- SSH problem — Read from socket failed: Connection reset by peer
- 6 Answers 6
- How to Fix «ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer» Error
- What Causes the “Connection reset by peer” SSH Error?
- Check the hosts.deny and hosts.allow File
- How to Edit hosts.deny File
- How to Edit hosts.allow File
- Check if fail2ban Banned Your IP Address
- Check the sshd_config File
- SSH — Connection reset by peer — Linux Host
SSH problem — Read from socket failed: Connection reset by peer
I get Read from socket failed: Connection reset by peer . I don’t even begin to know where to look to solve this. Anyone have any clues?
Both just connected to each other over ethernet cable via a router. They have SSH’d in both directions in the past.
Good and bad news: I answered my own question. I’ll type that out below. Thanks for your help all the same.
6 Answers 6
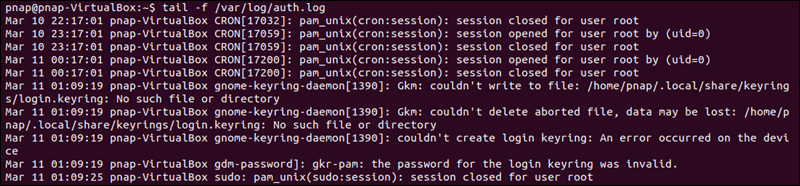
- start monitoring the server’s log file tail -f /var/log/auth.log
- add -v to get a verbose output at the client end ssh user@computerB -v
This might give you more details about the cause. if the rsa and dsa keys are missing on the server, fix them by:
ssh-keygen -t rsa1 -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key ssh-keygen -t dsa -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key This worked for me. Though I had to be root to run the following: ssh-keygen -t dsa -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key
Keys re-generation definitely work. In my case it was changing machine IP address after openssh installed (and keys generated during install).
After doing this I lost any chance of connecting to my server. Had to ask for hosting provider’s help. Still awaiting their answer. Centos 7 with cPanel.
I re-installed the SSH bits by doing:
sudo apt-get --reinstall install openssh-server openssh-client This fixed all my problems.
Could be a coincidence. That the problem stopped happening at the time you reinstalled ssh isn’t an airtight assurance of cause and effect. By the way, which side did you reinstall? Or both? In any case, «this question is unlikely to help future visitors».
änthräX’s method is very helpful. It works for me!
Basically I think, after installed ssh, key files are needed.
The only revision I made was to use rsa instead of rsa1 :
ssh-keygen -t rsa -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key ssh-keygen -t dsa -f /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key That modified method worked for me.
This was the problem in my case. The ssh server package with the current Ubuntu release for the Utilite ARM machine installed with the OP’s symptom. After running these two commands (which I did as root), I can finally ssh in. Thanks a lot. +1
It’s because somehow the permissions of the files inside /etc/ssh have changed. So change the permission of the files like the example given below:
chmod 644 ssh_config chmod 600 moduli Finally the file permissions should look like something like given below,
[root@hostname ssh]# ls -latr total 172 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2047 Aug 12 2010 ssh_config -rw-------. 1 root root 125811 Aug 12 2010 moduli -rw-------. 1 root root 963 Mar 1 16:02 ssh_host_key -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 627 Mar 1 16:02 ssh_host_key.pub -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 382 Mar 1 16:02 ssh_host_rsa_key.pub -rw-------. 1 root root 1675 Mar 1 16:02 ssh_host_rsa_key -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 590 Mar 1 16:02 ssh_host_dsa_key.pub -rw-------. 1 root root 668 Mar 1 16:02 ssh_host_dsa_key -rw-------. 1 root root 3845 May 7 11:52 sshd_config After changing the permissions try connecting from putty, should work fine..
How to Fix «ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer» Error
A remote machine has prevented an SSH connection you were attempting to establish or maintain. The “ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer” message is not specific enough to immediately explain what triggered the error.
To be able to resolve the issue successfully, we first need to identify its cause. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the likely causes and provides the most effective solutions.
By reading this tutorial, you will learn how to fix the “ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer” Error.
- Necessary permissions to access remote server
- A user account with root or sudo privileges
What Causes the “Connection reset by peer” SSH Error?
The “ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer” error indicates that the remote machine abruptly closed the Transition Control Protocol (TCP) stream. In most instances, a quick reboot of a remote server might solve a temporary outage or connectivity issue.
Note: Network-based firewalls or load-balancers can sometimes distort IPs or security permissions. This type of problem can be resolved by contacting your service provider.
Learning how to troubleshoot this issue, and determining the underlying cause, helps you prevent future occurrences on your system. The most common causes of the “ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer” error are:
- The connection is being blocked due to the Host-Based Access Control Lists.
- Intrusion prevention software is blocking your IP by updating firewall rules (Fail2ban, DenyHosts, etc.).
- Changes to the SSH daemon configuration file.
Check the hosts.deny and hosts.allow File
The hosts.deny and hosts.allow files are TCP wrappers. As a security feature, these files are used to limit which IP address or hostname can establish a connection to the remote machine.
Note: Inspect the hosts.deny and hosts.allow files on the remote server, not on the local client.
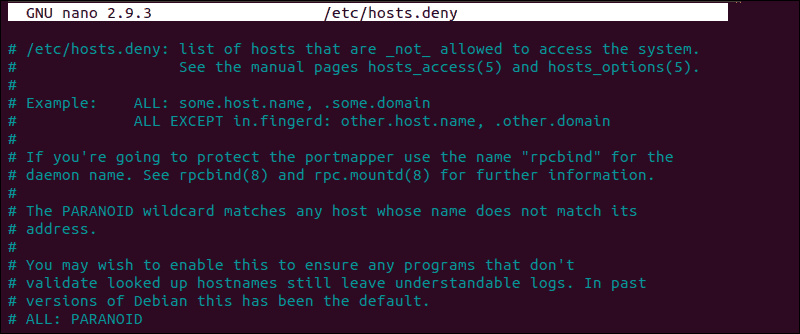
How to Edit hosts.deny File
Access your remote server and open the hosts.deny file using your preferred text editor. If you are using nano on a Debian based system, enter the following command:
Empty lines and lines starting with the ‘#’ symbol are comments. Check if you can locate your local IP or host-name in the file. If it is present, it should be removed or commented out, or else it prevents you from establishing a remote connection.
After making the necessary changes, save the file and exit. Attempt to reconnect via SSH.
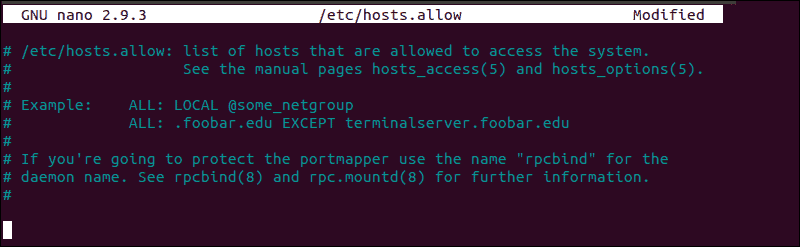
How to Edit hosts.allow File
As an additional precaution, edit the hosts.allow file. Access rules within the hosts.allow are applied first. They take precedence over rules specified in hosts.deny file. Enter the following command to access the hosts.allow file:
Adding host-names and IPs to the file defines exceptions to the settings in the hosts.deny file.
For example, a strict security policy within the etc/hosts.deny file, would deny access to all hosts:
Subsequently, you can add a single IP address, an IP range, or a hostname to the etc/hosts.allow file. By adding the following line, only the following IP would be allowed to establish an SSH connection with your remote server:
Keep in mind that such a limiting security setting can affect administering capabilities on your remote servers.
Check if fail2ban Banned Your IP Address
If you’ve tried to connect on multiple occasions, your IP might be blocked by an intrusion prevention software. Fail2ban is a service designed to protect you from brute force attacks, and it can misinterpret your authentication attempts as an attack.
Fail2ban monitors and dynamically alters firewall rules to ban IP addresses that exhibit suspicious behavior. It monitors logs, like the hosts.deny and hosts.allow files we edited previously.
In our example, we used the following command to check if the iptables tool is rejecting your attempted connections:
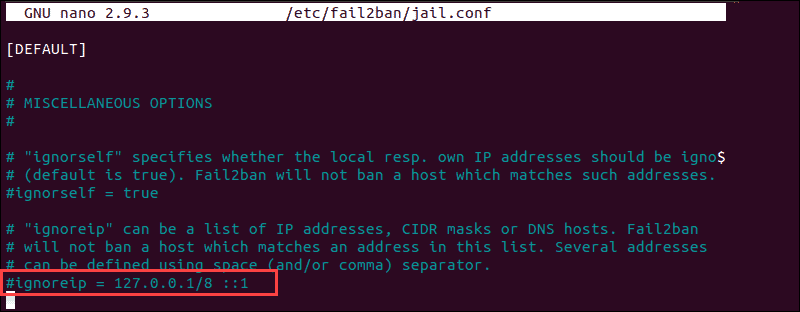
sudo iptables -L --line-numberThe output in your terminal window is going to list all authentication attempts. If you find that a firewall is indeed preventing your SSH connection, you can white-list your IP with fail2ban. Otherwise, the service is going to block all future attempts continuously. To access the fail2ban configuration file, enter the following command:
sudo nano /etc/fail2ban/jail.confEdit the file by uncommenting the line that contains «ignoreip =» add the IP or IP range you want to white-list.
Fail2ban is now going to make an exception and not report suspicious behavior for the IP in question.
Check the sshd_config File
If you are continuing to experience the ‘ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer’ error, examine the authentication log entry. By default, the SSH daemon sends logging information to the system logs. Access the /var/log/auth.log file after your failed attempt to login. To review the latest log entries type:
The output presents the results of your authentication attempts, information about your user account, authentication key, or password.
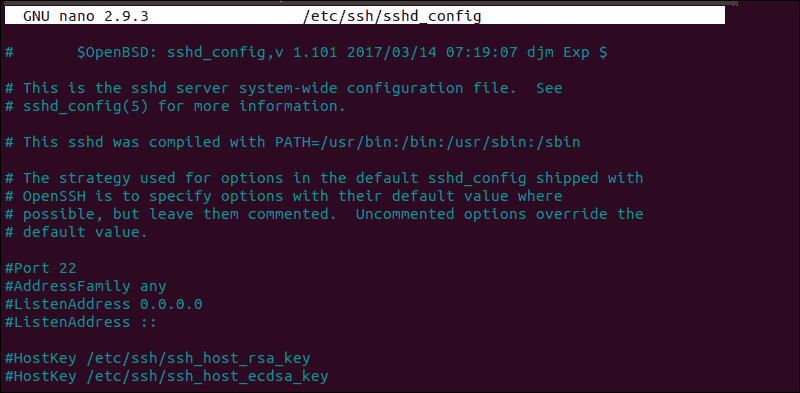
The log provides you with information that can help you find possible issues in the sshd configuration file, sshd_config. Any changes made to the file can affect the terms under which an ssh connection is established and lead the remote server to treat the client as incompatible. To access the sshd_config file type:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configThe sshd configuration file enables you to change basic settings, such as the default TCP port or SSH key pairs for authentication, as well as more advanced functions such as port-forwarding.
For example, the MaxStartups variable defines how many connections a system accepts in a predefined period. If you have a system that makes a large number of connections in a short timeframe, it might be necessary to increase the default values for this variable. Otherwise, the remote system might refuse additional attempted ssh connections.
Anytime you edit the sshd_config file, restart the sshd service for the changes to take effect:
Only edit the variables that you are familiar with. A server can become unreachable as a result of a faulty configuration file.
You have thoroughly checked the most common reasons behind the “ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer” error. By looking at each possibility, in turn, you have successfully solved the issue and now know how to deal with similar problems going forward.
The number of potential causes is vast and difficult to troubleshoot in every respect. Ultimately, if the error persists, it might be necessary to contact your host.
SSH — Connection reset by peer — Linux Host
I have a hosting account with Linux shared hosting account with GoDaddy, recently my ssh access stopped working, this is the error:
Toms-MacBook-Pro:production tom$ ssh tomheather50@192.186.452.73 ssh_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer
This happens on my wifi connection however if I create a mobile phone hotspot and connect through my phone’s 3g network I can successfully connect with no errors. I have contacted GoDaddy support various times over the past 2 days and they have not been much help at all, simply put they have said I should just connect through the mobile network!! After sending a traceroute to them I got this response.
We are tracking instances of connections dropping and being intermittent through Level 3 and their IP 4.34.191.254. I noticed that your connection that is having difficulty is being routed through this path while the connection that did work is not routing through. We are reaching out to Level 3 Communications to see if they can identify and fix this situation. We are seeing more cases like yours pop up from both Europe and the US. In the meantime I would recommend using a connection that does not trace through Level 3 if at all possible.
I’m not sure what means and it staggers me that GoDaddy can not ensure i can connect through my wifi connection ! Any advice, explanation and of course help would be great please guys.