- Concatenate Files in Linux Command Line
- How to concatenate files in Linux
- Concatenate multiple files in standard output
- Concatenate and save file contents to a new file
- Add additional data from standard input while concatenation
- Concatenate command output to file
- Get more out of the cat command
- Concatenating Files in Linux
- Concatenating Files Using cat Command
- Concatenating Files Using cat Command with Wildcards
- Concatenating Files Using paste Command
- Concatenating Binary Files Using dd Command
- Conclusion
Concatenate Files in Linux Command Line
Want to concatenate two files in the Linux command line? Here’s how to do that with the cat command.
In simple terms, concatenation refers to connecting two character stings.
For example, there are two character strings: snow and ball . So when you’d concatenate them, it will form a single string snowball .
While using Linux, you’d often find yourself in a situation where you have to concatenate two or more files.
So in this guide, I will share multiple examples to concatenate files.
How to concatenate files in Linux
When you consider the concatenation of text files in Linux, the cat command rules the whole category.
For demonstration, I will be using two text files named TextFile1 and TextFile2 and their file contains are as follows:
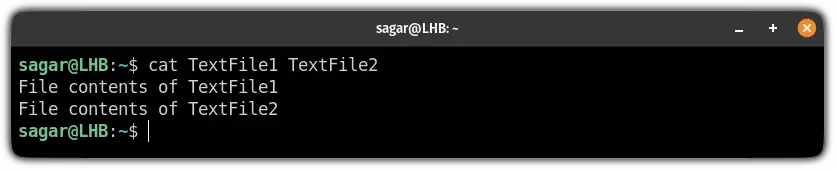
[email protected]:~$ cat TextFile1 File contents of TextFile1 [email protected]:~$ cat TextFile2 File contents of TextFile2Now, let’s jump to the examples part.
Concatenate multiple files in standard output
This is the simplest concatenation that is used by most of the users where you combine the output of multiple files in the standard output:
Concatenate and save file contents to a new file
Above, I explained how you can concatenate multiple files but it won’t save any changes.
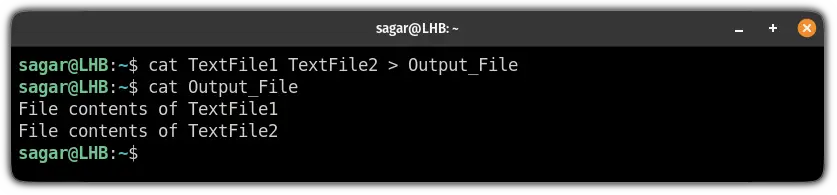
So if you want to concatenate files and save the output to another file, you can redirect the output data stream to a new file.
For example, here, I have concatenated the file contents of TextFile1 and TextFile2 and saved the output to a new file named Output_File :
cat TextFile1 TextFile2 > Output_FileBut it will override the file contents of Ouput_File (if any) and you may lose sensitive data.
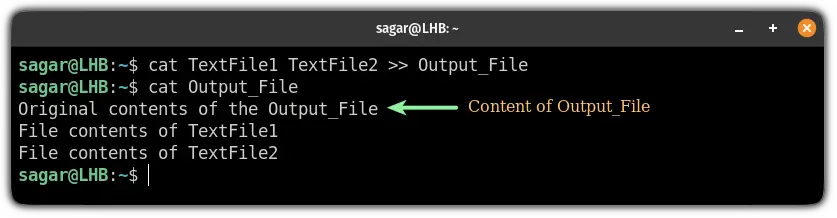
To concatenate and save the output to another file without overriding, use the >> instead of > :
cat TextFile1 TextFile2 >> Output_FileAnd as you can see, the contamination of two files was saved below the content of Output_File .
Add additional data from standard input while concatenation
It’s not always the case where you just want to concatenate the file contents of two different files, you may also want to add additional data to it.
So let’s say I want to concatenate two files TextFile1 and TextFile2 but I want to add some additional data and in that case, using the standard input is the best choice.
Which can be invoked by the — flag.
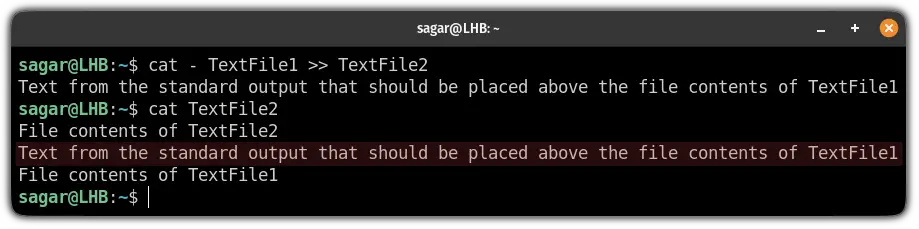
For example, I want to add data above the content of TextFile1 , so I will be using the following:
cat - TextFile1 >> TextFile2It will be executed as a normal cat command where you add simple text.
Once you are done adding text, save the file and exit from using the Ctrl + D .
For your reference I added the following line:
Text from the standard output that should be placed above the file contents of TextFile1And as you can see, here, I concatenated two files with additional data from the standard input.
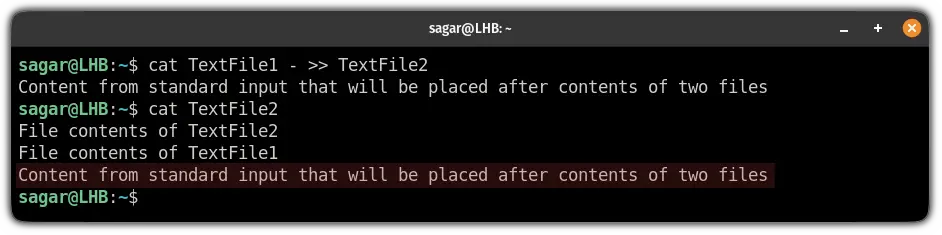
Similarly, if you want to add additional data after the contamination of two files instead of the above, you can refer to the following:
cat TextFile1 - >> TextFile2Here, I have entered the following in the standard input:
Content from standard input that will be placed after contents of two filesConcatenate command output to file
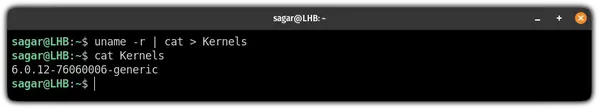
If you want to concatenate the output of a command to a specific file using the cat command, you can refer to the given command syntax:
For example, here, I have concatenated the kernel version that I’m currently using to a file named Kernels :
But did you know that you can also redirect the output, errors, and standard input to a file?
It is quite easy and can be very helpful in cases where you just want to concatenate the errors only:
Get more out of the cat command
While most of the users use the cat command to create and read files but what if I tell you that you can do a lot more with it?
Even I wasn’t aware of its power until I read the following guide:
I hope you will find this guide helpful.
And if you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comments.
Concatenating Files in Linux
Linux is an operating system, it become popular for its open-source nature, flexibility, and reliability. Including its many features, Linux also provides powerful tools for managing files and data, including ability to concatenate files. The concatenation is process of joining two or more files together, creating single file that contains contents of all original files.
In this article, we will explore different methods of concatenating files in Linux, including examples and subheadings.
Concatenating Files Using cat Command
The cat command is a powerful tool for managing text files in Linux. It can be used to create new files, view contents of existing files, and concatenate files. syntax for using cat command to concatenate files is as follows −
In this example, file1 and file2 are two files that we want to concatenate, and newfile is name of new file that will contain concatenated contents. «>» symbol is used to redirect output of cat command to a new file.
For instance, let us assume we have two text files, file1.txt and file2.txt. We can concatenate them using following command −
$ cat file1.txt file2.txt > newfile.txt
This command will create a new file named newfile.txt that contains concatenated contents of file1.txt and file2.txt.
Concatenating Files Using cat Command with Wildcards
The cat command can also be used with wildcards to concatenate multiple files at once. A wildcard is a special character that represents one or more characters in a filename. most commonly used wildcard is asterisk (*), which represents any number of characters.
The syntax for using cat command with wildcards to concatenate files is as follows −
In this example, file* represents any number of files that start with word «file.» «>» symbol is used to redirect output of cat command to a new file named newfile.
For example, if we have three files named file1.txt, file2.txt, and file3.txt, we can concatenate them using following command −
This command will create a new file named newfile.txt that contains concatenated contents of all three files.
Concatenating Files Using paste Command
The paste command is another tool that can be used to concatenate files in Linux. Unlike cat command, which simply joins contents of two or more files together, paste command merges contents of two or more files side by side. syntax for using paste command to concatenate files is as follows −
paste file1 file2 > newfile
In this example, file1 and file2 are two files that we want to concatenate side by side, and newfile is name of new file that will contain concatenated contents.
For example, if we have two text files, file1.txt and file2.txt, we can concatenate them side by side using following command −
$ paste file1.txt file2.txt > newfile.txt
This command will create a new file named newfile.txt that contains merged contents of file1.txt and file2.txt side by side.
Concatenating Binary Files Using dd Command
The dd command is a powerful tool for managing binary files in Linux. It can be used to create new binary files, view contents of existing binary files, and concatenate binary files. syntax for using dd command to concatenate binary files is as follows −
dd if=file1 of=newfile bs=1M conv=notrunc dd if=file2 of=newfile bs=1M seek=1 conv=notr
In this example, file1 is first binary file that we want to concatenate, newfile is name of new binary file that will contain concatenated contents, and bs=1M specifies block size to be used for operation.
The «if» parameter specifies input file, while «of» parameter specifies output file. «notrunc» parameter prevents existing data in output file from being truncated, while «seek» parameter is used to seek to a specific offset in output file.
For example, if we have two binary files, file1.bin and file2.bin, we can concatenate them using following commands −
$ dd if=file1.bin of=newfile.bin bs=1M conv=notrunc $ dd if=file2.bin of=newfile.bin bs=1M seek=1 conv=notrunc
The first command creates a new binary file named newfile.bin that contains contents of file1.bin. second command appends contents of file2.bin to newfile.bin, starting at offset 1.
In addition to commands discussed in this article, there are several other tools available in Linux that can be used to concatenate files. For example, awk command can be used to join two or more files based on a common field. join command can also be used to merge two files based on a common field, while comm command can be used to compare two sorted files line by line.
It is important to note that when concatenating files, it is important to ensure that resulting file is still in a usable format. This means that files should be of same format, such as both being text files or both being binary files. Additionally, it is important to ensure that files are concatenated in correct order, so that resulting file is complete and accurate.
Another important consideration when concatenating files is encoding of files. For text files, it is important to ensure that encoding is consistent across all files to prevent issues with special characters and formatting. In some cases, it may be necessary to convert encoding of files before concatenating them to ensure that resulting file is usable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, concatenating files in Linux is a powerful and flexible way to manage files and data. cat, paste, and dd commands provide different methods for concatenating text and binary files. By using these commands, users can combine multiple files into a single file, creating a more efficient and manageable way to store and access data. Knowing how to concatenate files in Linux can be a useful skill for developers, system administrators, and anyone else who works with files and data on a regular basis.