- gcc⚓︎
- Подготовка⚓︎
- Настройка⚓︎
- Для multilib⚓︎
- Значения параметров⚓︎
- Сборка⚓︎
- Тестирование⚓︎
- Установка⚓︎
- При использовании раздельных каталогов:⚓︎
- Проверка работоспособности⚓︎
- Установленные файлы⚓︎
- How to Install and Use GCC Compiler on Linux System
- GCC Compiler on Linux
- 1. Install GCC Compiler on Debian/Ubuntu Linux
- 2. Install GCC Compiler on Arch Linux
- 3. Install GCC Compiler on Red Hat and Fedora Linux
- Get Started with the GNU Compiler Collection
- Remove GCC Compiler from Linux
- Final Words
gcc⚓︎
Пакет содержит набор компиляторов GNU для таких языков как Си и Си++.
Версия: 11.2.0
Размер: 77.14Mb
Приоритет: Необходимый
MD5: 31c86f2ced76acac66992eeedce2fce2
SBU (Сборка временной системы): 14.8
Подготовка⚓︎
Исправьте пути установки библиотек:
sed -e '/m64=/s/lib64/lib/' \ -e '/m32=/s/m32=.*/m32=..\/lib32$(call if_multiarch,:i386-linux-gnu)/' \ -i.orig gcc/config/i386/t-linux64 Настройка⚓︎
На данном этапе необходимы только компиляторы для C и C++, однако вы можете собрать компиляторы для любых поддерживаемых GCC языков программирования, перечислив их через запятые в опции configure —enable-languages=c,c++ . GCC поддерживает следующие языки — c,c++,d,fortran,go,objc,obj-c++ . вы можете собрать все доступные компиляторы, добавив параметр —enable-languages=c,c++,d,fortran,go,objc,obj-c++ . Если позднее вам потребуется компилятор для какого либо языка из этого списка — пересоберите GCC с его поддержкой.
mkdir -v build cd build ../configure --prefix=/usr \ LD=ld \ --disable-bootstrap \ --with-system-zlib \ --enable-languages=c,c++ --disable-multilib Для multilib⚓︎
mkdir -v build cd build ../configure --prefix=/usr \ LD=ld \ --disable-bootstrap \ --with-system-zlib \ --enable-languages=c,c++ --enable-multilib --with-multilib-list=m64,m32 Значения параметров⚓︎
—disable-bootstrap — предотвращает многократную пересборку GCC
LD=ld — сообщает GCC использовать ранее установленную версию компоновщика
Сборка⚓︎
Тестирование⚓︎
- Увеличьте размер стека по умолчанию
- Произведите тестирование от непривилегированного пользователя во избежание непредвиденных ситуаций с системой.
ulimit -s 32768 chown -Rv tester . su tester -c "PATH=$PATH make -k check" Тестирование этого пакета занимает достаточно много времени.
Для просмотра итогов теста выполните:
Известно, что 6 тестов, связанных с get_time , дают сбои. По видимому, это связано с локалью en_HK . Кроме того, тест COSTEXPR-52830 не удается.
Установка⚓︎
- Удалите ненужную директорию,
- Убедитесь, что владелец установленных заголовков корректный,
- По историческим причинам некоторые программы могут пытаться найти cpp в директории /lib . Создайте ссылку,
- Для поддержки LTO требуется следующая символическая ссылка,
- Переместите файлы в правильное место:
rm -rf /usr/lib/gcc/$(gcc -dumpmachine)/11.2.0/include-fixed/bits/ chown -v -R root:root \ /usr/lib/gcc/*linux-gnu/11.2.0/include,-fixed> ln -svr /usr/bin/cpp /usr/lib ln -sfv ../../libexec/gcc/$(gcc -dumpmachine)/11.2.0/liblto_plugin.so \ /usr/lib/bfd-plugins/ mkdir -pv /usr/share/gdb/auto-load/usr/lib,32> mv -v /usr/lib/*gdb.py /usr/share/gdb/auto-load/usr/lib mv -v /usr/lib32/*gdb.py /usr/share/gdb/auto-load/usr/lib32 При использовании раздельных каталогов:⚓︎
Проверка работоспособности⚓︎
Сейчас необходимо проверить работу gcc . Если всё нормально, то продолжайте сборку.
echo 'int main()<>' > dummy.c cc dummy.c -v -Wl,--verbose &> dummy.log readelf -l a.out | grep ': /lib' Ошибок быть не должно, а результат команды (учитывая различия в имени динамического компоновщика, зависящие от платформы) будет следующий:
Requesting program interpreter: /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2] Проверим что задействованы правильные стартовые файлы. Выполните команду:
grep -o '/usr/lib.*/crt[1in].*succeeded' dummy.log /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/11.2.0/../../../../lib/crt1.o succeeded /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/11.2.0/../../../../lib/crti.o succeeded /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/11.2.0/../../../../lib/crtn.o succeeded В зависимости от архитектуры, приведенное выше может немного отличаться. Разница будет в названии каталога после /usr/lib/gcc . Здесь важно обратить внимание на то, что gcc обнаружил все три файла crt * .o в каталоге /usr/lib .
Проверим то, что компилятор выполняет поиск корректных заголовочных файлов:
grep -B4 '^ /usr/include' dummy.log #include search starts here: /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/11.2.0/include /usr/local/include /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/11.2.0/include-fixed Проверим, что компоновщик использует корректные пути поиска:
grep 'SEARCH.*/usr/lib' dummy.log |sed 's|; |\n|g' SEARCH_DIR("/usr/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/lib64") SEARCH_DIR("/usr/local/lib64") SEARCH_DIR("/lib64") SEARCH_DIR("/usr/lib64") SEARCH_DIR("/usr/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/lib") SEARCH_DIR("/usr/local/lib") SEARCH_DIR("/lib") SEARCH_DIR("/usr/lib"); Проверим, что используется корректная стандартная библиотека
grep "/lib.*/libc.so.6 " dummy.log attempt to open /usr/lib/libc.so.6 succeeded Проверим, что используется корректный динамический компоновщик:
grep "found ld-linux*" dummy.log Результат выполнения должен быть (учитывая различия в имени динамического компоновщика, зависящие от платформы):
found ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 at /usr/lib/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 Если вывод не соответствует вышеуказанному, или вообще не получен, значит, что-то не так. Изучите и повторите шаги, чтобы выяснить, в чем проблема. Перед продолжением процесса необходимо решить любые проблемы.
rm -v dummy.c a.out dummy.log Установленные файлы⚓︎
Программы: c++ (ссылка на g++), cc (ссылка на gcc), cpp, g++, gcc, gcc-ar, gcc-nm, gcc-ranlib, gcov, gcov-dump и gcov-tool
Библиотеки: libasan., libatomic., libcc1.so, libgcc.a, libgcc_eh.a, libgcc_s.so, libgcov.a, libgomp., libitm., liblsan., liblto_plugin.so, libquadmath., libssp., libssp_nonshared.a, libstdc++., libstdc++fs.a, libsupc++.a, libtsan. и libubsan.
Директории: /usr/include/c++, /usr/lib/gcc, /usr/libexec/gcc и /usr/share/gcc-11.2.0
How to Install and Use GCC Compiler on Linux System
While building the Linux kernel, the developers had to build a free and open-source compiler to create the kernel and modules. The GCC compiler was build under the GNU project. In the current version of all Linux distributions, the GCC compiler comes pre-installed inside the operating system. You can use the GCC compiler to compile C, C++, Ada, Go, and a few other object-oriented programming languages. You can compile codes on your terminal shell through the GCC compiler on a Linux system.
GCC Compiler on Linux
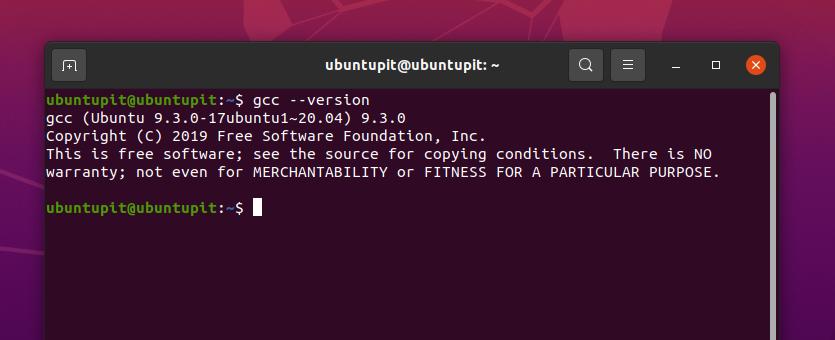
The word GCC stands for GNU Compiler Collection. Linux kernel is mostly built on the object-oriented and C programming language. Before installing the GCC compiler on your Linux system, you need to check whether it is already installed on your system or not.
If you get the following message on your shell, you don’t need to install it. If you can’t find the GCC on your machine, you need to install it on your system. This post will see how to install and get started with the GNU Compiler Collection on Linux distributions.
1. Install GCC Compiler on Debian/Ubuntu Linux
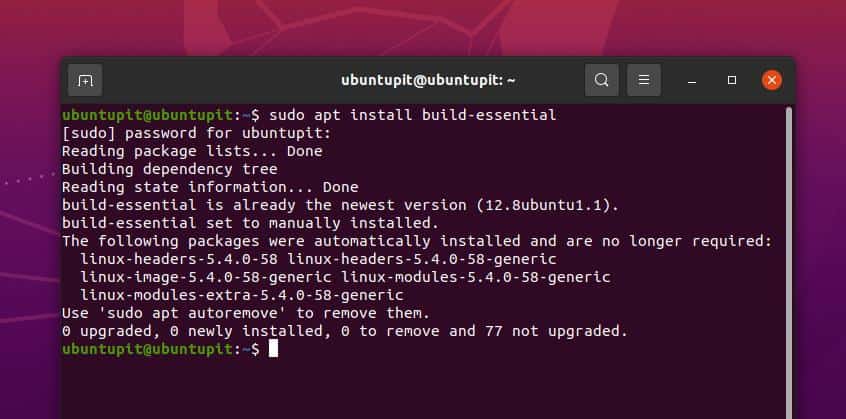
On Ubuntu and other Debian distributions of Linux, the GCC compiler comes inside the build-essential packages. The entire package contains GNU C, C++ compiler, and a few more essential library functions and tools. You can run the following aptitude command-line given below to install the GNU Compiler Collection on your Debian Linux distribution. I must note, the following command will require root privileges.
sudo apt install build-essential
2. Install GCC Compiler on Arch Linux
Installing the GCC compiler on an Arch-based Linux system is a straightforward process. You can run the following Pacman command given below on the terminal shell of your Arch Linux system to install the GNU Compiler Collection. Here, I am using the Manjaro KDE Linux to represent the Arch family, and the following command will work on other Arch-based Linux systems as well.
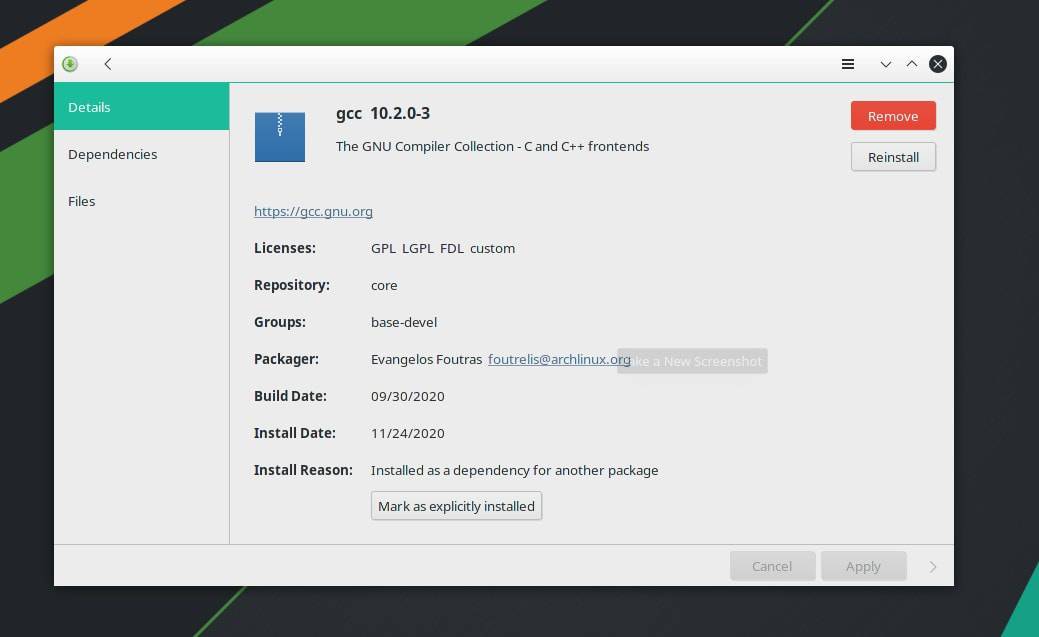
You can also get the GCC compiler on an Arch-based system through the Software Installation and Remove system. You just need to open the software store and search for the GCC compiler. Once you find the package, you are just a few clicks away from removing, installing, or reinstalling it on your system.
3. Install GCC Compiler on Red Hat and Fedora Linux
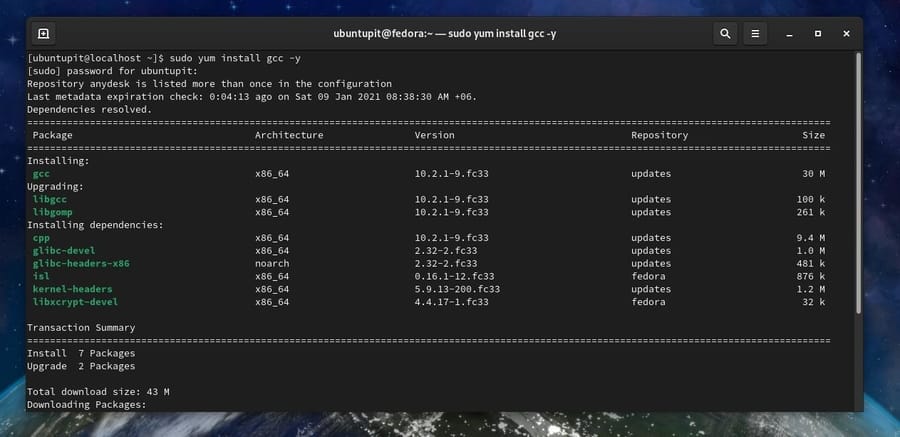
If you are a Red Hat or a Fedora Linux user, this step is for you. You can install the GCC compiler on your system by running the following command given below. Red Hat Linux users need to run the YUM command with superuser access.
sudo yum groupinstall 'Development Tools'
Fedora Linux users need to run the following DNF command on the terminal shell to get the GNU Compiler Collection on their system.
sudo dnf groupinstall 'Development Tools'
If you face any issues installing the tool, you can run the following command to install the GNU Compiler Collection directly on your Red Hat-based system.
Get Started with the GNU Compiler Collection
Till now, we have how you can install the GNU Compiler Collection on your favorite Linux system. Here, we will see how you can create your first project and run it through the GCC compiler. I’m going to show how you can write a simple code for C programming language to print ‘Hello Ubuntupit.’
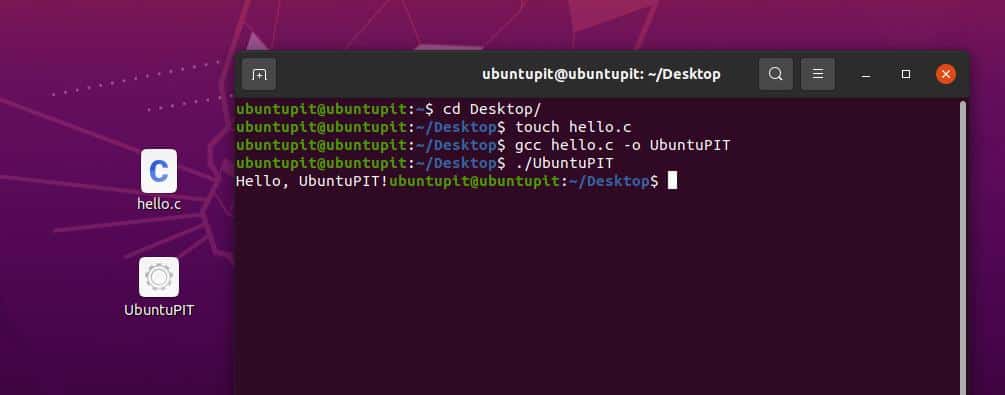
First, open your terminal shell, and select a directory to store the code. I’m picking the Desktop directory to save the file. If you don’t choose and directory, it will set the home directory of your Linux filesystem by default. Now, run the following touch command on your terminal shell to create a new file.
Once the file is created, open the file using a notepad or script editor. Now copy and paste the following codes given below inside your blank script. Then save and exit the file.
We can now compile the code through the GCC compiler on our Linux system. Run the following command on your terminal shell to compile the code. You can give a new name to your code while compiling. Here, I’m naming the compiled file as Ubuntupit. We will later use the name to run the code. We can run the C programming code on our Linux terminal through the dot slash (./) command on the terminal shell.
Run the following command on your terminal shell to execute the compiled file through the GCC compiler on your Linux system. Here the -o flag is used to indicate the output file.
$ cd Desktop/ gcc hello.c -o UbuntuPIT ./UbuntuPIT
You can see that the code has successfully compiled and run through the GCC compiler on a Linux system.
Remove GCC Compiler from Linux
You might need to remove the GNU Compiler Collection from your Linux system if you find any broken package or repository issues. Here is the process how you can remove it from your Linux machine. Run the appropriate command from the following command-lines to remove the GCC compiler on your Linux system.
You can remove GNU Compiler Collection from Debian/Ubuntu Linux by running the following command.
sudo apt-get install --skip-broken gcc
Run the following command to remove GNU Compiler Collection from Red Hat and Fedora Linux.
sudo yum remove --skip-broken gcc
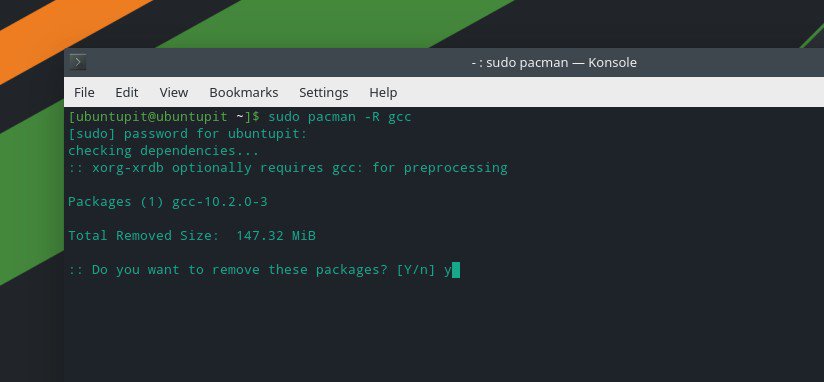
Arch Linux users need to run the following Pacman command to remove the broken GNU Compiler Collection package.
To remove the GNU Compiler Collection from Arch Linux, you can also use the default software center method that I have described previously.
Final Words
Using GCC compiler is the most effortless method to build and run the C program on any Linux system. If you are a newbie on programming or love the free and open-source software, you will enjoy using the GNU Compiler Collection. In the entire post, I have described the method of installing the GCC compiler on Linux distributions and how you can get started with it.
Please share it with your friends and the Linux community if you find this post useful and informative. You can write to us with your opinions regarding this post in the comment section.