How to Use GCC to Compile a C Program on Linux and Windows
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA. Nicole Levine is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. She has more than 20 years of experience creating technical documentation and leading support teams at major web hosting and software companies. Nicole also holds an MFA in Creative Writing from Portland State University and teaches composition, fiction-writing, and zine-making at various institutions.
There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article’s instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 1,001,899 times.
Are you ready to turn your C code into an executable program? The GNU C compiler, also known as GCC, is a simple Linux-based C compiler that’s easy to use from the command line. If you’re using Linux, including Ubuntu, Fedora, and Linux Mint, you can install GCC from your distribution’s package manager. On Windows 10 and 11, you can use GCC in a Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) shell, or by installing an open source tool called MinGW. This wikiHow guide will teach you the easiest ways to compile a C program from source code using GCC.
- To make sure GCC is installed, run the command gcc —version.
- Type gcc source_file.c -o program_name and press Enter to compile your source code.
- Replace source_file with the name of your source code file, and program_name with the name you’d like to give your compiled program.
Using Linux
- Ubuntu, Debian, & Linux Mint:
- In a terminal window, type sudo apt update and press Enter.
- Type sudo apt install build-essential and press Enter. [1] X Research source
- Type gcc —version and press Enter to verify your installation.
- In a terminal window, type sudo dnf group install «Development Tools» and press Enter. [2] X Research source
- Type gcc —version and press Enter to verify your installation.
- For example, if your source code is in a folder called Documents that’s inside your home directory, use cd ~/Documents .
- If you need to compile a program from multiple source files, use the syntax gcc -o [executable_name] sourcefile1.c sourcefile2.c sourcefile3.c .
- If you see errors and want to see more information about them, use gcc -Wall -o errorlog file1.c . [3] X Research source Then, view the “errorlog” file in the current directory with cat errorlog .
- To compile multiple programs at once with multiple source code files, use gcc -c file1.c file2.c file3.c .
Run your newly-compiled program. Type ./[executable_name] but replace “[executable_name]” with the name of your program.
Using Windows Subsystem for Linux
- If you haven’t already enabled Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), you can install it with a single command from the command prompt or PowerShell. Start Command Prompt or PowerShell as an administrator, and then run this command to install Ubuntu: wsl —install . [4] X Research source
- If you see the WSL help text when running the command, you may have already enabled WSL. Instead, run the command wsl —list –online to see a list of Linux distributions, then use wsl —install -d (e.g., Ubuntu) to install Ubuntu.
- Type sudo apt update and press Enter.
- Type sudo apt-get install build-essential gdb and press Enter. [6] X Research source
Go to the directory that contains your source code. Use the cd commanad to change to the directory in which you’ve saved the source code you want to compile.
- If you need to compile a program from multiple source files, use the syntax gcc -o [executable_name] sourcefile1.c sourcefile2.c sourcefile3.c .
- If you see errors and want to see more information about them, use gcc -Wall -o errorlog file1.c . [7] X Research source Then, view the “errorlog” file in the current directory with cat errorlog .
- To compile multiple programs at once with multiple source code files, use gcc -c file1.c file2.c file3.c .
Run your newly-compiled program. Type ./[executable_name] but replace “[executable_name]” with the name of your program.
Using MinGW for Windows
- To get the latest version of the installer, click the mingw-get-setup.exe link.
- If the download doesn’t begin automatically, click Save or Download when prompted.
- MinGW can only compile 32-bit versions of software. However, all 32-bit software compiled with MinGW will execute properly on a 64-bit system. [9] X Research source
- If you need to compile 64-bit software, try MinGW-w64, a port of MinGW. You can download it from https://www.mingw-w64.org. [10] X Research source Alternatively, you can use Windows Subsystem for Linux.
-
- MinGW recommends using the default installation folder ( C:\MinGW ). If you must change the folder, don’t use a folder with spaces in the name (e.g. “Program Files”).
Select Basic Setup to view the basic C compiling tools. If you want more options, you can select All Packages to see all available libraries and build tools.
- At the very least, you will want to install MinGW32-base and MinGW32-gcc-g++. If you need to compile code written in objective C, you should also mark MinGW32-gcc-objc for installation.
- Click the Installation menu in the upper-left corner.
- Click Apply Changes.
- Click Apply.
- Click Close once the installation is done.
- Type environment in the search bar next to the Start menu.
- Click Edit the system environment variables in the search results.
- Click Environment Variables…
- Select the Path variable in the «System variables» section.
- Click Edit beneath the top box (under “User Variables”)
- Click New.
- Type C:\MinGW\bin in the new space. Note that if you installed MinGW to a different directory, enter C:\path-to-that-directory\bin .
- Click OK, and then OK again. Click the one remaining OK button to close the window.
- Type cmd in the search bar next to the Start menu.
- Right-click Command Prompt in the search results, then select Run as Administrator.
- Click Yes to allow changes.
Go to the folder where your source code is saved. For example, if your source code file called helloworld.c is located in C:\Source\Programs, type cd C:\Source\Programs and press Enter.
- If you receive an «Access is denied» or «Permission denied» error message when compiling a program or running the output executable file, check the folder permissions and make sure you have full read/write access to the folder that contains the source code. If that doesn’t work, try temporarily disabling your virus software. [11] X Research source
Community Q&A
What do I do if there are two tables in the environmental variables window? In which table and directory should I add an environmental variable?
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHowThanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHowTheoretically, as long as a file contains the necessary binary machine code, it could be run by a processor. One example is how on Windows, a screensaver is simply a program (just like a .exe) but with the .scr extension. However, as far as I know, most modern operating systems will not attempt to execute a file if it does not identify the file type as being executable, so you would need to somehow trick the operating system into actually starting a new process using the code from the file.
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHowcc command in Linux with Examples
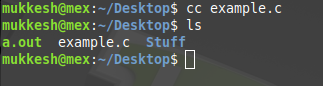
cc command is stands for C Compiler, usually an alias command to gcc or clang. As the name suggests, executing the cc command will usually call the gcc on Linux systems. It is used to compile the C language codes and create executables. The number of options available for the cc command is very high. The most important options are explained below with examples.
Example: Below command will compile the source_file.c file, and create the default executable output file, a.out.
Important Options:
- cc command with -o option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, and create a executable output file with the specified name.
cc command with -Wall option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, and check for all errors and warnings in the program.
cc example.c -Wall -o examp_out
cc command with -w option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, but suppress all the warnings.
cc command with -g option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, and create a debugging version of the executable output file. This output file can be used by the debugger, and is usually much larger in size than the normal output files.
cc example.c -g -o examp_out_debug
cc command with -c option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, and create an object file source_file.o, which can later be linked to create an executable output file.
cc command with -Ldir option: This command, while compiling the source_file.c file, will also search the specified directory for header files.
cc example.c -L /home/mukkesh/Desktop
cc command with -ansi option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, and makes sure that the code follows strict ANSI standards. This will make sure that the code is portable to be compiled on any other system.
cc command with –dump options: These commands specified below will print the version of the cc command, the default target machine and built-in specification strings.
cc command with -v option: This command will compile the source_file.c file, and gives a verbose output.