history of all last executed commands permanently in the file.
$ cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history
Note: A normal user can only view his/her own command history, but the root user can view the command history of all other users on the system.
You can learn more about the bash history file and useful history commands here: The Power of Linux “History Command” in Bash Shell.
Always remember that all commands you run are recorded in a history file, so do not type plain-text passwords on the command line. If you have questions or thoughts to share with us, make use of the feedback form below.
How to Delete History in Linux Easily
The .bash_history file located in the user’s home directory keeps the history of commands you typed on the terminal. This helps users to reuse listed commands without retyping it.
If you don’t want others to see your typed commands for any reason, you can easily delete the history. In this guide, we learn how to delete history from Linux.
1. Delete History List Command Line
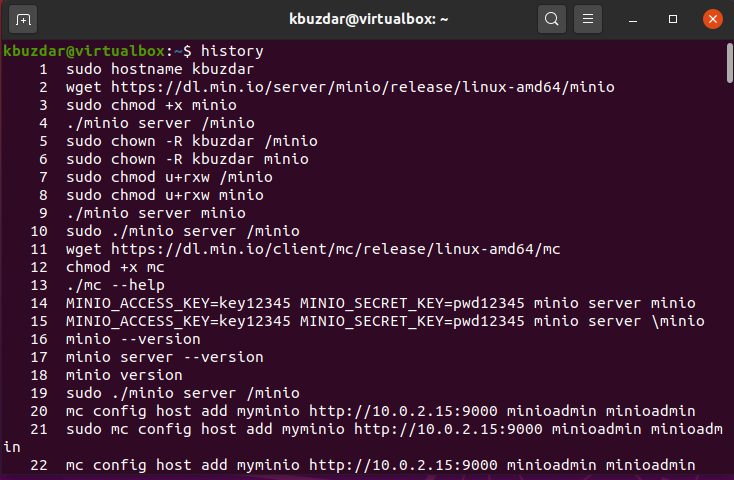
To see your bash history using history command, type:
$ history 1 history 2 vim .bash_history 3 exit 4 historyTo delete history list from the command line, use the following commands:
2. Delete specific command from history
From the history list if you want to delete specific command, use the following syntax:
For example to delete the sixth entry history list, type:
3. Delete history without a trace
To clear the bash history completely without a trace on the server, one solution is to link ~/.bash_history to /dev/null.
$ cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_historyAlternatively, you can use the wipe tool to securely delete .bash_history file:
4. Turn off bash history
The $HISTFILE variable store the bash history file location.
You can stop history logging into the history file by adding unset HISTFILE to user profiles.
$ echo "unset HISTFILE" >> /etc/profileor$ echo "unset HISTFILE" >> /home/tom/.bash_profile
Alternatively, you can set zero values to HISTSIZE and HISTFILESIZE in the .bashrc file.
5. Delete History Range
If you want to delete N lines from the bash history, you may use the following one-liner.
for i in ; do history -d START_POSITION; doneSTART_POSITION is the line number in the history list from where you need to start deleting.
N is no of the entries you want to delete.
For example to delete 13 entries from line 986, type:
for i in ; do history -d 986; doneConclusion
In this guide, we learned how to clear history in Linux. Thanks for reading, please share your feedback and suggestions in the comment section.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks
About The Author
Bobbin Zachariah
Bobbin is a seasoned IT professional with over two decades of experience. He has excelled in roles such as a computer science instructor, Linux system engineer, and senior analyst. Currently, he thrives in DevOps environments, focusing on optimizing efficiency and delivery in AWS Cloud infrastructure. Bobbin holds certifications in RHEL, CCNA, and MCP, along with a Master’s degree in computer science. In his free time, he enjoys playing cricket, blogging, and immersing himself in the world of music.