- How to setup a network between a windows computer and a linux computer?
- 1 Answer 1
- Accessing network applications with WSL
- Accessing Linux networking apps from Windows (localhost)
- Accessing Windows networking apps from Linux (host IP)
- Connecting via remote IP addresses
- Accessing a WSL 2 distribution from your local area network (LAN)
- IPv6 access
- Доступ к сетевым приложениям с помощью WSL
- Доступ к сетевым приложениям Linux из Windows (localhost)
- Доступ к сетевым приложениям Windows из Linux (IP-адрес основной системы)
- Подключение через удаленные IP-адреса
- Доступ к дистрибутиву WSL 2 из локальной сети (LAN)
- Доступ по протоколу IPv6
How to setup a network between a windows computer and a linux computer?
I connected my Windows computer to my Linux computer with an Ethernet cable. The problem is that the Linux interface enp5s0 doesn’t acquire an IP and when I try to ping the Windows computer it says network unreachable. I have tried systemctl start dhcpcd@enp5s0.service but it fails to start with
Which should be normal, but then how do I set an IP for the Linux machine in this network of two? And how do I enable the Linux machine to ping and download files from the Windows machine?
wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/… shows you how to setup a static IP. You may want to set up Samba for file sharing.
are you sure you are either a cross-over cable between your two computers or at least one of the network interfaces have signal auto-sensing capability ?
@MelBurslan: Fortunately, many Ethernet adapters from the last decade support both types of cables so hopefully one of them supports it.
Sorry to contradict you @RuiFRibeiro, but I’ve seen 100mbps adapters that support both cables 12 years ago.
1 Answer 1
In order to acquire an IP adress on the Linux machine using the DHCP method you have to install an DHCP-Server on the Windows machine first and configure it.
I assume that is not really what you want. In order to exchange network packages between both hosts you have to assure that both hosts are on the same network. In this hardware setting the best way to do so is to manually set up static network configurations on both hosts.
Configuration on the Windows (7?) machine:
When the cable is connected via ethernet your networking notifier in the windows task bar should show a wired connection symbol (or a spinning circle notifying you it is trying to automatically get an IP via DHCP).
Click on the symbol and then open the network and sharing center. On the right hand side of the upcoming window you should see something like an underlined «LAN-connection 1». Click on it an then go to «Properties». In the upcoming list mark «Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)» and then again click on «Properties». Now check «Use the following IP-Adresses» (or something like that — I only have the german version of Windows on my screen and can’t tell what the exact english translation is). Now type in the following fields:
- IP-adress: 10.0.0.1
- subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- gateway: 10.0.0.2 (does not matter as there is no way out of your small two host network. Using the following configuration steps, your Linux host will be the gateway host)
Configuration on the Linux machine (Debian/Ubuntu):
Open up a terminal window and do the following commands (as superuser):
ifconfig enp5s0 up ifconfig enp5s0 10.0.0.2 ifconfig enp5s0 netmask 255.255.255.0 You have now set up a small network containing the two hosts with the Linux machine being the gateway host (when the Linux host has a second interface connected to an WAN and the forwarding is set up properly then it can act as a «real» internet-gateway for the windows machine).
Verify the setup using the ping command on the both hosts (the terminal can be used on both OSes to do so).
And both should consecutively show up successfully issued ping packets.
Accessing network applications with WSL
There are a few considerations to be aware of when working with networking apps, whether you are accessing a Linux networking app from a Windows app or accessing a Windows networking app from a Linux app, you may need to identify the IP address of the virtual machine you are working with, which will be different than the IP address of your local physical machine.
Accessing Linux networking apps from Windows (localhost)
If you are building a networking app (for example an app running on a NodeJS or SQL server) in your Linux distribution, you can access it from a Windows app (like your Edge or Chrome internet browser) using localhost (just like you normally would).
Accessing Windows networking apps from Linux (host IP)
If you want to access a networking app running on Windows (for example an app running on a NodeJS or SQL server) from your Linux distribution (ie Ubuntu), then you need to use the IP address of your host machine. While this is not a common scenario, you can follow these steps to make it work.
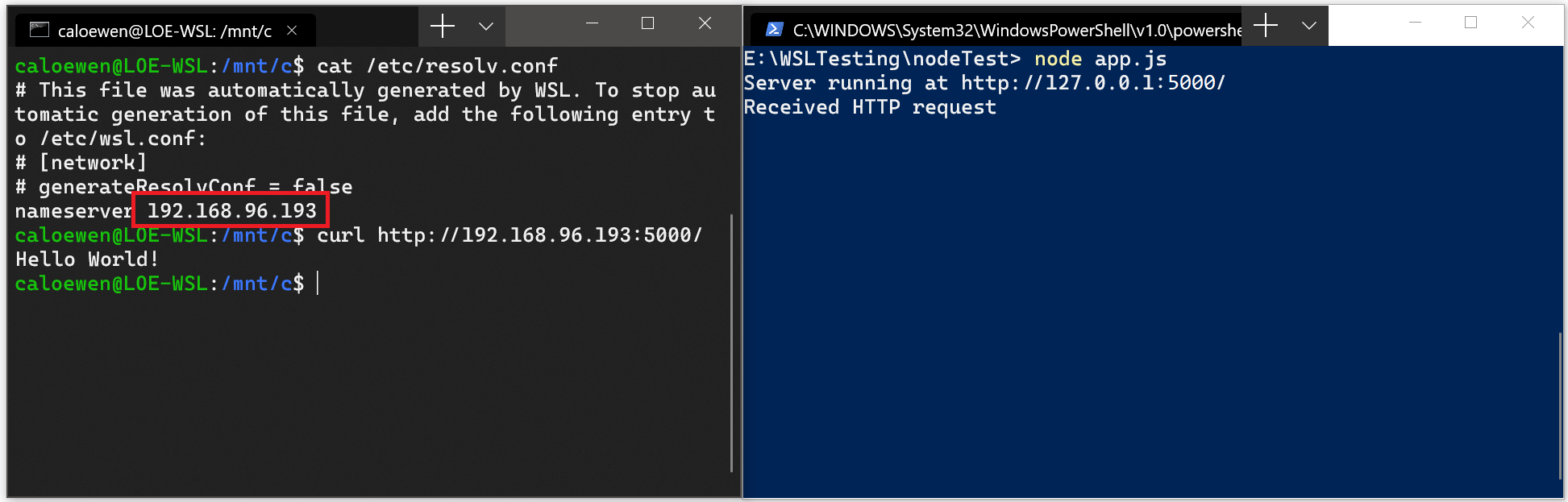
- Obtain the IP address of your host machine by running this command from your Linux distribution: cat /etc/resolv.conf
- Copy the IP address following the term: nameserver .
- Connect to any Windows server using the copied IP address.
The picture below shows an example of this by connecting to a Node.js server running in Windows via curl.
Connecting via remote IP addresses
When using remote IP addresses to connect to your applications, they will be treated as connections from the Local Area Network (LAN). This means that you will need to make sure your application can accept LAN connections.
For example, you may need to bind your application to 0.0.0.0 instead of 127.0.0.1 . In the example of a Python app using Flask, this can be done with the command: app.run(host=’0.0.0.0′) . Please keep security in mind when making these changes as this will allow connections from your LAN.
Accessing a WSL 2 distribution from your local area network (LAN)
When using a WSL 1 distribution, if your computer was set up to be accessed by your LAN, then applications run in WSL could be accessed on your LAN as well.
This isn’t the default case in WSL 2. WSL 2 has a virtualized ethernet adapter with its own unique IP address. Currently, to enable this workflow you will need to go through the same steps as you would for a regular virtual machine. (We are looking into ways to improve this experience.)
Here’s an example Windows command to add a port proxy that listens on port 4000 on the host and connects it to port 4000 to the WSL 2 VM with IP address 192.168.101.100.
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=4000 listenaddress=0.0.0.0 connectport=4000 connectaddress=192.168.101.100 IPv6 access
WSL 2 distributions currently cannot reach IPv6-only addresses. We are working on adding this feature.
Доступ к сетевым приложениям с помощью WSL
При работе с сетевыми приложениями (будь то получение доступа к сетевому приложению Linux из приложения Windows или получение доступа к сетевому приложению Windows из приложения Linux) необходимо учитывать несколько моментов. Вам может потребоваться определить IP-адрес используемой виртуальной машины, который будет отличаться от IP-адреса локального физического компьютера.
Доступ к сетевым приложениям Linux из Windows (localhost)
Если вы создаете сетевое приложение (например, приложение, работающее на NodeJS или SQL Server) в дистрибутиве Linux, вы можете получить к нему доступ из приложения Windows (например, используя Microsoft Edge или Chrome) с помощью localhost (как обычно это и происходит).
Доступ к сетевым приложениям Windows из Linux (IP-адрес основной системы)
Если вы хотите получить доступ к сетевому приложению, работающему в Windows (например, к приложению, работающему на NodeJS или SQL Server) из дистрибутива Linux (напр., Ubuntu), необходимо использовать IP-адрес основной системы. Хотя это происходит и нечасто, для этого можно выполнить следующие действия.
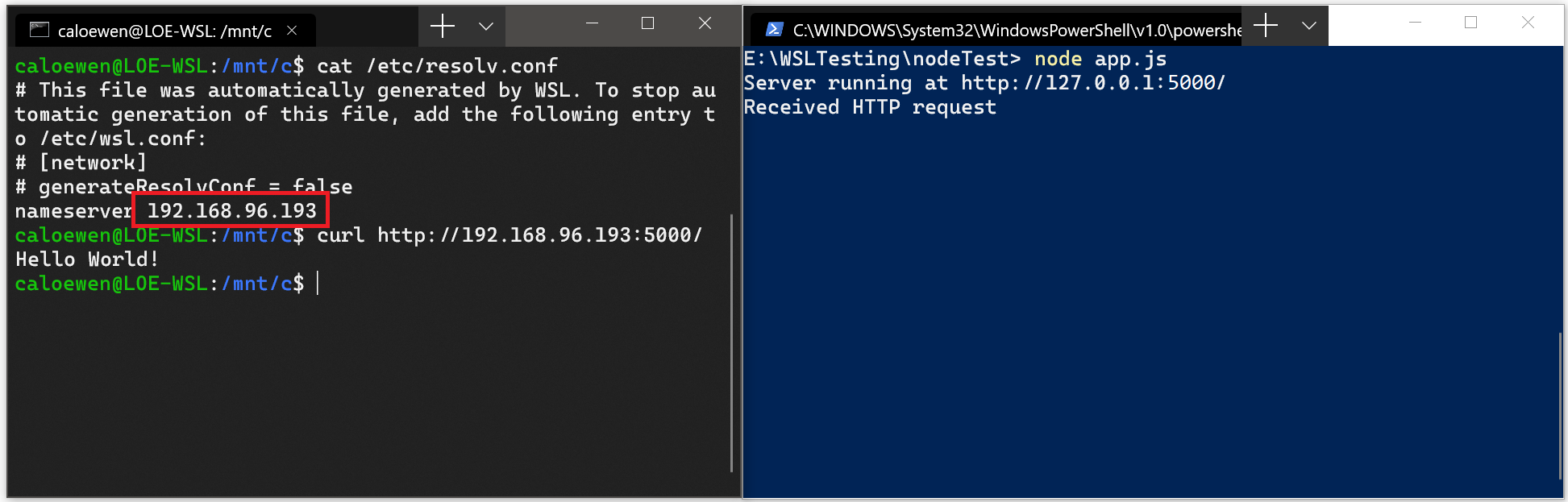
- Получите IP-адрес основной системы, выполнив следующую команду из дистрибутива Linux: cat /etc/resolv.conf
- Скопируйте IP-адрес в строке, начинающейся с nameserver .
- Подключитесь к любому серверу Windows, используя скопированный IP-адрес.
На изображении ниже показан пример подключения к серверу Node.js под управлением Windows через cURL.
Подключение через удаленные IP-адреса
При использовании удаленных IP-адресов для подключения к приложениям они будут рассматриваться как подключения из локальной сети (LAN). Это означает, что необходимо убедиться, что приложение может принимать подключения по локальной сети.
Например, может потребоваться привязать приложение к 0.0.0.0 вместо 127.0.0.1 . В примере приложения Python, использующего Flask, это можно сделать с помощью команды app.run(host=’0.0.0.0′) . При внесении этих изменений не забывайте о безопасности, так как это позволит устанавливать подключения из вашей локальной сети.
Доступ к дистрибутиву WSL 2 из локальной сети (LAN)
При использовании дистрибутива WSL 1, если к компьютеру можно получить доступ из локальной сети, то приложения, работающие в WSL, могут быть также доступны в локальной сети.
Это нетипичная ситуация в WSL 2. В WSL 2 имеется виртуализированный адаптер Ethernet с собственным уникальным IP-адресом. В настоящее время для включения этого рабочего процесса необходимо выполнить те же действия, что и для обычной виртуальной машины. (Мы ищем способы улучшить это взаимодействие.)
Ниже приведен пример команды Windows для добавления прокси-сервера порта, который прослушивает порт 4000 на узле и подключает его к порту 4000 к виртуальной машине WSL 2 с IP-адресом 192.168.101.100.
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=4000 listenaddress=0.0.0.0 connectport=4000 connectaddress=192.168.101.100 Доступ по протоколу IPv6
В настоящее время дистрибутивы WSL 2 не могут обращаться к IPv6-адресам. Мы работаем над добавлением этой возможности.