- Connecting to a Remote Server Over SSH on Linux
- Before You Begin
- Open the Terminal
- Connecting to the Remote Server Over SSH
- Ending the SSH Session
- Sending Commands Over SSH
- Sending a Single Command
- Sending Multiple Commands
- Using sudo
- Going Further
- Troubleshooting SSH Connection Issues
- Increasing Security
- Как подключиться к серверу по SSH с помощью пароля или ключа
- Проверка службы SSH на сервере
- Использование пароля
- Подключение на Windows
- Подключение на Linux и macOS
Connecting to a Remote Server Over SSH on Linux
Estamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
A secure shell (SSH) is used for secure communication between devices. When most people refer to SSH, it is within the context of connecting from a local computer to a remote server, commonly for administration tasks related to website hosting.
This article covers the basics of connecting to a remote server (such as a Linode) over SSH on a Linux system.
Before You Begin
- Ensure you have a Linux server with an SSH server (like OpenSSH) installed. Most Linux distributions have an SSH server preinstalled. If you wish to deploy a new server, follow the Creating a Compute Instance guide to create a Linode.
- Your local computer needs an SSH client that can be used through a terminal application. Most modern Linux distributions have SSH installed and ready to use.
Open the Terminal
On your local computer, open the terminal application you wish to use. The terminal allows you to access your operating system’s shell environment and run programs through the command line.
If you’re using Linux through the command line, you are already in the terminal and can skip this section. If you are using Linux through a desktop environment (a graphical interface), you’ll need to locate and open the terminal application that comes with your Linux distribution and desktop environment. In most cases, pressing Ctrl + Alt + T on your keyboard opens the default terminal.
- Gnome: The default terminal emulator is Gnome Terminal. Gnome is the default desktop environment for Ubuntu.
- KDE: The default terminal emulator is Konsole. KDE is the default desktop environment for Manjaro.
If this key combination does not work for you, other instructions for opening a terminal vary depending on the Linux distribution and desktop environment you are running. In many cases, you’ll want to open the application search tool and search for “terminal”.
Connecting to the Remote Server Over SSH
- Within the terminal, enter the following command, replacing [username] with the username of the remote user and [ip-address] with the IP address or domain name of the remote server.
If the server’s SSH port is something other than 22, it needs to be specified in the SSH command. To do this, use the -p option as shown in the command below. Replace [port-number] with the port number that the remote SSH server is using.
The authenticity of host ‘example.com (93.184.216.34)’ can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:d029f87e3d80f8fd9b1be67c7426b4cc1ff47b4a9d0a84. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?You can verify the fingerprint by following the instructions on the Verifying the Authenticity of a Remote Server guide.
If you recently rebuilt your server, you might receive an error message when you try to connect. This happens when the remote host key changes. To fix this, revoke the key for that IP address.
Warning: Permanently added 'example' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.Once you have successfully connected, your terminal should be using the remote shell environment for the server. Your command prompt should now show the username and hostname configured for the server. You can now run any commands that you have available on that server. This includes many of the basic Linux commands, such as ls , cd , rm , and those covered in Using the Terminal guide. Getting to know these commands will help you navigate around your server.
Ending the SSH Session
After you are done, log out of the session by typing exit . The terminal then shows something similar to:
logout Connection to 93.184.216.34 closed.At this point, the shell prompt returns to the one for the local workstation and the terminal application can be closed if it’s no longer needed.
Sending Commands Over SSH
Instead of using SSH to open your remote server’s console, you can run commands on your server without leaving your local shell environment. This can enable you to quickly run commands both locally and remotely in the same terminal window.
Sending a Single Command
To run a single command on your remote server, use the following command. Replace [username] with the username of the remote user, [ip-address] with the IP address or domain name of the remote server, and [command] with the command you wish to run.
As an example, running ssh me@192.0.2.0 ls lists all the files in the home directory of the user called me . This can be useful to find the uptime of the server ( ssh me@192.0.2.0 uptime ) or maybe determine its Linux distribution and version ( ssh me@192.0.2.0 lsb_release -a ).
Sending Multiple Commands
To run multiple commands on your remote server (one after the other), use the following command. Replace [command-1], [command-2], and [command-3] with the commands you wish to run.
The commands should be separated by a semi-colon ( ; ) and all of the commands together should be surrounded by double quotation marks ( » ). For example, if you wanted to create a file named bar.txt in a directory called foo within the user me’s home directory, run: ssh me@192.0.2.0 «mkdir foo; cd foo; touch bar.txt .
Using sudo
It’s recommended to disable root access over SSH and only log in to your remote server through a limited user account. However, some commands require elevated privileges, which can usually be accomplished by prepending the command with sudo . If you attempt to do this while running commands directly through the SSH command, you may receive an error such as “no tty present” or there isn’t a “stable CLI interface”. To run the sudo command in these instances, use the -t option, which forces a psuedo-terminal allocation. For example, to update your packages on a Debian-based system, run ssh linode@example.com -t «sudo apt update» .
Going Further
Troubleshooting SSH Connection Issues
If SSH isn’t connecting you to your Linode, you may need to investigate the state of your server. See the guide Troubleshooting SSH for assistance.
Increasing Security
- Now that you can connect from your Linux machine to the Linode over SSH, save not only time but also make the connection even more secure by using SSH public key authentication. For more information, see SSH add keys.
- See the “Harden SSH Access” section of Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to review how to secure SSH on the server’s side, and the Advanced SSH Server Security for more information on making it even more secure.
This page was originally published on Friday, June 25, 2021.
Как подключиться к серверу по SSH с помощью пароля или ключа
SSH — зашифрованный протокол для удаленного управления серверами. Для подключения через него вы можете каждый раз вводить пароль или настроить авторизацию по ключу. Второй вариант безопаснее, но у него есть свои особенности. В этой статье мы рассмотрим оба метода подключения, а вы уже сами выберите, какой способ удобнее.
Проверка службы SSH на сервере
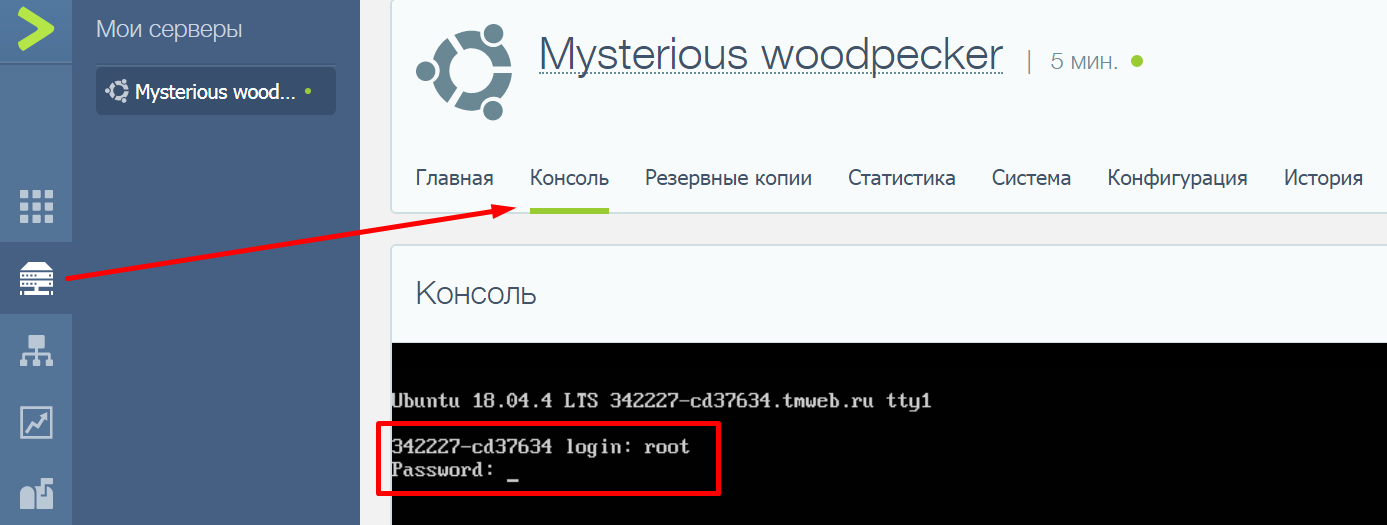
Доступ по SSH обычно можно включить при создании сервера или во время настройки конфигурации. Убедиться в том, что он разрешен, можно через консоль. Она доступна в панели управления сервером.
Например, у меня VDS на Timeweb. Чтобы попасть в консоль, я авторизуюсь по логину и паролю, выданному хостером, выбираю свой сервер в списке VDS и перехожу на вкладку «Консоль».
Чтобы пользоваться консолью, нужно авторизоваться. Логин и пароль для доступа к серверу хостер присылает в письме. Сначала нужно ввести логин и нажать на клавишу Enter. Появится строка Password. В ней необходимо ввести пароль и снова нажать на клавишу Enter.
Важно: в целях безопасности при вводе пароля на экране не отображаются никакие символы, даже привычные звездочки.
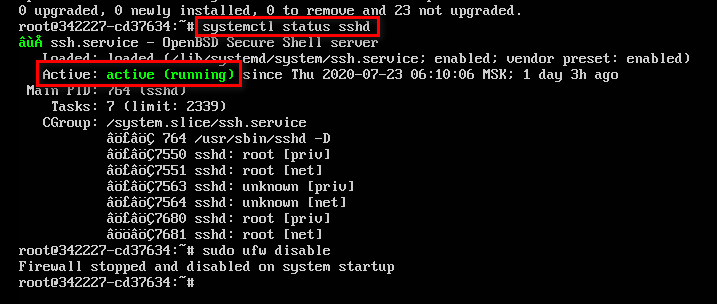
После авторизации в консоли можно проверить, запущена ли служба SSH на сервере.
- Выполните команду systemctl status sshd.
- Обратите внимание на строчку Active. В ней должна быть выделенная зеленым запись active (running). Это состояние говорит о том, что служба запущена.
Если служба не активна, добавьте ее самостоятельно. Выполните команду sudo apt install openssh-server и подтвердите установку пакетов.
Кроме того, для подключения вам может понадобиться настройка брандмауэра. Чтобы межсетевой экран не блокировал входящие соединения, можно на время отключить его командой sudo ufw disable.
Использование пароля
Начнем с инструкции о том, как подключиться к удаленному серверу через SSH по логину и паролю. Это самый простой способ. Хостер предоставляет вам IP-адрес, логин и пароль. Этого достаточно для того, чтобы установить соединение с удаленным сервером.
Подключение на Windows
Моя основная система — Windows. Раньше для подключения к серверу через SSH я пользовался сторонней утилитой PuTTY, потому что в операционной системе не было встроенного компонента. В «десятке» он появился, так что теперь можно подключаться к SSH через командную строку (cmd).
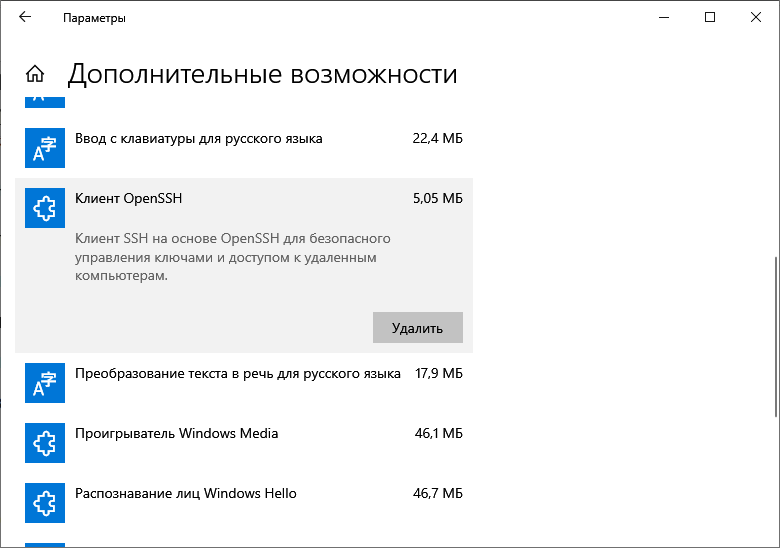
Чтобы включить встроенный в систему OpenSSH:
- Откройте «Параметры» (Win + I) и перейдите в раздел «Приложения».
- Выберите опцию «Управление дополнительными компонентами».
- Нажмите «Добавить компонент».
- Выберите в списке OpenSSH Client и нажмите «Установить».
- После завершения установки перезагрузите систему.
Теперь разберемся, как подключиться к SSH через cmd. Запустите командную строку и выполните запрос вида ssh root@185.104.114.90.
Значение root — логин для подключения, вы получили его в письме при создании сервера. 185.104.114.90 — IP-адрес сервера. Его можно посмотреть в панели управления сервером или в том же письме, которое прислал хостер. У команды может быть также дополнительный параметр -p, после которого прописывается номер порта. По умолчанию используется порт 22. Если у вас настроен другой порт, нужно явно его указать, — например, полный адрес может выглядеть так: ssh root@185.104.114.90 -p 150.
После выполнения команды клиент SSH предложит добавить устройство в список известных. Введите в командной строке yes и нажмите на Enter. Затем укажите пароль для доступа к серверу. На этом подключение к серверу через SSH завершено — теперь все команды будут выполняться на удаленной машине, к которой вы подключились.
На версиях младше Windows 10 1809 нет встроенной поддержки протокола OpenSSH. В таком случае понадобится сторонняя утилита. Смотрим, как через PuTTY подключиться по SSH:
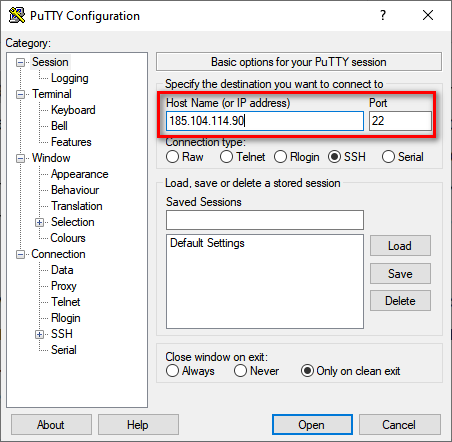
- Запустите PuTTY.
- На вкладке Session укажите Host Name (IP-адрес сервера), Port (по умолчанию 22, но если вы в конфигурации сервера указали другой порт, нужно задать его номер).
- Убедитесь, что тип соединения установлен SSH.
- Нажмите на кнопку Open, чтобы подключиться.
Если вы ввели правильные данные, появится окно консоли, в котором нужно указать логин и пароль для подключения к серверу. При первом запуске также отобразится запрос на добавление устройства в список известных.
Подключение на Linux и macOS
Теперь посмотрим, как подключиться по SSH через терминал на Linux. Для этого не требуется установка дополнительных компонентов, все работает «из коробки».
- Запустите терминал. Обычно для этого используется сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Alt+T. Найти терминал также можно по пути «Главное меню» — «Приложения» — «Система».
- Выполните команду для подключения. Синтаксис такой же, как на Windows, — ssh root@ 185.104.114.90 . Если порт не стандартный, то нужно явно его указать: например, ssh root@ 185.104.114.90 -p 150. Вместо root вы указываете свое имя пользователя, а вместо 185.104.114.90 — IP-адрес своего сервера.
- Если хост и порт указаны верно, на следующем шаге появится запрос на ввод пароля. При первом подключении также будет предложение добавить новое устройство в список известных. Для этого введите yes и нажмите на клавишу Enter.
На этом подключение завершено. Теперь все команды, которые вы вводите в терминале, будут выполняться на удаленной машине.
Если IP-адрес или порт указаны неверно, то на экране появится сообщение об ошибке — Connection Refused. Это может также говорить о том, что доступ запрещен брандмауэром на удаленном сервере (если вы его не отключили). Чтобы разрешить подключение через SSH:
- на сервере с Ubuntu/Debian выполните команду $ sudo ufw allow 22/tcp;
- на сервере CentOS/Fedora выполните команду $ firewall-cmd —permanent —zone=public —add-port=22/tcp.
Цифра 22 в синтаксисе — номер порта. Если вы используете другой порт, то укажите его явно.
Если вы знаете как подключиться через SSH на Linux, то справитесь с этой задачей и на macOS. В операционной системе Apple тоже есть встроенный терминал. Синтаксис команды для подключения не меняется: ssh root@ 185.104.114.90 , где root — ваш логин, а 185.104.114.90 — IP-адрес сервера, с которым вы устанавливаете соединение.