- Difference between Linux and Windows
- Linux vs Windows: Key Difference Between Them
- Types of Files
- General Files
- Directory Files
- Device Files:
- Difference between Windows and Linux Users
- Regular User
- Root User
- Service user
- Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
- Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
- Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
- Linux vs Windows – Difference Between Them
Difference between Linux and Windows
Linux: Linux could be a free and open supply OS supported operating system standards. It provides programming interface still as programme compatible with operating system primarily based systems and provides giant selection applications. A UNIX operating system additionally contains several severally developed parts, leading to UNIX operating system that is totally compatible and free from proprietary code. Windows: Windows may be a commissioned OS within which ASCII text file is inaccessible. it’s designed for the people with the angle of getting no programming information and for business and alternative industrial users. it’s terribly straightforward and simple to use. The distinction between Linux and Windows package is that Linux is completely freed from price whereas windows is marketable package and is expensive. Associate operating system could be a program meant to regulate the pc or computer hardware Associate behave as an treater between user and hardware. Linux is a open supply package wherever users will access the ASCII text file and might improve the code victimisation the system. On the opposite hand, in windows, users can’t access ASCII text file, and it’s a authorized OS. Let’s see that the difference between Linux and windows:
There are 3 types of user account –
(1) Regular , (2) Root , (3) Service account
There are 4 types of user account –
(1) Administrator , (2) Standard , (3) Child , (4) Guest
Linux vs Windows: Key Difference Between Them
When we compare file system in Windows and Linux, in Microsoft Windows, files are stored in folders on different data drives like C: D: E:
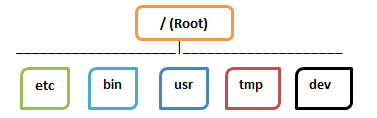
But, in Linux, files are ordered in a tree structure starting with the root directory.
This root directory can be considered as the start of the file system, and it further branches out various other subdirectories. The root is denoted with a forward slash ‘/’.
A general tree file system on your UNIX may look like this.
Types of Files
In Linux and UNIX, everything is a file. Directories are files, files are files, and devices like Printer, mouse, keyboard etc.are files.
Let’s look into the File types in more detail.
General Files
General Files also called as Ordinary files. They can contain image, video, program or simply text. They can be in ASCII or a Binary format. These are the most commonly used files by Linux Users.
Directory Files
These files are a warehouse for other file types. You can have a directory file within a directory (sub-directory).You can take them as ‘Folders’ found in Windows operating system.
Device Files:
In MS Windows, devices like Printers, CD-ROM, and hard drives are represented as drive letters like G: H:. In Linux, there are represented as files.For example, if the first SATA hard drive had three primary partitions, they would be named and numbered as /dev/sda1, /dev/sda2 and /dev/sda3.
Note: All device files reside in the directory /dev/
All the above file types (including devices) have permissions, which allow a user to read, edit or execute (run) them. This is a powerful Linux/Unix feature. Access restrictions can be applied for different kinds of users, by changing permissions.
Difference between Windows and Linux Users
There are 3 types of users in Linux.
Regular User
A regular user account is created for you when you install Ubuntu on your system. All your files and folders are stored in /home/ which is your home directory. As a regular user, you do not have access to directories of other users.
Root User
Other than your regular account another user account called root is created at the time of installation. The root account is a superuser who can access restricted files, install software and has administrative privileges. Whenever you want to install software, make changes to system files or perform any administrative task on Linux; you need to log in as a root user. Otherwise, for general tasks like playing music and browsing the internet, you can use your regular account.
Service user
Linux is widely used as a Server Operating System. Services such as Apache, Squid, email, etc. have their own individual service accounts. Having service accounts increases the security of your computer. Linux can allow or deny access to various resources depending on the service.
- You will not see service accounts in Ubuntu Desktop version.
- Regular accounts are called standard accounts in Ubuntu Desktop
In Windows, there are 4 types of user account types.
Windows Vs. Linux: File Name Convention
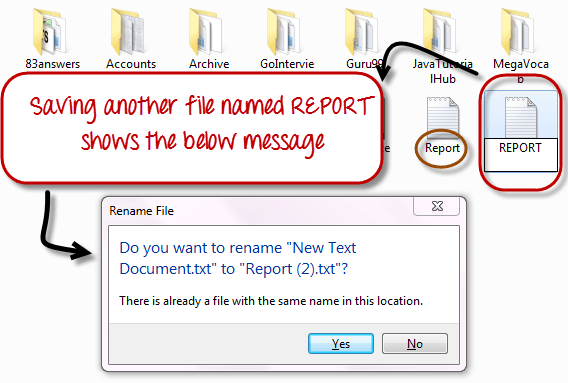
In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder. See below –
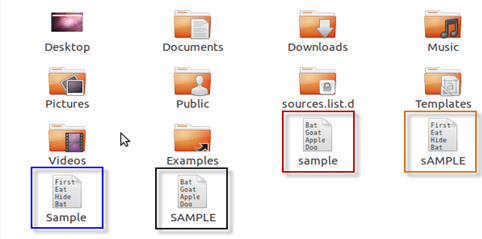
While in Linux, you can have 2 files with the same name in the same directory, provided they use different cases.
Windows Vs. Linux: HOME Directory
For every user in Linux, a directory is created as /home/
Consider, a regular user account “Tom”. He can store his personal files and directories in the directory “/home/tom”. He can’t save files outside his user directory and does not have access to directories of other users. For instance, he cannot access directory “/home/jerry” of another user account”Jerry”.
The concept is similar to C:\Documents and Settings in Windows.
When you boot the Linux operating system, your user directory (from the above example /home/tom) is the default working directory. Hence the directory “/home/tom is also called the Home directory which is a misnomer.
The working directory can be changed using some commands which we will learn later.
Windows Vs. Linux: Other Directories
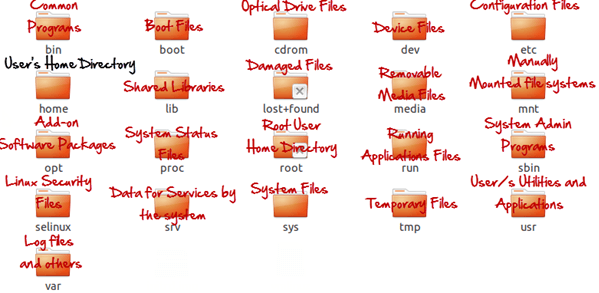
Comparing Windows vs Linux for other directories, in Windows, System and Program files are usually saved in C: drive. But, in Linux, you would find the system and program files in different directories. For example, the boot files are stored in the /boot directory, and program and software files can be found under /bin, device files in /dev. Below are important Linux Directories and a short description of what they contain.
These are most striking differences between Linux and other Operating Systems. There are more variations you will observe when switching to Linux and we will discuss them as we move along in our tutorials.
Linux vs Windows – Difference Between Them
Here is the main difference between Windows and Linux:
| Windows | Linux |
|---|---|
| Windows uses different data drives like C: D: E to stored files and folders. | Unix/Linux uses a tree like a hierarchical file system. |
| Windows has different drives like C: D: E | There are no drives in Linux |
| Hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are considered as devices | Peripherals like hard drives, CD-ROMs, printers are also considered files in Linux/Unix |
| There are 4 types of user account types 1) Administrator, 2) Standard, 3) Child, 4) Guest | There are 3 types of user account types 1) Regular, 2) Root and 3) Service Account |
| Administrator user has all administrative privileges of computers. | Root user is the super user and has all administrative privileges. |
| In Windows, you cannot have 2 files with the same name in the same folder | Linux file naming convention is case sensitive. Thus, sample and SAMPLE are 2 different files in Linux/Unix operating system. |
| In windows, My Documents is default home directory. | For every user /home/username directory is created which is called his home directory. |