- Remote Desktop connection from Mac to Ubuntu
- 4 Answers 4
- Connecting to a Remote Server Over SSH on a Mac
- Before You Begin
- Open the Terminal
- Connecting to the Remote Server Over SSH
- Ending the SSH Session
- Sending Commands Over SSH
- Sending a Single Command
- Sending Multiple Commands
- Using sudo
- Going Further
- Troubleshooting SSH Connection Issues
- Increasing Security
- Connecting to Linux over RDP from a Mac is very easy and fun.
Remote Desktop connection from Mac to Ubuntu
It shouldn’t be #2 and 3 since I can ssh to the server just fine. So I suspect #1 is the culprit.
For RDP you need a desktop. If you have one installed then installing and configuring xrdp should be as in your linked answer.
David — when @CelticWarrior says «you need a desktop», he doesn’t mean a laptop wont work. He means you need a gui installed on your Ubuntu server. If you have a basic server from the «server» download link on ubuntu.com, it won’t have a gui (aka a desktop) unless you added and configured one (i.e. Unity, Gnome, etc.). Without a desktop/gui, something like xrdp will not work.
James: Ah I see. So in the link in the OP, I followed those instructions and installed xRDP and xfce4. Aren’t these all that is needed to set up the «desktop?»
4 Answers 4
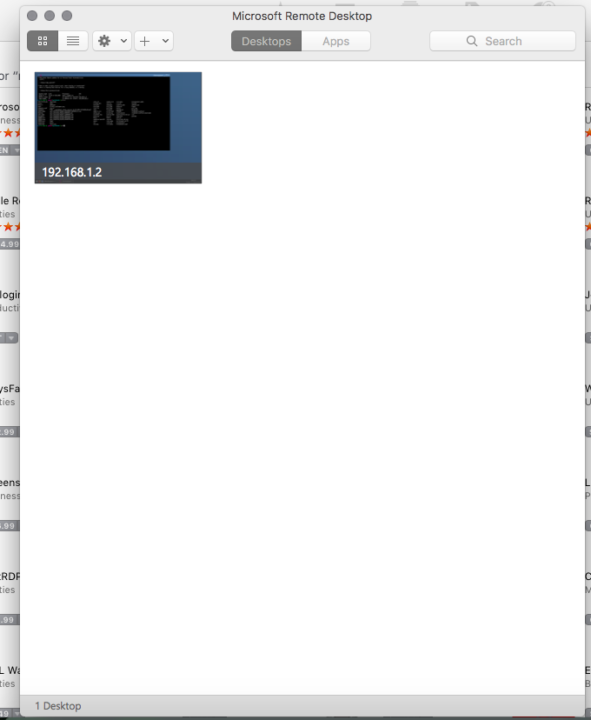
You can use Microsoft Remote Desktop from App Store. Set up your Ubuntu this way:
If you don’t have desktop installed:
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop
Enable XRDP to start on boot:
If you have a firewall make sure that the 3389 port is open:
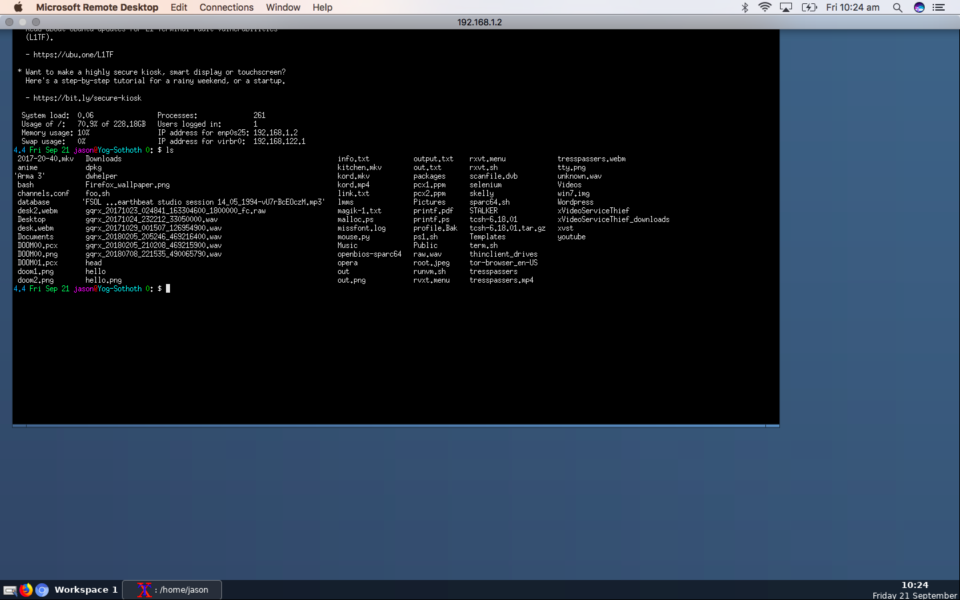
Now connect with Microsoft Remote desktop to your Linux machine.
I successfully logged-in remotely from my iMac macOS Mojave desktop into my hackintosh, which is a retrofitted 2012 Apple Macbook Pro running smoothly Ubuntu 16.04:
From the Ubuntu Desktop in 16.04
- Download and install vino by running sudo apt-get install vino within the Ubuntu terminal.
- Next run vino-preferences .
- After the vino application preferences window prompts, ensure that the «Allow other users to view your desktop» and «Allow other users to control your desktop» options are selected beneath the «Sharing» field; it is also recommended to select the «You must confirm each access to the this machine» and «Require the user to enter system-password».
- Run sudo-reboot and then log-in to the Ubuntu 16.04 desktop.
- Retrieve and the device-IP address by running ifconfig -a ; the local-IP address of the device will be returned within the terminal-output under the field: «inet addr:» (e.g. inet addr: 10.3.1.233 ). After noting the local-IP address of the device, proceed with the next set of instructions from your macOS desktop.
From Ubuntu 18.04-2 LTS
- Evidently, vino functionality was merged in Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS Gnome Control Center, so it’s much easier- simply go to «Settings».
- Within «Settings», scroll down to the «Sharing» tab within the left-hand side of the window.
- Turn on «Screen Sharing»- select «Allow connections to control the screen» and «Require a password» underneath «Access Options» then proceed with the below instructions to remotely access your Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS desktop from your macOS desktop.
Logging-in From macOS Mojave
- Access the «Spotlight» by hitting CMD + Space-bar
- Within the Spotlight field, enter vnc://your_server_ip:5900 (e.g. vnc://10.3.1.233:5900 ).
- If successful, the Screen Sharing application should automatically launch within your macOS desktop to remotely view your Ubuntu 16.04 or Ubuntu 18.04.2-LTS device on your local-network as depicted by the screen-shot below- enjoy!
Connecting to a Remote Server Over SSH on a Mac
Estamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
A secure shell (SSH) is used for secure communication between devices. When most people refer to SSH, it is within the context of connecting from a local computer to a remote server, commonly for administration tasks related to website hosting.
This article covers the basics of connecting to a remote server (such as a Linode) over SSH on macOS.
Before You Begin
Ensure you have a Linux server with an SSH server (like OpenSSH) installed. Most Linux distributions have an SSH server preinstalled. If you wish to deploy a new server, follow the Creating a Compute Instance guide to create a Linode.
Open the Terminal
On your local computer, open the terminal application you wish to use. The terminal allows you to access your operating system’s shell environment and run programs through the command line.
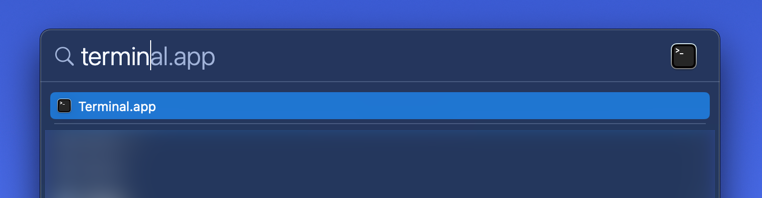
The default terminal emulator for macOS is called Terminal. To open this program, access Spotlight by pressing Cmd + Space on the keyboard and type “Terminal” in the search box. In the search results, click on Terminal.app. Refer to Apple’s Open or Quit Terminal on Mac guide for additional methods of opening Terminal.
As alternatives to the Terminal app, other popular and highly customizable macOS compatible terminal applications include iTerm2 and Hyper.
Connecting to the Remote Server Over SSH
- Within the terminal, enter the following command, replacing [username] with the username of the remote user and [ip-address] with the IP address or domain name of the remote server.
If the server’s SSH port is something other than 22, it needs to be specified in the SSH command. To do this, use the -p option as shown in the command below. Replace [port-number] with the port number that the remote SSH server is using.
The authenticity of host ‘example.com (93.184.216.34)’ can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:d029f87e3d80f8fd9b1be67c7426b4cc1ff47b4a9d0a84. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?You can verify the fingerprint by following the instructions on the Verifying the Authenticity of a Remote Server guide.
If you recently rebuilt your server, you might receive an error message when you try to connect. This happens when the remote host key changes. To fix this, revoke the key for that IP address.
Warning: Permanently added 'example' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.Once you have successfully connected, your terminal should be using the remote shell environment for the server. Your command prompt should now show the username and hostname configured for the server. You can now run any commands that you have available on that server. This includes many of the basic Linux commands, such as ls , cd , rm , and those covered in Using the Terminal guide. Getting to know these commands will help you navigate around your server.
Ending the SSH Session
After you are done, log out of the session by typing exit . The terminal then shows something similar to:
logout Connection to 93.184.216.34 closed.At this point, the shell prompt returns to the one for the local workstation and the terminal application can be closed if it’s no longer needed.
Sending Commands Over SSH
Instead of using SSH to open your remote server’s console, you can run commands on your server without leaving your local shell environment. This can enable you to quickly run commands both locally and remotely in the same terminal window.
Sending a Single Command
To run a single command on your remote server, use the following command. Replace [username] with the username of the remote user, [ip-address] with the IP address or domain name of the remote server, and [command] with the command you wish to run.
As an example, running ssh me@192.0.2.0 ls lists all the files in the home directory of the user called me . This can be useful to find the uptime of the server ( ssh me@192.0.2.0 uptime ) or maybe determine its Linux distribution and version ( ssh me@192.0.2.0 lsb_release -a ).
Sending Multiple Commands
To run multiple commands on your remote server (one after the other), use the following command. Replace [command-1], [command-2], and [command-3] with the commands you wish to run.
The commands should be separated by a semi-colon ( ; ) and all of the commands together should be surrounded by double quotation marks ( » ). For example, if you wanted to create a file named bar.txt in a directory called foo within the user me’s home directory, run: ssh me@192.0.2.0 «mkdir foo; cd foo; touch bar.txt .
Using sudo
It’s recommended to disable root access over SSH and only log in to your remote server through a limited user account. However, some commands require elevated privileges, which can usually be accomplished by prepending the command with sudo . If you attempt to do this while running commands directly through the SSH command, you may receive an error such as “no tty present” or there isn’t a “stable CLI interface”. To run the sudo command in these instances, use the -t option, which forces a psuedo-terminal allocation. For example, to update your packages on a Debian-based system, run ssh linode@example.com -t «sudo apt update» .
Going Further
Troubleshooting SSH Connection Issues
If SSH isn’t connecting you to your Linode, you may need to investigate the state of your server. See the guide Troubleshooting SSH for assistance.
Increasing Security
- Now that you can connect from your Linux machine to the Linode over SSH, save not only time but also make the connection even more secure by using SSH public key authentication. For more information, see SSH add keys.
- See the “Harden SSH Access” section of Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to review how to secure SSH on the server’s side, and the Advanced SSH Server Security for more information on making it even more secure.
This page was originally published on Friday, June 25, 2021.
Connecting to Linux over RDP from a Mac is very easy and fun.
I managed to connect to an Ubuntu 18.04 machine from a Macintosh very easily. I used the Microsoft Remote Desktop app from the app store. This allows a systems administrator on a Macintosh machine to RDP to a Windows machine to operate the desktop as if they were sitting in front of it. But you may also use a Linux machine over RDP as well. Get this app here. Connecting to Linux over RDP from a Mac is a simple way to administer a Linux machine from a Macintosh PC.
https://itunes.apple.com/au/app/microsoft-remote-desktop-10/id1295203466?mt=12. Then install xrdp on the Ubuntu machine to allow RDP connections from a remote machine.
Now the user may run the RDP app and connect to the remote Ubuntu machine very easily. This is of course just as easily managed from a Windows machine.
Just enter your username and password to connect to the Ubuntu session. I just hate the Macintosh app store, I was asked to add payment details to install a free app. But I set payment details as “none” and added a valid phone number and it let me install the app. Nevertheless, it works and this is a great way to connect to a remote machine. Just ensure you are logged out of your Linux machine before logging in over RDP. But this is just a minor annoyance to be sure. When you get such benefits by the ability to connect to a Linux server over RDP.
Looks very good too. So if you are a Macintosh user and are looking for a good Remote Desktop app for a Mac, look no further than the Microsoft offering, as it works very well. I got a message when connecting regarding the operating system, as it could not detect what it was connecting to, but just click next and it works fine.
I recommend Xrdp, it makes Linux life easier, you can connect to your Linux box from any Windows or Mac PC and administer it simply, over a Remote Desktop connection, very nice to be able to use graphical desktop applications on a real desktop in a window or full screen. There is a tip on this page on how to control which desktop environment appears when you connect. On my machine, it opens Fluxbox instead of MATE or Gnome, but that is fine. This really works for me as a remote administration solution.
The remote Desktop feature requires TCP port 3389 to be open. Also, opening UDP port 3389 enables acceleration since RDP 8.0. So if the PC you want to RDP into is on the other side of NAT, make sure this port is allowed through NAT. This port may be changed in Windows easily using Powershell.