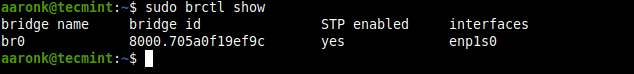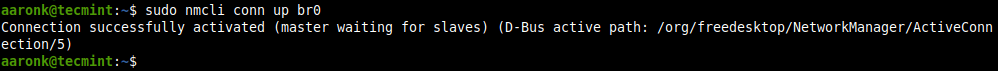- How to Configure Network Bridge in Ubuntu
- Installing Network Bridge Utilities in Ubuntu
- Creating a Network Bridge Using NetPlan in Ubuntu
- Creating a Network Bridge Using Nmcli in Ubuntu
- Creating a Network Bridge Using nm-connection-editor Tool
- How to Use a Network Bridge in a Virtualization Software
- Using a Network Bridge in Oracle VirtualBox
- Using a Network Bridge in KVM
- How to configure a Linux bridge interface
- Preparation
- For Ubuntu or Debian:
- For CentOS, RHEL and Fedora:
- Create a Linux Bridge from the Command Line
- Create a Linux Bridge Permanently
- Configure a Permanet Bridge Interface on Ubuntu or Debian
- Configure a Permanet Bridge Interface on CentOS, RHEL or Fedora
- Support Xmodulo
How to Configure Network Bridge in Ubuntu
Linux supports the implementation of a software network bridge to reproduce the function of a network bridge, a networking device that interconnects two or more communication networks or network segments providing a way for them to work as a single network. It acts almost like a network switch, and in a software sense, it is used to implement the concept of a “virtual network switch”.
A typical use case of software network bridging is in a virtualization environment to connect virtual machines (VMs) directly to the host server network. This way, the VMs are deployed on the same subnet as the host and can access services such as DHCP and much more.
In this article, you will learn different ways to set up a network bridge in Ubuntu and use it within a virtualization environment to create virtual networking in a bridged mode under VirtualBox and KVM, to connect Virtual Machines to the same network as the host.
On this page:
Installing Network Bridge Utilities in Ubuntu
Begin by installing the bridge-utils package which contains utilities for configuring the Ubuntu ethernet bridge using the apt package manager as shown.
$ apt-get install bridge-utils
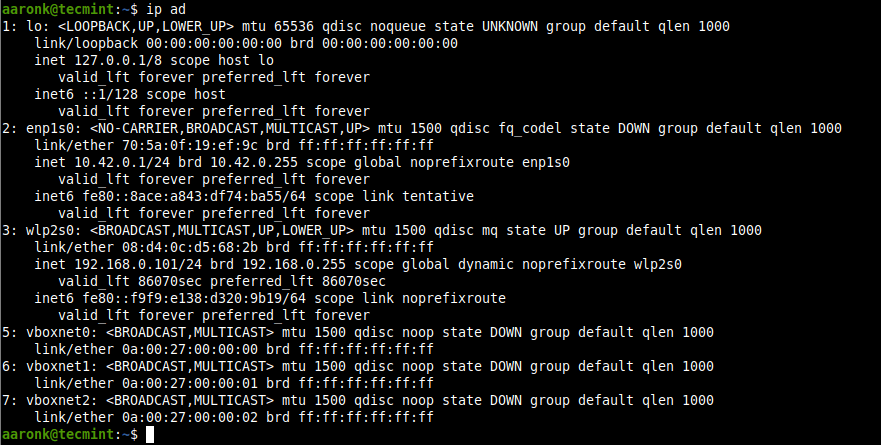
Next, identify the interface name for your ethernet device using the IP command as shown.
Creating a Network Bridge Using NetPlan in Ubuntu
Netplan is a simple and easy-to-use front-end utility for configuring networking in Linux using the YAML format. It currently supports NetworkManager and systemd-netword as backend tools.
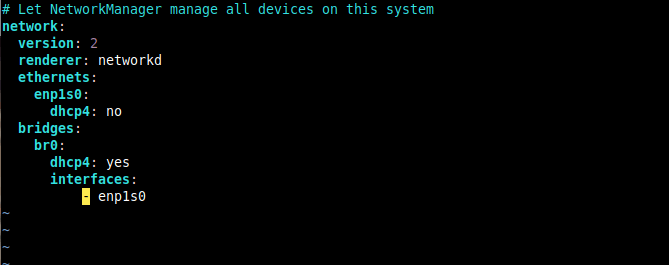
To configure networking for an interface such as a bridge, edit your netplan configuration file found in /etc/netplan/ directory.
The following is an example configuration file, where the renderer is systemd-netword which is the default (replace enp1s0 with your ethernet interface name).
network: version: 2 renderer: networkd ethernets: enp1s0: dhcp4: no bridges: br0: dhcp4: yes interfaces: - enp1s0
Save the configuration file and apply the configuration to enable the bridge network by running the following command.
Then use the brctl command to show all bridges on the system. In this case, the Ethernet interface is automatically added as a port to the bridge.
If you want to bring down or deactivate the created network bridge, then delete it using the following commands.
$ sudo ip link set enp1s0 up $ sudo ip link set br0 down $ sudo brctl delbr br0 OR $ sudo nmcli conn up Wired\ connection\ 1 $ sudo nmcli conn down br0 $ sudo nmcli conn del br0 $ sudo nmcli conn del bridge-br0
Creating a Network Bridge Using Nmcli in Ubuntu
nmcli is a widely-used network manager command-line tool to administer NetworkManager (create, show, edit, delete, activate, and deactivate network connections) and displaying network device status.
To create a network bridge using nmcli, run the following command.
$ sudo nmcli conn add type bridge con-name br0 ifname br0
Then add the Ethernet interface as a port in the bridge as shown (remember to replace enp1s0 with your device name).
$ sudo nmcli conn add type ethernet slave-type bridge con-name bridge-br0 ifname enp1s0 master br0
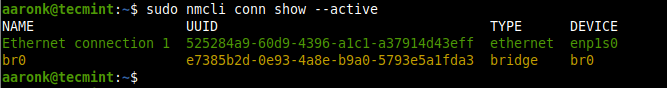
Next, confirm that the bridge has been created by showing all network connections.
$ sudo nmcli conn show --active
Next, activate the bridge connection as follows (you can use either the connection/interface name or the UUID).
$ sudo nmcli conn up br0 OR $ sudo nmcli conn up e7385b2d-0e93-4a8e-b9a0-5793e5a1fda3
Then deactivate the Ethernet interface or connection.
$ sudo nmcli conn down Ethernet\ connection\ 1 OR $ sudo nmcli conn down 525284a9-60d9-4396-a1c1-a37914d43eff
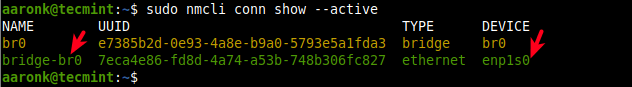
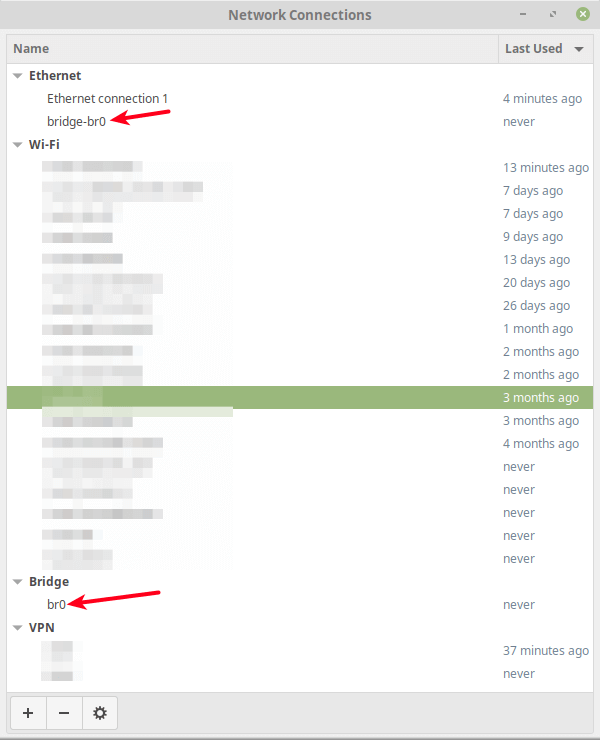
Now try to view active connections once more, the Ethernet interface should now be a slave in the bridge connection as shown in the following screenshot.
$ sudo nmcli conn show --active
Creating a Network Bridge Using nm-connection-editor Tool
To open the nm-connection-editor application, run the following command from the terminal.
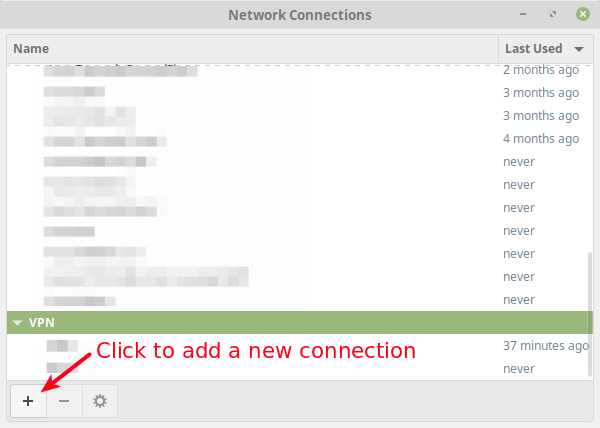
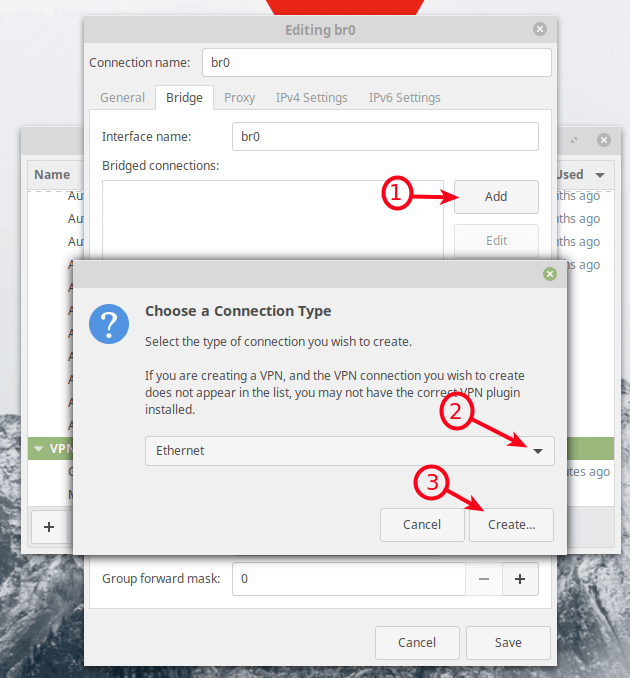
From the network connections editor window, click on the + sign to add a new connection profile.
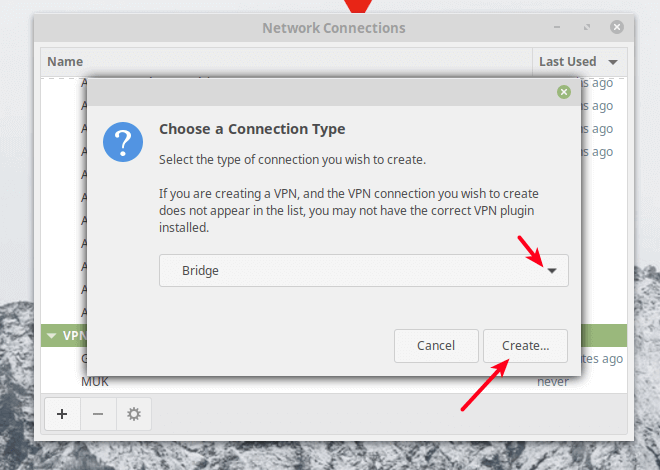
Next, choose the connection type as Bridge from the drop-down and click Create.
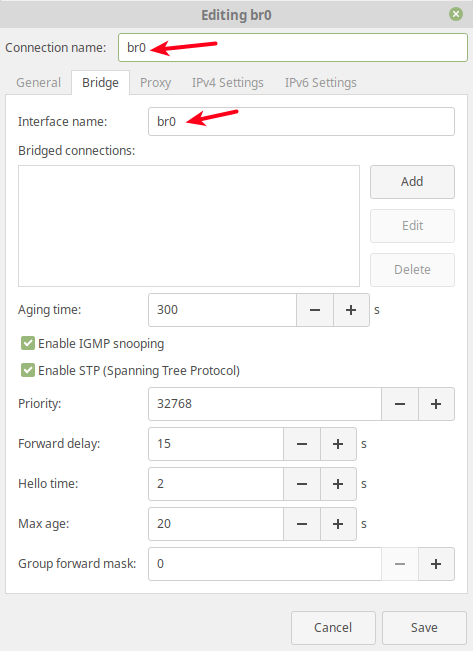
Next, set the bridge connection name and the interface name.
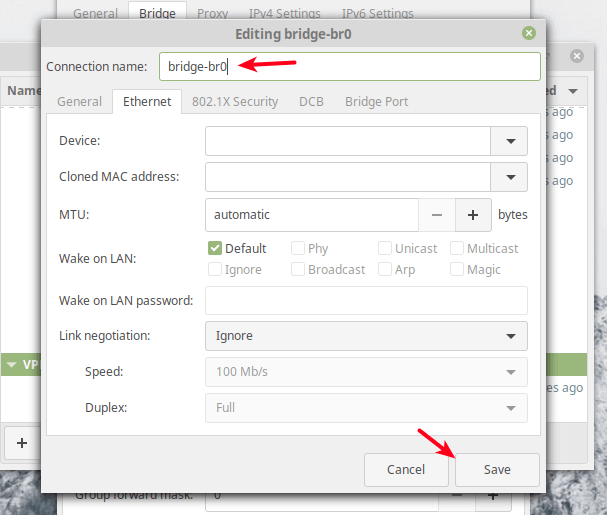
Then click the Add button to add the bridge slave ports i.e the Ethernet interface as shown in the following screenshot. Select Ethernet as the connection type and click Create.
Next, set the connection name according to your preference and click Save.
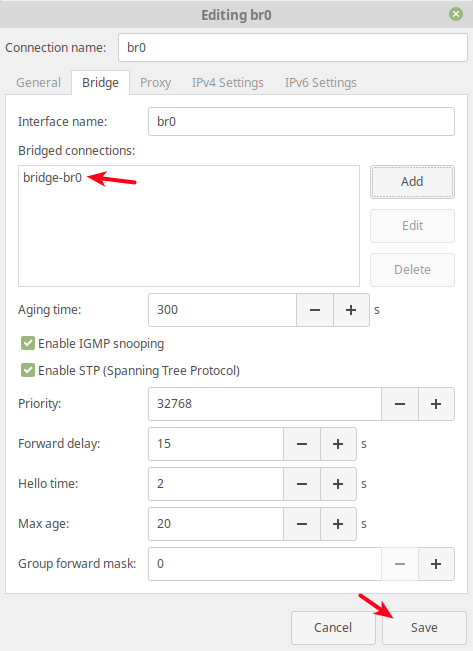
Under bridged connections, the new connection should now appear.
Now if you open the network connection editor once more, the new bridge interface and the slave interface should exist as indicated in the following screenshot.
Next, activate the bridge interface and deactivate the Ethernet interface, using the nmcli command.
$ sudo nmcli conn up br0 $ sudo nmcli conn down Ethernet\ connection\ 1
How to Use a Network Bridge in a Virtualization Software
After setting up a network bridge (virtual network switch), you can use it in a virtualization environment such as Oracle VirtualBox and KVM to connect VMs to the host network.
Using a Network Bridge in Oracle VirtualBox
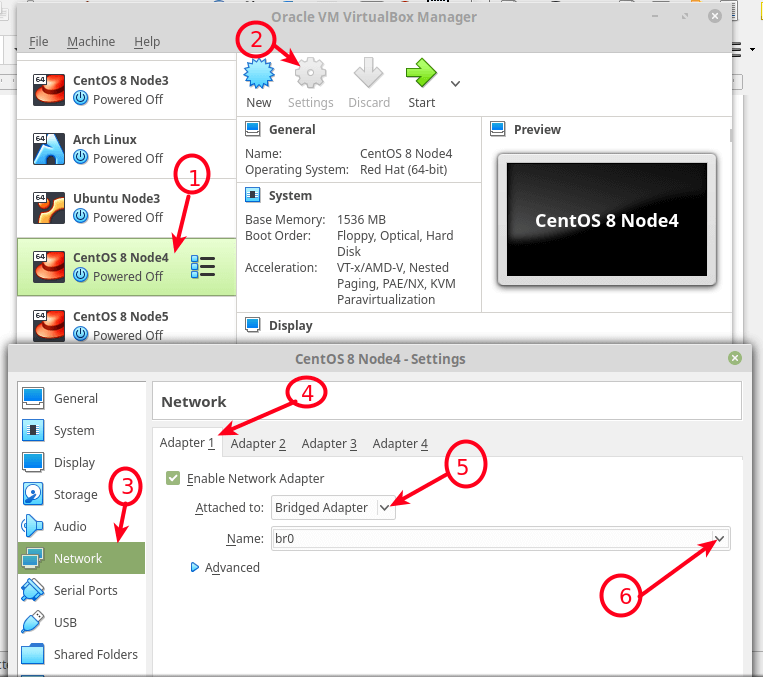
Open VirtualBox, then from the list of VMs, select a VM, then click on its settings. From the settings window, go to the Network option and select an adapter (e.g Adapter 1).
Then check the option Enable Network Adapter, set the value of the attached to the field to Bridged Adapter, then set the Name of the bridged interface (e.g br0) as indicated in the following screenshot. Then click Ok.
Using a Network Bridge in KVM
You can use the new network bridge under KVM by adding the —network=bridge=br0 option while creating a new virtual machine, using the virt-install command.
# virt-install --virt-type=kvm --name Ubuntu18.04 --ram 1536 --vcpus=4 --os-variant=ubuntu18.04 --cdrom=/path/to/install.iso --network=bridge=br0,model=virtio --graphics vnc --disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/ubuntu18.04.qcow2,size=20,bus=virtio,format=qcow2
From the web console, it will be select automatically. Besides, you can also configure a network bridge using the virsh command-line tool, and a VM’s XML configuration file.
For more details, read the netplan and nmcli man pages (by running man netplan and man nmcli ) as well as virtual networking in libvirt and virtual networking in VirtualBox. You can post any queries to us via the comment section below.
How to configure a Linux bridge interface
In computer networking, a bridge is a network device that interconnects more than one LAN segment at Layer-2. Bridges can filter traffic between different segments, thereby reducing the amount of traffic on LAN, even with many LAN segments. This bridge functionality is built into the Linux kernel, so one can set up a software bridge interconnecting multiple network interfaces.
In this post, I will describe how to configure a Linux bridge interface.
Preparation
In a server environment, a Linux bridge can be created with a user-space command-line tool called brctl . This tool allows you to create, remove and administer Linux Ethernet bridges.
To use brctl command, you need to install the following package.
For Ubuntu or Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install bridge-utils
For CentOS, RHEL and Fedora:
$ sudo yum install bridge-utils
Create a Linux Bridge from the Command Line
To create a bridge named br0 :
To remove a bridge named br0 :
To add interfaces eth0 and eth1 to a bridge br0 :
$ sudo brctl addif br0 eth0 $ sudo brctl addif br0 eth1
To remove an interface eth0 to a bridge br0 :
$ sudo brctl delif br0 eth0
It is worthwhile to note that a Linux bridge created by brctl is not persistent, meaning that any bridge created by brctl will automatically be destroyed upon boot. If you would like to have a permanent bridge configuration, you need to use a separate configuration file in /etc .
Create a Linux Bridge Permanently
In the rest of the tutorial, I will describe how to create a permanent Linux bridge interface from the command line using /etc configuration. If you want to use GUI-based Network Manager to configure a Linux bridge, refer to this tutorial instead.
As an example, I will create a Linux bridge called br0 and add eth0 and eth1 interfaces to the bridge.
Configure a Permanet Bridge Interface on Ubuntu or Debian
You need to edit /etc/network/interfaces as follows.
If the bridge br0 is to be assigned an IP address by DHCP:
auto eth0 iface eth0 inet manual auto eth1 iface eth1 inet manual auto br0 iface br0 inet dhcp bridge_ports eth0 eth1
If the bridge br0 is to be assigned a static IP address:
auto eth0 iface eth0 inet manual auto eth1 iface eth1 inet manual auto br0 iface br0 inet static bridge_ports eth0 eth1 address netmask gateway
If you want to set up a transparent bridge between eth0 and eth1 , you don’t need to assign any IP address to the bridge. In that case, the following will do.
auto eth0 iface eth0 inet manual auto eth1 iface eth1 inet manual auto br0 iface br0 inet manual bridge_ports eth0 eth1
Configure a Permanet Bridge Interface on CentOS, RHEL or Fedora
You need to update existing eth0/eth1 configuration in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1 , and add bridge configuration in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-br0 .
$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0 TYPE=Ethernet BRIDGE=br0
$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
DEVICE=eth1 TYPE=Ethernet BRIDGE=br0
If the bridge br0 is to be assigned an IP address by DHCP:
$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-br0
DEVICE=br0 TYPE=Bridge ONBOOT=yes DELAY=0 BOOTPROTO=dhcp ONBOOT=yes
If the bridge br0 is to be assigned a static IP address:
$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-br0
DEVICE=br0 TYPE=Bridge BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR= NETMASK= GATEWAY= ONBOOT=yes
To set up a transparent bridge between two interfaces:
$ sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-br0
DEVICE=br0 TYPE=Bridge BOOTPROTO=none ONBOOT=yes
If you want to customize or inspect the bridge settings (e.g., MAC learning), refer to this tutorial.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.